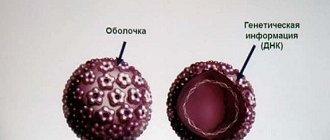
In the modern world, papillomavirus is considered a fairly common infection that was known to mankind in the distant past. People suffered from an abundance of warts and tried to treat them in accessible ways. It was possible to isolate the pathogen only in the middle of the last century. Today, science knows about 130 strains of the virus, many of which have been studied in detail. Based on the classification, all types were divided into 3 groups. The greatest threat is posed by strains included in the third category due to their high oncogenic risk. One of them is HPV 56.
Characteristic features of the development of HPV 56 in a woman’s body
Most of the population around the world suffers from human papillomavirus or is a latent carrier of it. It is the latter that pose a particular danger, since they have the ability to infect others in the absence of external signs. Even a slight weakening of the immune system leads to the spread of the virus, and the risks of complications for men and women differ significantly.
General understanding of HPV 56 and its symptoms
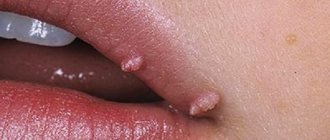
Papillomavirus type 56 in men and women manifests itself in the form of genital warts. The danger of infection lies in the fact that the pathogen is not detected immediately, but after a long period, which can reach several years. But in the active phase, it can provoke the development of the most dangerous forms of oncological pathologies - carcinoma or sarcoma of the genitourinary system.
Attention! Type 56 is particularly malignant, which multiplies in the cellular structures of the skin and on the mucous epithelium of the urogenital zone. Its distinctive feature is its high compatibility with other types of HPV.
Infection options
When diagnosing HPV type 56 in women, many are interested in what kind of strain it is and in what ways it can be transmitted. The main route of transmission of papillomavirus is unprotected sexual intercourse, and any method of intercourse poses a threat. With close contact of the skin, transmission of the pathogen occurs with almost 100% probability. Since the maximum concentration of cells is found in vaginal secretions and semen, even a condom cannot completely protect against infection, but can only reduce the likelihood of infection.
As for the contact and household method of transmission of the virus, there are only isolated cases of infection when using personal hygiene products - razors, manicure instruments. Presumably the pathogen enters a healthy body through microtraumas on the skin or mucous epithelium.
Factors that provoke virus activity
When HPV type 56 DNA is detected during an examination, doctors indicate possible threats to health, and in the absence of adequate therapy, the degeneration of affected cells into cancer cells.
In women, the virus with genotype 56 begins to show its activity due to the following factors:
- weakening of immune defense;
- increased estrogen levels, which is typical during pregnancy or menopause;
- concentrations of estradiol in the body of women who have crossed the 40-year mark.
The onset of the development of the pathological process can be determined by the presence of characteristic growths in the perineal area or by chance during a routine examination by a gynecologist.
The progression of the disease is often indicated by the following symptoms:
- pain syndrome localized in the lower abdominal cavity;
- spotting not associated with the monthly cycle;
- discomfort and pain during sexual intimacy;
- problems with urination;
- development of inflammatory processes in the genitourinary organs - cystitis, erosion.
Dangerous consequences for women
The virus strain number 56 almost always causes the development of cancer of the urogenital tract. This is due to the fact that during the progression of the disease, the pathogen exhibits active vital activity and invades healthy cells, changing the genetic code. As a result, atypical structures begin to form, which leads to the appearance of neoplasms or dysplasia.
It is important to know! Women with HPV 56 are most often diagnosed with cervical cancer, which is caused by cell mutations. Cancer of the external genitalia and anus occurs much less frequently.
Due to the different speed of the pathological process, it is impossible to predict at what point the cells will degenerate into cancer. Typically this period lasts 10-40 years, but in individual cases it can be reduced to 1-2 years.
HPV 56 during pregnancy
With strong immunity during pregnancy, doctors do not note the development of negative reactions. In the case of infection with HPV type 56, pregnancy in women proceeds without complications, however, in the presence of multiple neoplasia on the genitals of the expectant mother, the fetus often experiences damage to the larynx.
If the protective forces are weakened in the early stages, the pathogen cells can infect trophoblasts, which, together with the endometrial tissue, form the placenta.
As a result of their destruction, the ability of the embryo to develop normally disappears, which leads to its death and spontaneous miscarriage.
Due to the active reproduction of the virus, papillomas form on the walls of the urethra, which increases the risk of developing complications such as:
- a decrease in the lumen of the urethra, as a result of which the process of urination is disrupted;
- difficulties in self-delivery naturally;
- the development of inflammatory processes, which often have a detrimental effect on the condition of the fetus.
It is important to know! Laryngeal papillomatosis in an infant is characterized by the formation of growths on the mucous membrane of the throat, trachea, and vocal cords. This leads to respiratory problems and hoarseness. In case of chronic pathology, the virus penetrates the bronchi. In severe cases, asphyxia may develop.
Transmission routes
When infected, integrating into DNA, HPV type 66 promotes pathological changes in the composition and properties of cells. Under the influence of oncogenic type papillomavirus, the affected cell is transformed, which first causes cervical neoplasia, and subsequently cancer.
Infection with HPV type 66 occurs mainly through sexual contact with a carrier of the infection. Moreover, contact can be anything: vaginal, oral or anal. If barrier contraceptives are not used during sex, then the infection from the carrier’s body enters the partner’s body.
If sexual intercourse was unprotected, then the probability that a healthy partner will be infected reaches 60%. But condoms are not fully capable of protecting against infection, since the smallest viral elements pass through the pores of the latex product. In addition, the risk of infection increases significantly with a large number of sexual partners.
A domestic method of infection cannot be ruled out. This can happen when using someone else's personal belongings: towels, washcloths, underwear, cosmetics. Often infection occurs in public places: saunas, baths, water parks. A pregnant woman can infect her child during fetal development or during childbirth.
Men and virus type 56: what you need to know
HPV type 56 is diagnosed much less frequently in men compared to women. Their incubation period can last from 2-3 weeks to several years. The latent course of the disease is directly dependent on the resistance of the body - the stronger the defenses, the longer the symptoms do not appear. During the period of active reproduction, acute condylomas or warts form in men. In the absence of adequate therapy, the likelihood of developing Bowen's disease (intraepidermal cancer) and bowenoid papulosis increases. When overinfected, viral cells are able to penetrate the urethra, causing urination problems.
Small pointed formations in the form of papillae are found in the perineum, anus, and penis. They can often appear on the feet, arms, chest, neck, and armpits. Localized in the urogenital area, papillomas often cause itching and bleed during sexual intercourse.
Bowen's disease can be identified by a characteristic bright red plaque on the skin of the genitals, which has ragged edges. With bowenoid papulosis, multiple pinkish rashes are observed on the penis.
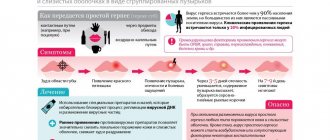
Symptoms of the disease
The main viral symptom is papillomas of various shapes. They are not always visible, as they sometimes appear on the mucous membranes and dermis.
There are cases when one person is a carrier of several oncogenic strains, and this threatens the development of cancer.
How can a woman understand that she has papillomavirus? It's not difficult if you know the symptoms.
- Pointed growths, that is, condylomas, appear on the genitals of women.
- Often, already two months after the infection, condylomas begin to appear. This will allow you to determine the last sexual contact without protective equipment.
- Condylomas are characterized by a small stalk. It is this that gives impetus to the inflammatory process and should be removed from the inside.
Papillomas look like growths with papillae. Sometimes they are adjacent to the skin or mucous membrane, or they can simply stand on a leg. This type of virus usually manifests itself as pink condylomas with light dots on the edges.
Often the disease is almost asymptomatic. But if itching appears in the genital area, rashes appear and the skin turns red, then we can talk about the development of the active phase.
Differential diagnosis
At the beginning of development, the presence of type 65 virus in the body can be detected during diagnostic measures, at later stages of the formation of papillomas - during an external examination.
To obtain results in women during a colposcopy, the doctor takes a Pap smear. In 25-30% of cases the test is positive.
It is more difficult to determine infection in men. To obtain accurate data, material from the mucous membranes of the nose, urethra, and genitals is used. If the development of anal cancer is suspected, a rectal smear is done for HPV type 56.
If human papillomavirus is diagnosed in a child, it is necessary to obtain a smear from the larynx and do a blood test for antibodies to this strain.
More informative methods are used to confirm the diagnosis. One of them is PCR - polymerase chain reaction. It allows you to isolate viral DNA from an affected cell, and a preliminary result is obtained within a few minutes, and a more accurate result is obtained after a day.
Another highly accurate method, according to reviews from patients and specialists, is the Digene test, which allows you to detect the presence of a pathogen in the blood and determine the viral load (the number of HPV particles).
Causes of appearance and location of localization
The virus cannot develop in the body of a healthy person. We need factors that trigger activation.
The main ones can be noted:
weak immune system.- Metabolic disorder.
- Predisposition to cancer along a genetic line.
- Exacerbation of chronic pathologies of the genital organs.
- External stimuli.
- Rooms with high moisture content.
To avoid becoming infected with the virus, you should not go to the bathhouse or sauna without slippers.
The type of virus can be determined by its location. With the genital areas, of course, it is more difficult, since formations of different strains may appear there.
But HPV 56 is characterized by certain places:
- uterus.
- Anus area.
- Genitals and surrounding area.
- Urethra.
If condylomas are detected in these areas, you should immediately consult a doctor. The disease in its advanced stage is very difficult to treat.
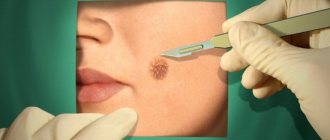
Treatment of papillomas
Any specific therapy that can permanently cure any type of HPV has not yet been developed. Therefore, the main measures are aimed at removing tumors and reducing the concentration of pathogen cells in the blood. Treatment of HPV type 56 in women, as well as in men, is carried out comprehensively using surgical methods and drug therapy. Surgical treatment is carried out to remove tumors: condylomas, warts, papillomas. For this, modern ectopic methods are used:
- laser removal;
- cryodestruction;
- curettage;
- radio wave therapy;
- electrocoagulation;
- chemical destruction with salicylic or trichloroacetic acid;
- surgical excision.
A radical method is amputation of the cervix. It is performed in a hospital setting for medical reasons. The remaining procedures are considered minimally invasive and painless. To obtain the most productive result, specialists combine surgical intervention with the use of medications.
Drug therapy for HPV type 56 is carried out using the following drugs.
- Antiviral agents - “Cycloferon”, “Viferon”, “Panavir”, “Allokin-alpha”.
- Immunomodulators – “Lavomax”, “Immunal”, “Isoprinosine”
- Cytostatics – “5-fluorouracil”, “Podofilin”, “Vinblastine”.
Taking into account the prevalence of the viral process, the patient’s age and the presence of concomitant pathologies, the doctor prescribes a combination therapy regimen that includes some of the above drugs. The course course lasts on average 10-14 days. If you have a regular sexual partner, both should be tested.
Prevention recommendations
The first and main way to protect yourself from infection with HPV type 56 is protected sex. Vaccination is also considered a necessary measure. Injections can be done:
- children 11-13 years old;
- women under 26 years of age;
- men under 21 years of age.
Sera "Gardasil", "Cervarix" do not contain live genetic material of the virus, therefore they are considered safe.
Minor side effects may occur after vaccination:
- swelling of the skin;
- mild pain at the injection site;
- redness of the area of skin where the vaccine was given;
- tingling in muscles;
- slight increase in body temperature.
Other preventive measures are:
- lifestyle changes;
- nutrition correction;
- maintaining personal hygiene;
- taking vitamin and mineral complexes to strengthen the immune system;
- elimination of stress, depression, hypothermia;
- giving up bad habits;
- timely treatment of concomitant diseases;
- regular examination by a gynecologist;
- careful choice of sexual partner.
It is important to know! Quite often, patients resort to traditional methods of removing warts and other formations on the skin. Doctors strictly prohibit taking such actions, as this can lead to progression of the disease and rapid growth of the tumor.
Folk remedies often have a healing effect, but they should be used only after consultation with a specialist. Following simple recommendations will help you protect yourself from infection or cope with pathology and live a normal life.
Traditional therapy
Among the traditional treatments for HPV, there are only drugs that will help maintain and strengthen the immune system. For this purpose, decoctions of medicinal herbs, various tinctures and ointments are prepared. If the papillomas are located on the outer part of the genital organs, then they can be lubricated with beaten egg white. It will help dry out the formation and slow down its growth.
To stop the growth of genital warts, you can prepare a horse chestnut bath. To do this, approximately 7 kg of fruits need to be poured with boiling water, wrapped and left for 10 hours. After this, the prepared infusion is added to bathing water for 2 weeks, then washing and thoroughly drying the genitals. After treatment, towels and underwear must be washed in hot water with added powder.
Treatment of infection with folk remedies is possible only if they are compatible with traditional methods. Be sure to consult a specialist before starting therapy. After undergoing therapy, at least 3-4 times a year, it is necessary to undergo a preventive examination. You should also protect your body from diseases.