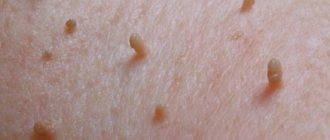
Thread-like papillomas, or, as representatives of official medicine call them, acrochords, are small growths on a thin stalk on the surface of the epidermal layer. The difference from other warty growths is their oblong shape. The main reason for the appearance is the activation of the human papillomavirus, which either penetrates the body initially, or is activated after hibernation in the presence of favorable conditions (weakened immune system). The only effective method of dealing with the problem is removal using various methods.
Papilloma color: why does it change?
Papillomas (aka warts) can be found on the body of almost every person.
The cause of skin growths is the penetration of the HPV virus into the blood. The main route of transmission of infection is sexual contact with a sick partner. In some cases, human papillomavirus infection can be acquired through household means. The main danger of the disease is the possibility of malignancy of the wart. A clear sign of the onset of degeneration is a change in the color of the papilloma. But this is not the only reason why growths can change color.
The main reasons for the appearance of papillomas on a child’s body
Papillomatosis can be congenital or acquired. The last option is the most common.
A child most often becomes infected through household contact.
. Any contact with infected dishes, toys, or other personal hygiene items can be dangerous for the baby and cause the appearance of papillomas on the child’s body. All children who visit public places - children's institutions, swimming pools, gyms, schools - are at risk. HPV can also be transmitted through kisses between a baby and sick people.
Self-infection of a child often occurs
. In this case, the pathogen, which is found almost everywhere, can enter the body if the baby does not wash his hands often enough, bites his nails, or licks his fingers.
As for congenital papillomatosis, infection occurs during childbirth
— the virus is transmitted from an infected mother to the baby. There is no exact data regarding whether intrauterine HPV infection is possible.
Usually, from the moment the pathogen enters the body until the manifestation of papillomatosis, a fairly long period passes - from a couple of months to several years.
The following factors contribute to the appearance of external symptoms of the disease, such as papillomas on the body of a child:
- Weakening of the immune system;
- Frequent infectious or colds;
- Long-term use of medications, especially antibiotics;
- Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- The presence of severe allergic reactions;
- Frequent stress, nervous tension.
Sometimes papillomas appear against the background of the above conditions, but after the negative factor ceases to affect the child’s life, self-healing occurs. The mechanism for this has not yet been fully explored. However, it is worth remembering that only the external manifestations of papillomatosis go away. The virus remains in the body in a “dormant” state.
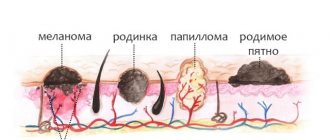
Dark papillomas: probable causes
The color of warts can vary from flesh-colored to deep brown. And this is a physiological norm. In some cases, brown and red papillomas initially form on the human body (see photo below).
All of these are acceptable options, provided that the warts do not grow or change color. If you observe any visual changes, for example, the papilloma has darkened, then this is an obvious reason to seek medical advice. It is better to play it safe and undergo the necessary examinations that will help determine the cause of the change in shade than to get oncology.
The causes of darkening of the wart can be:
- regular damage to the tumor. If a growth has formed on the scalp, then constant violation of its integrity is an inevitable process. Similar regular injuries occur with warts located, for example, in the armpit or groin. It can be caused by shaving or wearing underwear that is too tight;
- joining the damage to a secondary bacterial infection. In this case, there is redness around the papilloma, and the wart itself may become inflamed and darken. An additional symptom of infection is swelling of healthy tissues and pain in the formation itself;
- increasing the body's immune defense. If suddenly the papilloma turns black and falls off, the cause may be the activation of the body’s immune abilities. The condition does not pose a danger;
- use of medications. After treatment with special compounds, the death of the papilloma is observed, a brown color or a darker shade is observed - the wart’s reaction to cauterization.
But the transformation of a once pink wart into a black papilloma may indicate the beginning of degeneration. In this case, there must be special symptoms indicating the development of a pathological process.
MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF THE RF: Papillomavirus is one of the most oncogenic viruses. Papilloma can become melanoma - skin cancer!
Initially (from the moment they appear on the human body), dark-colored papillomas can form as a result of:
- strong changes in hormonal levels;
- the body is in a stressful state.
In any case, if the wart darkens, it is necessary to obtain qualified medical advice.
Red papillomas - pathology or normal?
The growth may initially be red in color, which is due to the structural features of the neoplasm tissue. Red papillomas are sometimes observed in newborn babies. Infections suffered by the mother during pregnancy can cause such growths on the body of babies. But if a flesh-colored wart or pink papilloma turns red, then this is a serious cause for concern.
Redness of the papilloma can be caused by a number of reasons. This:
- regular injury to the tumor;
- taking hormone-containing medications;
- using alkaline-containing products to remove warts on your own;
- suffered a stressful situation.
If the papilloma is red and painful, then, most likely, a secondary bacterial infection has occurred due to injury. In this case, in addition to the fact that the papilloma has become red, the following signs may appear:
- changing the original form;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor;
- burning;
- itching;
- soreness of the wart.
If the papilloma has enlarged and turned red, then this may be a signal of the beginning of the process of degeneration.
Papilloma has turned black: what is the reason and what is the danger of the condition?
Quite often, people visit a dermatologist with the complaint that the papilloma is turning black. Pathology can be caused by various reasons.
Black papilloma becomes a result of:
- injury to the formation and attachment of a secondary infection. As a result of the pathological influence of protozoa or viruses, the wart may turn black;
- the growth turns black after treating its surface with products intended for removal at home;
- the wart may change color due to activation of the immune defense. The body fights the virus and, as a result, the wart darkens and falls off on its own.
On a papilloma, a black dot may appear as a result of constant trauma to the surface of the neoplasm.
Sometimes regular violation of the integrity of the wart can provoke the beginning of the process of degeneration. Signs of malignancy are:
- the color of the wart changes. Most often, at the beginning of the rebirth process, they turn black;
- Not only itching is noted, but also quite severe pain;
- both the wart itself and the previously healthy surface of the skin turn red. Additionally, an inflammatory process can be recorded;
- The skin growth may begin to dry out on its own. Later it simply falls away;
- the surface of the formation can transform into a painful ulcer.
If such symptoms appear, immediate medical attention is necessary.
Brown papilloma: a reason for concern or a normal condition?
If a brown papilloma initially appeared on the body (see photo), then there is no reason to worry. You should only think about visiting a doctor if there is a visual change in the tumor - darkening of the wart, or an increase in its original size.
Skin growths change their color to brown for standard reasons:
- injury to education;
- secondary infection caused by injury;
- sudden hormonal changes that have occurred in the body of a sick person, etc.
If traumatization of the growth occurs, you need to consult a specialist. This will help to avoid the development of serious complications in the future, in particular, to prevent the process of malignancy.
White papillomas
It is important to remember that warts, under the influence of certain factors, can not only change color to a darker shade, but also become light. The growths turn white as a result of death. The reason is the lack of nutrition of the neoplasm. A similar effect can be achieved by tying the base of the wart.
The skin formations also become white after the growth is removed using special techniques, in particular freezing with liquid nitrogen (cryodestruction).
A change in the color of a tumor is always a reason to seek qualified help. Since only a specialist can determine the cause of the process. The patient will be given a full medical examination, which will help identify the true causes of the change in the color of the skin growth.
Red papilloma
What color are papillomas? The growth that forms on the skin may initially be red. Most often they are observed in newborn babies. They, like white papilloma, are caused by infections suffered by a pregnant woman. They shouldn't be a cause for concern.
However, if the flesh-colored papillomas turn red, then this is an alarming “bell”. Redness of a wart can be caused by:
- regular injury;
- taking hormones;
- stressful situations;
- the use of alkali-containing drugs.
Red, brown, white papillomas. What does the color say?
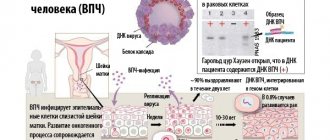
Papillomas are benign neoplasms, the appearance of which is caused by damage to the body by the human papilloma virus. Infection can occur during unprotected sexual intercourse and through direct contact with a carrier of the virus. For most people, the virus is in an inactive phase, due to which they are not even aware of its presence.
The growths may differ in color and shape, but they are all harmless until they begin to change. An increase in size, change in color and shape may indicate the degeneration of a neoplasm into a malignant tumor. In this case, treatment must be started urgently.
Symptoms
Papilloma (epithelial growth) may appear suddenly. They are most often discovered by chance if they are located in skin folds, under the armpits, etc. Children may develop neoplasms on the skin of the face, hands, soles, and, less commonly, on other parts of the body. The disease manifests itself by the appearance of warts, moles, and growths. In addition to the skin, the mucous membranes of the nose, mouth, larynx, and bronchi may be affected.
The shape of papillomas can be different: flat, voluminous, elongated, in the form of a fungus on a stalk. Their color varies from white to brown. Most often, these formations are localized in the acquired form of the disease on the face, in the axillary region, on the neck, feet, palms, and in the periungual area.
With congenital papillomatosis, these growths often appear on the oral mucosa and larynx. But the localization of papillomas in infants can be different: on the eyelid, on the eye, on the auricle, on the tonsil, on the face.
Neoplasms appear in the form of a single growth or a whole group of papillomas. Papillomas can grow up to 2-5 cm in diameter, can grow and occupy a significant area of the skin or mucous membranes. When these unsightly formations appear, especially on the face, children may develop psychological complexes. In rare cases, papillomas can degenerate into a malignant tumor.
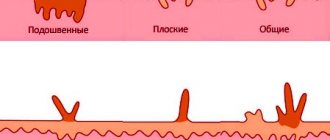
Depending on the appearance and location, there are several types of papillomas:
- vulgar: warts are round in shape, small in size, covered with a rough, keratinized layer of skin; most often occur on the back of the hands and buttocks, knees, but can also appear on other parts of the body;
- flat papillomas: they look like a small elevation above the skin level of the same color; in infants, these formations may be accompanied by itching and inflammatory changes at the site of scratching;
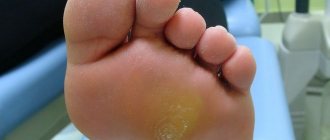
- plantar papillomas: they look like dense small warts of a yellowish color with small small dots inside, located on the sole of the child; may cause pain and difficulty walking; dry callus (outwardly similar to a wart), does not have dark spots;
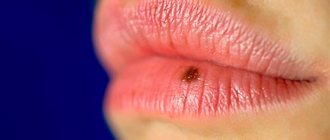
- small filamentous warts: localized on the face, neck, armpits and groin folds; they look like thin papillae on a stalk, and may have an extension at the end; color - normal skin or with a slight pink tint; if they are subjected to friction by clothing, they can separate on their own with the appearance of a drop of blood in this place;
- juvenile papillomatosis of the larynx: papillomas are localized in the glottis and cause breathing and speech problems; this serious disease (fortunately, very rare) is typical for infants born from an infected mother and is detected in the first months of life;
- epithelial hyperplasia is a type of papillomatosis: small thread-like papillomas form on the oral mucosa (palate, tongue, inner wall of the cheek); They can, despite their small size, cause discomfort in the child, so their treatment should not be delayed;
- warty dysplasia: looks like rough red-brown spots on the skin of the hands and feet; develops very rarely, but can have a malignant course (in 30% of cases).
Warts can appear in a child more than once, which is a manifestation of serious problems in the body and weakened immunity.
Most often, papillomas do not cause concern or pain. When itching and scratching occur, they can become infected and inflamed. It is impossible to tear them off forcibly, as this threatens the spread of the virus in the body and the appearance of a large number of papillomas.
If the papilloma is localized in the inguinal fold or near the anus, the child’s discharge can cause irritation and ulceration of the formations. In this case, to avoid such complications, you need to carefully monitor the hygiene of the genital organs.
Red papilloma: cause of appearance and changes
Sometimes initially red papillomas appear on the body. This is due to a number of structural features of the growth. This phenomenon should not cause alarm. Red papillomas are often noticed on the skin of infants. Their appearance is explained by the fact that the mother suffered an infectious disease during pregnancy.
In the same case, if the initially pink or flesh-colored growth suddenly turns red, then this phenomenon cannot be ignored.
This process can be triggered by a number of factors:
- The growth is constantly injured;
- The patient takes medications that contain hormones;
- In order to remove the growth, alkali-based products were used;
- Exposure to stress.
If the papilloma suddenly turns red and causes unpleasant pain, then most likely it was injured. As a result, in addition to the viral infection, a bacterial infection also appeared.
In cases where a red papilloma appears instead of the usual one, the following symptoms may appear:
- Change in size and shape;
- Itching and burning;
- Unpleasant odor;
- Pain in the area of the growth.
Enlargement and redness of the tumor often indicates its degeneration into a malignant tumor. If these symptoms appear, it is strictly forbidden to hesitate to consult a doctor.
Why did the papilloma change color?
Black papillomas
If the color of the papillomas has become dark, then this is an alarming “bell”, since it can cause serious diseases. A darkened tumor may indicate the degeneration of papilloma into a malignant tumor.
Most often, the tumor darkens because it is injured by a comb, clothing and other objects. If the papilloma not only begins to darken, but also hurts and does not return to its usual state, you need to contact a specialist who will prescribe effective treatment.
Prolonged stressful situations and taking hormonal medications can also provoke darkening. An equally common cause of darkening of papilloma is exposure to medications. A change in its color indicates that the tissue of the formation has begun to die.
When treating, for example, white or flesh-colored papillomas with acetic acid, liquid nitrogen and other alkaline agents, the defect will also change its color. Under such circumstances, darkening should not be a cause for concern - this process is natural.
Quite often there are situations when a tumor on the body suddenly turns black over a long period of time, then falls off without any intervention. At the same time, the person did not experience any discomfort. This occurs due to strengthening of the immune system and changes in hormonal levels and should not be a cause for concern.
Brown papillomas: the danger of changing the growth
Shades of neoplasms can vary from flesh-colored to dark brown. This is considered the norm. Often a brown papilloma immediately forms on the body. There is no reason to worry about this.
In the same case, if the color and size of warts and papillomas suddenly change, then you should definitely seek help from a doctor. With its help, it will be possible not only to determine the cause of the modification of growths, but also to avoid their degeneration.
Among the main reasons for these changes, doctors identify the following:
- Regular damage to the growth. For example, when papillomas form on the head, a violation of their integrity is simply inevitable. The same will systematically happen with warts localized in the groin or armpits. In this case, the specialist will tell you how to get rid of brown spots that are subject to regular damage;
- The damage was accompanied by a bacterial infection. There is redness of nearby tissues, inflammation and darkening of the growth. Accompanying symptoms include painful growth and swelling of healthy skin;
- Protective function of the immune system. Blackening and falling off of the tumor indicates activation of the immune system. In this case there is no danger;
- Use of medications. Patients who got rid of growths using special means also observe their darkening. This is a natural reaction of the neoplasm to cauterization;
If the papilloma was pink and turned black, then this may indicate that its degeneration into a malignant formation has already begun. The pathological process will be indicated by a characteristic clinical picture.
In addition, hormonal imbalance and exposure to stress can cause the growth to change color.
Symptoms of the disease
It should be noted that if there are no symptoms of the disease, parents often do not suspect the presence of the virus in the child’s body.
This delays visiting a specialist and prescribing drug therapy. Usually, the main sign of infection is the wart itself, which can appear on any area of the skin or mucous membranes. The most common place for papilloma to appear is the hands, forearm, armpits, fingers, and face. Neoplasms in children can affect the oral cavity and larynx. In certain situations, warts are noted on the organs of the reproductive system, near the anus.
The growths come in different shapes, sizes and shades. Mostly, they are single or multiple growths that merge in certain situations with each other, forming a kind of crust that rises above the skin.
There are times when a child is worried about symptoms such as itching and painful discomfort. This occurs due to scratching or tearing off the warts, which begin inflammation and spread to other parts of the body. When they occur on the organs of the reproductive system, the signs of the disease also often cause inconvenience. In such a situation, the reason may be biological secretions (urine, feces), irritating the child’s sensitive skin.
White papilloma: causes of colorless growth
Papillomas on the body, regardless of what color they were originally, can become either dark or very light. There are a number of reasons for this. Most often, this process is caused by the death of the growth and the cessation of food supply to it. Such a change is noted after ligating the papilloma or removing it using special methods.
It is possible that lightening will be observed after treating the growth with natural celandine juice. There are papillomas that turn white because the body independently begins to fight the virus. As a result, benign neoplasms die off.
Are papillomas dangerous in a child?
Medical scientists have been able to identify about 170 strains (types) of HPV, some of which carry a risk of developing cancer. In other cases, warts on the body are not dangerous if they are not injured or cut off. Small children are unable to control their actions and often tear off or scratch the papilloma while playing. This is dangerous, bleeding may begin, there are many small vessels inside, the epidermis is thin and fragile. An injured viral growth can cause infection to another child.
Regular friction, damage and active picking of warts causes inflammation, which increases the risk of secondary infection.
Doctors do not advise delaying treatment of the disease. Regular monitoring of the development of papillomatosis is required.
Black papilloma: when is it time to sound the alarm!
Particular attention should be paid to growths that have acquired a black color. The reason for this may be:
- Attachment of a bacterial infection as a result of damage to the neoplasm. The cause of the color change may be the pathological influence of viruses or protozoa;
- Blackening of the tumor is caused by the use of medications that are intended to remove tumors at home;
- The immune system fights the virus. As a result, the papilloma turns black and falls off;
- The appearance of a black dot may be due to damage to the surface of the growth.
A change in the color of a tumor as a result of its constant damage can cause its malignancy (degeneration into a malignant tumor). Among the main features of this process are the following:
- The growth changes its color shade. In most cases it turns black;
- The patient suffers from severe pain and itching:
- Redness of the papilloma and nearby tissues;
- Inflammatory process;
- The neoplasm dries out without any additional impact on it. After a short time it disappears;
- At the site of the papilloma, an ulcer appears, which can hurt and even bleed.
Patients who have one or more of these symptoms should seek help from a medical facility as soon as possible.
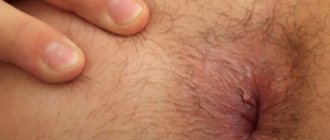
Papilloma in children on the ear, what to do: is treatment necessary?
Causes of the disease: provoking factors
Papillomas on a child’s ear are a benign formation, so do not panic. They can be acquired or, on the contrary, congenital. Babies most often become infected with HPV in the womb and during childbirth. The acquired type of disease is transmitted through household means, for example through dishes, household items and close contacts.
This occurs as a result of such factors:
- weakened immunity;
- disruption of the digestive system;
- allergic reactions;
- long-term use of medications;
- severe nervous and emotional shock.
Is treatment necessary if a child was born with papilloma on the ear?
Today, dermatologists are divided into two camps regarding papillomas in a newborn’s ear (see photo):
- The first believe that the growth needs to be monitored and only when it multiplies, enlarges or becomes inflamed should removal be resorted to.
- Others believe that the wart must be removed immediately to avoid injury to it, which can lead to the spread of infection and inflammation of the ear.
The choice of which side to join depends entirely on the parents, but it is worth noting that there are many more supporters of the second statement.
Sometimes there are cases that a baby is already born with a growth on the ear. This happens if the mother has a large number of tumors throughout the body, and HPV in the blood has a very high concentration. In this case, therapy should begin immediately, since over time, warts will begin to appear on other parts of the body.
Drug treatment of papilloma on the ear
Methods for removing warts in newborns
In most cases, treatment of papillomas near the ear of a newborn does not produce tangible results. Then doctors resort to removing the warts. This is necessary to avoid the proliferation of tumors and the formation of inferiority complexes.
Modern medicine identifies the following methods for removing warty growths:
- Cryodestruction is the most effective method of removal. The doctor uses a special apparatus to apply nitrogen to the formation. A wound appears that heals in a few days. This method is absolutely painless and does not require anesthesia.
- Exposure to high frequency current. The neoplasm is destroyed as a result of exposure to high temperature, which leads to boiling of the liquid in the tissues of the wart. The disadvantages of this method of removal are its severe pain and long period of wound healing.
- Laser removal - this method allows you to get rid of warts of any size. Before the procedure, anesthesia is administered. At the same time, healthy tissue is cauterized, stopping bleeding. After the procedure, a scar remains, which will resolve in a few months.
- Removal with a radio knife is a method during which a wart is irradiated one-time with special high-frequency ionizing radiation. The procedure is quick and painless. Can be used when the tumor size is no more than 3 cm.
- Cauterization - this method involves the destruction of wart tissue by applying a special agent made from inorganic and organic acids to its surface. Before the procedure, a painkiller is administered. The healing process takes a long period, after which a scar remains.
It is worth noting that in most cases, cryodestruction is used to remove tumors as the safest and most painless method.
Traditional methods of treating papilloma
You can use proven methods of traditional medicine:
- it is necessary to apply a soaked piece of cotton wool in 3% hydrogen peroxide to the growth 2 times a day;
- lubricate the wart with celandine juice or several times a day with the white of a chicken egg;
- Apply a cotton swab soaked in fresh cabbage juice.
Prevention measures
The appearance of papillomas on the skin can be prevented. Doctors say that if all recommendations are followed, the virus living in the body may never be activated. This is also indicated by reviews of patients who managed to cope with the disease.
Among the main preventive measures are the following:
- All diseases (infectious, viral, chronic) must be treated in a timely manner;
- Get rid of all bad habits without exception;
- Proper nutrition. The diet should contain a lot of vegetables and fruits;
- Psychological stability in stressful situations;
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- Sports activities;
- Complete rest;
- Strengthening the immune system.
Prevention and prognosis
Timely treatment of papillomatosis in a child has a favorable prognosis. The outcome of the disease depends on the type of pathogen. The virus is more dangerous for girls, as it can cause cervical cancer. If left untreated, the growths periodically intensify their growth.
Over time, they provoke physical and aesthetic discomfort. Large papillomas are damaged more quickly, leading to bleeding and secondary infection. After successful therapy, there is a risk of relapse, which is associated with the inability to completely eliminate HPV from the body. To reduce the risk of relapse it is recommended:
- wash your hands frequently;
- use disposable paper napkins in public places;
- wear only your own clothes;
- give up bad habits: biting nails, picking wounds, sucking fingers;
- good nutrition;
- active lifestyle;
- strengthening the body's defenses;
- timely treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases.
In case of relapse, it is recommended to undergo a repeated comprehensive examination to prevent complications and eliminate the activity of the virus.
What to do if the papilloma has darkened
HPV (human papillomavirus) - the cause of the formation of papillomas - has many varieties. Some of them are characterized by a high probability of malignant degeneration, while others are relatively safe. To know for sure, you need to monitor the development of tumors and consult a doctor if atypical transformations appear. One of these warning signs is a change in the color of the papilloma: for example, it has darkened or turned brown.
Types of papillomas
A papilloma is a growth on the skin or mucous membrane, often shaped like a fungus on a thin base. The shade ranges from white to brown. The incubation period is mainly 3 months. HPV begins to show its greatest activity six months after infection. The growths can be single or multiple (colonies). Depending on their location and type, they are divided into the following varieties:
- Vulgar. They are small formations of a round shape. The top layer of papillomas is covered with keratinized skin. The growth is localized on various parts of the body, but most often they are observed on the inside of the hands and on the buttocks.
- Flat. Minor growths above the skin, flesh-colored. Babies sometimes itch, which results in irritation and inflammation in the affected area of the skin.
- Plantar. Localized on the sole. They are characterized by a dense structure, flesh-colored or yellowish in color. These neoplasms must be distinguished from ordinary calluses, since they are similar in appearance. Small dark dots can be observed inside the wart, but they are absent in the callus.
- Thread-like. They form on the face, neck, under the arms, in the groin and close to it. They are small papillae, which are attached to the upper layer of the skin by means of a thin base; at the end they can expand somewhat. The standard color of such neoplasms is flesh-colored, but it can also be pink. Small papillae can separate on their own due to friction with clothing, in which case drops of blood can form on the skin.
- Laryngeal papillomatosis. It is a serious illness that occurs in children due to the development of a virus inside the organ. A common location for growths is often the glottis, which provokes speech disorders and breathing problems. If a respiratory disease occurs, the walls of the throat swell, which may result in difficulty breathing, and in the most difficult situations, suffocation. The disease is typical for children at 1 month of age, therefore a pregnant woman needs to take care of the health of the fetus and take measures before birth in order to sanitize persistent foci of infection.
- Epithelial hyperplasia. A type of disease that develops on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity - tongue, palate, inner surface of the cheeks. New growths are small thread-like growths. This type can cause significant inconvenience to the child, so therapy should be carried out without delay.
- Warty dysplasia. Looks like red-brown rough spots on the baby's arms and legs. This form of the disease is observed infrequently, but in certain situations it can provoke a malignant course.
The human papillomavirus can be acquired or congenital; in many situations, a growth in a child is formed when the mother is a carrier or is susceptible to this disease. During the process of passing through the birth canal, the infection enters the baby’s body and carries out its negative functioning.
If you suspect this disease, you should consult your pediatrician. He will prescribe a full diagnosis of the child’s body, tests, and determine the factors that provoked the pathology. Regularly occurring neoplasms in a child signal problems within the body. By detecting papillomas in a timely manner and carrying out the necessary therapy, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of adverse consequences in the child.
Reasons for changes
There may be many reasons why the papilloma turns black or changes its shape or size:
- Natural healing process. As the drug is exposed, the growth may turn black and dry out, gradually dying off. Usually, products with a necrotic effect are used for this purpose: Solcoderm, Superchistotel. If you do not interfere with this process, the papilloma will fall off on its own, leaving no scars on the skin.
- Trauma to papillomatous formation. In case of accidental or intentional damage (partial or complete tearing off), bleeding begins, as a result of which the wart can become infected, inflamed or fester.
- Swelling, maceration and hyperemia of the skin around the papilloma are signs of systematic exposure to tight underwear, razor blades or outerwear. Most often, large folds of skin suffer from this (areas under the armpit, on the buttocks, between the legs). Against this background, the papilloma may change its color: for example, black dots may appear on it - signs of internal hemorrhages.
- Senile changes. As a person ages, existing warts may increase in size and become brown in color.
Appearance and localization
Not everyone knows what acrochords look like and what they are. They can be distinguished from other types of warts by their characteristic features. The main feature of filiform papilloma is its long and thin stalk.
The head may be thicker and harder. To study these tumors in more detail, you should look at the photo of filamentous papilloma.
It is a dense but elastic wart that is dark brown or pink in color. The shape of the head can be oval or spherical. The length of such skin growths is usually 3–5 mm, but in some cases the acrochords grow up to 10 mm.
Initially, a small bumpy bump appears on the skin, which can easily be confused with a mole. But then it stretches out and takes on a characteristic shape. Often these warts grow in groups.
In this case, they often grow together, resembling a cockscomb. Solitary acrochords most often appear in adolescents and young adults.
Filiform warts prefer areas of the body where the skin is thin and delicate, as well as various folds and depressions with high humidity.
- Surface of the eyelid;
- Area around the eye;
- Paranasal area;
- Almost the entire surface of the skin on the neck (it is this area that is most often subject to the growth of neoplasms). Growths are especially common on the sides of the neck;
- Folds in the groin area;
- The area under the breasts in females;
- Armpits (in some cases the entire surface of this area is affected).
Acrochords are rarely found on the soles, legs, thighs, arms, back, and buttocks. The skin in these places is too dense and rough for them.
On the face, filamentous warts usually appear on the eyelids, near the nose, and on wrinkles in the forehead. Their favorite place is the neck, especially its lateral surface. They often grow in the armpits and groin. Women may find acrochords under the mammary glands.
How dangerous are changes?
If the formation suddenly turns black, changes shape, increases in size and hurts, it is necessary to undergo diagnostics for its malignant degeneration.
Sometimes the patient is bothered by specific symptoms: the papillomatous formation may itch and hurt, and atypical discharge (blood, skin secretions) is often observed.
Signs of malignant degeneration
Cases of malignancy of papillomas are quite rare in dermatological practice . We can talk about malignancy if the following processes occur with the neoplasm:
- Changes in the outlines of the papillomatous growth.
- Unreasonable bleeding and pain to the touch.
- Rapid growth and enlargement of the lesion.
- Swelling and hyperemia of the skin (it may harden around the growth).
- The appearance of dark spots: the papilloma may not become completely black, but in fragments. Typically, the formation of nodules and blackheads is an external sign of hemorrhages resulting from injury or excessive pressure on the tumor. In some cases, such nodules indicate the onset of malignant degeneration.
If you have one or more of the above symptoms, you should consult a dermatologist. The sooner the problem is detected, the greater the chances of a speedy recovery.
Symptoms and signs of papilloma
Papillomas are most often found in folds, under the arms, on the skin of the face, and on the hands and feet. The mucous membranes of the nasal cavity, larynx and bronchi may also be affected. They can grow up to 2-5 mm in diameter, occupying large areas of the affected skin and mucous membranes. Types of papillomas in children:
- Vulgar – are warts of a round shape, relatively small in size, covered with keratinized skin
- Flat papillomas - look like a small elevation above the skin level of the same color
- Small filamentous warts - look like papillae on the skin, thickened at the end, have a light pink color
- Plantar papillomas - look like dense small yellowish warts with small dots inside
- Juvenile papillomatosis of the larynx - papillomas are located in the glottis area: breathing and speech functions are difficult. It is one of the most severe types of HPV; fortunately, it is rare and is transmitted mainly during childbirth from an infected mother.
- Epithelial hyperplasia – characterized by the presence of papillomas on the oral mucosa
- Warty dysplasia - appears very rarely, is characterized by the presence of red-brown spots on the skin of the hands and feet, can have a malignant course
The appearance of warts in a child most often indicates a decrease in immunity. Most often, papillomas do not cause discomfort, but if itching and scratching occur, they can become inflamed and infected. If papillomas occur in the area of the inguinal fold or near the anus, the child’s discharge can also cause irritation and infection.
What to do with a wound from a fallen off papilloma
If, as a result of treatment, the wart has darkened or turned blue, dried out and began to fall off by itself, the tear site must be disinfected . Microdamages of the skin after tearing off a papillomatous growth may not be visible to the naked eye, but are open to infection. To prevent this from happening, the wound must be treated with hydrogen peroxide, Panthenol or Miramistin ointment and then covered with an adhesive plaster.
The tear site should be monitored until complete healing. If this process takes longer than 4-5 days, you should consult a dermatologist.
What are acrochords and their features
A pedunculated papilloma, referred to as an acrochord, is a papillary-type growth, elastic and soft on palpation. The formation does not exceed 1-2 cm in size (the maximum indicator of acrochords), is represented by a group of processes 0.1-0.3 mm in size, which are similar in appearance to a torn thread of skin.
The growth of papillomas is provoked under the influence of activation of low-oncogenic HPV, warts cannot degenerate into a cancerous tumor.
The color can range from light beige to brown. Under the influence of solar or artificial insolation, acrochords on the body can turn black and become inflamed. People with thin, delicate dermis, old people, pregnant women, and menopausal women are often susceptible to cutaneous filiform papillomas.
Diagnostics
If papillomatous growths are localized in intimate areas, for example, on the genitals or buttocks, an initial examination of the patient can be carried out by a gynecologist or urologist.
- Dermatoscopy.
- Polymerase chain reaction method: carried out to determine the DNA of the pathogen. The purpose of the test is to identify which strain of HPV provoked the disease, or rather, the degree of its oncogenicity.
- Histology: analysis is prescribed if cancer is suspected.
If histology does not reveal any pathological processes, the patient has nothing to worry about.
Where do they appear?
Filiform warts are selective in their localization. Throughout life, they can grow in different areas of the skin. In most cases, they form in areas where the epidermis is thinnest and where skin folds are present. In middle-aged people, such formations most often appear in the folds of the groin area. As we age, papillomas can appear in women under the breasts and in both sexes under the arms and on the neck.
As deep wrinkles appear and the epidermis thins, the skin of the face can be affected by warts. Especially often, filament-type papillomas occur on the forehead, eyelids and near the nose. In people over 65 years of age, the formation of warts of this type is observed on the hands and fingers, where the skin rapidly becomes thinner, becomes dry and greatly loses its elasticity. On the thighs, palms, feet, buttocks, back and other places where the skin is quite rough and elastic, such papillomas never appear.
Treatment
If the diagnosed strain of HPV is oncogenic, the only acceptable method of treating papillomas is surgery . In this case, the use of any medicinal chemicals, as well as folk remedies that cause necrosis of the lesion, is prohibited.
If the likelihood of malignancy of the blackened papilloma is low, it can be eliminated using standard control methods:
- Hardware techniques: freezing the lesion with liquid nitrogen, cauterization with a laser, radio wave knife.
- The medicinal method is with the help of drugs that have a destructive effect on the growth: Verrukacid ointments, Solcoderm, Panavir, Cryopharma, Super-celandine, Salipod patch. Under no circumstances should congenital growths on the skin be removed using this method.
- Home remedies: cauterization with celandine juice, compresses based on vinegar essence (diluted with glycerin 1:1).
In addition to all the above measures, it is necessary to take vitamin supplements and immunostimulants (Lykopid, Cordyceps).
Treatment and removal methods
Treatment of filamentous papillomas should only be carried out by a qualified specialist after a preliminary examination. You should not experiment and treat papillomas yourself. Only a doctor can correctly select the method of therapy in each specific case individually. Self-healing usually does not occur. It is important to get rid of growths, as they can become injured and inflamed.
The most effective methods to combat the problem are as follows:
1. Removal with a laser beam. One procedure is enough. There are no scars or complications. A small crust appears at the treatment site, which disappears on its own after a few days.
2. Radio wave surgery . It involves exposing the desired area of the skin to a device with high-frequency radio waves. These radio waves completely destroy papilloma tissue.
3. Cryodestruction . Involves exposure to liquid nitrogen at very low temperatures. The principle of operation is similar to the methods described above.
4. Method of electrocoagulation.
There are also effective pharmaceutical products:
- The drug is super clean . Using a solution of alkalis, chemical destruction of the growth tissue is achieved.
- Solcoderm solution. It is a concentrate of acids.
- The drug verrucacid . Processing is carried out within two weeks.
- Collomak . Gently destroys wart tissue.
Folk remedies
A positive effect can be achieved by treating the disease comprehensively: using traditional and folk medicine.
The following home remedies are most effective in fighting HPV:
- Celandine juice. Squeeze from a cut of a fresh plant, apply pointwise to papillomatous growths in the morning and evening.
- Rubbing with lemon essential oil or a mixture of tea tree and mint oils. You can repeat the procedure every 3 hours as needed.
- Aloe pulp. Cut off a fresh leaf of the plant, peel it from thorns and peel, and apply it to the affected area for 2-3 hours. The product can be left overnight, covered with a band-aid (for this it is better to use a paste of ground aloe pulp).
- Vinegar essence 70%. Apply directly to the growths using a cotton swab 1-2 times a day for a week. The essence can also be diluted with glycerin 1:1.
Traditional methods
Alternative medicine offers safer and more gentle methods for removing acrochodras. Their only drawback is their low effectiveness in the fight against multiple papillomas. But they do an excellent job with single growths that have appeared on the skin recently.
You can try to remove filamentous papillomas using the following traditional medicine:
- Celandine juice. They should treat the acrochord itself. The fresh sap of the plant dries out the growth, causing it to fall off safely. To see the effect of treatment, it is necessary to use this remedy for 2-3 weeks;
- Rowan fruits. Ripe berries are suitable for treatment, which must be ground into a paste and applied to the problem area. It is advisable to secure the fruits on top with an adhesive plaster and bandage. Rowan helps suppress the activity of viral infection and destroy cells of pathogenic growth;
- Garlic. The principle of using this product is the same as in the previous recipe. Garlic compresses help get rid of acrochordas in just a couple of weeks.
Sometimes patients who do not want to wait for the results of long-term treatment try to remove filamentous papilloma with a regular thread. To do this, they pull it over the base of the growth. Due to this compression, it stops receiving nutrition, which is why it begins to die. However, this method does not always work. In addition, it is very dangerous, as it can cause an inflammatory process around the papilloma. After such self-medication, the patient will require complex therapy.
Thread-shaped papillomas in adults and children appear due to problems with the immune system. Therefore, during the treatment of viral tumors, one should not forget to take medications that increase the body’s protective properties. These measures will help avoid relapse of the disease in the future.
Methods for diagnosing filamentous papillomas
To make an accurate diagnosis, you will need a consultation with a specialist and a series of studies. On the Internet you can find photos of filamentous papillomas, but you should remember that at the initial stage of formation, these growths can be confused with other formations. Differential diagnosis is carried out to distinguish acrochords from the following benign rashes: chicken pox, pyoderma, molluscum contagiosum, genital condylomas, mole, pedunculated fibroma.
Initially, the specialist conducts a visual examination of the patient and assesses the number and size of growths. If necessary, a dermatoscope is used - a special microscope for examining the epidermis. It helps detect blood clots in blood vessels and signs of angiopathy.
Also, most likely, you will need to donate blood for tests. The presence of papillomavirus is confirmed by PCR analysis, as well as a number of other, more in-depth blood tests - for the concentration of the virus, its strain, oncogenicity, etc.
If all of the above methods for diagnosing filamentous papillomas turn out to be insufficiently informative, the doctor may prescribe a histological analysis or biopsy of the skin formation.