HPV is a human papillomavirus that causes the appearance of warts, condylomas, papillomas and cancerous tumors. There are more than 100 strains, some of them have oncogenic activity, others do not cause pathological degeneration of cells. The viral infection is transmitted during sexual contact, through self-infection through abrasions, cuts, and from a sick mother to a child during childbirth. How does HPV and pregnancy proceed? Does the virus pose a threat to the intrauterine development of the fetus?
Harmful effects of the papilloma virus on women
HPV, which affects a woman’s genitals, is often asymptomatic, but leads to serious illnesses:
- Cell dysplasia.
- Cervical cancer, etc.
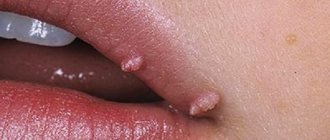
HPV manifests itself in women in the form of papilloma and condylomas (pointed and flat). Papilloma (flesh or pinkish in color) has the shape of a papilla. According to statistics, cervical papilloma is in second place after herpes, which affects the genitals. In 99% of cases of cervical cancer, the root cause is HPV.
Cell degeneration can occur slowly or rapidly. Condylomas are susceptible to this process. Flat condylomas are more dangerous in oncological practice, since they are susceptible to the rapid degeneration of a benign formation into a malignant one.
The papillomavirus has a powerful effect on the immune system, destroying it, which affects the health of the woman, the pregnancy and the health of the offspring. It is possible to become pregnant with HPV, but monitoring is required.
Diagnostic methods
According to statistics, every second woman is diagnosed with at least one strain of HPV, so when confirming the diagnosis, there is no need to sound the alarm. It is important to remember that the virus is activated when the immune system is weakened, and with the onset of pregnancy this always happens without exception. The main task of the expectant mother is to direct all her efforts to strengthen her immune system.
If a gynecologist suspects HPV, he will prescribe all the necessary examinations for the pregnant woman. Typically these include:
- visual examination by a doctor of a woman’s body to detect condylomas;
- colposcopy of the cervix (diagnostics allows timely diagnosis of changes in the tissues of the cervix);
- PCR research allows you to identify an organism by the structure of its RNA and DNA;
- To identify pathological cells, cytological examination of tissues is carried out;
- biopsy.
Conceiving a child with papilloma
HPV is not an obstacle to conception and is compatible with pregnancy. But this cannot be stated unequivocally. It is appropriate to mention some factors:
- Type of virus.
- Its localization.
- Size and shape.
- HPV response to pregnancy.
- Individual characteristics of the body.
Together, these factors prevent conception. They also give direction to the course of pregnancy. But it is acceptable to give birth with HPV.
During pregnancy, the virus begins to progress rapidly, which reduces the function of the immune system. Planning a pregnancy is obvious.
In what cases does pregnancy become impossible:
- The destructive effect of the virus leads to a malfunction in the immune system, the body becomes vulnerable to infectious diseases that prevent pregnancy.
- Pregnancy does not occur when there is a malfunction in the immune system and during conception, when the process of programming the immune system is disrupted. In this case, the pregnancy is terminated at the very beginning (or later): the body rejects the embryo as something foreign. Here we consider options for immune infertility.
- In some cases, the fertilization process is complicated by changes in the composition of the cervical mucus, which contributes to normal fertilization. Such processes are caused by the presence of genital warts on the mucosa. Cervical fluid serves as a conductor for sperm. Changing its composition prevents this and a woman cannot become pregnant with papilloma, or the process becomes much more complicated.
Will HPV prevent you from getting pregnant?
The presence of human papillomavirus infection does not affect the possibility of conception and the normal course of pregnancy.
Against the background of infection, local immune defense decreases. The development of dysbacteriosis, inflammatory processes in the reproductive sphere, and mycosis in the vagina is possible. The chance of getting pregnant with human papillomavirus is reduced.
With the active course of papillomatosis with the appearance of vegetations on the external genital organs, the question of possible pregnancy does not arise. The process is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms, pain during sexual intercourse, itching, and decreased secretory function of the mucous membrane, which makes sexual intercourse difficult.
Modern methods of treating HPV involve the prescription of system-wide and local antiviral drugs in the form of suppositories, sprays, and ointments. The formations are removed using minimally invasive techniques. During treatment, sexual activity is prohibited. It is possible to become pregnant naturally only after the end of the rehabilitation period and tissue healing.
Planning
Planning a pregnancy with HPV is natural and advisable. It is possible to get pregnant with cervical papilloma, but the virus causes a number of complications. The first thing you need to do when planning a pregnancy is to get tested for HPV.
A cytology smear is the minimum required to diagnose it. If the reaction is positive, the doctor prescribes treatment, after which pregnancy is possible. Getting rid of HPV is a reality.
Complex pathology may require surgical intervention, as a result of which pregnancy (in rare cases) becomes impossible. In such cases, experts recommend IVF (in vitro fertilization).
Symptoms of the disease in pregnant women
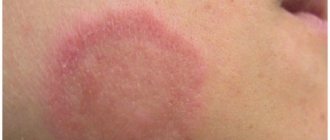
The tumor does not cause discomfort or pain. Formations resembling warts appear on the mucous membranes of the genital organs and in the anal area. These are soft, moist, flesh-colored or pinkish papillae. Sometimes their shape can resemble cauliflower inflorescences.
Large and small, convex and flat, numerous or single. The incubation period after contact with an infected partner is several weeks (sometimes several months). For diagnosis, cytological examination (smear) and colposcopy (visual examination using an optical device) are used. During pregnancy, a biopsy is not performed.
There are cases when HPV, first detected in a woman during pregnancy, completely disappears after childbirth or becomes significantly smaller when it comes to heavy growths.
Reasons for the development of the disease
The causative agent HPV has a complex structure and parasitizes in the upper layers of the skin. You can become infected through contact with a virus carrier.
Main routes of infection:
- sexual intercourse (the likelihood of infection does not decrease even with oral or anal sex);
- airborne droplets;
- direct contact with a contaminated object, for example, someone else's toothbrush, razor, towel, etc.;
- visiting public places, for example, a beauty salon, dentistry;
- intrauterine infection (immediately during childbirth).
As a rule, the causative agent of the disease is in a latent state in the human body, since it is contained by the immune system. But with the onset of pregnancy, the virus may become more active , and the following reasons contribute to this:
- Changes in hormonal levels that are inevitable with the onset of pregnancy. The body undergoes transformations in the functioning of the endocrine and reproductive systems, and immunity also decreases. If the disease makes itself felt already during pregnancy, the woman must undergo appropriate tests to identify the strain.
- Rapid weight gain. Observations have shown that obese women are more susceptible to the disease. The growth of papillomas increases closer to the third trimester, since this period is accompanied by rapid weight gain.
- Excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis) and friction. Benign formations love areas that sweat profusely, and also come into contact with clothing, accessories, etc. To avoid activation of the virus, you should carefully monitor personal hygiene.
If tumors grow on the skin, HPV can be recognized without additional diagnostics. If papillomas are actively growing on the cervix, the pathology can be diagnosed only after a thorough gynecological examination. But if the following symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor who is managing your pregnancy:
- unusual vaginal discharge (changes in abundance, color, as well as the presence of an unpleasant odor);
- formation of condylomas near the anus or genitals;
- pain in the pubic area;
- discomfort during urination;
- burning sensation during sexual intercourse.
How dangerous is the disease for pregnant women?
Is it possible to give birth if you have HPV? An exciting question. Sometimes HPV infection during pregnancy occurs without consequences. More often there is a significant increase in papilloma, which is an obstacle to childbirth. The primary virus can lead to termination of pregnancy at all stages.
During pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes serious changes, especially in the immune and endocrine systems. HPV makes the body practically helpless, unable to resist infections, viruses, etc. HPV types 16 and 18 are especially dangerous, which tend to degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Relapse and significant progression of the disease require immediate treatment, however, during pregnancy it may become impossible. HPV entails a decrease in the functioning of the immune system, which leads to the occurrence of infectious, viral diseases. Every infection in this situation is fraught with harmful consequences. In the absence of natural protection, the body of the expectant mother suffers on many levels.
How does HPV affect pregnancy?
No association has been found between infection and miscarriage, premature birth, or other pregnancy complications. In addition, the risk of transmitting the virus to a child is considered very low. If a pregnant woman may be infected with high-risk HPV types associated with cancer, her doctor will monitor her during pregnancy to watch for changes in cervical tissue. She should also tell the doctor if she has had cervical surgery. In some pregnant women with HPV, tissue changes may increase during pregnancy. If possible, doctors delay treatment because it can sometimes lead to premature birth.
If a pregnant woman has genital warts, the doctor will monitor their growth. Changes in hormones during pregnancy can lead to an increase in the number of warts. Sometimes the growths will bleed. Depending on their number, the doctor may delay treatment until after delivery. But if the warts become so large that they cause an obstruction in the vagina, they may need to be removed before giving birth.
Treatment
A woman infected with HPV is at risk. The level of risk depends on the type of HPV, which can be determined through a thorough examination. Dangerous types of the virus require immediate treatment:
- Surgical method.
- Removal of papilloma using laser.
- Cryotherapy (liquid nitrogen treatment).
A pregnant woman cannot undergo such treatment, so it is postponed until the postpartum period. For any type of HPV, immunomodulators are prescribed, since when infected with HPV, it is the immune system that suffers first.
Pharmaceutical drugs are not prescribed to a pregnant woman; it is permissible to use natural remedies that strengthen the immune system: echinacea, licorice root, bee products, nuts, berries, etc. The role of nutrition is extremely important!
Nutrition should not be easily balanced, the emphasis should be on natural vitamins and minerals (micro- and microelements), which are found in large quantities in green vegetables and algae. A pregnant woman's daily diet should include carrots, green apples, and pomegranate.
Individually, the doctor prescribes (if there is an obvious threat) antiviral drugs, which are selected carefully, with minimal risks for the child.
At the same time, the woman’s condition and the importance of taking these drugs are assessed so that their benefits outweigh the adverse effects on the fetus. Constant supervision of doctors (gynecologist, oncologist, immunologist) during this period is mandatory. The main treatment is carried out after childbirth.
Is it possible to remove papilloma during pregnancy?
Is it possible to remove a papilloma or wart during pregnancy? Pregnant women are often interested in this question. A specialist usually does not remove papilloma of various strains during pregnancy. However, there are situations when they simply need to be removed surgically (if the health or life of the child and mother is threatened).
Removal of growths during pregnancy can be done using different methods:
Removal of growths during pregnancy can be done using different methods.
- laser;
- growths can be cauterized by electrical discharges (electrocoagulation);
- neoplasms are removed with liquid nitrogen;
- surgically.
Thus, the answer to the question whether papillomas can be removed during pregnancy is positive. But this can only be done in emergency cases.
Consequences for the child
The mother's disease risks infecting the child with HPV during childbirth. In practice, these cases are less than 50%, but they exist. HPV in a baby does not always appear immediately; it can only happen after several months or even years.
However, there are cases of rapid manifestations when the virus affects the larynx of a newborn. This picture is observed in the first month of his life and is fraught with serious consequences.
Some experts advocate performing a caesarean section in infected women, but this is not confirmed by experience, since HPV is transmitted to the child during such births.
In cases where the virus infects the trophoblast (future placenta), which nourishes the embryo, the pregnancy is terminated in the early stages.
What is papillomavirus infection
HPV, the genital human papillomavirus, is a viral infection that affects about 6,200,000 new people every year. There are 100 different types of papillomavirus, including about 30 types that are spread through sexual transmission. HPV is transmitted through genital skin-to-skin contact, which in most cases occurs through sexual activity, including oral, anal and vaginal intercourse. The virus can be transmitted even if a person has no symptoms.
Childbirth
When papillomas literally “line” the birth canal, doctors still resort to cesarean section, since the risk of infection of the child in this case increases significantly.
Perhaps this is the only possible complication. Control? Yes, more closely. But childbirth proceeds as expected.
After birth, mother and baby should be tested for the presence of the virus. If the virus is detected, it is necessary to undergo appropriate treatment, which, first of all, should be aimed at strengthening the immune system. A good immune system can resist HPV.
Why do papillomas appear during pregnancy?
There is no clear answer to the question of why warts (papillomas) appear during pregnancy. To date, it has not been scientifically revealed why growths form on the body, on the neck, labia, in the vagina, in the navel, in the urethra, etc. In medical practice, it is customary to identify the following causes of papilloma during pregnancy:
- Hormonal changes in the body. Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection in this case occurs due to the active production of hormones, which enhances the growth of epithelial cells.
- Injury to the skin as a result of friction with clothing. The growths may appear due to the fact that the expectant mother is rapidly gaining weight. Clothes become small. Most often, growths appear in the armpits, chest and groin areas. The papillomavirus begins to grow, which causes discomfort during pregnancy. As a rule, growths appear in the second and third trimester. Papillomas after pregnancy usually go away on their own.
- Weakening of the immune system and exacerbation of chronic diseases (including HPV). Therefore, if papillomas appear in intimate and other places during pregnancy, this is not surprising.
If a woman has a lot of moles and papillomas, she worries: are they dangerous? The appearance of growths during pregnancy is usually not dangerous. Only discomfort. Therefore, HPV and childbirth are two compatible concepts. However, if the mother is infected, the pathology can pass to the child. The virus is dangerous for the baby. Therefore, treatment if papilloma occurs is mandatory during pregnancy.
If quite a lot of small papillomas appear after childbirth, this is also quite common. The reason for their occurrence is that the body is under stress after pregnancy and the birth of a child. Reviews from women who have gone through this say that the resulting growths will go away on their own after some time.
If papillomas come out after pregnancy and their growth continues for a long time, you need the help of a specialist. He must determine the strain of the virus. If HPV 16, 18, 58 or HPV type 45 is detected, it is life-threatening. Such strains of infection are oncogenic and can develop into cancer.
The appearance of growths during pregnancy is usually not dangerous
When papillomas grow, they are easily injured. As a result, infection may occur in the wound or blood poisoning. Therefore, if the growth has increased, you need to consult a doctor to avoid serious consequences.