Lipoma (wen) is a formation that forms on any part of the human body in the form of a small dense nodule. One of the common places where wen is localized is the abdomen.
As a rule, a pathological neoplasm in this location does not cause discomfort, but sometimes a lipoma can cause a number of serious complications. In this case, drug or surgical treatment is indicated.
What is a wen?
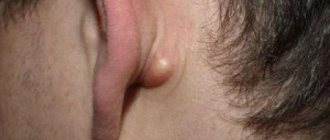
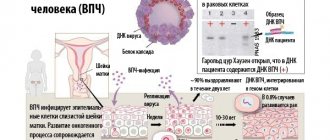
Lipoma (wen) is an accumulation of adipose tissue under the skin, enclosed in a capsule of connective fibers. The formation is benign in nature and can manifest itself in various sizes, up to 7 cm in diameter.
What education looks like, photo
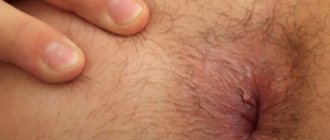
Externally, the tumor has clear-cut boundaries. The formation is elastic and can change shape when pressed, but then returns to its original size.
It appears on the skin at the location of the fat layer and sebaceous glands. In rare cases, a tumor can form on a person's internal organs.
The formation, if it does not affect soft tissues, does not cause pain, but the child may feel discomfort, especially when pressing on the lipoma.
Manifestations
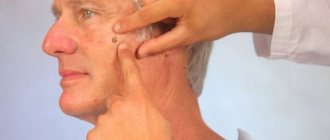
In the initial stages, a lipoma manifests itself as a small lump slightly rising above the skin. At this stage, the neoplasm is a capsule of dense connective tissue, inside of which there is a small number of fat cells.
As fat accumulates, the lipoma enlarges. In its structure it has a lobular structure. The surface of the wen has clearly defined boundaries and a symmetrical structure. With volumetric growth, symmetry may be disrupted.
In the initial stage of development, palpation reveals a soft elastic knot . By increasing the density, one can judge the age of the neoplasm: the denser the node, the older it is. When the lipoma grows slightly, the color of the skin does not change and there is no pain.
As its size increases, the skin may acquire a reddish tint due to damage to small blood vessels. If the tumor has deformed the nerve endings, then its growth is accompanied by pain, which manifests itself not only upon palpation, but also during physical exertion, as well as at rest.
Wen structure
Symptoms will also depend on the exact location of the formation. As it grows in the subcutaneous layer, a pedunculated , which has its own neurovascular bundle. As a result, the lipoma gives off severe pain even with minor injury.
Retroperitoneal lipoma appears as a small, localized inflammation resembling an inflamed, painful lymph node or boil.
How does esophageal cancer progress: symptoms and signs of the disease. This article lists the types of benign brain tumors.
What is the differential diagnosis of brain tumors? Information at https://stoprak.info/vidy/golovy-i-shei/mozg/diagnostika-opuxoli.html link.
Why do wen appear in children?
In childhood, benign formations can appear for the following reasons:
- disruptions in the metabolic process;
- improper process of breakdown of adipose tissue in the body;
- improper hygiene;
- malfunction of the sebaceous glands;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- genetic predisposition to problems;
- disturbance in the hormonal background of the child;
- insufficient intake of vitamins.
In some parts of the body, wen can appear as a result of insufficient mobility and prolonged stay in one position.
Locations of wen
Lipomas in children can occur in absolutely any part of the body, but most often:
- face - most often formed in infancy;
- legs;
- breast;
- gum;
- area behind the ears;
- scalp;
- armpit area;
- back.
Small formations most often go away on their own, but there are formations that require removal or a special treatment method.
Classification
The ICD-10 code is D17 (benign formations of adipose tissue).
From a histological point of view, they are divided into:
- Nodular lipomas (the node may have a capsule, consists of numerous lobules, is located inside the capsule; 85% of lipomas are represented by a nodular form).
- Diffuse lipomas (represents a wen without a capsule, grows into neighboring organs and tissues). Dercum's disease and Madelung's neck are autoimmune diseases characterized by a diffuse type.
Classic fatty lipoma sometimes affects neighboring tissues and organs, depending on this there are:
- fat formation;
- fibrolipoma (connective tissue process);
- angiolipoma (affects blood vessels);
- myolipoma (a combination of fat and muscle tissue, damage to the mammary glands);
- myxolipoma (a fat tissue cell connects to the mucous membrane);
- myelolipoma (formation in the bone marrow);
- hibernoma (formation is typical during fetal development, the main role is played by brown fat in the fetus).
According to the structure of education, they are divided into:
- encapsulated (a capsule is formed inside the organ);
- ring-shaped (forms a “necklace” on the neck - Madelung’s neck);
- tree-like (formation in articular cavities);
- petrified (deposition of calcium salts inside the lipoma);
- cavernous (involving blood vessels).
In addition to generally accepted classifications, formations are also divided according to their anatomical location. There are subcutaneous, retroperitoneal, and intraorgan tumors. They form in the mammary gland, in the spinal canal, muscles, and grow near the sweat glands.
Diagnostics of education
Before starting treatment for a tumor on a child’s body, it is necessary to determine the type of tumor and the reasons that provoked this kind of problem.
Most often, an external examination of the damaged area and palpation is sufficient for a specialist.
However, cases may arise with the use of additional diagnostic measures:
- examination of tissue in formation to identify malignant cells;
- X-ray of the tumor when the lumps are in difficult places.
After the examination, the specialist prescribes treatment, which can be carried out at home if there is no danger to the child’s health.
Treatment with folk remedies
Before using folk remedies, consult your doctor.
You can also get rid of lipoma using traditional medicine, but it should be noted that doctors have divided opinions on this matter. In any case, before using any alternative medicine, you should definitely consult a specialist. So, the most popular means:
- Vishnevsky ointment. The ointment should be applied in a thin layer to a bandage or gauze, then applied to the wen and secured. After 11-13 hours, the bandage needs to be changed, so you need to do compresses for 3-4 days, then take a break for a day or two and repeat the procedure again.
- Cinnamon. A patient who has wen under the skin needs to eat 1 tbsp per day. l. cinnamon. The procedure must be repeated until the lipomas completely disappear.
- Hirudotherapy. Treatment of lipomatosis with leeches is a very effective remedy, as they quickly relieve a person of all fatty growths.
- Hydrogen peroxide. Lubricating the formation or applying compresses with hydrogen peroxide to it helps ensure that after some time the contents of the wen begin to come out.
- Vinegar or iodine. The surface must be lubricated with vinegar or iodine for a long time, until the wen completely disappears.
- Lamb fat. Before use, lamb fat must be heated in a water bath, and then rubbed into the formation until it disappears completely.
It is worth noting that treatment of lipomatosis with the help of traditional medicine in some cases can take a long time, and you also need to remember that only those fatty tissues that are located directly under the skin are amenable to such methods.
When should a lipoma be removed from a child?
A growth on a child’s body is removed in the following cases:
- when the tumor is located on the child’s neck and there is a threat of compression of the blood vessels;
- the wen quickly increases in size and causes pain to the child;
- education negatively affects the functioning of internal organs;
- the lipoma turns red and itches;
- The fatty deposits are located in an open area and require removal for cosmetic purposes.
Wen removal in children is carried out upon reaching 5 years of age, unless complex cases arise that require urgent intervention on the recommendation of a doctor.
How is a lipoma removed from a child?
Lipoma removal can be done using a variety of techniques.
Which include:
- surgical method - a specialist uses a scalpel to make a small incision and remove the lipoma along with the capsule. Suitable for large size wen. The disadvantage of this method is the scar after the procedure;
- endoscopic method - using surgical instruments, a small incision is made, through which the fat capsule is destroyed and the contents are removed out. This method leaves virtually no traces, but may cause the problem to reappear;
- laser intervention – using a laser beam, fatty tissue is destroyed. The advantage is the almost complete absence of bleeding and possible complications. Disadvantages include scarring;
- cryodestruction - using liquid azo, the wen is frozen. The formation disappears on its own without scars, but this method is used only for small formations. Very often, one procedure may not be enough, and a complex of treatments is required;
- puncture method - involves puncturing the formation and pumping out its contents. It is carried out by a specialist under completely sterile conditions; such intervention is not carried out independently.
Only a specialist can determine the correct method of intervention. For children, removal is performed under local anesthesia.
Skin care after wen removal
After the operation, there will be a suture on which a sterile bandage is applied. The intervention site must be treated with a special antiseptic prescribed by the doctor.
The child should not touch the lipoma removal site, otherwise infection may occur. It is also not recommended to wet the wound with water before removing the suture.
With normal healing, the suture is removed after 7-10 days. It is also necessary to avoid regular rubbing of clothing with the site where the wen is removed. When using laser removal, it is not recommended to be in direct sunlight for the first few days.
Tumor characteristics
Gastric lipoma is a formation that develops from fat cells of the submucosal layer of the organ and comes in two types: submucosal and subserous.
Submucosal lipoma is characterized by endogastric growth, plunging into the wall of the organ. Subserosal, on the contrary, grows into the lumen of the stomach, protruding the serous membrane.
According to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), gastric lipoma is classified as a benign tumor of the abdominal organs and has a code of D-17.5.
The size of the tumor varies from the size of a small pea to a massive conglomerate of several kilograms.
Lymphofollicular hyperplasia of the stomach is a pathological proliferation of follicular tissue of the mucous or submucosal layer of the organ against the background of disruption of the endocrine organs.
Why is wen dangerous for children?
The formation of wen is not dangerous for the child and can be treated quickly. However, in some cases, a harmless formation can cause harm.
Such cases include:
- the wen is located in a place where blood vessels accumulate and there is a risk of compression and impaired blood circulation;
- The wen is located in the head area and increases in size. Which can result in vascular thrombosis in the brain area;
- a wen has appeared on the eyelids, such formations can negatively affect the child’s future vision and require urgent intervention;
- after damage, the wen becomes inflamed and a purulent process appears.
In some cases, wen can develop into a malignant formation. Therefore, when the first symptoms appear, you must contact a specialist to diagnose the problem.
Complications
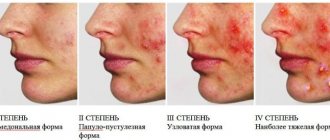
Small wen cause concern only in isolated cases. As a rule, the main part of the complications is caused by large growths . Complications of lipoma include:
- Infection of the tumor as a result of injury. The main danger is that the infection can spread to adjacent healthy tissue and enter the abdominal cavity.
- Compression of the main vessels. This leads to a pronounced disruption of the metabolic processes of a certain area, which can result in tissue necrosis.
- Damage to nerve fibers, which will lead to numbness of the skin.
- Degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant one. This complication occurs in isolated cases and is provoked by regular injury or irritation of the lipoma.
Prevention measures
Wen can develop in almost any person, including a child.
To reduce the risk of a problem occurring, the following prevention methods must be followed:
- reduce the risk of hypothermia;
- promptly treat all chronic diseases;
- Carry out regular body hygiene to reduce the risk of clogged pores;
- monitor the quality of products used for food;
- Provide your child with regular activity and healthy sleep.
Wen can manifest itself with various symptoms, but removing the problem on your own can lead to complications and further development of lipoma.
In childhood, a child’s skin is very sensitive to external and internal changes, so any disruptions in the body are manifested by rashes or formations; wen can also indicate serious illnesses.
Therefore, before starting treatment, it is necessary to find out the factor that provoked the appearance of lipoma and use the recommendations of a specialist.
In what cases are pharmaceutical drugs used, and in what cases is surgery performed?
The use of a special substance (micropreparation) for introduction into the lipoma capsule is most suitable in cases where the growth is small in size. This allows you to guarantee complete resorption of the formation. When the lipoma is large, there is a possibility that the reaction will not occur completely, and the cells will soon grow again.
Also, surgery is a more effective method in cases where dynamic growth of the lipoma head is noticed. Firstly, resorption from the drug occurs over several months. And under these circumstances, such a phenomenon is not acceptable for the patient. Secondly, a rapid increase in growth may indicate the beginning of degeneration into a malignant tumor. In this case, immediate intervention is necessary.
Another indication for surgery is lipomatosis. When the digestive organ is sufficiently damaged by the growth of fatty tissue, conservative treatment is out of the question. Urgent surgery is needed to clear out the stomach tissue. Moreover, the procedure is quite painstaking and requires a lot of experience and precision from the surgeon.
The use of drugs is also unacceptable in the presence of allergic reactions to substances of a similar spectrum.
Postoperative care and prevention
After surgery to excise a gastric lipoma, the patient needs to completely reconsider his previous lifestyle. You should give up bad habits. Avoid eating fatty, spicy, smoked foods. As a rule, doctors recommend split meals and a diet called “table No. 5” for patients who have suffered such diseases. This diet includes the required amount of all nutrients based on daily needs. At the same time, it completely excludes foods that create a burden on the digestive organs.
Treating diseases is much more difficult than taking precautions. Therefore, in order to maintain the functioning of his stomach, a person needs to take a responsible attitude towards his health. You should not abuse fatty meats, smoked meats, alcohol and spicy foods. You should not eat fried foods regularly. It can lead to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The diet must be correct - nutritious, balanced and regular.
If you experience symptoms of stomach malfunction, you should consult a doctor.
A disease detected in a timely manner is much easier to cure. The article has been verified by the editors