Causes of a lump in the groin
Factors that provoke unpleasant symptoms include both serious diseases requiring surgical intervention and superficial skin problems.
- Furunculosis due to bacteria entering the area of the hair follicle.
- Varicose veins running in the groin.
- Vesiculitis in men is an inflammatory process in the seminal vesicles, accompanied by severe pain and impaired sexual function.
- Cryptorchidism is a phenomenon in which one or both testicles in boys are located not in the scrotum, but in the groin area or in close proximity to it.
- Appendicitis, in which a soft-touch lump in the right groin is accompanied by pain in the abdominal cavity and right leg while walking.
- The prolapse of a stone into the ureter is characterized by the appearance of a solid formation.
- Consequence of injury.
The reasons for the appearance of a ball in the groin, which should be considered in more detail, include: hidradenitis, pathologies of the Bartholin gland in women, hernia, lymphoma, atheroma.
Treatment of lumps in the groin area in women
It is important to remember that self-medication of neoplasms is strictly contraindicated. Even a small bump in a woman’s groin can be a sign of serious pathology. Treatment should be prescribed exclusively by your attending physician after a thorough examination. Depending on the etiology of the appearance of the formation in the groin, one or another therapy tactic is selected. If the lump is an inflamed lymph node, then treatment will be aimed at eliminating the underlying disease. As the infectious agent is neutralized, the lymph node will decrease in size.
Pathologies such as varicose veins, inguinal hernias and benign neoplasms may require the inclusion of various surgical procedures in the treatment complex. Pathologies such as varicose veins, inguinal hernias and benign neoplasms may require the inclusion of various surgical procedures in the treatment complex. For blockage and inflammation of the glands located in the groin area, local treatment with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of ointment or gel is most often used. In the prevention of hidradenitis, furunculosis and bartholinitis, careful adherence to the rules of intimate hygiene plays an important role.
Remember that it is most effective to treat the disease in the early stages. You should not ignore the appearance of lumps in the groin area; timely consultation with a doctor will help avoid many unpleasant complications.
Sebaceous cyst
Atheroma is a benign formation that can form on any hairy part of the body.
It is caused by blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous gland and the accumulation of a large amount of secretion, which has nowhere to go out.
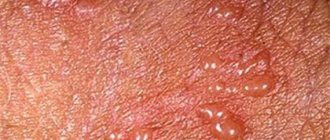
The lump does not cause concern, seems mobile when touched, does not hurt, has an even outline, is located under the skin, and therefore does not change its shade.
Atheroma in the groin area is most often caused by certain factors:
- Wearing underwear made of synthetic material that is too tight.
- Injury to the sebaceous gland duct during depilation, ingrown hair.
- Failure to comply with the rules of intimate hygiene, infection in the hair follicle.
- Excess weight and metabolic disorders.
- Changes in hormonal levels.
- Lack of vitamins.
- Increased sweating.
Many, after consulting with an oncologist and learning that this lump is not malignant, are afraid to remove the cyst. Therefore, considering that the formation does not bother them, sometimes they wait until the atheroma seriously grows to 5 cm in diameter. An enlarged ball can become inflamed, which will lead to unpleasant symptoms:
- Swelling, pain, change in skin color in the affected area.
- A liquid similar to pus with an unpleasant odor begins to be released from the blocked duct.
- Increase in temperature, loss of strength.
- Lack of appetite, vomiting.
These signs indicate the development of a serious inflammatory process that requires immediate medical attention. As a rule, atheroma in a calm state is easily removed surgically. To do this, you need to undergo a series of tests and be referred for surgery. Sometimes the patient is discharged home on the same day, in other cases he has to stay in the hospital for less than a week.
After excision, the cyst no longer forms in this area. It is also necessary to seek medical help if an abscess appears or the atheroma bursts under the skin as a result of injury.
Etiology
The following diseases can provoke the formation of a ball in the groin in women:
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes. Lymph washes all tissues and cells of the body, neutralizing the harmful effects of pathogenic microbes. A large number of lymphatic vessels and nodes through which fluid flows are localized in the groin area. If the lymph cannot cope with aggressive pathogenic microflora, bacterial waste products are not removed from the body and clog the vessels of the lymphatic system. Inflammatory damage to the lymph nodes occurs, accompanied by their enlargement and the formation of subcutaneous lumps.
- Hernia. During physical activity, heavy lifting, or intense strain during coughing or defecation, women may develop an inguinal hernia. The characteristic protrusion is a movable lump under the skin, easy to straighten with your fingers, but it appears again even with slight tone of the peritoneal muscles.
- Varicose veins of the superficial femoral veins. In women who remain in a static position for a long time, undergo heavy physical activity, or during pregnancy, varicose veins of the femoral veins are often observed. The disease manifests itself by the formation of dense and painful pulsating balls under the skin.
- Folliculitis. Inflammation of the hair follicles is manifested by the formation of dense balls - pustules, through the center of which the hair shaft passes.
- Furunculosis. The penetration of pyogenic bacteria (in particular Staphylococcus aureus) into the hair follicles, the surrounding sebaceous glands and connective tissues is accompanied by an acute inflammatory process with the formation of boils - dense balls filled with purulent-necrotic exudate.
- Aneurysm of the femoral artery. Thinning of the walls of the femoral artery often causes the development of pulsating subcutaneous swellings.
- Atheroma. When the sebaceous gland is blocked, caused by the cessation of the outflow of secretions from its excretory canals, benign tumors appear - cysts filled with dead cells and sebum.
- Lipoma. Benign wen in the groin area forms in the layers of connective tissue under the skin. Such a neoplasm does not have a tendency to degenerate into a malignant tumor, but can grow deep into the periosteum through the muscles and vascular bundles.
- Neurofibroma. The development of a benign neoplasm in the soft tissues, formed by the sheaths of nerve endings, is accompanied by the appearance of a dense subcutaneous ball in the groin of women at the site of the tumor.
- Lymphoma. Oncological pathology of lymphatic tissues, in which, as a result of uncontrolled division and accumulation of lymphocytes, the lymph nodes significantly increase in size, is accompanied by the appearance of painless subcutaneous lumps at the site of tumor development.
Any changes in the skin in the intimate area may indicate serious pathological processes in the body. If a ball is detected in the groin of women, even if its appearance is asymptomatic and does not cause discomfort, it is necessary to seek medical help.
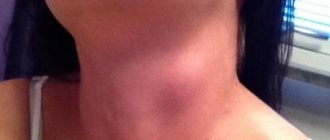
Lymphadenitis
Inflammation and enlargement of the lymph node, which is not an independent disease.
A similar formation can be observed in different parts of the body, including in the groin on the right or left. Lymphoma in this area is caused by pathological conditions such as:
- Infections of a viral, fungal or bacteriological nature.
- Malignant tumors of organs located in the abdominal cavity, sarcoma.
- Non-healing, weeping ulcers on the legs.
- Syphilis.
- Tuberculosis.
- Prostatitis.
- Taking medications that affect lymph circulation.
Often, an increase in nodes in the groin area is associated with infection with sexually transmitted diseases. In this case, a gynecologist or urologist will be able to make a diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. If a lump appears, it is important to consult a doctor immediately. It is not easy to determine lymphadenitis, since it has symptoms similar to other pathologies:
- Increased body temperature of the patient, chills.
- Pain when walking and palpating.
- Discomfort in the lower abdomen.
- Changes in skin color during an active inflammatory process.
- Swelling of tissues.
It is important to diagnose lymphoma on time, since the diseases that cause it require immediate treatment. In addition, there is a high risk of suppuration, a breakthrough of the inflamed node, in which bacteria will enter the abdominal cavity. This often leads to serious problems.
To get rid of the symptoms of lymphadenitis, antimicrobial drugs are used - antibiotics Azithromycin, Flemoxin, Amosin, Summed, etc. Physiotherapy and compresses with ichthyol ointment are also prescribed. Sometimes surgery is required.
Causes
A lump in the groin area is a dense, mobile neoplasm that protrudes above the surface of the skin. The appearance of a lump may be accompanied by pain, burning and itching, an increase in body temperature, or it may be asymptomatic, disturbing the woman as a cosmetic skin defect.
Only a doctor can correctly establish the cause that provoked the development of a neoplasm, determine the degree of danger to the body and select appropriate methods of therapy after an initial examination and palpation of the lesion, as well as studying the results of laboratory tests. Lumps in the groin area can be a symptom of the following pathological processes:
- Folliculitis. Caused by the penetration of a bacterial infection into the hair follicle, the development of the inflammatory process in the hair follicle is usually accompanied by the formation of a dense subcutaneous formation - a painful purulent compaction surrounding the hair shaft and the adjacent sebaceous gland. The appearance of a small (from 1 to 3 mm in diameter) lump on the pubis with pus can be caused by microtrauma of the skin received during depilation, increased sweat production, and irritation by synthetic fabrics of the underwear. Antibacterial drugs are used to treat the disease.
- Furunculosis. When folliculitis becomes complicated due to overactive sweat glands or irritation of the skin, foci of infection can rapidly spread to the surface of the skin. This process is accompanied by the formation of dense, painful neoplasms filled with purulent exudate, enlarged lymph nodes, and an increase in body temperature. In order to relieve inflammation and eliminate the pathogenic influence of infection, a course of antibiotics and local application of antibacterial ointments are prescribed.
- Inguinal lymphadenitis. Against the background of the development of a sexually transmitted disease, as well as during inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs, concomitant inflammation of the lymph nodes is observed with an increase in their size, the appearance of noticeable pain and discomfort when performing movements. This process is also accompanied by an increase in body temperature and general weakness. At an early stage of pathogenesis, conservative drug therapy is prescribed. If a purulent process develops at the site of compaction, surgical intervention is recommended.
- Lipoma. If there are metabolic disorders, weakened immune defenses, or diabetes mellitus, a benign tumor formed by adipose tissue cells may appear in the groin area. Lipoma has the appearance of a limited, painless new growth of soft consistency, not fused with the surrounding tissues. The elasticity and color of the skin at the site of tumor development are preserved. A benign lump is removed surgically to prevent its degeneration into liposarcoma, a malignant tumor.
- Pseudofolliculitis. When the direction of hair growth is disrupted, when the hair shaft does not break through the skin and begins to grow deep into the epidermis, a red, painful and itchy lump is formed. Hyperkeratosis and shaving of unwanted hair in the intimate area can provoke pathology. The inflamed purulent abscess is opened by a doctor using a sterile instrument.
- Atheroma. Atheroma is often localized in the groin area - a benign cyst that occurs against the background of poor personal hygiene, hormonal imbalance, sexually transmitted infection or mechanical trauma to the skin. Such a seal is movable, elastic, outlined with a clear contour. When atheroma suppurates, swelling, pain and redness are observed. To prevent secondary infection and transformation of the tumor into a purulent abscess, the lump is surgically removed.
- Inguinal hernia. Women who have suffered damage to the ligamentous apparatus of internal organs or who are obese may develop an inguinal hernia. A movable seal appears on the pubis, which protrudes when exerting itself or coughing. The hernia must be removed through surgery.
A lump in the groin of women on the left is formed under the influence of the same reasons as on the right. The pathogenesis of the disease differs only in the opposite location of the tumor. Seals can also be formed on both sides simultaneously. Self-medication of pubic lumps in women on the right, on both sides or on the left is strictly not recommended. The use of traditional and alternative medicine methods and self-removal of the seal is fraught not only with the development of sepsis and the rapid spread of infection on the surface of the skin, but also with the formation of malignant tumors. To protect your health and effectively get rid of an uncomfortable problem, you need to promptly seek medical help.
Hidradenitis
This disease most often affects people from the onset of puberty to 55-60 years of age.
It is expressed in purulent inflammation of the sweat glands as a result of staphylococcus bacteria entering them. As a rule, pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the ducts located in the groin area as a result of scratching, after shaving, hair removal or through small wounds.
An environment with high humidity on this part of the body is favorable.
Cones filled with pus can pop up on one or both sides. In this case, the following symptoms are observed:
- A small, dense, itchy nodule appears in the groin.
- The lump quickly grows, acquiring a pear-shaped shape.
- The inflamed area begins to hurt and swell.
- Body temperature rises.
- The patient complains of weakness and lack of appetite.
After a week, the heavily swollen node opens on its own. Thick pus with ichor flows out of it. An ulcer remains, after healing of which tissue scarring is observed.
At the first signs of inflammation of the sweat gland, you should consult a dermatologist, since several more similar nodules may appear in the groin, the merging of which into one large inflamed boil will bring severe suffering and the possibility of developing sepsis.
We recommend:
A lump with pus on the pubis in women;Furuncle in the groin in women;
A ball on the neck under the skin.
Treatment is carried out with antibiotics. Also, a patient who suffers from relapses of hidradenitis is recommended to follow a special diet, avoiding sweets, spices and fatty foods. Instead, you should enrich your diet with vitamins. The places most often exposed to the appearance of purulent nodes are wiped 4 times a day with boric alcohol.
Tumor in the groin in women
A tumor in the groin is a serious signal that can precede many diseases. The manifestation of a tumor in women most often indicates systemic disorders in the body. swelling may occur in the area between the leg and groin, directly on the external genitalia.
Enlarged lymph nodes are a protective reaction of the body, but with a high risk of infection, this manifestation can be dangerous for the body. A tumor in the groin does not occur on its own, but becomes a cause of disruption of internal organs, inflammatory processes, and infectious diseases.
Therefore, other causes of inflammation can be
- sexually transmitted diseases in women and men;
- reproductive dysfunction;
- purulent inflammatory foci, furunculosis.
Even minor mechanical damage can provoke inflammation of the lymph nodes against a background of weakened immunity. Therefore, the role of the immune system in this is significant.
How it manifests itself
Inflammation in the groin in women
A tumor in women in the pelvic area and legs occurs with some symptoms, which include pain and dysfunction against the background of general inflammation. It is necessary to distinguish between damage to the lymph nodes due to oncology and minor inflammation.
When oncological diseases manifest themselves, the lymph nodes are immobile and can have different consistencies. In the case of inflammatory processes, they are mobile and resemble a ball when palpated. The disorder is manifested by general malaise, weakness, increased body temperature, and discomfort when walking.
The affected area becomes red, itching, burning, and bleeding may occur due to irritation.
With systemic diseases of the body, generalized damage to the organs of the lymphatic system occurs more often, therefore, if the swelling between the leg and groin is not an isolated manifestation, then the problem must be sought in a disruption in the functioning of the internal organs.
Enlarged lymph nodes can indicate processes such as metastasis in oncology, tuberculosis, syphilis, and the initial manifestation of HIV. The penetration of infection through the lymphatic system allows the body to remove unwanted microorganisms naturally. But in some situations, a malfunction may occur and the lymph stagnates, which leads to the appearance of swelling in the groin area.
If the tumor is caused by infectious diseases, it is necessary to find the source of pathology and direct efforts to treat it. In this case, the swelling may go away on its own.
If cancer is suspected, it is necessary to undergo a complete examination of the body in order to exclude metastasis.
The hernia also manifests itself as swelling, and in this case, surgical treatment followed by physiotherapeutic recovery will be required.
Often, swelling in the groin is not a consequence of inflammation of the lymph nodes, but the beginning of the development of a wen in women. They affect women mainly after 45 years, the wen looks like a small lump, it is absolutely painless and does not cause any harm to the body. The cause of a wen may be heredity, a genetic failure, or a metabolic disorder.
The principle of treatment of formations is based on the elimination of possible complications, after which surgical intervention is performed according to indications. After treatment, the body quickly recovers without any consequences.
Source: //www.no-onco.ru/opuxoli/rakovye-opuxoli/opuxol-v-paxu-u-zhenshhin.html
Inflammation of the Bartholin gland
In women, a ball in the groin may appear due to a problem in the intimate area.
This is the main symptom of the pathological process occurring in the Bartholin gland, which is responsible for producing secretions during sexual arousal.
An increase in size is most often caused by the following factors:
- Violation of intimate hygiene rules.
- Sexually transmitted infections, including syphilis, herpes, thrush.
- Inflammation of the urinary canal.
- A complication of recovery after an abortion.
- Wearing underwear that is too tight and rubs delicate skin.
- Weakening of the immune system.
Inflammation of the Bartholin gland can occur without visible symptoms, but most often a woman experiences increased secretion production, redness and enlargement of the labia, pain during intercourse, fever, nausea, inflammation of the lymph nodes, the ball in the groin becomes the size of a chicken egg.
You can get rid of the problem after consulting a gynecologist, diagnosing the reasons that caused the enlargement of the gland and taking a course of antibiotics.
Features of therapy
The development of various diseases is usually accompanied by characteristic symptoms and requires an individual approach to treatment.
With oncological and inflammatory processes, as well as the formation of an abscess, there is itching, soreness and redness of the skin, general weakness, fever, changes in the blood picture, weight loss and enlarged lymph nodes. Inflammations are treated with antibiotics and physiotherapeutic procedures; abscesses and tumors are most often removed surgically.
Hernial protrusion is accompanied by pain radiating to the abdominal area, an increase in the tumor with muscle tension, and disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. Varicose veins appear as pulsating bumps with a bumpy surface. Both diseases are treated through surgery.
The formation of a lump under the skin in the groin area may signal the development of a serious pathology. To protect your health and effectively get rid of the disease, you need to consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Is treatment possible at home?
In this situation, treatment at home can only be done after a doctor’s examination and diagnosis, otherwise you can only make things worse for yourself.
To reduce inflammation and remove pain, the following methods are used:
- Warm and cold compresses; in the presence of swelling and pus, the procedure is not performed.
- It is recommended to prepare a drink based on honey and lemon juice. Mix the juice with water and add a teaspoon of honey. Take three times a day.
- Chamomile tea. The plant reduces inflammatory processes of any nature. Brew the drink like regular tea, drink several times a day.
- Treat the bulge with castor oil, rubbing the product in a circular motion. If the patient is allergic to castor oil, you can use peppermint oil; just take a couple of drops to treat the area. Mint will not only relieve inflammation, but also kill pathogenic microbes.
- Turmeric is no less effective. A paste-like mass is made from turmeric and honey. Using gentle movements, rub the paste into the bump. Perform the manipulation twice a day for seven days.
If the condition worsens after a day, treatment should be stopped and see a doctor immediately.