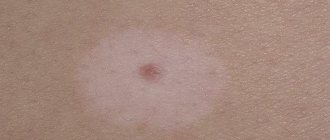
Fibromas are benign tumors that appear on internal organs and soft tissues, most often localized on the feet and soles. Correct diagnosis and proper treatment will solve existing problems, eliminating the recurrence of tumors. Fibroids on the leg can often become injured, bleed and cause discomfort when walking, so it is necessary to promptly consult a doctor and remove the tumors.
Description of the disease
Fibromatosis of the foot is usually understood as benign growths localized in various parts of the body. The tumor can develop on the surface of the skin and deep in the muscle tissue. Fibrous tumors are most often diagnosed in adults, and in rare cases they are observed in children and adolescents.
Experts distinguish two types of fibroids:
- Benign ones consist of fibrous tissue; cells, due to various factors, have switched to an uncontrolled and disorderly process of division.
- Malignant ones are extremely rare; they consist of cancer cells that kill healthy tissue, replacing them with various pathological formations.
It has been established that in 99% of cases benign fibroids are diagnosed , which, subject to timely examination and proper treatment, do not pose any threat to human life. However, when such tumors appear, it is necessary to perform appropriate diagnostics, including a tumor biopsy, which will exclude cancer and other dangerous diseases.
Therefore, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor for an examination and prescription of quality treatment.
Indications and contraindications
In modern medicine, there are a number of absolute and relative reasons for which fibroid excision is performed. The most common of them are:
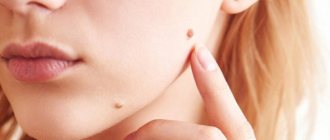
- personal requirement . Often the desire to get rid of existing growths arises when they appear on open areas of the body (face, neck, hands).
- Localization of pathological nodes in those places where they are constantly injured (groin area and armpits) or cause discomfort (oral cavity, uterus, ovaries).
- The presence of pronounced clinical signs.
- Development of inflammatory processes, suppuration and necrosis in the area of fibroma.
- Combination of growths with other types of tumor (for example, ovarian).
- Significant increase in tumor growth in a short period of time.
- Lack of positive results from conservative methods of therapy.
Radical methods of treating fibroids are not used if there is damage to nearby tissues by herpes or a viral infection.
Before surgery, the patient must be in satisfactory health.
Contraindications for women include pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Alternative treatment methods are also used if the patient is intolerant to anesthesia drugs.
Symptoms of fibroids
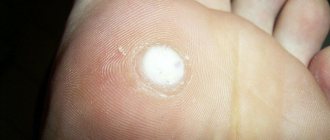
Fibroma, depending on the degree of tissue growth, can manifest itself in the form of soft and hard formations, each of which differs in size, structure and symptoms. A solid fibroma is a tumor with limited mobility. Most often it appears in the deep muscle layers, gradually growing, slightly rising above the healthy skin. Upon palpation, you can feel a dense formation that has a homogeneous structure.
Initially, the diameter of such a tumor is no more than 5-10 millimeters. However, over time, without proper treatment, it increases to 10 centimeters.
The vessels are compressed, blood flow is disrupted and associated symptoms appear.
Soft fibromas on the leg under the skin are wrinkled neoplasms with a heterogeneous loose structure. Such tumors appear exclusively in the upper layer of the epidermis.
A soft fibroma usually has a wide, flat base with a thin stalk, consisting of connective tissue.
The size of the tumor will be individual, from 1 to 4 centimeters in width and length. Soft tumors are painless, but due to their shape and location they can cause a lot of inconvenience when walking, rubbing their legs, which forces most patients to see a doctor for treatment and removal of the tumors.
Reasons for appearance
Today, doctors do not know exactly the reasons for the appearance of fibroids on the skin and internal organs. Experts identify several factors that can lead to the formation of tumors. These include:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Mechanical and thermal injuries, chemical exposure.
- Violation of metabolic processes.
- Problems with hormonal balance.
- Dysfunction of the endocrine glands.
- Excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
It is necessary to avoid frequent mechanical injuries to the feet, so it is imperative to choose shoes that do not rub or pinch.
It has been established that certain pathologies, including diabetes and acromegaly, contribute to metabolic disorders in the body, which leads to the appearance of fibroids on the legs and arms.
Preparing the patient for removal
There is no specific preparation for fibroid resection. The patient undergoes a minimum number of tests:
- General and biochemical analysis of blood and urine;
- blood group and Rh factor;
- analysis for an allergic reaction to anesthesia components.
The patient must also undergo a preliminary consultation with a surgeon.
If the tumor is located in the respiratory tract, but not in the mouth, for example, in the pharynx or larynx, the patient is referred for consultation to an otolaryngologist.
A few days before surgery, it is recommended to limit the intake of medications that can cause bleeding.
Classification of neoplasms
Fibromas on the legs differ in their shape, growth rate, localization and specificity of the cells that make up the tumor. The doctor must not only correctly identify the pathology, but also correctly qualify it; it is on this that in the future the methods of treating the tumor and the possibility of removing them will completely depend.
Based on the rate of formation, it is customary to distinguish two categories of fibroids:
- Diffuse ones are not limited in growth, are localized in the muscles and legs, and as they develop, they can involve nearby glandular and vascular tissues in pathological processes.
- Limited hip fibromas are characterized by a slow growth rate, their size does not exceed 10 centimeters, which is due to the presence of a restraining capsule.
The growth rate and structure of cells can be determined by conducting an appropriate examination, including computed tomography, which makes it possible to determine the presence or absence of pathological processes in healthy tissues located near the tumors.
Depending on their location, fibroids on the legs can be divided into two types:
- Dermafibromas can be located on the legs, located on the inner surface of the thighs and lower legs.
- Plantar pain is located on the arches of the feet and is characterized by pain when pressing and walking.
Neoplasms are often observed in women during menopause and after pregnancy, which is explained by hormonal imbalances.
Therefore, it is imperative to undergo general diagnostics of the body, making it possible to prevent various dangerous diseases.
Features of treatment
In each specific case, the methods of treatment and removal of the tumor are chosen by the surgeon based on the patient’s clinical picture and the diagnostics performed. If the fibroma belongs to the category of limited and benign, and its size is 1-2 centimeters, then surgery or any active therapy is not required in such a case.
However, if the tumor interferes with walking, often rubs and bleeds, and constantly increases in size, then it is necessary to promptly consult a doctor to prescribe appropriate treatment.
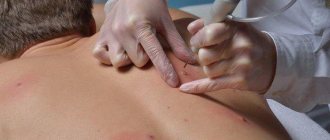
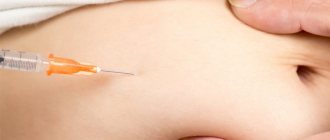
Conservative treatment of fibroma of the left finger is possible in cases where the tumor does not increase in size. Therapy consists of introducing special drugs into the tumor, including injection of diprospan. Such treatment will be effective only for small tumors that do not tend to increase in size. If the injections do not produce any results, removal of the tumor is prescribed.
Operative methods
Most often, when a fibroma is detected, surgical treatment is prescribed, which will allow the neoplasm and affected adjacent tissues to be removed using special equipment or surgically. In each specific case, the doctor chooses therapy depending on the characteristics of the existing tumors.
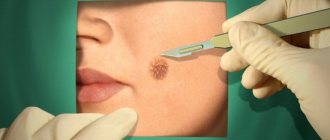
During surgical removal, the operation is performed under local anesthesia, and only large and numerous formations will require the use of general anesthesia. The doctor makes an incision in the skin, excising the affected tissue. If it is necessary to remove a small soft fibroma, the pedicle is trimmed with a scalpel, cutting out the tumor with its base, after which sutures and a tightening bandage are applied.
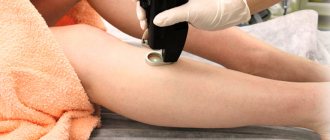
Laser therapy is popular , when using special equipment without injection anesthesia, the affected area is excised, which eliminates pain and the formation of scars with redness at the site of the removed tumor. Injured tissues are additionally cauterized under the influence of the laser, which accelerates their healing, so the patient’s recovery after such an operation takes only a few days.
If there are contraindications for treating fibroma with a laser or removing it using the classical surgical method, the radio wave method can be used, which effectively solves the problems of soft tumors. By exposure to completely safe waves, tumor cells are separated from healthy tissue, while avoiding injury to ligaments, tendons and muscles located near the tumor. This technology is bloodless and painless, and the patient’s recovery takes no more than a week.
Also popular is the method of removing shin fibroids using electrocoagulation , which involves exposing existing tumors to electric current at a certain frequency. This technology is completely painless, the whole procedure takes only a few minutes, allowing you to remove fibroma-affected cells. Coagulation can be used to eliminate tumors with a diameter of no more than 2 centimeters.
In rare cases, patients experience self-healing, which is typical for thin-pedunculated fibroids. Such tumors appear when there is a metabolic disorder, and when the body is restored, the tumors gradually die off and soon completely resolve. However, patients should not hope for self-healing, and if such small fibroids are detected, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor for diagnosis and quality treatment.
Prevention of complications
After surgery to remove fibroids, tissue integrity is restored. If the excision was performed during surgery, then it takes an average of 3 months, and with the help of laser and radio wave therapy this period is halved. To prevent possible complications, you must follow the recommendations of your doctor.
- Protect skin from direct sunlight.
- Refuse to perform physical activity.
- Do not visit saunas and steam rooms.
- Do not swim in open waters.
- Organize your diet correctly.
- Constantly strengthen your immune system.
It is important to try to undergo a complete examination and try to find out what caused the growth of fibroids. Elimination of the provocateur factor makes it possible to further prevent the appearance of new benign formations.