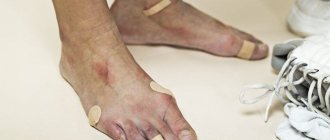
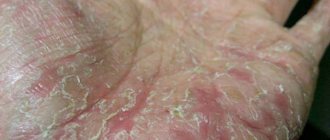
Eczematous dermatitis is the most common form of contact dermatitis, characterized by a delayed hypersensitive reaction. The most vulnerable to this disease are the hands and lower extremities, since there is a high probability of developing an allergic reaction to household home remedies.
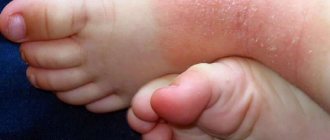
The disease can affect patients of any age and gender, but in children the symptoms are most severe, accompanied by negative consequences. Therefore, it is recommended to carry out mandatory treatment of eczematous dermatitis at an early stage of development.
Main causes of the disease
The skin surface of a person with a healthy body has a natural protective function, which, with prolonged exposure to irritants, loses immunity and the ability to quickly regenerate.
The dermis of patients with an allergic predisposition after contact with antibodies (antigens) produces a delayed response.
Contact eczematitis
At this point, the irritant interacts with the tissues of the epidermis and releases protective antibodies, increasing sensitivity to foreign substances. Subsequent contacts with allergens are accompanied by inflammation of the skin.
Eczematous dermatitis can affect all parts of the body, but mainly the arms, neck and lower extremities, which are exposed to toxic irritants - at home or at work.
The rash appears at the site of contact with aggressive substances, which include:
- Household chemicals (shampoos, gels, washing powders);
- Cosmetics (creams, tonics, lotions, decorative cosmetics);
- Finishing materials (glue, polyurethane foam, putty);
- Rubber, wool, latex, synthetics (clothing, shoes);
- Rubber (gloves, drains, equipment for laboratory research);
- Metal – silver, zinc alloy (clasps, buttons, jewelry);
- External medicines containing lanolin, antibiotics, hormones (gels, ointments, rubbing products).
Hereditary predisposition is a common cause of symptoms of eczematitis, which can occur in patients at any age.
The development of eczematous dermatitis is often facilitated by dysfunction in the body of patients with weak immunity. These include people living in unfavorable environmental conditions or working in industrial production.
Contact eczematitis on the face
The risk group includes patients suffering from diseases of the upper respiratory tract, circulatory, nervous and digestive systems.
Any source of infection predisposes to the development of pathology - dental caries, chronic sinusitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, inflammation of the tonsils.
Eczematous dermatitis: causes
Most often, the provoking factors in the development of this pathology are household and industrial chemicals, as well as medications. Among the provocateurs are the following:
- Industrial or household chemicals.
- Chromium.
- Metal decorations.
- Cobalt.
- Rivets on denim.
- Metal alloys.
- Braces or dental crowns.
In addition to the factors described above, there are internal reasons for the development of eczematous dermatitis:
- chronic infections;
- burdened heredity;
- disruption of metabolic processes;
- weakened immune system;
- outbursts of emotions;
- disorders of the liver or gastrointestinal tract.
In addition, this pathology can occur as a result of allergic reactions to fluff, wool, pollen and dust, as well as due to the presence of fungal infections.
Symptoms
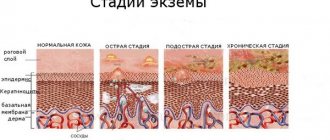
Eczematous dermatitis is closely associated with allergic and inflammatory reactions. It occurs in two forms - acute and chronic. The disease begins quickly and lasts for a long period of time. Over time, it can develop into coin-shaped eczema.
Coin eczema
Relapses are one of the main features of eczematous disease. Each form of eczematitis has its own symptoms.
Acute dermatitis is accompanied by the following manifestations:
Eczematous dermatitis
Redness or erythema - occurs as a result of blood filling the capillaries of the dermis. Swelling. When pressed, the swelling in a certain area of the skin turns pale.- Erosion or eczema is an inflammatory rash that often occurs over moving joints, the face, groin area, and scalp. It appears in the form of bubbles filled with exudate (liquid). When opened, they dry out and form crusts.
- Peeling - occurs as a result of the accelerated death of keratinized scales of the epidermis, degradation of sweat and sebaceous glands. It is the last stage and ends with pigmentation.
- Pain, burning, general malaise, fever.
Chronic eczematous dermatitis occurs as a result of prolonged exposure to irritants such as friction or pressure. Patients complain of symptoms such as thickening and tension of the skin, with a rough, sharply defined pattern, infiltrates, and itching at the site of injury.
Exposure to radiation and ultraviolet radiation contributes to the formation of a bullous reaction (edema).
Bullous reaction
As a result of an advanced type of eczematous dermatitis, individual areas of the skin atrophy and alopecia develops (hair loss or complete baldness).
Note! Eczema is an advanced form of eczematous dermatitis that occurs when patients try to self-medicate or when the diagnosis is inadequate. The specialist must be able to differentiate the types of inflammation, identify provoking factors and prescribe individual treatment for each patient.
Eczema and dermatitis: differences and similarities
Almost every person experiences skin diseases throughout their lives. There are many types of dermatological diseases, as well as the reasons due to which they arise. This is due to the wide distribution of household chemicals, endogenous influences, a variety of infections, and against the backdrop of all this – the reduced functioning of the human immune system.
Similarities and differences between diseases
With both dermatitis and eczema, inflammation of the skin occurs. The skin is affected by various types of rashes, inflamed, and itchy. There are many factors underlying the development of dermatitis; eczema often occurs as a consequence of dermatitis, this is their difference.
When the acute inflammatory manifestations of dermatitis subside, crusts, blisters or scales remain on the skin, this is eczema, a consequence of dermatitis.
Having found out the nature of the appearance of dermatitis, it can be cured, but if eczema has developed, then its relapses can be observed throughout the patient’s life. These frequent relapses distinguish eczema from dermatitis.
Classification and types of dermatitis
There are dermatitis of exogenous and endogenous nature. The difference lies in what irritant caused the skin inflammation and rash.
Endogenous species include:
- Seborrheic (localized in places where sebaceous glands accumulate, can even affect the scalp and genitals).
- Infectious (the body's reaction in the form of a rash in response to infection).
- Post-vaccination rash (mainly at the site of vaccine administration).
- Inflammation of the skin and rashes due to inflammatory diseases of internal organs (pyelonephritis, pancreatitis, exacerbation of cholecystitis, etc.).
- Neuropsychic effects (itching lasts up to several hours, then disappears).
- Food (the body’s response to allergens in food that the body cannot tolerate; stale foods; food containing many dyes and various chemical additives, for example, synthetic crab sticks or any sweet fizzy drink).
- Medicinal (allergic reaction to any medicine; inadequate dose of a medicine; low-quality or expired medicines).
Exogenous species include:
- Dermatitis due to the external influence of certain herbs.
- Dermatitis caused by the influence of parasitic insects.
- Chemical causes (allergy to various chemicals and synthetic substances).
- Due to the external use of medications (iodine, various creams and ointments).
- Exposure to electricity (through faulty electrical appliances and even lightning).
- Effect of temperature (dermatitis from extreme heat or low temperatures).
Signs of occurrence
With any type of dermatitis, various rashes appear on the skin, ranging in color from blue to red.
The patient experiences itching and sometimes burning. Swelling of the skin and pain may occur. After treatment, severe symptoms disappear, leaving behind dry skin and flaking for some time.
Pigmentation or scarring may remain permanently. If the skin is severely inflamed, the temperature may rise.
Complications may develop:
- addition of a secondary infection, development of purulent complications;
- atrophy of the skin;
- oncological neoplasms;
- disfigurement due to scarring of the skin.
Diagnosis and treatment
To make a diagnosis, it is necessary to identify the exact cause of the development of the inflammatory process. To do this, allergy tests, blood tests, and a general examination of the patient are performed. Depending on the irritant, individual treatment is prescribed.
If the dermatitis was caused by allergens, you need to eliminate the known allergen, and also take medications prescribed by the doctor. For dermatitis caused by nervous stress, sedatives and topical ointments are recommended. Inflammations and rashes after hypothermia or exposure to high temperatures are treated with special gels, ointments, and anti-inflammatory drugs.
What is eczema?
Types of eczema:
- neuropathic;
- reflex;
- paratraumatic;
- microbial;
- professional.
The most common and complex is atopic eczema, the occurrence of which is still not fully understood by scientists. There are suggestions that the reasons for its development lie in the poor functioning of the immune system; it can be inherited.
Eczema develops as a complication of dermatitis, against the background of nervous stress, allergies, and various irritants. With a mild form of eczema, the rash is pale in color and looks like flaky spots.
In severe forms, the spots become saturated in color, the rash becomes weeping, and blisters appear. When scratching the rash, infection can occur, so the disease is often complicated by secondary infection. As the disease subsides, the rashes decrease, crusts and sometimes scars remain.
Reasons for development
The causes of occurrence are determined either by internal factors or external ones.
External factors:
- dyes, household chemicals;
- synthetic clothing;
- abuse of preservatives;
- flavorings.
Internal factors:
- genetic predisposition;
- malfunction of the immune system;
- pathology in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- stress, nervous disorders;
- internal chronic infections.
Dermatitis that occurs due to harmful professional work often has complications in the form of eczema. Therefore, to heal the skin, it is necessary to stop such work altogether, otherwise diseases will arise constantly.
For eczema that occurs due to the presence of chronic diseases, microbial diseases, or pathology of the endocrine system, treatment is aimed primarily at eliminating the primary sources. It is clear that until the inflammation of the internal organs is cured, or the virus is eliminated, eczema cannot be cured.
Symptoms of eczema
They are individual. It can be:
- peeling;
- weeping blisters;
- cracks;
- ring-shaped lesions;
- rash;
- skin redness;
- itching
Any type of dermatitis or eczema is treated by a specialist dermatologist.
The first, main step in diagnosis is to identify the exact symptoms of the disease, so for each patient the treatment is individual and different from others.
For effective treatment, it is necessary to identify the sources of irritation; only a doctor can do this. Depending on the type of disease, corticosteroids, phenylamides, antibacterial and antihistamines, ointments and gels, sedatives are prescribed, physiotherapy is carried out, and an individual diet is selected.
In severe forms of the disease, treatment in a hospital is necessary.
Loading…
Source: https://doloypsoriaz.ru/dermatit/vidy-01/chem-otlichaetsya-ekzema-ot-dermatita.html
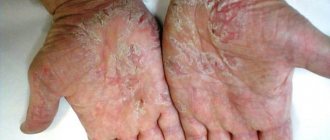
Manifestations of the disease on the hands
Eczematized dermis of the hands is the most common manifestation of the disease in the adult population. This is a simple type of skin pathology. Prolonged contact with household detergents (detergents) and organic solvents provokes inflammatory processes on the skin of the hands.
Contact eczematitis
Prolonged contact with water is a common cause of pathology; constant friction of the skin leads to “cement eczema”.
Eczematoses can be observed on the hands of housewives, sellers of household chemicals, people working in the service sector who use cleaning products, detergents and gloves.
In dermatology, substances that irritate the skin of the hands are divided into three types:
- Chemical - alkali, acids, paints, salt solutions, cement, plaster;
- Biological – plant juice and pollen;
- Physical – friction, compression, sudden changes in temperature conditions.
The appearance of the first eczematous signs on the skin is a signal to consult a doctor. Self-administration of medications and home treatments can lead to re-inflammation or an allergic reaction.
Eczematous dermatitis appears only on the surface of the skin where there has been contact with chemical or metal substances, and atopic dermatitis, which has similar symptoms, develops in areas remote from the contact.
Dry dermatitis on hands
This can happen immediately, within a day, after eating a certain food, and the rash appears on the cheeks and is manifested by severe itching with small rashes.
Note! There are several dozen types of dermatitis and each requires a specially developed medicine. The similarity of symptoms - itching and rash misleads patients who are trying to be treated with universal anti-allergy drugs.
Photo of eczematous dermatitis
More about dermatitis
Dermatitis is also an inflammatory skin disease. Most often, this is an acute reaction to the influence of some irritating factor, external (exogenous) or internal (endogenous).
Exogenous stimuli include:
- various chemicals (cosmetics, household chemicals, etc.);
- Sun;
- freezing;
- contact with clothing, shoes, jewelry;
- plant pollen;
- animal hair;
- medications;
- vaccines during vaccinations;
- insect bites;
- food, etc.
Endogenous factors:
- various diseases;
- stress;
- overwork;
- infectious and fungal diseases;
- foci of chronic infections, etc.
Dermatitis is usually an acute pathology and resolves with treatment. It rarely becomes chronic, with the exception of atopic dermatitis.
Types of dermatitis:
- allergic;
- contact;
- atopic;
- neurodermatitis;
- infectious;
- fungal;
- seborrheic.
Rashes with this disease can be of a different nature - wet or dry, with blisters or papules, with cracks or crusts, etc. They are almost always accompanied by itching.
Diagnosis of pathology
To establish the cause of eczematitis, it is necessary to analyze the last month of the patient’s life. It is important to determine which irritant the skin came into contact with.
If it is not possible to indirectly establish the cause, two weeks after the rash disappears, tests for the allergen are carried out. To do this, applicators with an irritant (up to a dozen allergens) are applied to the skin and after a few hours the body’s reaction is checked.
During this time, symptoms may appear on the skin that indicate the presence of pathology. Eliminating the allergen helps get rid of unpleasant symptoms.
Along with identifying the irritant, the attending physician refers the patient to such specialists as: otolaryngologist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, dentist, immunologist. An examination by these specialists can reveal the presence of an underlying disease that provokes relapses of eczematous dermatitis.
An accurate diagnosis is established after a full laboratory examination, which includes a biochemical blood test, stool tests for dysbacteriosis, and a study of the functioning of the digestive system.
Skin diseases have similar symptoms, but each of them requires its own treatment. Only a dermatologist is able to conduct an adequate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
How is dermatitis different from eczema?
Eczema is an inflammatory skin disease that causes itchy, moist rashes. It occurs under the influence of various irritating factors against the background of a predisposition formed as a result of changes in the immune system. As a result, the body begins to react abnormally to the action of irritants, which is clinically manifested by skin rashes.
Classification and types of eczema:
- true;
- professional;
- microbial;
- fungal;
- varicose;
- seborrheic.
At the onset of the disease, local redness and swelling are noted on the skin. Then bubbles with serous contents appear. They burst, the liquid flows out and forms a wet surface with cracks.
After a while, the affected areas dry out and form crusts, after peeling off which healthy skin remains. But in parallel, new rashes may appear, prolonging the course of eczema. And if it is not treated, the disease will become chronic with frequent relapses in the form of new episodes of the disease.
At the same time, the skin gradually thickens, peels off, and even during periods of remission does not look the same as before.
Short description
Drugs for the treatment of eczema are selected according to the course of the disease and on an individual basis. The type of eczema and the degree of inflammation of the skin are determined. Reasons for development:
- heredity;
- thyroid disorders;
- stress and overwork;
- reaction to the influence of external and internal factors;
- metabolic disease;
- reaction to medications;
- disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- diabetes;
- avitaminosis;
- renal failure.
Treatment of eczema on the hands includes general therapy. It is impossible to cure eczema on the hands without pathogenic therapy. Its function is to weaken mutation processes in the body and the effects of external factors.
May include non-specific therapy for the treatment of eczema of the fingers. If the disease is severe, hemosorption, plasmapheresis and enterosorption are prescribed.
Biostimulants are also prescribed - injections of aloe extract or placenta. In addition, they can also appoint:
- treatment of eczema against the background of clearly defined neurotic disorders of the central nervous system;
- intoxication therapy;
- hormonal therapy;
- vitamin therapy;
- antihistamine therapy;
- immunomodulators;
- antimicrobial therapy;
- symptomatic treatment;
- increased calcium in the patient’s blood;
- use of diuretics.
The natural desire of every person faced with the problem of eczema is to quickly find out the names of medications and reduce discomfort, but you should not neglect visiting a doctor. After all, the course of the disease manifests itself individually for everyone.
Kidney problems may cause eczema
Medications for eczema
The first step in choosing medications is to determine the main cause of the rash. Depending on this, treatment is prescribed with the appropriate dosage and duration of administration.
Medicines in tablets for eczema should be taken exactly as prescribed by the doctor, in order to avoid side effects and negative consequences of improper use of drugs.
Tablets for eczema on the hands are mainly based on the content of corticosteroids, antihistamines, vitamins and pain relievers, suppressing itching and burning sensations. Antihistamines block the effects of the main causative agent of the inflammatory process, histamine.
- Tranquilizers eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
- Glucocorticosteroids are hormones secreted by the adrenal glands. Most often, topical agents such as creams, ointments, etc. are used.
- Vitamins for eczema are an integral part of treatment, since many patients are susceptible to seasonal or year-round vitamin deficiencies.
- Antibiotics for eczema are prescribed very rarely, and only when absolutely necessary, that is, when ulcers or eczema of an infectious nature appear.
- If the rashes are associated with gastrointestinal problems, medications are prescribed to improve the functioning of the digestive tract: Festal, Pancreazyme, as well as probiotics.
- Enterosorbents are drugs that absorb toxins in the gastrointestinal tract. Prevents toxins from entering the blood.
Source: https://yazdorov.win/allergiya/chem-dermatit-otlichaetsya-ot-ekzemy-2.html
Treatment
Along with the use of external agents, patients need to treat the underlying diseases that provoke dermatitis.
An important step in the treatment of eczematous dermatitis is the elimination of exposure of the skin to substances that cause an allergic reaction.
Desitin
Mild symptoms (in the absence of weeping erosions) are treated with ointments for eczema and dermatitis.
Dry skin is moisturized with oil-based topical products. The initial stage of the disease, with mild redness, is treated with zinc-based ointments such as Desitin or Bepanten.
When weeping eczema appears, talkers are used to relieve inflammation, itching and redness. These are effective medical products, with different compositions. The preparations are based on alcohol, talc, medicinal fats of animal origin, and zinc oxide.
At the last stage - if peeling and dryness occurs, healing ointments for dermatitis are required - Levomekol, Actovegin, Solcoseryl.
Severe chronic relapses are treated with hormonal ointments. One of the effective remedies approved for treating eczematous dermatitis during pregnancy and lactation is Prednisolone ointment.
Lokoid and Dexamethasone are prescribed as a light hormonal medicine. These remedies help with symptoms of advanced eczema.
What is the difference between eczema and dermatitis?
About dermatitis Symptoms Types of dermatitis Treatment of dermatitis
Many skin diseases present with similar symptoms, making diagnosis and choosing the right treatment difficult. In particular, such similar pathologies are dermatitis and eczema.
Both of these diseases are characterized by moist rashes with itching, blisters and crusts, both develop due to the action of irritating factors. And yet these are two different nosologies.
What is the difference between eczema and dermatitis? Why are these two conditions classified as two different diseases?
More about eczema
Eczema is an inflammatory skin disease that causes itchy, moist rashes. It occurs under the influence of various irritating factors against the background of a predisposition formed as a result of changes in the immune system. As a result, the body begins to react abnormally to the action of irritants, which is clinically manifested by skin rashes.
Classification and types of eczema:
- true;
- professional;
- microbial;
- fungal;
- varicose;
- seborrheic.
At the onset of the disease, local redness and swelling are noted on the skin. Then bubbles with serous contents appear. They burst, the liquid flows out and forms a wet surface with cracks.
After a while, the affected areas dry out and form crusts, after peeling off which healthy skin remains. But in parallel, new rashes may appear, prolonging the course of eczema. And if it is not treated, the disease will become chronic with frequent relapses in the form of new episodes of the disease.
At the same time, the skin gradually thickens, peels off, and even during periods of remission does not look the same as before.
More about dermatitis
Dermatitis is also an inflammatory skin disease. Most often, this is an acute reaction to the influence of some irritating factor, external (exogenous) or internal (endogenous).
Exogenous stimuli include:
- various chemicals (cosmetics, household chemicals, etc.);
- Sun;
- freezing;
- contact with clothing, shoes, jewelry;
- plant pollen;
- animal hair;
- medications;
- vaccines during vaccinations;
- insect bites;
- food, etc.
Endogenous factors:
- various diseases;
- stress;
- overwork;
- infectious and fungal diseases;
- foci of chronic infections, etc.
Dermatitis is usually an acute pathology and resolves with treatment. It rarely becomes chronic, with the exception of atopic dermatitis.
Types of dermatitis:
- allergic;
- contact;
- atopic;
- neurodermatitis;
- infectious;
- fungal;
- seborrheic.
Rashes with this disease can be of a different nature - wet or dry, with blisters or papules, with cracks or crusts, etc. They are almost always accompanied by itching.
The main differences between eczema and dermatitis
As mentioned above, eczema is characterized by a chronic course, while dermatitis is predominantly acute. This is the main difference between eczema and dermatitis.
Another important difference is in the mechanism of disease development. Dermatitis is caused directly by irritating factors. For eczema to occur, changes in the immune system are necessary, which provoke perverse skin reactivity.
The rashes associated with these two diseases can be very similar. But eczema is distinguished by the presence of false polymorphism - the simultaneous presence of various elements of the rash in the lesions. With dermatitis, there is a gradual evolution of rashes and polymorphism phenomena are almost never observed.
Atopic dermatitis and eczema
Atopic dermatitis and eczema have many similarities in their manifestations and development mechanisms.
The main differences lie in the age of the patients - adults are more susceptible to eczema, children are more susceptible to atopic dermatitis.
The rashes also differ - in the first case the process is wet, in the second it is dry without bubbles. Often, atopic dermatitis in childhood leads to the development of true eczema in adults.
Allergic dermatitis and eczema
In most cases, allergic dermatitis and eczema are very different. Despite the fact that the same allergens can cause both of these diseases.
In the case of dermatitis, there is a clear connection between its occurrence and contact with plant pollen, animal hair, consumption of certain foods, etc.
The rash is accompanied by severe itching, usually dry, without weeping. In parallel, lacrimation, sneezing and rhinitis are observed.
With eczema, data on contact with allergens cannot always be identified. The rashes are moist, with blisters and cracks, and over time turn into a dry rash with crusts. There are no associated symptoms from the eyes and nose.
Contact dermatitis and eczema
Contact dermatitis is difficult to confuse with eczema. With this disease, the rashes are localized strictly at the point of contact with the irritating factor and appear almost immediately after contact with it. The rash is swollen, hyperemic spots, without blisters or weeping, with clear boundaries.
With eczema, blisters and weeping are observed, turning into dry crusts. The rash zone can be localized anywhere, regardless of contact with irritating substances and allergens.
You can clearly see the difference in skin manifestations in these two pathologies in the photo.
When exposure to the allergen is eliminated in contact dermatitis, recovery occurs spontaneously. Eczema requires long-term treatment. This is another difference between these two diseases.
Neurodermatitis and eczema
Neurodermatitis also develops with changes in the body's reactivity system. The reason for this is allergenic and neurogenic factors. This disease is often accompanied by disturbances in the balance of the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems, which is manifested by vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Rashes with neurodermatitis are similar to those with eczema and are also accompanied by severe itching, which intensifies at night (this is not the case with eczema). But the rash may contain elements that are unusual for eczema - nodules, papules, congestive erythema, etc. In parallel, irritability, anxiety, sleep disturbances, and weight loss are observed. Therefore, there are neurogenic causes of the disease.
Seborrheic dermatitis and seborrheic eczema
The clinical manifestations, causes and treatment of seborrheic dermatitis and eczema are very similar. Most often, eczematous rashes with this type of disease appear after the manifestation of dermatitis as a complication. The course of the disease is significantly influenced by the nature of nutrition, the state of the hormonal and nervous systems.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CmnyVLAsWYM
The rash can be either dry or wet (oily). The color of the crusts and the severity of peeling depend on this.
The only difference between these two pathologies is that dermatitis is provoked by a violation of the secretion of the sebaceous glands. With the development of eczema, there is also an inflammatory reaction on the part of the skin due to its impaired reactivity. But clinically there are no differences, and the treatment of these two diseases is also similar.
Infectious dermatitis and microbial eczema
Infectious dermatitis, as a rule, is one of the symptoms of various infectious diseases - measles, rubella, scarlet fever, chickenpox, etc. The nature of the rash depends on the type of infection that caused the pathology. The rash can manifest itself as papules, vesicles, spots, hemorrhages, etc. Itching is not always accompanied.
Deep skin lesions develop when infected with streptococcus and staphylococcus. In this case, painful pustules of various sizes are found on the skin (up to boils or carbuncles). The course is acute and does not become chronic.
Microbial eczema most often occurs as a complication of other types of eczema, but can also be a primary disease.
In this case, eczematous rashes differ from the classic course by their purulent nature - the contents of the blisters are cloudy, the surface is weeping with purulent discharge, the crusts are yellow, dirty yellow, gray or with a yellow-green tint.
Accompanied by itching and pain. The course of microbial eczema can be acute or chronic, which, first of all, depends on the timeliness of treatment.
The nature of the rash is the main difference between dermatitis and eczema during an infectious process.
Fungal dermatitis and fungal eczema
Fungal eczema is rarely an independent disease; it often occurs as a complication of another eczematous process.
Fungal dermatitis develops as a primary pathology on any area of the skin or mucous membranes if there is mechanical damage and the body’s defenses are weakened.
The hands and feet are most susceptible to infection by fungi; nails can also be involved in the process. These are typical localization zones. But the disease can occur on any area of the skin.
With fungal dermatitis, the rashes are often dry, with crusts and peeling. Eczema of fungal etiology is characterized by a weeping process with cloudy discharge and dirty-colored crusts. The exact nature of the lesion can only be determined by scraping and identifying fungi and their spores.
Dermatitis and eczema are very similar diseases with a fine line between them. Only a specialist - a dermatovenerologist - can distinguish one from the other and prescribe the correct treatment.
You shouldn’t tempt fate and try to decide for yourself what kind of pathology you had to face.
Trust your doctor, with his help you will have a better chance of maintaining the health and beauty of your skin for many years.
about dermatitis
Source: https://MedoDerm.ru/dermatit/chem-dermatit-otlichaetsya-ot-ekzemy.html
Diet
The effectiveness of therapy depends on adherence to a correct lifestyle and a nutritious diet. It is necessary to exclude from consumption foods such as chocolate, nuts, seafood, citrus fruits, salty and smoked foods.
During this period, it is important to supply the patient’s body with vitamins and nutrients to relieve inflammation and rapid skin degeneration. The diet consists of eating light foods to relieve stress on the digestive system.
Sample menu includes:
- Beef meat – stewed and boiled;
- Dairy products;
- Porridge on water with the addition of vegetable oil - from rice, pearl barley, oatmeal, buckwheat;
- Unleavened bread;
- Greens and vegetables, raw and stewed - cabbage, zucchini, radishes, radish, asparagus, celery, dill;
- Fruits of green and white varieties - apples, peaches, pears, cherries;
- Decoctions of dried fruits, rose hips and medicinal herbs;
- Mineral water without gas in large quantities.
Following a diet throughout the course of the disease, giving up bad habits, overexertion and stress can eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of eczematous dermatitis and avoid subsequent relapses.
Causes of atopic eczema
People who have a genetic predisposition to allergization of the body are characterized by an increased level of immunoglobulin E in the blood. In the normal state of the immune system, this protein takes part in neutralizing various types of infection. But if there is a failure in it, his behavior becomes aggressive.
Immunoglobulin E combines into a single complex with the allergen and affects healthy tissues of the body. With the development of eczema, this is manifested by the appearance of rashes on the skin and a number of accompanying symptoms.
Treatment at home
Natural remedies help primarily relieve the main symptoms of eczematitis - itching and inflammation. The use of folk recipes, agreed upon with a doctor, has an effect at the initial stage of the emerging pathology.
You need to be careful if there are cracks - they are easy access for any infection. If possible, it is better to cover the damaged skin with a band-aid. Skin surface treatment is carried out in a clean room, using only disinfected utensils and tools.
Some of the simple and affordable remedies for eliminating signs of eczematous dermatitis at home are recipes such as:
- Soda solution - 500 ml of water boiled and cooled to room temperature, one teaspoon of sodium bicarbonate. Stir thoroughly and apply to the sore skin with a sterile cotton swab.
- Potassium permanganate - dilute potassium permanganate in warm boiled water until it turns light pink. Carefully wash the damaged surface.
- Oak bark decoction is a universal remedy containing tannins that relieves inflammation and accelerates healing. One teaspoon of bark is poured into 500 ml of water and boiled for 5 minutes. Hands or feet are immersed in the cooled solution and held for 30 minutes. The remaining damaged areas are washed with sterile cotton wool soaked in the solution.
- A decoction of birch buds - two tablespoons of buds are poured into 1 liter of boiling water, brought to a boil and kept in a steam bath for 15-20 minutes. Sterile wipes are soaked in the cooled solution and lotions are made, which are kept for up to 30 minutes.
- Potato juice is an effective remedy for any contact skin irritation. Quickly relieves pain from burns and inflammatory processes. Thoroughly washed and peeled potato tubers are doused with boiling water and grated on a fine grater. Using a sterile gauze pad, squeeze out the juice. Apply lotions for 30 minutes.
To speed up the recovery process of the dermis and avoid subsequent relapses of the disease, dermatologists recommend stopping the use of soap and detergents - pharmacies sell special products that replace them.
The patient should avoid contact with any household chemicals, dyes, and solvents. During treatment, it is better to remove all jewelry and use only plastic gloves.
It is better to follow all recommendations even after treatment - the restored epidermis still has a weak, delicate structure.
Alternative therapy methods
For atopic eczema, homeopathy, acupuncture, oligotherapy, heliotherapy, reflexology, and yoga help improve the condition of the body. The selection of homeopathic remedies and their dosages should be carried out by a specialist. Acupuncture restores proper circulation of vital energy in the body affected by the disease, improves the condition of the immune system, and relieves allergic manifestations.
Heliotherapy uses solar treatments to treat various diseases. Scientists have noticed a beneficial effect of sun radiation on lesions, but it should be moderate; the best time for walking in the fresh air or visiting the beach is before 11.00 and after 15.00. The therapeutic effect of oligotherapy is based on saturating the body with microelements, the deficiency of which is usually found in atopic dermatitis and eczema. These substances are very important for maintaining healthy skin.
Reflexology uses massaging, pressure and rubbing of the reflex zones located on the hands and feet. The procedure has a positive effect on the nerve endings located in these parts of the body, triggering the body’s self-healing processes.
The surface of the palms and feet is interconnected with other organs and systems, so treatment sessions help normalize blood circulation, improve the immune system, improve mood and well-being. Yoga helps the body relax as much as possible and relieve the negative effects of stress. Controlling your breathing during exercise allows you to saturate all the cells of the body with oxygen and improve the functioning of vital organs.