Causes of ear dermatitis
There are several different conditions that can cause dermatitis of the auricle or ear canal. All these pathological processes have their own provoking factors and trigger conditions.
- Atopic eczema is quite often localized in the parotid area. If ear dermatitis appears in a child, as a rule, it is based on an atopic process. The disease is caused by hereditarily caused defects in the functioning of the immune system in combination with environmental factors. This leads to a breakdown of the protective barrier of the epidermis, making it vulnerable to infections and allergies.
- A contact reaction is an inflammation of the skin in response to direct contact with an irritating or allergenic substance.
- Seborrheic lesion is a condition associated with improper functioning of the sebaceous glands, which often causes ear dermatitis in infants.
- Otitis externa is a bacterial process when, with prolonged inflammation and poor hygiene, an infection occurs. This process can be both acute and chronic.
How does it appear?
The cause of seborrheic dermatitis of the ear is pathogenic fungi. Seborrhea of the ear may appear for various reasons, the main ones being:
- disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- prolonged nervous tension;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- avitaminosis;
- hereditary predisposition;
- weakening of immune defense due to chronic pathologies;
- puberty;
- a consequence of damage to the scalp.
As for the hormonal cause of the disease, it is the predominance of androgens over estrogens.
Symptoms of ear dermatitis
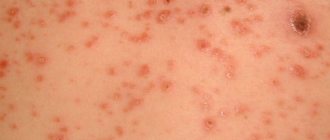
Auricular eczema causes symptoms similar to eczema on any other part of the body. Patients may have:
- Dry, flaky skin around the external auditory canal, on the concha and in the parotid area,
- The same changes can affect the external canal of the auditory organ,
- Redness and swelling of the ear and parotid area,
- Itching around and inside the ear canal,
- Clear discharge from the ear.
Often these changes extend to the area behind the ear and affect the fold where the ear joins the head.
For most people, symptoms of eczema are mild or moderate. But in some cases the itching is very pronounced, and then the following symptoms also appear:
- The skin becomes bright red or dark,
- Severe swelling appears,
- There are areas of very dry and sensitive skin,
- The flaky areas take on a rough, leathery appearance,
- Inflamed skin becomes wet, bleeds and becomes covered with drying yellowish crusts,
- An infection of the external auditory canal occurs.
Infectious inflammations are a special group of ear diseases that require a careful approach to treatment, so these conditions must be treated under the supervision of a doctor. The infection can be primary, when microorganisms infect a healthy ear, or secondary, when it develops against the background of some kind of skin disease. Otitis externa often affects swimmers. Pool water entering the ear washes away protective wax and causes dryness.
Symptoms of infectious external otitis:
- Ear pain, which can be very intense,
- Itching of the ear canal,
- Discharge of fluid or pus from the ear,
- There may be some degree of mild hearing loss,
- The temperature may rise.
If these manifestations appear, you cannot self-medicate; you need a doctor to select medications.
Prognosis and prevention
Treatment of ear seborrhea ends favorably, but this does not exclude the recurrence of the problem. To prevent the development of the disease, it is recommended:
- regularly wash your head and ears with special shampoos, which your dermatologist will help you choose;
- exclude easily digestible carbohydrates from the diet;
- do not get overcooled, protect your ears from the cold with a hat;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- take vitamin complexes with zinc, magnesium and selenium.
After treatment for ear seborrhea, you need to change headphones, hearing aids and jewelry.
Ear dermatitis in an adult
Ear dermatitis is common in older people, and in adults it is usually contact eczema or bacterial inflammation. Contact eczema is caused by metal jewelry, glasses, headphones, earplugs, as well as hair dye, some care products, and perfume, which is sometimes applied to the earlobes. Bacteria can enter the outer ear canal through bathing, swimming in pools and especially in open water, and when the skin inside the ear is damaged, such as by scratching or cleaning the ears.
Allergic itching in the ears: cause, treatment
Itching in the ears may well appear as a result of an allergic reaction. Modern shampoos contain a large number of substances, many of which can cause allergies during hair washing. Allergies are provoked not only by detergents, but also by the use of low-quality headphones made from cheap toxic materials, and specialized headwear, such as latex swimming caps. In such cases, the cause of the disease is obvious, and it can be easily eliminated by eliminating the allergen and taking an antihistamine. This nature of the disease is less serious, since allergies do not pose a great danger and serious problems with the body. However, this phenomenon must be combated in order to protect health from the development of possible complications.
Infection causing itchy ears: cause, treatment
If the problem is caused by a fungal infection, then therapy will depend on the general health of the patient, his age category, the clinical picture of the disease, the type of pathogen and his susceptibility to a particular medicine. Antifungal drugs include clotrimazole, nystatin, econazole and many others.
Doctors can recommend a correct and thorough way to clean the ears, which will not cause harm and will help keep the ears clean without disturbing the natural microflora. Cleanliness is the key to health, but even it should be in moderation.
By excessively cleaning the ears, a person disrupts the natural microcosm and exposes the auricles to the risk of infection by microbes. In any matter relating to personal hygiene, it is necessary to observe moderation and act thoughtfully, listening to your own feelings. Don’t forget about the issue of preventing ear itching in order to protect yourself from possible problems.
Earwax is formed in the ears for a reason, but to serve as a kind of lubricant and protection of the ear canals from the penetration of small insects.
If at any point there is too much wax in the ear, it forms a plug, causing itching in the ears, noise, ringing and even deafness. Also, the sulfur plug begins to put pressure on the eardrum, which is not designed for such excessive loads, which can cause attacks of dizziness, which negatively affect the overall health of the body.
Ear dermatitis in a child
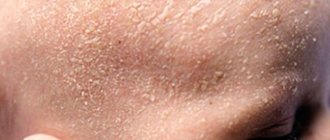
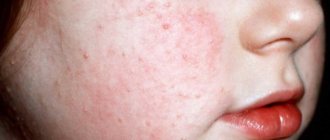
Ear dermatitis in the form of seborrheic and atopic (as shown in the photo) are the most common causes of skin lesions in the ear area in children. Seborrhea affects the area behind the ears, the postauricular fold and the concha itself. Peeling appears and yellowish greasy crusts accumulate. The itching is not very pronounced. In this case, the scalp is also significantly affected. Sometimes parents notice a connection between pathology and errors in diet. Treatment consists of mechanical removal of the crusts after softening with almond oil. Children outgrow this problem; in adulthood, the ears are affected much less frequently.
Atopic eczema manifests itself as intense itching with peeling and weeping, and is often localized in the ear canal. Atopy is often common when eczema is located in a baby on the cheeks, neck, skin folds, and is combined with bronchial asthma and seasonal pollen allergies.
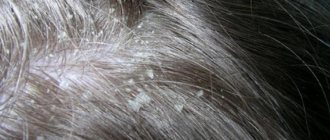
Forms and complications of seborrheic dermatitis
There are pediatric and adult forms of seborrheic dermatitis.
Sometimes the disease is associated with psoriasis (seborrheic psoriasis).
The severity of the disease varies from mild dandruff to severe erythroderma. Dandruff affects the scalp in the hair growth area. In 70% of children, seborrheic dermatitis usually appears by 3 months of age and resolves spontaneously by 6-12 months.
In adults, seborrheic dermatitis begins in adolescence. Predominant in young and elderly people. More often affects men.
Treatment of ear dermatitis
Depending on the underlying cause, treatment for inflammation of the skin around the ear may vary. However, in most cases it begins with general home measures and changes in routine. This approach includes:
- Rinse your ears with warm (but not hot) water every evening,
- Using a gentle, hypoallergenic moisturizer immediately after water treatments to “lock in” moisture and prevent skin dehydration,
- Eliminating all triggers that come into contact with the skin. Thus, the condition is often provoked by metal earrings, which contain nickel. They need to be replaced with hypoallergenic gold-plated or silver ones,
- Wearing a hat that covers the ears during the cold season, since cold can serve as a provoking factor for the development of the described pathology,
- Switching to the use of hypoallergenic skin care products that do not contain dyes, fragrances, ethyl alcohol and harsh surfactants,
In any case, before starting treatment of any skin lesion in the parotid area, you should consult your doctor. Only a specialist can correctly diagnose and select the right treatment, even if therapy can be carried out with home remedies.
Treatment of ear dermatitis with medications
In some cases, ear dermatitis does not respond to methods such as changing the regime and caring for the skin of the ears, in such cases it must be treated with pharmaceutical products.
Sometimes you have to choose the right remedy. If the first prescribed treatment does not show the expected effect, the doctor will prescribe an alternative method or a new combination of drugs.
Treatment may include various combinations of the following:
- Steroid hormones in the form of ointments are applied to the affected areas, which are itchy and weepy. Often ear dermatitis is located in the fold behind the ear, in this case glucocorticoid ointment is especially indicated, and patients leave good reviews about its effectiveness. Drugs from this group relieve inflammation, eliminate itching, swelling, peeling and other symptoms. If the skin lesion is located inside the canal, steroids are applied in the form of drops.
- Antihistamines are drugs in tablets whose main effect is antipruritic.
- Antifungal agents are effective in the seborrheic process, in the development of which, as scientists suggest, a microscopic fungus plays a role. Often these drugs are prescribed simultaneously with other groups of drugs.
- Antibiotics are indicated for bacterial dermatitis, or otitis externa.
- Non-hormonal ointments and drops have different directions of action. Compositions with moisturizing additives help retain moisture in the dermis and affect dryness and flaking. Salicylic emulsion exfoliates and eliminates dead epithelial cells. Herbal extracts and naftalan oil soothe and fight inflammation. Natural oils (coconut, shea, almond) effectively soften and “lock in” moisture. Olive oil, on the contrary, is not recommended, since studies have confirmed that it disrupts the barrier functions of the epithelium.
Diagnostic methods
Since seborrheic dermatitis, which affects the human ear, is similar in its appearance to allergic reactions , a thorough diagnosis is needed.
If you have this pathology, you should contact a dermatologist, who will conduct an examination, review your medical history, and identify possible causes of ear seborrhea. Most often, one visit to the doctor is enough for him to make an accurate diagnosis.
Important!
In some cases, it will be necessary to take scrapings from the affected areas of the ear to identify pathogens. This analysis allows you to determine the type of pathogen and prescribe the correct treatment.
Classification of the disease
There are several types of ear dermatitis, similar in their symptoms, but formed under the influence of various provocateurs.
Contact – manifests itself when the skin is directly exposed to external irritants.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=8kvatWhZ82U
This type of dermatitis in the ears can be triggered by the following irritants:
- hair care products,
- glasses frames made from materials that cause allergies,
- hair dye,
- ear drops,
- headphones and hearing aids made from low-quality materials,
- jewelry with a high nickel content,
- jewelry,
- allergenic food,
- plant pollen,
- household chemicals,
- fluff and fur of pets.
Manifests itself in the form of the following signs:
- redness and swelling of the ear in the contact area,
- peeling and itching of the skin.
This type of disease is easily diagnosed and, when the irritant is eliminated, is quickly cured.
Occurs under the influence of provoking factors:
- insufficient skin hydration,
- weakening of the immune system,
- predisposition to allergies.
Clinical manifestations:
- the occurrence of unbearable itching,
- bright red spots and blisters with serous contents,
- formation of crusts in the area of inflammation,
- the appearance of cracks and weeping wounds,
- addition of secondary infections.
It is impossible to completely get rid of the disease, but with the help of treatment, atopic dermatitis can be transferred to a stage of long-term remission without exacerbations.
Seborrheic is the most dangerous type of disease, arising under the influence of a pathogenic fungus on the scalp, and then spreading to the ear area. If left untreated, the infection may spread to the cheeks and neck.
Seborrheic dermatitis in children appears as a result of the residual presence of maternal hormones.
Factors of occurrence:
- hereditary predisposition,
- hormonal imbalances (in adolescents, pregnant women),
- insufficient dose of vitamin B in the body,
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, liver and other internal organs,
- drug therapy,
- nervous instability.
Characterized by the following features:
- fatty scales on the surface of the ears,
- color change,
- swelling of the skin,
- the appearance of nodular formations with liquid contents, spontaneously opening,
- coarsening and dryness of the epidermis.
Acute form - occurs immediately and entails severe itching and fever. Redness and swelling, a rash in the form of blisters and papules (nodules) are observed. The lesion quickly reaches the ear canal and is accompanied by pain and the appearance of boils. The level of hearing decreases noticeably, which can lead to irreversible consequences.
Chronic form - observed with a prolonged course of the disease. There is ear congestion, peeling of the surface of the auricles, and the appearance of weeping erosions. Skin changes spread to the area around the auricle. It is characterized by periods of intensification of the inflammatory process (with pronounced symptoms) and attenuation of the disease. Phases of exacerbations and remissions will follow each other until the necessary treatment is applied.
Dermatitis can occur due to the following factors:
- exposure to chemicals on the external auditory canal;
- prolonged discharge of purulent contents and itching behind the ears;
- any types of dermatitis, especially seborrheic;
- decreased immunity;
- the presence of chronic infections in the body;
- allergic predisposition;
- symptoms of general intoxication of the body;
- metabolic disorders, etc.
In addition, the cause of the development of dermatitis can be scratching behind the ears and mechanical damage to the ear, which leads to secondary infection and the development of dermatitis.
Symptoms of dermatitis in childhood can be observed due to the persistence of residual maternal hormones in the body of children. In addition, there is an opinion that seborrheic dermatitis, which often accompanies ear diseases, can be inherited by children.
The disease in children most often develops in the first months of life and, as a rule, goes away on its own.
However, it should be understood that this does not mean that these symptoms in children can be ignored
Treatment is carried out taking into account the general condition of the baby. In young children, treatment can be carried out externally, and in more severe cases, hydrocortisone ointment is recommended, which is considered the weakest hormonal agent and is quite suitable for children.
Causes of appearance in people
There are several types of ear dermatitis. The most common of them is seborrheic. Contact, allergic and microbial forms of pathology are less common.
The causes of seborrheic dermatitis in the ears are:
- Weakened immunity. It is observed in persons with severe diseases of internal organs after antibiotic therapy. A decrease in immunity also occurs in patients with malignant neoplasms after courses of radiation and chemotherapy, while taking high doses of corticosteroids.
- Metabolic pathology. These include diabetes mellitus, pathologies of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands and other endocrine glands, disorders of protein and lipid metabolism.
- Hypovitaminosis. It is observed in the winter-spring period, subject to a strict unbalanced diet, fasting, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas.
- Hormonal imbalances. They can occur during puberty, pregnancy and menopause.
- Genetic predisposition. Patients whose immediate relatives suffer from these ailments are more prone to seborrhea, including seborrheic ear dermatitis.
- Frequent stress, excessive psychological and physical stress, lack of sleep and proper rest.
In addition to seborrhea, there is also contact dermatitis, which appears due to exposure to the following factors:
- Wearing hearing aids, earplugs, low-quality jewelry (earrings, piercing jewelry made of plastic or medical steel), frequent use of in-ear headphones.
- Using aggressive detergents (shampoos, hair conditioners, dyes, styling products) that can cause skin irritation and allergies.
- Wearing tight synthetic hats or swim caps that cause extreme pressure.
- Use of inappropriate ear drops in the treatment of otitis media.
Ear dermatitis can be complicated by the addition of bacterial or fungal flora, which most often occurs when:
- Scratching and damaging the skin of the ear canal.
- Using someone else's headphones or earplugs.
- Incorrect use of cotton swabs for cleaning ears.
A major role in the development of seborrheic dermatitis is played by microorganisms from the genus Malassezia, which are activated by improper ear hygiene and excess sebum.