Psoriasis is a chronic skin disease. In recent years, an increasing number of the population is suffering from it, which may be due to changes in environmental conditions. Previously, this disease was known as lichen planus. For the first time, the skin disease psoriasis appears in people between 20 and 30 years old. Damage in this disease affects the skin, nails and joints.
There are various assumptions about what causes psoriasis, however, this aspect has not been fully studied. There is a theory according to which there are two types of this pathology, but the main causes of psoriasis are not clear.
The first type is a disease in the origin of which a hereditary factor plays a role in changes in the immune system. More than half of psoriasis patients suffer from this form. The skin is primarily affected.
The second type is not associated with immunity and heredity and appears after 40 years. The lesion mainly affects the joints and nails.
The essence of the disease
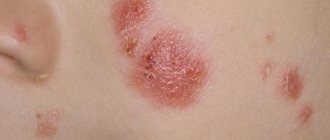
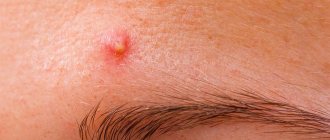
With psoriasis, areas of inflammation form on the skin. They are represented by a papular (nodular) rash. Papules have a flat surface, rise above the skin, feel dense to the touch, and look like red or pink spots. The disease begins with one spot. It increases in size. Smaller ones form around the first outbreak.
In psoriasis, skin cells divide too quickly
Due to active division in the inner layers of the dermis, the stratum corneum of the skin is constantly renewed. Dead scales imperceptibly peel off from the surface and are replaced by other cells. The update cycle takes 28 days. With psoriasis, this process is reduced by 7 times. A new layer of dead cells forms in 4 days. Superficial dead cells do not have time to exfoliate from the skin during this time. Dead cells accumulate on inflamed spots, forming large dry scales.
Pathological changes occur due to attacks on skin cells by the immune system. Psoriasis is of an autoimmune nature.
What to do if you have psoriasis?!
|
Prevention of the initial stage of psoriasis
Key prevention measures:
- wearing loose-fitting items made from natural fabrics;
- avoiding skin injury;
- compliance with the regime and proper rest;
- proper diet (excluding fried foods, fatty meats, sweets and baked goods, spices, berries with a high content of vitamin C and citrus fruits);
- giving up bad habits (alcohol, cigarettes, nightlife);
- regular skin care (moisturizing and protection from aggressive UV rays).
Compliance with medical prescriptions and preventive measures means a multiple reduction in the risk of relapse.
Why does the immune system fail?
The causes of malfunctions in the functioning of immune cells have not been fully established. During research, it was proven that there are many provocateurs for psoriasis.
Often close relatives of patients have a similar problem. Hence the genetic theory of the origin of psoriasis. Sometimes pathology develops due to chronic intoxication of the body. It is believed that improper functioning of the intestines (increased permeability of its cells) contributes to the accumulation of waste and toxins in the body. There are suggestions that skin inflammation is caused by hormonal changes. Psoriasis is often diagnosed in people with diabetes and obesity. Women are at risk during menopause.
Unanticipated immune reactions can cause systemic and skin infections. Untreated dermatitis and chronic allergic rashes, as well as severe viral infections, end with psoriasis.
It has been proven that the disease is associated with neuroses and stress. Psycho-emotional stress, severe shocks and stressful situations can activate autoimmune reactions. If the disease has already begun, nervousness worsens its course.
Psoriasis is diagnosed equally often in men and women. Pathology also has no age restrictions. Most often, the first manifestations of psoriasis occur in young people 16-23 years old, as well as in older people - 57-60 years old.
Causes
Psoriasis, including psoriasis on the face, is, not without reason, considered one of the most mysterious diseases. Disputes about its etiology have not subsided to this day. Among specialists there are adherents of the primacy of endocrine, autoimmune, psychosomatic theories, and recently the genetic theory of the occurrence of psoriasis has become increasingly popular. To some extent, this is confirmed by the ubiquitous statistics, which claim that every third out of four people who develop this dermatosis have one of their close relatives who is also its carrier. Perhaps only three circumstances do not cause much controversy among experts:
- The disease is multi-etiological in nature: it is not possible to explain its origin by one cause;
- This pathology can be driven into a stable stage of remission for years, even decades, but there is no final cure for it;
- transmission of psoriasis through direct contact is excluded: it is not contagious.
Be that as it may, unsightly psoriatic rashes, which can cover almost any part of the body, including those that cannot be hidden from the eyes of others, cause psychological discomfort, first of all, to the patient himself.
Symptoms of the disease
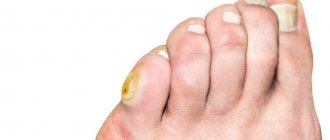
The first reddish spots are most often localized on the flexor surfaces - knees, elbows, shoulders. Somewhat less often - on the neck, back and buttocks. In some patients, the first lesions appear on the scalp and are disguised for a long time as seborrheic dermatitis or common dandruff. In people employed in hazardous conditions, psoriasis begins on the palms or soles and affects the nails.
The manifestation (manifestation) of pathology is accompanied by the formation of 1 small spot on the skin. It doesn't itch or hurt. Peeling may attract a person's attention. Single psoriatic spots are often confused with lichen.
Next, peeling forms on the surface of the spot. As the pathology progresses, more and more skin cells are involved in inflammation, and the spot increases in size. It grows along the periphery, with pronounced peeling remaining in the center.
Due to their dense structure and obvious differences from healthy areas of the dermis, psoriasis spots are usually called plaques.
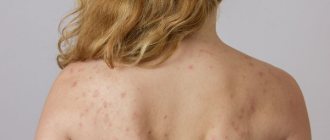
Psoriatic plaques are often located symmetrically on the body
Further progress leads to the “reproduction” of plaques. New spots appear around the first, smaller in diameter. Sometimes new lesions form in other parts of the body. Gradually they merge with each other, forming symmetrical patterns on the body.
With psoriasis, joint damage can occur. Psoriatic arthritis develops. The patient feels pain in the joints. Over time, they become deformed, a person moves with difficulty, and loses the mobility of some joints.
How does psoriasis develop?
The spots become more numerous during the progressive stage (developmental stage). New elements often appear in areas of skin damage (after scratches, insect bites, cuts), chronic irritation (rubbing with clothes, scratching). When the number of plaques increases, the patient may suffer from itching, a feeling of tightness, and burning. With proper treatment, progress stops.
During the stationary stage, new rashes do not form on the patient’s body, and old ones stop increasing in size. The previously pink substrate under peeling acquires a bluish tint. The plaques themselves become denser and harden. A small depression forms around them - pseudoatrophy, which disappears over time.
Next comes the regression phase - relief of the symptoms of psoriasis. The skin is gradually restored.
Peeling disappears from the central part of the plaques, and they gradually acquire a normal color. The peripheral zones are restored last. After complete elimination of the horny scales, tissue swelling slowly goes away.
The spot may have a purple tint
When remission is achieved, the localization zones of psoriatic plaques differ little from healthy skin. The duration of each stage differs for each patient. Doctors managed to establish a single pattern. In the warm season, the symptoms of the pathology soften or completely subside, and in the fall they become more active.
A little about the varieties
Psoriasis can develop in different forms. Separately, psoriasis of the palms and soles is distinguished, as well as the arthropathic type of the disease. They are quite rare, as is the pustular form. With it, small pustules (vesicles filled with pus) form in the plaque area. They increase in size and merge with each other. Pustules that are large in diameter are called “purulent lakes.” This form of psoriasis is dangerous due to infection entering the body and blood poisoning.
The exudative form of psoriasis is common. A characteristic feature is a different type of scales. In the normal course they are white-gray, in the exudative form they are white-yellow and dense. The particles are formed by a mixture of keratinized cells and exudate released in the area of inflammation; in medicine they are called crust scales. Psoriasis plaques in this form itch and crack. This increases the risk of infection of the lesions with pathogenic bacteria.
Seborrheic type of psoriasis is quite common. With it, the first plaques appear on the scalp, most often on the crown and back of the head. Increasingly, the plaques protrude onto the neck, area behind the ears, and forehead. With this course, a “psoriatic crown” is formed - a complete lesion of the scalp affecting the face.
What to do if plaques appear
If you have signs of psoriasis, you should see a dermatologist.
The appearance of round, nodular formations of pink color is a reason to consult a specialist. Psoriasis is treated by a dermatologist. The sooner the disease is brought under control, the greater the chance of slowing its progression and ensuring sustainable remission. Patients hesitate to visit the hospital in the hope that the spot will disappear on its own. If left untreated, the disease can progress dramatically - spreading to healthy areas and affecting the entire body. In this case, they talk about a generalized form of psoriasis. It is extremely difficult to treat. This form can develop after extensive burns, severe infectious diseases, or poisoning.
How will the examination be carried out?
Diagnosing psoriasis is usually not a problem. The disease has characteristic features:
- the phenomenon of stearin stain - when scraping off the scales, the peeling only intensifies, and the gray-white surface of the plaque becomes even whiter;
- terminal film phenomenon - after scraping the entire layer of keratinized scales, a thin transparent film separates, under which a smooth, inflamed pink substrate is visible;
- the phenomenon of pinpoint bleeding - after removing the film, small drops of blood appear on the surface of the plaque.
In the atypical course of the disease, it is differentiated from lichen planus, pustular form of syphilis and seborrheic eczema. Sometimes a histological examination of the skin in the affected areas (biopsy) is required.
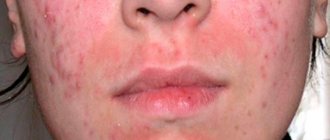
Types of psoriasis on the face
The disease itself has a rather complex classification with many varieties. According to the type of course, it can be conditionally divided into two large groups: with pustular and non-pustular course. It is curious that each species has its own “prerogative” areas of damage. This is especially true for isolated types that do not fall under the general classification, for example, seborrheic-like manifestations. This circumstance greatly helps doctors carry out accurate diagnostics, and therefore choose the optimal treatment tactics.
The severity of the course distinguishes between mild and severe forms of psoriasis, depending on the total area of the lesion and systemic manifestations of the disease.
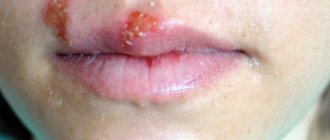
It should be noted that the face does not belong to the most typical areas of psoriatic lesions. In any case, it is most characteristic of the seborrheic form of vulgar psoriasis, which subsequently spreads to the border with the hairline and further, under it, giving, at first glance, the impression of ordinary dandruff.
Stages of the disease
Psoriasis on the face is characterized by rapid development due to the sensitivity of the skin in this area. We have already talked in detail about the initial stage of psoriasis on the face. This is followed by a stage called stationary, when the plaques acquire lightish shades, the shape of the papules becomes round, with silvery scales. As a rule, these metamorphoses appear within about a month after the onset of the disease.
The next stage is considered to be attenuated. At this stage, the plaques are no longer visible on the skin and turn pale. The desire to scratch them disappears, the papules are surrounded by dense and keratinized borders. This process lasts, on average, from two months to six months.
How is scaly lichen treated?
Psoriasis is commonly known as psoriasis. Traditional healers treat the disease with infusions and decoctions of herbs, and homemade ointments. Such therapy takes a long time and is not always successful. If psoriasis worsens, you should consult a doctor and undergo a comprehensive examination. Therapy begins with eliminating provoking factors, prescribing a diet, and medications. Only medications that can quickly stop inflammation and slow down the progression of the disease. When the acute symptoms subside, the doctor himself may recommend phyto-baths and lotions.
Hormones
Psoriasis is treated with several types of ointments (creams or lotions). The most common option is hormone-containing drugs. They eliminate inflammatory reactions by suppressing the body's defense cells. Such drugs are prescribed for a short course. Treatment is completed gradually so as not to provoke withdrawal syndrome and another relapse. Popular products are Belo-Derm, Hydrocortisone, Cutivate, Elokom.
Cutivate cream and ointment
For weeping psoriasis or severe cracking of plaques, medications are prescribed in which the hormone is combined with an antibiotic and antifungal substance (Kremgen, Triderm).
Hormone therapy is also used in the form of injections. In case of severe exacerbation with pronounced spread of plaques, Diprospan injections are prescribed in a short course. The drug suppresses the immune system and ensures a rapid onset of remission. In some cases, they manage with courses of tablet drugs (Methylprednisolone, Metypred, Prednisolone).
Other means
Ointments with calcipotriol - Daivobet and Daivonex - give a good effect in the treatment of psoriasis. If the patient is not going to have children, retinoid ointments (with vitamin A) may be prescribed. Such products increase skin sensitivity to sunlight and require caution in use.
After achieving remission, drugs are prescribed that can restore the skin. Among them are salicylic ointment (exfoliates the stratum corneum), Kartalin, Naftaderm, Ichthyol, Psoricap, Magnipsor, Skin-Cap and others.
Preparations for oral administration
In the complex treatment of psoriasis, hepatoprotectors (Gepabene, Heptral, Enerliv), sorbents (activated carbon, Enterosgel, Polysorb), and enzyme preparations (Mezim, Panzinorm, Festal) are prescribed. These products cleanse the body and eliminate possible intoxication.
A good effect is achieved by regular use of sedatives (Novo-Passit, tincture of valerian or motherwort). Vitamin therapy is often prescribed. This approach is preferable for nail psoriasis (pathology may indicate vitamin deficiency).
When joints are affected and plaques spread throughout the body, chemotherapy and cytotoxic drugs are prescribed. They slow down cell division (including skin cells), allowing damaged areas to recover.
Supporting activities
For psoriasis, doctors recommend spa treatment. It is preferable to stay in places with a high level of mineralization of water bodies and active solar radiation. The resorts of Israel are considered the most suitable. After treatment there, remission occurs in 98% of patients.
To alleviate the symptoms of psoriasis, radiation, laser therapy, paraffin baths, and electrophoresis are prescribed. It is necessary to normalize sleep and wakefulness, and completely eliminate moments of overexertion from life.
Treatment of psoriasis
Modern strategies for treating the disease involve the use of a whole range of methods. It is important to adhere to three main goals:
- achieve quick initial positive results;
- track the ineffectiveness of some methods and cancel them, but continue to use what helps;
- bring the patient into remission.
Among the types of treatment for psoriasis, there are two:
- non-medicinal;
- medicinal.
Non-drug treatment
If it is possible to do without medications, doctors always try to use this. Several non-drug therapy factors can play a significant role in the treatment of psoriasis.
Daily regime
People suffering from psoriasis should:
- try to quit smoking;
- exclude alcohol (even beer);
- wear clothes and sleep on linen only made from natural fabrics;
- replace washing powder with laundry soap;
- cut your nails short;
- wash only in the shower, do not visit the bathhouse or sauna;
- try to eliminate stress.
Diet for psoriasis
Positive dynamics in the treatment of psoriasis are well influenced by a low-protein diet, limiting protein to 30 g per day. Patients who do unloading once a week show good results. On this day you can eat 2-3 tomatoes, a few lettuce leaves, 1 cucumber, 2-3 glasses of green tea and 300 ml of unsweetened soda.
General principles of dietary nutrition for psoriasis include:
- freshly squeezed citrus juices;
- fresh or stewed vegetables;
- unsalted fish;
- flour products made only from rye flour;
- dried fruits, fruits;
- nuts (no more than 50 g per day).
You should also limit or exclude: meat, grains, smoked meats, sugar, potatoes, cheese, beans, oils, sweets, coffee.
More information about the features of the diet for psoriasis in this material.
Spa therapy
Spa therapy is not the last place in the treatment of psoriasis. This is an excellent anti-relapse factor. The following balneological resorts are popular:
- Hot key;
- Nemirov;
- Sergievskie Mineral Waters;
- Lyuben the Great;
- White church;
- Nalchik;
- Naftalan;
- Evpatoria.
Psoriasis can also be treated at the Dead Sea. The main advantage of spa therapy: the power of nature in the fight against disease. Water procedures, a balanced diet, clean air and soft sun - all this will reduce the symptoms of psoriasis and go into remission.
A type of spa therapy for varicose veins is treatment with Garra Rufa fish. These small creatures do not have teeth, but with their lips they gently eat away particles of flaky skin and improve microcirculation of the outer skin. In addition, the procedure gives an excellent relaxing effect.
Physiotherapy
Among the physiotherapeutic methods in the fight against skin psoriasis, the following are used:
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- selective phototherapy;
- laser therapy;
- X-ray therapy;
- cryotherapy (cold treatment);
- electrosleep;
- phonophoresis.
With the help of physiotherapy you can achieve good aesthetic results, because... Almost all methods involve different types of external effects on the skin. The plaques become smaller and healthy skin cells form.
Photochemotherapy
This method is highlighted separately because it is one of the most effective in the treatment of psoriasis. It is used even for severe forms of the disease that are difficult to respond to other physiotherapeutic procedures. Photochemotherapy involves exposing the skin to long-wave UVA rays. Therefore, another name for the method is PUVA therapy (PUVA).
Drug treatment
Treatment of psoriasis with medications also helps relieve the main symptoms and put the patient on the path to recovery. There are three stages of general (systemic) drug treatment of psoriasis:
- Emergency therapy. It is carried out during the acute period of the disease and is intended to relieve acute symptoms. Medications include steroids and sometimes immunosuppressants.
- Transitional stage. It involves the gradual introduction of weaker drugs, which will be subsequently taken by the patient in courses.
- Current maintenance therapy.
Drug therapy also includes the use of external drugs:
- creams;
- foam;
- gels;
- lotions;
- ointments;
- sprays
Hormonal ointment based on hydrocortisone, used to treat psoriasis
The drugs can be purchased or made according to traditional medicine recipes. The products can be left in the open air or under an airtight bandage. The maximum effect in the treatment of psoriasis is achieved by a combination of drug and non-drug therapy. All means and methods are selected by the doctor.