In medical practice, there are many types of skin diseases. They look unaesthetic, contribute to disturbances in the functioning of the body, and cause the patient a lot of physical troubles. One example of such diseases are various types of lichens. Ringworm is a common infectious disease that affects one or more areas of the skin. A common location for the rash is the scalp. The main danger of this disease is hair loss and the appearance of deep marks after wounds. This form requires urgent examination and comprehensive treatment.
Types of pathological spots on the head
The scalp can be affected by ringworm, lichen planus and asbestos lichen:
- The first pathology is infectious in nature, it is caused by fungal microorganisms.
- The second appears due to a lack of vitamin A in the body and is hereditary.
- The third refers to inflammatory pathologies and develops against the background of other dermatological diseases.
Let us consider separately the features of these 3 forms of skin diseases.
Possible complications and prevention
The nature of the complications that arise from ringworm depends on the type of fungus and the degree of neglect of the pathology. In severe cases, when the infiltrative-suppurative form of the disease develops, hair growth completely stops in the affected areas.
Ringworm, in addition to aesthetic discomfort, does not create problems for the patient. Complications arise if a secondary infection occurs through open wounds formed due to excessive scratching.
In order to prevent the spread of ringworm, it is important to isolate the carrier of the pathogen. In addition, you must:
- disinfect personal items;
- observe the rules of hygiene;
- exclude contact with street animals;
- regular cleaning of premises;
- examining pets using a Wood's lamp if they often walk alone on the street;
- taking vitamin complexes in the autumn-winter period.
Ringworm
The disease is caused by pathogenic fungi of the genus Microsporum and Trichophyton. In medicine, the terms “Trichophytia” and “Microsporia” are used to clarify the type of causative agent of the disease. This form of pathology is also called dermatomycosis, dematophytosis and dermatophytosis.
Note. Trichophytosis is transmitted only from person to person (symptoms of the disease appear after 2 - 6 weeks). Microsporia - infection occurs from domestic animals (cats, dogs, rodents). The first signs of the disease can be observed 5 - 7 days after infection.
Children and people with weakened immune systems most often suffer from ringworm. Infection occurs through contact, when using other people's combs and hats. If an animal is infected, it is impossible to immediately notice traces of the disease on it. Indeed, at the initial stage of development, a small spot can be hidden under his long hair on any part of the body.
You can find more detailed information about ringworm in this material.
What do lichen spots look like?
Depending on the characteristics of the development of the disease, ringworm is divided into:
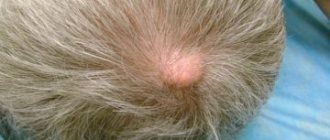
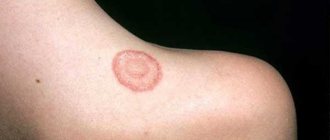
- Surface. Round spots with clear, bright pink borders form on the skin. Peeling is noticeable in their center. Bubbles may appear along the edges, and over time, yellow crusts appear instead. Black dots (remnants of broken hair) are present on the inflamed areas of the skin. The disease is most often diagnosed in children.
- Chronic. It occurs in older people who have previously suffered from a superficial form of the pathology. The spots are small, non-inflamed, do not have clear contours, and are usually located on the back of the head and temples. The hairs break off at the very root. Peeling of the skin is noticeable in the center of the spots. The person constantly feels itching.
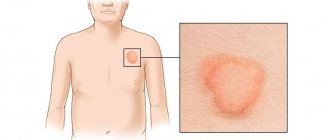
- Suppurative-infiltrative (deep). Infection occurs only from animals. The pathogen gets on the human body and multiplies in its hair follicles. Large bright red spots (5 - 10 cm in diameter) with an uneven surface form on the skin; the presence of purulent tubercles makes them look like a growing tumor. Inflammation lasts for 2-3 months. Accompanied by an increase in temperature, painful enlargement of the lymph nodes and an allergic rash. As recovery progresses, loose brown crusts appear in the center of the spots. In men, the infiltrative-suppurative type of pathology can affect the beard and mustache area.
How to cure skin?
To cure ringworm, you need to see an infectious disease specialist or dermatologist. You should not self-medicate, especially if we are talking about the infiltrative-suppurative form of the disease. Treatment of existing types of ringworm is aimed at suppressing the development and complete destruction of the fungus that causes the disease. Patients are prescribed topical (antifungal ointments, creams, gels, solutions) and oral medications (tablets).
The list of the most recommended medications includes:
- Shampoos (Nizoral, Dermazol, Sulsena, Cynovit, Degtyarny) and ointments (Lamisil, Nizoral, Mycozoral, etc.) made on the basis of clotrimazole, ketoconazole, zinc, tar, terbinafine. Mycoseptin").
- Tablets "Griseofulvin", "Ketoconazole", "Terbinafine", "Itraconazole" and "Fluconazole".
- Iodine 5%, salicylic acid 3% - recommended for treating lichen spots in the morning.
- Sulfur-salicylic and sulfur-tar ointment - it is recommended to apply to lichen spots before bedtime.
Note! Oral antifungal medications may cause an allergic reaction. To avoid this side effect, never take the pills without a doctor's prescription.
For the treatment of ringworm, modern medicine recommends “talkers”, which are made directly in pharmacies. Vidal's milk (consists of 6 components: camphor, alcohol, glycerin, salicylic and boric acid, sulfur solution), and Lassara paste (made from salicylic acid, zinc oxide, petroleum jelly and starch).
To cure chronic ringworm on the head, patients are prescribed, in addition to these medications, to take vitamins (groups B and C) and immunomodulators (Reaferon, Dekaris). Medicines are prescribed that help strengthen the walls of blood vessels (Ascorutin, Detralex) and improve blood circulation.
Note. To ensure complete recovery from ringworm, you must undergo a bacterial culture test (a microfragment of recovered skin is taken for examination). The procedure is carried out 3 times: immediately after treatment, after 7 days and after 2-3 months. Ringworm can be considered cured if the results of 3 procedures are negative. Otherwise, the dermatologist conducts an additional examination and changes the treatment regimen.
A dermatologist will tell you in the following video how long it takes to treat ringworm, whether you need to cut your hair during its treatment, which tablets and ointments are best to use:
What's happened
Follicular keratosis, also known as pilaris, is a disease that affects the openings of the pilosebaceous follicles. The exact reasons for the development of the pathological process are unknown. The disease is presumably transmitted genetically, and vitamin A deficiency also plays a role.
Most often, pilaris affects children's skin. With age, the symptoms of lichen become less noticeable, and by old age they may disappear completely.
Lichen pilaris is characterized by the formation of a large number of follicular nodules covered with horny scales. When palpating the damaged area, there is a feeling of the grater surface.
Note! Follicular keratosis is localized on the head and cheeks. On the body, lesions of lichen pilaris can be seen on the joints of the arms and legs.
Lichen planus
Other names of the pathology: Lassuer-Little syndrome - name. in honor of the early explorers, lichen cicatricial and follicular erythematosus. The disease rarely affects human skin, and it is not the epithelium that is affected, but the hair follicles. The reason for its occurrence is still controversial. According to scientists, the pathology is hereditary in nature, can be transmitted from either parent, and develops when there is a lack of vitamin A in the body (necessary for the health of the immune system).
Clinical picture
The symptoms that precede the appearance of lichen follicularis on the scalp first manifest themselves as a feeling of itching, then the appearance of a pointed nodular rash and hair loss. In this case, papular rashes can form not only on the head, but also on other parts of the body (torso, limbs - on the folds).
Note! With lichen follicularis, the skin at the site of its appearance does not become inflamed. The affected surface is rough.
Bald spots form in the temple area, on the back of the head and crown. They have a round shape, and with medical inactivity they begin to slowly increase. Merging, small bald spots form large areas of baldness on the patient’s head (they can affect the entire scalp).
Skin affected by lichen follicularis differs from healthy areas in having a shiny and noticeably stretched surface. In most cases, the diseased skin has a color close to natural, but may change to blue-pink. Serous crusts form at the site of scratching.
Note. Lichen planus is difficult to cure, because often after an improvement in the patient’s clinical condition, an exacerbation of the disease follows.
Diagnosis of the disease
Lichen follicularis cannot be diagnosed through general and biochemical analysis (blood and urine tests). The external symptoms of this form of skin disease do not always appear the same. Typically, upon examination, patients present with a lichenoid rash (shiny, flat nodules) and hair loss.
When conducting a histological examination in pathological foci, the following is revealed:
- Dystrophic change in the basal layer of the skin (adjacent to the dermis).
- The presence of infiltrate in the spinous layer of the epidermis (located above the basal layer).
- Unevenness of the granular layer of the epidermis.
In order to clarify the diagnosis, a differential diagnosis is carried out, which makes it possible to separate lichen planus from monilethrix (pathology causes hair atrophy throughout the body) and keratosis pilaris (horny plugs form at the mouths of the follicles).
Features of treatment
Doctors have still not been able to formulate an effective treatment regimen for lichen pilaris.
To treat this form of the disease, patients are prescribed the following drugs:
- “Plaquenil”, “Delagil” are anti-malarial drugs that have an anti-inflammatory, antiprotozoal (activity against protozoan parasites: amoebas, lamblia, trichomonas) and a strong immunosuppressive effect on the body (suppresses the excessive activity of the immune system when it begins to attack the body’s cells, mistaking them for alien).
- Vitamin A or “Aevit” - participates in the formation of the structure of hair and nails, fat accumulation, normalizes metabolism, strengthens the immune system.
- Local preparations with corticosteroids (Prednisolone, Tetracycline, Hydrocortisone) have an immunosuppressive (depresses the immune system) and anti-inflammatory effect.
In order to restore the natural shade of damaged skin, patients may be prescribed photochemotherapy.
Also, lichen can be treated with ointments, which are usually not used to treat lichen on the head, but if you have lichen on the body, then this is the most effective treatment with these drugs.
Symptoms of Devergie's disease
Devergie's disease has characteristic manifestations in the form of:
- the presence of islands of healthy epidermis interspersed with rashes;
- the skin in the affected area is red or carrot-colored;
- formation of pointed papules with keratin plugs.
So are things like:
- formation of peeling flakes of different diameters;
- hyperkeratinization of the skin of the palms and feet;
- deformation and change in color of the nail plate;
- forming beignet cones.
Symptoms of Devergie's disease occur in many dermatoses and manifest themselves as:
- sensation of skin tightening;
- painful sensations caused by cracks in hyperkeratosis;
- itching, peeling.
Lichen pilaris is not characterized by an effect on the general condition of the patient. Sometimes in the acute phase it may be accompanied by a slight change in condition.
Lichen asbestos
Other names of the pathology: follicular keratosis, asbestos pityriasis. The disease is inflammatory in nature. Most often, this form of lichen is observed in children of preschool and primary school age and adolescents, as well as in persons with weakened immune systems. The pathology gets its name from the formation of a flaky white layer on the scalp that resembles asbestos fibers.
Reasons for appearance
Sometimes even laboratory analysis does not allow us to establish the exact root cause of asbestos-like lichen. In some patients, this form of skin pathology may develop against the background of normal fungal inflammation (Pityrosporum ovale). The following can also provoke the appearance of asbestos lichen:
- The initial stage of psoriasis (non-infectious skin disease, scaly lichen).
- A complicated form of seborrheic eczema (a chronic skin disease with weeping and itchy lesions).
- A difficult to treat streptococcal infection (can cause scarlet fever, erysipelas, rheumatism, sore throat, etc.).
- Scalp injury.
Symptoms
Lichen asbestos is usually localized on the crown of the head and closer to the forehead, less often on the back of a person’s head. The shape of the pathological foci is poorly expressed. What distinguishes lichen from other types of similar skin pathologies is its silver-gray hue. White flaky crusts cover not only the inflamed skin, but also the hair. In this case, the hairs do not break off, but remain in place, but look lifeless.
An additional sign of asbestos lichen is itching, which a person constantly feels. Scratching causes the lesions to appear inflamed and slightly swollen. Due to the fact that keratinized scales glue the hair to the surface of the skin, the normal blood supply to the skin is disrupted and the hair follicles no longer receive the necessary nutrition. This condition also provokes inflammation. After removing the white plaque, you can observe the damaged skin of a bright pink color.
Note! Improper treatment of asbestos-like lichen leads to the disease taking a chronic form or transforming into psoriasis. Inadequate treatment of skin disease also contributes to degeneration of hair roots and sebaceous glands.
Diagnostics
It is possible to clarify the type of lichen spots on the head through a comprehensive diagnosis. Since asbestos lichen has symptoms similar to eczema, psoriasis and other dermatitis, an examination of the patient by specialized doctors (surgeon, neurologist, dermatologist, endocrinologist) is part of a comprehensive examination.
Note. An analysis of flaky skin fragments is required, which can show the presence of pathogens in them. Taking this into account, the direction of treatment is determined.
Treatment methods
If the diagnosis is confirmed, the patient is assigned:
- Salicylic oil - applied at night to the affected areas to facilitate the removal of the flaky layer. The oil can remain on the head under the hood for 12 hours. Then wash your hair with any baby shampoo. The hair is combed with a fine-toothed comb.
- Ointments and creams (“Clotrimazole”, “Lamisil”, “Griseofulvin”) - treat skin that has been previously cleared of flaky film.
- Antihistamines (“Tavegil”, “Suprastin”) - to relieve itching.
- Vitamin complexes containing sulfur and vitamins B6 - B12 (Revalid, Perfectil) strengthen the immune system and help restore the scalp.
Note! With a positive course of treatment, it is possible to completely get rid of asbestos-like lichen in 1 month.
Causes of the disease
The etiology of this disease has not been precisely established. According to experts, lichen pilaris is inherited. The appearance of such pathology in adulthood is referred to as the acquired type.
The main factors provoking the development of the disease are:
- low level of the body's immune defense;
- infectious skin lesions;
- dysfunctions of the nervous system;
- increased dryness of the scalp;
- non-absorption and deficiency of vitamin A;
- endocrine diseases;
- negative environmental conditions;
- poor nutrition;
- presence of bad habits;
- the influence of sudden temperature changes.
Such causes of the disease are observed in most cases, but their exact direct effect on the activation of the pathological process has not been established.
Question answer
Do I need to completely shave off my scalp if I have ringworm?
Even if there are several skin lesions and they are small, it is not necessary to cut off all the hair; doctors do not require this. Just remove the strands so that it is convenient for you to treat pathological spots with ointment.
You have been prescribed antifungal tablets "Griseofulvin", what should you take with them so that they are well absorbed?
Antifungal drugs are washed down with milk and kefir. These products contain fats necessary for better absorption of the drug. Usually, the manufacturer indicates the rules for taking pills in the instructions. It is recommended to take Griseofulvin tablets with vegetable oil (1 tsp/1 tablet).
How can you wash your hair if you have shingles on your scalp?
For this purpose, use a thick foam of tar soap; do not rub the skin with the bar itself, otherwise it may be injured. You can also use shampoos that contain selenium sulphide 2% (Sulsena, Nizoral). The component promotes skin healing and kills fungal spores.
Is it true that antifungal drugs have a negative effect on the liver?
This is true, so during skin treatment it is very important to follow the dosage prescribed by your doctor. Keep in mind that even taking vitamin A, which is also prescribed for lichen, can damage the liver.
Can you get ringworm from a sick person just by sitting next to them?
Infection occurs when broken hairs or peeling scales fall from a sick person onto the skin of a healthy person. This can happen when a healthy person uses a sick person's comb or tries on his headdress. There is no chance of infection during normal communication.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of ringworm is carried out through an external examination of the affected area using a Wood's lamp. Additionally, scales are collected from the problem area and sent for bacteriological examination.
These procedures are carried out to differentiate ringworm from the following diseases:
- baldness;
- favus;
- candidiasis;
- acne;
- other forms of lichen.
If an infiltrative-purulent form of lichen is suspected, differentiation is carried out with phlegmon, staphylococcal sycosis, ostiofolliculitis, iodo- and bromoderma.