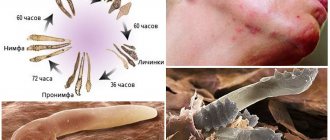
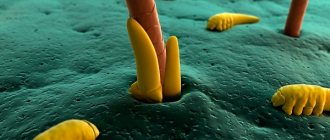
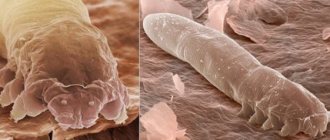
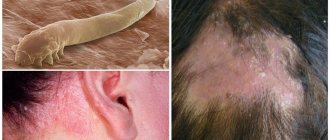
Demodicosis in humans (see photo selection) develops as a result of the activity of subcutaneous mites of the genus Demodex. Normally, these parasites are present in almost every inhabitant of the Earth, but they manifest themselves only in case of an excess of them in the human body, and against the background of weakened immunity, which cannot resist them.
In some cases, Demodex brevis and Demodex follicorum mites exhibit symbiotic properties, helping to establish the acid-base and hormonal balance of the skin. However, if there are too many of them, ulcerative lesions and scabs appear on the face, which can also appear on other parts of the body.
Demodicosis of the head
Symptoms. The sebaceous glands located on the head are very sensitive and instantly react to changes in hormonal levels and deterioration of the body's condition. The first symptom of demodicosis of the scalp is persistent erythema (manifested in the form of red, swollen spots) accompanied by acne. In addition, persistent redness and thickening of the scalp, itching, tension and irritation of the scalp, as well as the appearance of a rash, indicate demodicosis.
Peculiarities. Demodex mites often cause itching and flaking of the scalp. Microscopic parasites that “inhabit” hair follicles and feed on dying epidermal cells provoke the appearance of dandruff. Often, symptoms of demodicosis of the head are found in women who ineptly or too often use aggressive chemical compounds for dyeing and perming their hair . With demodicosis of the scalp, there is a danger of spreading the tick throughout the body on your fingers; you just need to first run them through your hair and then touch your face, chest or stomach. Manifestations of demodicosis of the scalp are a reaction to hormonal imbalance, long-term treatment with antibiotics and hormonal drugs, unhealthy diet (abuse of sweets, canned food, coffee, tea, pepper, as well as salty and smoked foods). Even the wrong shampoo can activate the mite, which will lead to the need for drug treatment for demodicosis of the head.
Treatment of demodicosis of the scalp is aimed at destroying adult mites and larvae, normalizing metabolic and regenerative processes, as well as strengthening the immune system .
Demodicosis of the head is treated with the use of the drug Metronidazole (Trichopol), which acts on the muscular system of the parasite, which first loses the ability to move and then dies. The drug is used in courses lasting up to six weeks. Usually two courses are carried out with a break of 20 days (at this time experts recommend taking purified sulfur twice a day, 500 milligrams). In addition, demodicosis of the scalp is treated with drugs such as Tinidazole, Fazizhin and Hingamin. However, you should remember that only a doctor can prescribe the drug, its dosage regimen and dosage. Sometimes (for example, in the presence of ulcers), antibiotics (Levomycytin, Tetracycline) and drugs with antifungal action are additionally used in the treatment of demodicosis of the head. Taking medications orally should be combined with the use of ointments - sulfur, ichthyol or Wilkinson's ointment.
Side effects and contraindications
If you choose or use the wrong remedies for demodicosis, unpleasant and dangerous consequences for health rarely occur:
- hives;
- itching;
- allergy;
- rashes.
If they occur, stop taking medications and consult a doctor. Also consider contraindications: they are indicated in the instructions. The most common:
- individual intolerance;
- pregnancy;
- lactation;
- age up to 6 years.
Demodicosis of hair
Symptoms. Demodicosis of hair is a consequence of mite damage to the scalp, since the life cycle of a mite that has “inhabited” the hair takes place in the hair follicles and sebaceous glands located in the skin. The parasite avoids sunlight and comes to the surface only in the evening and at night. You cannot see the tick - it is too small, but you can feel it, for example, by itching and tension covering the scalp . Demodicosis of hair leads to a deterioration in the appearance of hair, because... Living in the follicles, the mite leaves waste products there, thereby worsening the growth conditions of the hair shafts, which become dull and brittle, and in addition, noticeably thin out.
Peculiarities. Demodicosis of the hair is inextricably linked with demodicosis of the scalp, so both problems are solved simultaneously. Improving the condition of the skin and freeing the hair follicles from parasites will simultaneously improve the appearance and strengthen the hair shafts.
Treatment. It makes no sense to treat demodicosis of hair - the mite has the ability to “burrow” into the scalp, which should be treated with medication (the agents used for treatment are listed above). To improve the appearance of your hair, you should, with the help of a specialist (trichologist or dermatologist), choose a shampoo and balm that have not only cleansing, but also healing and moisturizing properties. During the treatment of demodicosis of the scalp, it is necessary to wear a hat that protects the hair from sunlight, wind and precipitation.
Traditional medicine in the fight against demodicosis
It will not be possible to cure demodicosis with traditional medicine alone, but every caring parent can use remedies that have stood the test of time as additional auxiliary therapy. To treat the consequences of subcutaneous mite reproduction you will need:
- Laundry soap. It is necessary to wash your face with soap and water every day, avoiding getting the product into your eyes.
- Tinctures of celandine and wormwood. Popular remedies for complicated demodicosis are prepared from medicinal plants that are easy to find in spring or summer. You can prepare a tincture on a water or alcohol basis by infusing the leaves of the plant in a large amount of liquid.
- Chamomile tincture. To treat affected areas of children's skin, soak a cotton pad in chamomile alcohol tincture.
- Tea tree oil. A popular traditional medicine, which is famous for its anti-inflammatory properties, is suitable for disinfecting mite-affected skin areas.
- Tar of birch bark. The concentrated substance is added to the medicinal ointment. Thanks to the active substance of tar, the reproduction of subcutaneous mites is reduced and the appearance of new foci of inflammation is prevented.
Demodex is a parasite that lives and feeds on the host. For children, tick infection does not go away without leaving a trace. Severe discomfort, pain and persistent itching annoy the child both day and night. Complications of demodicosis lead to the development of pathologies in the child’s body, so it is advisable to begin treatment for parasites at the first manifestations of the disease.
Facial demodicosis
Symptoms. Facial demodicosis is manifested by severe itching (increased after washing ), changes in skin texture ( the skin becomes “lumpy” ), pustular lesions of the skin, redness, dilated capillaries and peeling. A mite that has become active in one zone very quickly spreads over the entire area of the face, including the eyebrows and eyelashes, which, after the “attack” of the parasites, slow down their growth and fall out.
Peculiarities. Demodectic mange on the face develops in stages. The disease begins with pink-red spots, which after a while become covered with a very itchy acne. Treatment of demodicosis on the face must begin as soon as possible, without waiting for the mite to “master” new areas.
Some general information
The disease is caused by excessive activity of mites of the genus Demodex, follikulorum and breis species. These creatures are normally present in the skin of a healthy person, and treatment of demodicosis in children should not be limited to the extermination of opportunistic organisms.
Domestic medicine somewhat exaggerates the importance of the impact of the tick itself on the body. In the largest Western publications, on the contrary, demodicosis is not mentioned at all in connection with the diagnosis of acne, rosacea and other “classical” consequences of this disease in our understanding.
On the other hand, with weakened immunity, demodicosis is an undeniable problem. In addition, allergic reactions, especially in children prone to this, have not yet been canceled.
Facial demodicosis: video
Treatment. First of all, you should be tested for demodicosis - the corresponding diagnosis is made when five adult individuals are found on one square centimeter of skin . The most effective treatment is considered to be a combination treatment of facial demodicosis, for which drugs for external use and systemic therapies are used, including immunomodulators, multivitamin complexes and dietary supplements containing minerals and amino acids. To relieve itching, it is advisable to take antihistamines (antiallergic) drugs, for example, Suprastin, Tavegil or Diazolin, and antiparasitic drugs, such as Metronidazole and Ornidazole. Treatment of demodicosis on the face is a long process, carried out in courses separated by short breaks . If the disease is detected at an early stage, then you can get rid of the tick in one to one and a half months, and in advanced cases, treatment of facial demodicosis can take up to a year. It is clear that the cure primarily depends on the rapid destruction of parasites, for which Metrogil, Demalan ointments are used, as well as compositions containing tar, sulfur, zinc, sodium thiosulfate, azelaic acid, benzyl benzoate, ichthyol and even mercury (yellow mercury ointment). In addition, if you have facial demodicosis, it is very important to follow a diet: exclude spicy, salty and smoked foods, and also do not drink alcohol.
Symptoms. Demodectic mange of the eyes in humans occurs as a result of damage to the facial skin by an arthropod parasite that has “populated” the follicles of the eyelashes. Common symptoms for this pathology are tearing and eyelash loss. The vast majority of people with demodicosis of the eye note itching, burning and a sensation of a foreign body in the eyes. Rapid eye fatigue and sensitivity to bright light also indicate the presence of parasites.
Peculiarities. Demodectic mange of the eye in humans is an extremely unpleasant disease that disfigures the appearance of a person who is forced to put up with persistent redness and inflammation of the edges of the eyelids. However, the most unpleasant sensations are caused by the abundant foamy discharge that collects in the corners of the eyes and between the eyelashes . When dried, the viscous secretion remains in the area of the eyelash edge in the form of extremely unaesthetic scales. Demodicosis provokes blepharitis (chronic inflammation of the eyelid margin) and aggravates its course.
Treatment. Demodicosis of the eye in a person is diagnosed by an ophthalmologist. For laboratory research, a specialist takes four eyelashes from the upper and lower eyelids and examines them under a microscope - this does not take much time and is done in the presence of the patient. Treatment of eye demodicosis is carried out comprehensively and involves the use of antibacterial, antihistamine, acaricidal (antiparasitic) and immunomodulatory drugs, which are used internally and externally. The minimum duration of treatment is usually about a month, and the maximum (if a secondary infection cannot be avoided) is a year. Effective treatment of eye demodicosis is possible only with strict adherence to hygiene measures to reduce the likelihood of re-infection.
Treatment options
To treat pathology in children, drug therapy and traditional medicine are used. Comprehensive treatment includes:
- Strengthening the immune system. Before you start using medications, you need to strengthen your child’s body. To do this, the doctor prescribes vitamin complexes and immunomodulators.
- Nutrition adjustments. Harmful, heavy foods are excluded from the diet. The menu includes: cereals, vegetables, fruits, dairy and fermented milk products, berries. Also included is the intake of boiled or baked meat and fish.
- Treatment. The course of therapy and dosage of drugs is determined by the pediatrician. First of all, you should get rid of the pathogen - subcutaneous fat. Treatment uses topical ointments, tablets and drops to relieve symptoms.
- Precautions. If a child was infected from another person through skin-to-skin contact, it is necessary to protect the baby from contact with the patient for safety reasons.
- Skin treatment. Since children's skin is sensitive to various chemicals and herbs, you should be especially careful when choosing anti-mite ointments and creams. Gels containing tar and sulfur should be selected with a minimum concentration so as not to damage the skin. An allergic reaction is also possible. Before using the cream, you should consult your doctor.
- Personal hygiene. Parents need to be more careful about their children's hygiene. You need to wash your face and hands every day, cleanse your body of dirt and dust that has accumulated during the day.
In the first days, visible symptoms of the disease will disappear. But this does not mean that taking pills and using ointments should be stopped. Therapy must be completed completely to minimize re-infection. If 1-2 mites remain on the body, demodicosis will develop further.
Use of drugs
When diagnosing ophthalmic demodicosis, you need to consult an ophthalmologist. When the mite infects the eyes, drops and medicinal baths are used. You can do a preventive massage to relieve itching and improve blood circulation.
Drug therapy includes anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs. The active ingredient of the drug is metronidazole. It has a gentle effect on the child’s body without causing adverse reactions. Drugs are selected for each patient individually, taking into account age, existing contraindications and type of pathology.
Children can be treated for demodicosis with the following drugs:
External skin lesions are treated with creams and gels with the active ingredient metronidazole. These products destroy parasites, relieve inflammation and itching. Before use, you must carefully read the instructions for use.
Demodectic mange of the eyelids
Symptoms. Demodicosis of the eyelids is manifested by redness, itching, swelling and peeling in the area of the eyelash margin. The cause of demodicosis of the eyelids is the same microscopic demodex mite, activated as a result of hormonal imbalance, decreased immunity or exacerbation of a chronic disease . Even with the naked eye you can notice that the skin of the eyelids in the area of the ciliary edge is covered with gray-yellow scales that form after the thick, sticky secretions dry out, which makes it very difficult for a person to “open” his eyes in the morning.
Peculiarities. When demodicosis affects the eyelids and the face as a whole, a person experiences very severe itching, forcing him to scratch the affected areas. Since with demodicosis of the eyelids the patient cannot resist scratching the affected areas, the problems caused by parasites are often accompanied by infection and fungi, that is, a secondary infection that worsens the patient’s condition.
Treatment of demodicosis of the eyelids should begin with thorough cleansing of the eyelash edges from scales, for which alcohol tinctures of eucalyptus and calendula are used . This is done very carefully and slowly, since contact of the alcohol composition with the mucous membranes of the eye causes very unpleasant sensations. Using extreme caution, you need to apply special acaricidal ointments that reduce the number of parasites. When choosing medications, you should follow the recommendation of an ophthalmologist.
Rules for treatment at home
Treatment of demodicosis can be carried out using folk or home methods of exposure. One such product is kerosene. It is applied directly to the affected area and is not washed off for two to three days. Kerosene forms a specific moisture-proof film, which is easy to recognize from the outside and from under which the subcutaneous mite will try.
No less often, in order to cure the skin and get rid of demodex folliculorum, badyagu is used. Its advantage is that it neutralizes the inflammatory process and ensures the resorption of the seal. To reduce inflammation and its symptoms, calendula is used during treatment. The alcohol solution is optimal due to the fact that it has a positive effect on the healing of wounds and restoration of the skin due to demodicosis.
Advice: It should not be taken orally.
It is also permissible to prepare a decoction from the flower part of tansy and instill the composition three to four times a day, two to three drops, into both eyes. Improvement in the condition of the facial skin will be noticeable already on the fifth or sixth day after the start of the recovery course. However, in order to treat in this way, it is recommended to first consult with a specialist.
Demodicosis of eyelashes
Symptoms. Demodicosis of eyelashes is manifested by destruction (breakage) of eyelashes and their partial and sometimes complete loss. Due to the mucopurulent discharge that accumulates in the area of the ciliary edge of the eyelids, the eyelashes look greasy, their bases are covered with peculiar “muffs” that are almost impossible to wash off with water.
Peculiarities. With demodicosis of the eyelashes, the ducts of the sebaceous (meibomian) glands located along the edge of the eyelid are enlarged, and in addition, there is an increase in the number of newly formed capillaries .
Treatment of demodicosis of the eyelashes is carried out simultaneously with the treatment of demodicosis of the eyes and eyelids, takes a lot of time and requires certain skills. External agents (ointments with acaricidal action) kill parasites, but their effect must be supported by oral medications, for example, taking Trichopolum. To reduce the likelihood of relapse of the disease during and after treatment for eyelash demodicosis, you should adhere to a special diet (reduce salt intake, give up sweet, smoked and spicy foods) , and also disinfect bed linen and towels.
Treatment of complications of demodicosis and associated diseases
- acne (acne) - local products that reduce skin oiliness are recommended. Antibacterial complex creams are acceptable, taking into account the indications and age of the child;
- rosacea (rosacea) – the causes of this disease are still being debated. As a rule, therapy is aimed at limiting the process and reducing inflammation. In addition to ornidazole, secnidazole is used in the treatment of rosacea, but there is not yet enough data on the clinical effectiveness of this drug;
- keratoconjunctivitis must be treated immediately, as there is a risk of developing filamentous keratitis. The therapy is aimed at maintaining moisture - artificial tears are used: Na-bicarbonate, Actovegin emulsion, taufon. In addition, it is possible to artificially reduce the outflow of tears by blocking the lacrimal openings with silicone. Treatment of complications of demodicosis and associated diseases. An infection easily sets in on the inflamed mucous membrane of the eye, so antibiotic drops are prescribed for preventive purposes.
Under no circumstances should demodicosis in children be treated with creams containing homogeneous components. With long-term use, these drugs contribute to the exacerbation of demodicosis and associated infections.
In some cases, childhood forms of demodicosis resolve spontaneously, following changes in hormonal status. However, in most cases, the child needs constant monitoring and care. When the first signs of tick-borne infestation appear, consult a dermatologist.
Demodectic mange of the body
Symptoms of demodicosis of the body are similar to the signs of the presence of parasites on the face: the skin turns red, itches, peels, becomes acne-prone and acquires an unpleasant odor.
Peculiarities. Demodicosis of the body most often appears on the back, groin area, arms, legs and neck. Demodex on the body indicates an advanced stage of the disease , because it is believed that the demodex mite is initially activated on the head: in the face (especially the eyes) and scalp, and only then is transferred by hand to new areas.
Treatment. Manifestations of demodicosis in various areas of the body can only be confirmed by a dermatologist after conducting appropriate studies of skin scrapings, so experts do not advise self-treatment - demodicosis in fact may turn out to be rosacea, an allergic reaction or acne . When treating demodicosis of the body, the same drugs are used as to get rid of ticks on the face - these are acaricidal ointments, including traditional compositions based on sulfur and tar, as well as antihistamines that relieve itching and agents that strengthen the immune system.
Prevention of demodicosis in children
For prevention, it is important to maintain hygiene at home, in kindergarten and at school. The child should have his own towel for face and hands, which should be changed and ironed frequently. From an early age, you should teach your baby to touch his face and eyes less often with his hands, to eat right, to harden himself, to walk with him in the fresh air every day and to lead an active, healthy lifestyle. This will help strengthen the child’s immunity and not become infected with demodicosis.
Attention! The use of any medications and dietary supplements, as well as the use of any therapeutic methods, is possible only with the permission of a doctor.
Folk remedies for demodex eyelids
Traditional methods of treatment for the correction of demodicosis should be used with extreme caution. Incorrect prescriptions can cause deterioration of the condition, affect visual function, and cause eye irritation. For treatment, you can wash your eyes with decoctions of tansy or chamomile .
At the end of the therapeutic course, it is recommended to lubricate the edges of the eyelids with burdock oil. This stimulates eyelash growth and improves their condition.
In addition to all the listed methods for correcting demodicosis of the skin and eyelids, one should not forget about the treatment of provoking pathologies. It is important to promptly treat diseases of the digestive system, disorders of immune functions and metabolic processes. It is also necessary to follow a diet , refusing spicy, salty, sweet foods and alcohol.
If a demodex mite has been detected, treatment of the skin of the face and eyelids should be comprehensive. Relapses are possible, so it is strictly recommended to complete the full course of therapy, without neglecting the duration of use of the drugs. If the symptoms go away, this is not proof that the treatment has already been successful and can be stopped. Carefully following all the doctor’s advice will help you successfully get rid of this unpleasant disease.
Skin diseases and allergic reactions in children are not uncommon. However, the appearance of rashes, redness and pustules on the face and head is not always the result of an infection or allergy.
Parents are faced with situations when the on-duty antihistamine or local remedy for diaper rash does not bring the intended effect. In this case, it is possible that the characteristic symptoms are a consequence of the development of demodicosis.
What is this disease and its causative agent, what are the causes of its occurrence and, most importantly, how to treat demodicosis in children?