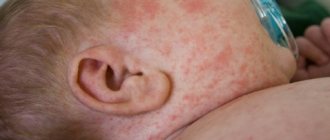
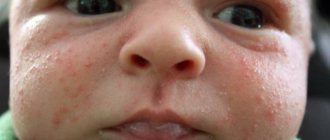
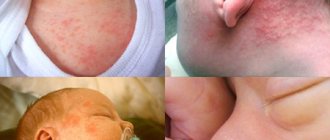
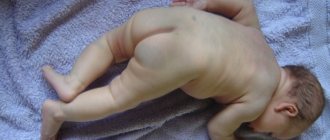
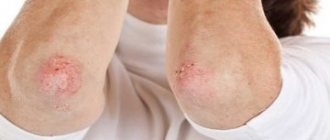
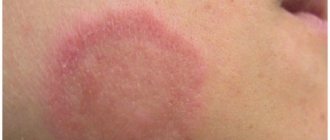
Children under one year of age often develop negative skin reactions. Rash, redness, itching cause discomfort to the baby and worsen the baby’s general condition. Often negative symptoms appear when exposed to an irritant, and an acute immune response develops.
Parents should know what allergies look like in infants, why unpleasant symptoms occur, and how to distinguish dermatological diseases from urticaria, childhood eczema or contact dermatitis. Recommendations from pediatricians and allergists will help cope with the problem.
Reasons for allergies in infants
The baby begins to learn about the variety of forms of food from the moment of complementary feeding with additional nutritional mixtures. Therefore, food allergies are most common among newborns.
Young mothers can use the Internet and look at photos of signs of allergies in newborn babies.
Casein, which is present in animal milk, requires active and coordinated actions of all body systems for digestion.
The lack of the necessary energy resource in a fragile child’s body causes a defensive reaction in the body. Substances that cause an allergic reaction have different ways of entering the child’s body.
Most often, a newborn may be allergic to complementary foods and breast milk.
How to distinguish allergies from prickly heat
In the table, parents will find signs that will make it easier to figure out what disease is developing in the baby:
| Signs | Allergy | Prickly heat |
| Localization area | Face, cheeks, forehead, inner knees, elbows, neck | Skin folds, buttocks, neck, upper back |
| What does the rash look like? | Various signs appear: from small blisters with liquid, ulcers to red spots and purple blisters measuring 10 cm or more | Small, pale pink or red rash, uniform, with blisters nearby |
| Reasons for appearance | The effect of irritants of various kinds - from aeroallergens to unsuitable products and natural factors | Overheating of the baby, poor care of delicate skin, heat and high humidity in the apartment, tight clothes made of non-natural fabrics, untimely change of diapers |
| Treatment | Signs disappear only after taking antihistamines, treating the skin with non-hormonal and hormonal (in severe cases) compounds | Negative reactions disappear with proper care of the baby’s skin, normalization of temperature and humidity in the home, and after the use of wound-healing ointments and creams |
Many parents ask: “How to distinguish allergies from skin diseases?” An acute immune response and pseudoallergy are always accompanied by additional symptoms that are not present in dermatological diseases.
On a note! Parents will have to suspect the effect of an allergen if the child not only has a rash, itching and redness on the body, but also the baby sneezes, coughs without sputum, swelling or severe swelling of the tissues is noticeable, liquid transparent mucus is released from the nose, the conjunctiva is red, and the eyelids itch. When babies have allergies, they develop digestive disorders and their overall health worsens.
The main symptoms of allergies in newborn babies
Young mothers should learn that in newborn children, physiological processes in the body proceed completely differently from those in adults. Therefore, you need to be extremely careful in any emergency situation.
Acute abdominal pain and excessive formation of gases are the first manifestations of allergies in a newborn baby. Usually, such symptoms are observed within a few minutes after ingesting the allergen.
Vomiting, nausea and diarrhea may occur three to four hours after eating. Often such manifestations occur in combination with a skin reaction. Local redness or rash appears.
You should regularly monitor the color of stool and the presence of mucus. This may also be a reaction of an unformed organism to protein of animal origin.
Symptoms of the disease
Recognizing this disease in a baby is not so difficult. Most often, allergies manifest in a newborn in the form of:
- diathesis and rashes on the face and other parts of the body;
- allergic rhinitis (nasal discharge);
- conjunctivitis (redness of the eyes);
- peeling on the scalp and face (on the eyebrows);
- diaper rash, which strangely appears with proper hygiene care.
There are also less common allergy symptoms that you should also pay attention to:
- dry mouth;
- vomit;
- dry cough;
- loose stools with admixtures of greens and foam;
- colic and flatulence;
- constipation, etc.
Types of allergic manifestations
When considering the issue of allergies in newborns, the factor of heredity should be taken into account.
By carefully analyzing the health status of direct relatives, you can draw the right conclusions and prevent the acute phases of allergies in your baby.
When do the first teeth appear in babies: when do they appear, the first symptoms and the order of teething (95 photos and videos)- Do children need ergoferon and why - instructions for use, recommendations and reviews from doctors (95 photos and videos)
Why there might be a bump on a child’s head: what to do and how to treat it quickly and easily. Modern and traditional methods of getting rid of cones (105 photos and videos)
It is important to be aware of the potential of the infant's immune system and to be especially careful with the diet. Specialized medical specialists conventionally divide allergies in newborns during breastfeeding into several types.
Food allergy. The most common allergen in infant food can be considered protein, which is found in breast milk or formula.
The baby’s body reacts with a skin rash, defecation disturbances, inflammation of the nasal mucosa, and difficulty breathing.
Contact allergy. When taking care of the cleanliness of your child’s body, you should not abuse chemical treatments on linen.
Achieving ideal cleanliness of linen is not easy, and the child’s body’s reaction to microparticles of detergents may not have a prognosis.
Causes of scrofula in children: signs, main symptoms, diagnosis and treatment (105 photos)- Fenistil for newborns - when it is prescribed, for whom it is contraindicated and when to use the drug (125 photos)
The first symptoms of cough in infants - causes, types, features and tips on how to treat coughs and colds (125 photos)
Cosmetics, pets, ornamental birds, all of this should have contact with the baby in the maximum dose.
By leafing through your relatives' medical records, you can make many useful discoveries about the causes of your baby's allergic reaction. This is a good way to study the history of a species.
Food allergies
Allergic reactions to food are often more severe. Often mothers believe that if a child is breastfed, then he is thus protected from allergies. But this is a misconception, since allergies in a child can also occur due to allergens contained in breast milk.
Symptoms
So, food allergy is a state of hypersensitivity to certain foods. It can manifest itself in different ways:
In the form of allergic skin lesions, such as:
- redness;
- rash;
- diathesis – itching, peeling on the skin of the cheeks;
- gneiss (formation of scales and peeling) on the eyebrows and scalp, urticaria;
- profuse prickly heat in case of slight overheating;
- persistent diaper rash, regardless of hygiene measures;
- Quincke's edema (an allergic reaction accompanied by sudden swelling of the skin, mucous membranes and subcutaneous tissue).
In the form of gastrointestinal lesions (edema of the mucous membrane):
- vomit;
- regurgitation;
- frequent loose stools mixed with greens or foam;
- colic;
- constipation;
- flatulence.
Less commonly, allergies in infants manifest themselves in the form of respiratory disorders (swelling of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract):
- runny nose;
- bronchospasm (in case of bronchospasm, air enters the airways with difficulty or does not enter at all).
Quincke's edema is especially dangerous. In this case, suffocation appears in the larynx, similar to the manifestation of bronchial asthma. First there is hoarseness and a barking cough, then shortness of breath and noisy breathing. The face becomes bluish, after which it turns sharply pale.
There are also combined lesions of the intestines and skin, bronchi and skin. Food allergies can precede other diseases: bronchial asthma, atopic dermatitis, etc.
Causes
In breastfed children, the cause of allergies may be foods eaten by the nursing mother, and if the baby is bottle-fed, then these are primarily foods consumed by the baby himself.
Heredity predisposes people to develop allergies. The risk of this disease increases in children whose families have documented cases of an allergic reaction. If one of the parents has an allergy, then the risk of developing this disease in his child is about 37%, and if both parents have allergies, the risk increases to 62%.
In addition to hereditary factors, an allergic reaction can be triggered by oxygen deficiency in the fetus (hypoxia) during pregnancy and during childbirth, acute respiratory viral infections suffered by the child and intestinal infections, which are accompanied by further disruption of the composition of the intestinal microflora.
The occurrence of allergies in an infant is associated with features of the digestive tract, such as reduced enzyme activity and low levels of production of IgA - antibodies on the surface of the gastrointestinal mucosa, which perform a protective function. And since newborns are characterized by high permeability of mucous membranes, allergens easily enter the bloodstream.
Also, of course, the occurrence of allergies can be associated with nutritional disorders of a nursing mother and excessive consumption of highly allergenic foods.
Maternal smoking during pregnancy, the presence of chronic bronchopulmonary and cardiovascular diseases, as well as infectious diseases suffered during pregnancy and antibiotic therapy have a negative impact.
It is believed that children whose mothers included highly allergenic foods in their diet during pregnancy include chicken eggs, cow's milk, caviar, seafood, red and orange vegetables and fruits, appropriate juices, as well as coffee, kiwi, chocolate, etc. cocoa, mushrooms, honey, nuts.
Diagnostics
If symptoms appear, you should consult a nutritionist, pediatrician or pediatric allergist. With severe manifestations of food allergies, especially with combined lesions (if there is, for example, a rash and gastrointestinal symptoms), hospitalization may be required.
The diagnosis is established using:
- parent survey;
- examination of the child;
- determining the connection between the occurrence of an allergic reaction and the consumption of certain products;
- blood tests: evidence of the disease may be an increased level of immunoglobulin E and an increased content of eosinophils;
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity, which allows to exclude non-allergic causes of symptoms from the intestines and stomach.
An indirect sign that the symptoms are the result of a food allergy may be the disappearance of the reaction after stopping the use of allergens and the positive effect of anti-allergy drugs.
Another important factor: which product you are allergic to. To identify significant pathogens of the disease, venous blood is collected from children and the presence of immunoglobulins E is detected.
You can detect the causative allergen using a food diary, where the mother regularly notes all the products received by the baby or directly by her throughout the day, feeding times, she should also indicate the composition of the dishes and the features of culinary processing, the manifestation of unwanted reactions (skin rashes, regurgitation, loose stools and etc.).
Treatment
If your child is allergic, you may need first aid:
- Call an ambulance. Get advice on how much antihistamine you should give your child.
- Give an antihistamine - Diprazine, Diphenhydramine, Suprastin, Diazolin, Claritin.
Direct treatment of the disease begins with a special diet and exclusion of the allergen. However, you should not self-medicate, otherwise you can make things worse. The treatment strategy in each case should be determined by an allergist, pediatrician or nutritionist.
If the child is breastfed, potential allergens are removed from the mother's diet within 1-2 weeks, including industrial products, which may contain preservatives, crystalline sugar, artificial colors and fat emulsifiers. Salt, sugar, fried foods and strong broths are completely excluded. They also limit the amount of dairy products consumed.
Important! For a baby with food allergies, it is necessary to maintain natural feeding.
Dietary recommendations are given to nursing mothers:
- Excluded from the diet:
- highly allergenic products: seafood, fish, caviar, mushrooms, chicken eggs, nuts, honey, coffee, chocolate, cocoa, berries and fruits of orange and bright red color, radish, radish, kiwi, avocado, pineapples, grapes, marinades, broths, sauerkraut, spicy and salty dishes, canned food, garlic, spices, onions;
- products containing preservatives, dyes: sauces, mayonnaise, ketchup, adjika, tkemali, chips, smoked meats, soft cheeses, ham, sausages, kvass, glazed drinks, beer.
- Limit: sour cream in dishes, whole milk (in cereals). Semolina, pasta and bakery products made from premium flour. Confectionery, salt, sugar.
- Allowed in the diet:
- fermented milk products: kefir, biokefir, cottage cheese, hard cheeses, acidophilus, bifidoc, yoghurts without fruit additives, etc.;
- cereals: corn, buckwheat, oatmeal, rice, etc.;
- fruits and vegetables: white and green in color;
- vegetable oil;
- soups: cereal and vegetarian;
- low-fat varieties of fish: pike perch, cod, hake, etc.;
- meat: lean pork, beef, turkey fillet and chicken, dried, boiled and in the form of steam cutlets;
- bakery products: rye bread, second-grade wheat bread, baked goods without custard and unleavened cookies;
- drinks: tea, fruit drinks, compotes, still mineral drinking water.
If the baby is on mixed or artificial feeding, the cause of the illness is most likely the cow's milk proteins (with the help of a special examination this can be determined for sure) in the mixture. In such a situation, complete or partial replacement with special hypoallergenic mixtures is required.
However, this diet also has disadvantages: a baby may be intolerant to soy, and hydrolyzed mixtures are expensive and have an unpleasant taste.
Next, if it is possible to identify the source of the allergy, you will need to make clarifications in the hypoallergenic therapy being carried out - you will need to exclude the product that causes the allergic reaction. A similar diet should be followed for 1-3 months.
As a result of stopping taking the allergen, the signs of allergy should decrease or disappear altogether, in which case a gradual expansion of the mother's diet is allowed (however, it is still necessary to exclude highly allergenic foods).
During treatment, the doctor may prescribe adsorbents, antihistamines, various ointments and creams for local treatment of the skin, including hormonal ones, and in especially severe situations, hormones are administered intravenously. Correction of intestinal microflora is also performed with preparations containing lacto- and bifidobacteria.
If the child is allergic
If the baby suffers from allergies, then the following measures must be taken:
- Complementary feeding should be avoided until 6 months of age. In addition, you should start with baby food that has a lower risk of an allergic reaction. It must include only one component.
- Citrus fruits, chicken eggs, cow's milk, wheat products, seafood, fish and nuts are recommended to be included in the diet after reaching the age of 1-2 years.
- It is necessary to control the regularity of bowel movements, especially if the baby has constipation, which increases the manifestations of the disease or is its main cause (allergens do not leave the intestines in a timely manner, as a result of which they cause allergies when absorbed into the blood.
- It is better not to use medications in the form of syrups that contain various additives (flavors, dyes) that can enhance or cause allergies.
- It is allowed to use only hypoallergenic cosmetics designed specifically for children (pH-neutral).
- During water procedures, you need to take water with a moderate temperature, and the duration of the procedure should be up to 20 minutes.
- It is recommended to filter the water used during bathing or leave it for 1 to 2 hours for dechlorination, after which boiling water should be added. It is not recommended to bathe your child in chlorinated water.
- Do not rub your child's skin with washcloths. After bathing, pat his skin dry with a soft towel, then apply a moisturizer to soften the skin.
- The child's clothing should be made from natural materials. Blankets and pillows should contain synthetic fillers; The child must be dressed rationally, avoiding overheating, which provokes the occurrence of allergic dermatitis.
- Materials for making toys must meet modern safety requirements.
- It is better to limit the use of detergents containing synthetics.
- It is not recommended to have pets or aquarium fish, as dry food for them can exacerbate an allergic reaction.
- Living areas should have cool, moderately humid, clean air.
- It is advisable to take more walks with your child.
As the child develops, the functions of the intestines and liver and the immune system improve. This allows you to count on the disappearance of allergies to formula, milk, vegetables, eggs, etc., especially if special anti-allergic measures are taken. Food allergies persist with adulthood in only 1-2% of cases.
Identification of allergies in newborns
The reaction of a child’s body to an allergen can be the most unexpected. Young mothers need to have a supply of certain knowledge in order to detect the disease in a timely manner and take appropriate measures.
It is worth highlighting several main signs of allergies:
Specific manifestations on the skin. Depending on sensitivity, the baby’s skin may become covered with a rash of varying degrees of density. Swelling or dry skin may occur. The place of such manifestation is usually the groin area, face, neck, buttocks.
Gastrointestinal manifestations. Here it is worth mentioning disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Immediately after eating, the baby begins to regurgitate and have abdominal pain. Combinations with skin reaction and inflammation of the lacrimal glands are possible.
Plantex for newborns - instructions for using medicine to improve digestion in the smallest (135 photos and videos)- Vitamins for hair: selection of a vitamin complex for skin and nails. Rating of effective vitamin complexes for hair growth (130 photos)
The first signs of otitis in children - the main causes, symptoms, forms, diagnosis and treatment of the disease (145 photos and videos)
Respiratory manifestations. The main reason for such manifestations is irritants that are present in the air. These include microparticles of pet hair, dust mites, and pollen from indoor flowers.
The baby's mucous membrane of the nasopharynx and lacrimal glands become inflamed. Coughing and heavy breathing become unbearable ordeals. Body temperature may not change.
Anxious state. A newborn child reacts to what is happening reflexively and cannot talk about his troubles. Therefore, you should be observant.
Length of time awake, mood, appetite, all this should be under the all-seeing eye of the mother.
Diagnosis by a specialized medical specialist
It is not always possible to identify the irritant to which an infant has an allergic reaction at home.
The patient's age does not imply interpersonal communication. Medical specialized specialists suggest conducting differential diagnostics in an inpatient setting.
The task of diagnosis is to identify diseases with similar symptoms. It is necessary to identify an intolerable product that is an irritant. Sample analysis is carried out in laboratories by qualified specialists and will help you understand what to do if an allergy is detected in a baby.
Often, the symptoms of intestinal infectious diseases can be similar to an allergic reaction of the body.
The correct decision can only be made by medical specialists after laboratory tests of samples of intolerable products or microparticles of suspected irritants.
Symptoms of an allergic reaction
- Peeling and redness of the skin on the child’s head.
- The appearance of whitish or yellowish plates (scales) on the hairy area, which gradually occupy an increasingly larger area. These formations can also be a sign of seborrhea or miliaria. At the same time, the scales do not cause itching, do not bother the baby, and are removed mechanically by softening and combing out. If the scaly formations gradually grow and cause concern in the baby, then this may be a sign of an allergy. If left untreated, the baby's head gradually becomes completely covered with scaly growths.
- Rashes on the scalp in the form of red spots or blisters with clear liquid. They cause severe itching, and when scratched, wet wounds or suppuration appear. Gradually, signs of an allergic reaction spread throughout the body.
- Sleep disturbances, restless behavior associated with burning and itching.
- Sometimes the signs of an allergic reaction in an infant are similar in appearance to the signs of acute respiratory diseases, but without an increase in temperature. The child feels uncomfortable, often cries, worries, and eats poorly. Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract are observed.
Therapy of allergies in a newborn child
Drug treatment of allergies is prescribed to infants in exceptional cases. We should not forget that medications themselves can cause an allergic reaction in the baby’s body.
Basically, experts try to identify the irritant and eliminate it from the diet. If pets are the allergen, then their presence in the room with the child should be excluded.
In order to cleanse the baby’s body of the formed toxic components, it is recommended to use harmless sorbents. They are absolutely safe for babies.
Sometimes the pediatrician prescribes medications that block histamine receptors to reduce the negative impact of the allergen. In this case, the drugs should not cause the effect of reducing the body's response.
For local effects, a special cream can be applied to the affected areas of the skin. It is a non-hormonal drug. This cream perfectly relieves inflammation, helps restore skin integrity and relieves itching.
In extreme cases, the attending physician may recommend the use of hormonal ointment. This treatment option can be used if previous medications did not give the expected result.
Treatment
Identify the allergen and eliminate it. Exclude from a nursing mother's diet foods that can cause an allergic reaction in the baby. When artificial feeding, switch the child to hypoallergenic formula . To relieve itching, irritation and inflammation of the baby's scalp, ointments and emulsions are used.
- Ointment "Radevit" . Relieves inflammation and itching. Apply a thin layer to damaged areas of the head twice a day. Course: from one week to a month.
- "Sudocrem" . Antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, analgesic. Relieves flaking, itching, and soothes the baby's inflamed skin. Application: Externally. Apply a thin layer of ointment to areas of irritation. Contraindications: Individual intolerance.
- "Bepanten" . Relieves redness and flaking. Has a healing effect. Application: 1-2 times daily.
- Cream "Elidel" . Application: No more than 2 times a day. Course: up to six weeks.
- Advantan ointment (1%) . A potent hormonal antiallergic and anti-inflammatory drug. Used for complications: the appearance of cracks and wounds on the scalp. Used after 4 months. Externally Apply a thin layer to skin damaged by an allergic reaction. Use 1 time daily. Course of treatment: no more than a month.
- "Tsindol" . Can be used during the first days of life. The suspension is applied to the scalp.
Antihistamines:
- "Suprastin" . From one to 12 months: intramuscular injections (0.25 ml.) or tablets (1/4) no more than 3 times a day. Grind and give in powder form, mixing with baby formula.
- "Fenistil" in drops . From one to 12 months. 3-10 drops no more than 3 times during the day.
Before using any product, be sure to consult your doctor!
Preventive actions
Popular wisdom says that it is always easier to prevent any disease than to treat it later. The case of allergies is no exception.
When a newborn appears in the family, you need to be observant of the child’s every breath. When breastfeeding a baby, the mother must strictly control and adhere to her food intake.
After preliminary consultation with a pediatrician, you can gradually introduce new foods into the baby’s diet. In this case, you should carefully monitor the baby's condition.
The room in which the baby stays must be ventilated daily. Wet cleaning of the premises should be carried out in his absence. You should try to avoid contact with pets.
Compliance with these basic rules of a healthy life will help to avoid or minimize the possibility of allergies in an infant.
Our future is in our children. Walk healthy.