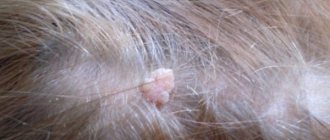
Papilloma on the tonsil is a neoplasm caused by the human papillomavirus, which in the initial stages appears as a small nipple-like structure on the lymphoid tissue. Such formations are mostly benign, but improper treatment can lead to tissue transformation, breathing complications, and a significant decrease in the protective functions of the tonsils. By ignoring the problem, a person puts his health at high risk. Self-determination of the disease and treatment is no less dangerous; only a doctor must diagnose papilloma on the tonsil, carry out removal or prescribe the correct therapy.
Causes
Frequent inflammatory processes in the pharynx, especially on the tonsils, due to exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis lead to the appearance of growths.
The papilloma virus provokes the appearance of skin compaction. Once in the human body, it is activated when the immune system is weakened.
There are several ways to become infected with the virus:
- sexual;
- domestic;
- autoinfection.
Violation of hygiene rules in public places with high humidity (swimming pools, baths) contributes to infection. Newborn babies can become infected during childbirth. A cut with a razor or damage with a toothbrush can allow the bacillus to enter the body.
But here’s what caseous plugs look like in the lacunae of a child’s tonsils and what can be done about such a problem.
The video shows why the disease occurs:
Weakening of the body's defenses and the growth of papilloma are possible for the following reasons:
- stress and depression caused by it;
- past infectious diseases;
- chronic fatigue syndrome;
- endocrine diseases;
- vitamin deficiency
Mechanical or chemical damage to the pharynx, burns to the mucous membrane are a predisposing factor for the appearance of growths.
You may also be interested in information about how to wash tonsil lacunae at home.
Inhalation of cigarette smoke, air contaminated with industrial waste or exhaust gases causes constant irritation of the mucous membrane, thereby activating the papillovirus.
Taking hormonal drugs and caries affect the immune state of the body.
In children, the cause of growth on the tonsil is chronic and acute diseases of the upper respiratory tract:
- chronic tonsillitis;
- laryngitis;
- pharyngitis;
- otitis.
The likelihood of the disease occurring is higher in children and women during periods of hormonal imbalance:
- up to 2 years;
- during adolescence;
- during pregnancy;
- menopause.
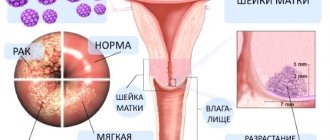
A doctor can determine papilloma by visually examining the pharynx using a laryngoscope.
The possibility of a neoplasm is examined using a biopsy.
You may also be interested in information about how tonsils are removed in adults and why such a procedure is performed.
Diagnostics
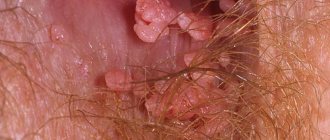
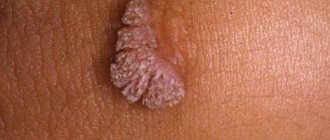
As a rule, a biopsy is not required to make a diagnosis; it is determined by appearance. Papilloma in the larynx has the appearance of a titrated berry. It is worth noting that small formations are often confused with an accumulation of lymphoid tissue. Then doctors recommend treating the throat with a special antiseptic for delicate mucous tissues.
This disease should not be confused with plugs - a purulent accumulation in the lacunae of the mucous membrane. They are removed manually and then washed several times with a special solution.
Is it necessary to remove papilloma?
The peculiarity of papillomas is their unpredictability. In 40% of cases this is a harmless skin formation. In some cases, they contribute to degeneration into warts or malignant neoplasms.
Symptoms at the initial stage of the disease:
- slight discomfort in the throat;
- sensation of a foreign object;
- cough;
- frequent sore throats.
When the tonsils are affected by papilloma, sore throats are more severe: with swelling that blocks the airways.
As the growth increases, the patient’s well-being worsens due to constant coughing. Papilloma makes breathing difficult and interferes with speaking.
But why tonsils in the holes can appear after a sore throat and what medications can cope with such a problem is described here.
In the video - is it necessary to carry out operations:
According to the degree of growth, papillomatosis is divided into:
- defeat in a separate area;
- on several;
- obstructive, blocking the windpipe.
Papilloma requires removal if there is a risk of its increase in size or the appearance of new growths.
You may also be interested in information about what stomatitis on the tonsils looks like and what pharmaceutical drugs should be used first.
The immune system can overcome single, small papillomas on its own within one to two years. In other cases, treatment is prescribed.
Postoperative therapy
The attending physician selects drugs that stimulate the immune system. If necessary, concomitant diseases of an infectious or inflammatory nature are treated. The rest of postoperative therapy depends on the patient: switching to a healthy lifestyle, maintaining personal hygiene, healthy eating, giving up bad habits. It is also recommended to take a course of vitamin and mineral complexes every six months.
Traditional recipes strengthen the immune system well: decoctions of herbs and seasonal berries. Before use, it is recommended to study possible contraindications, since some products significantly affect the functioning of internal organs (gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, blood vessels). Consultation with a therapist is recommended.
Removal methods
You can get rid of papilloma with:
- surgical intervention;
- cryotherapy;
- ultrasonic disintegration;
- electrocoagulation;
- chemical cauterization;
- radiotherapy.
When using a scalpel, the papilloma or papillomas are removed along with the affected area of the mucous membrane. The operation is performed under local anesthesia.
The video shows how you can get rid of this disease:
There is a risk of wound infection and relapse.
The laser cuts off the wart and cauterizes the area where it grew. The therapeutic effect is achieved in 1-3 sessions.
Here's how tonsil cryo is performed and what the price of such a procedure is.
- Cryotherapy - This is the freezing of tissues close to the papilloma using liquid nitrogen. The operation takes place within a few minutes. After 2-3 days, the damaged tissues die off along with the growth.
Apparatus for cryotherapy of papilloma - Ultrasound exposure to the tonsils is performed under local anesthesia . An applicator soaked in hydrogen peroxide is applied to the tonsil. Ultrasonic waves promote deep penetration of oxygen molecules into tissues, which causes the death of viruses and bacteria. To obtain a therapeutic effect, 8-10 sessions are performed. A repeat procedure is carried out after a few months.
- Electric cauterization is the effect of high-frequency electric current on the growth site. As a result, the blood vessels that feed the papilloma stick together. After 10 days, it dies and falls off, leaving a crust at the burn site. Unlike the surgical method, it is bloodless, has no relapses, and is painless.
Chemical cauterization means exposing the growth to acids, salts, and caustic alkalis:
- potassium permanganate solution;
- silver nitrate or lead;
- perhydrol.
The procedure lasts for a month, with breaks of 3-5 days, on an outpatient basis.
Radiotherapy is performed on an outpatient basis. Session duration is 20 minutes. The Surgitron radio wave scalpel excises the affected tissue along with papilloma and disinfects the affected area.
Symptoms
At the onset of the pathology, a person may not feel discomfort or any symptoms of papillomatosis. But as the growths increase in size and spread throughout the mucous membrane of the tonsil, the signs begin to gradually appear. In this case, a growth can form first on the left palatine tonsil, and then on the right tonsil. Or vice versa.
At the beginning of the pathology, a person may feel the presence of some foreign body in the throat, which can cause discomfort when swallowing and loss of appetite. Then, in most cases, a persistent cough appears due to irritation of the throat by growths.
In severe cases, papilloma on the tonsil is manifested by changes in the timbre of the voice and speech. A person may speak awkwardly or not pronounce some words. Also, a common pathology on the tonsils leads to difficulty breathing and oxygen deficiency to the brain.
Removal in adults
Methods for removing papilloma are prescribed depending on the patient’s health condition.
Pregnant women are contraindicated:
- use of radiofrequency method;
- ultrasound;
- chemical means.
Radiotherapy is not used if there are:
- cardiovascular disorders;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- malignant neoplasms.
Additional contraindications for prescribing electrocoagulation include blood clotting disorders and individual intolerance to electrical procedures.
But what a tonsil abscess without fever looks like and what can be done about such a problem is indicated here.
Possible complications of HPV
Papillomas on the tonsils are the most dangerous in childhood due to the narrower lumen of the larynx in children. The formation can grow into the palate and palatine arches, which further reduces the respiratory lumen. Respiratory failure develops.
In the absence of emergency medical assistance, asphyxia may occur. Therefore, if a child has a growth on the tonsil, it is necessary to begin treatment as soon as possible.
For adults, papillomas are less dangerous, however, complications can occur. One of the most dangerous is degeneration into a malignant formation.
REFERENCE! According to statistics, in 20% of cases papillomas can lead to cancer, therefore in modern medicine their presence is considered a precancerous condition.
Growing into the trachea, lungs and bronchi, papillomas can lead to respiratory failure. Another possible complication is cicatricial stenosis of the larynx, which appears with frequent relapses and subsequent treatment.
Removal in children
Removal of tonsils and growths from a child is carried out under local anesthesia.
To eliminate papillomas, use:
- cryogenic method;
- electrocoagulation;
- ultrasound.
These methods are the least traumatic, painless, and heal quickly.
Contraindications for treatment:
- presence of open wounds in the mouth;
- temperature;
- cold intolerance;
- blood diseases.
Removal by chemical means is not prescribed. The use of the radiofrequency method, laser and conventional scalpel is limited.
But how the vacuum rinsing of the tonsils occurs and what the price of such a procedure is, is described here.
Symptoms
The appearance of squamous cell papillomas on the tonsils can manifest itself with various symptoms. Most often a person feels the following discomfort:
- sore throat for no reason;
- feeling of a foreign object in the throat;
- discomfort when swallowing.
Also, if the papilloma increases, then the timbre of the person’s voice may change. Papilloma can hurt if it is damaged by hard food or frequent touching.
Growths that are too large can cause difficulty breathing. Such growths require immediate diagnosis and removal. The specialist only needs a visual examination to make a diagnosis. But to determine the type of tumor (malignant or benign), a biopsy is required. To do this, a fragment of tumor tissue is taken for analysis.
Reviews
- Svetlana F.: “ After a sore throat, a child developed a papilloma on his tonsil. At first it was the size of a small pea, and then it became the size of a bean. The son began to eat poorly, be capricious, and cough often. Electric cauterization was prescribed. Everything went very quickly. My throat tingled a little after the operation. The child spat out the papilloma the next day. A week later we saw a doctor. Everything has healed. I hope she doesn't grow any bigger."
- Tatyana K.: “When I swallowed, I felt something was bothering me. She didn’t see anything in the mirror herself. I contacted an ENT doctor. He said it was papilloma and advised me to do cryotherapy. The procedure itself is painless. But after it, I initially felt worse. There was a feeling that the tonsil was swollen. A day later everything returned to normal. When the wound healed, there was also slight discomfort. Now everything has healed, but you need to see a doctor in a month so that there is no relapse.”
You may also be interested in information about what reviews there are about purulent plaque on the tonsils without fever and what can be done about such a problem.
It is impossible to get rid of the papilloma virus that has entered the human body. Decreased immunity activates the bacillus. The appearance of a growth on the tonsil causes discomfort, can cause shortness of breath, and provoke an exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis. Modern treatment methods make it possible to remove papilloma painlessly, without relapses.
How to distinguish it from other formations and is it dangerous?
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Papillomas on the tonsils should be distinguished from tonsillitis, tuberculosis, and oral cancer. In acute tonsillitis, the tonsils look inflamed and deformed. Pus plugs are yellow and white in color. When pressed with a spoon, they separate from the mucous membrane of the tonsils and may crumble. Papilloma is flesh-colored, soft in consistency with a rough surface. Tonsillitis is accompanied by a sore throat, high body temperature, weakness, and bad breath.
A malignant formation differs from warts in the presence of ulcerations and a hard consistency.
Atypical tissue grows tightly together with the surrounding dermis. Cancer is accompanied by general clinical symptoms of a malignant process: a sharp decrease in body weight, constant fatigue, pale skin, poor appetite, unmotivated weakness.
Tuberculosis of the tonsils is manifested by swelling, hyperemia of the mucous membrane, and the presence of tubercles. Ulcerative defects are observed on the vocal cords. Patients complain of cough, hemoptysis, shortness of breath. Radiography and biopsy of the lesion help to distinguish papillomatosis from tuberculosis.