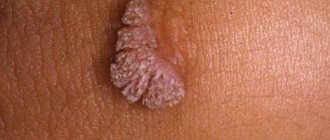
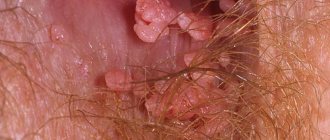
Discomfort and pain are the eternal companions of a physically and sexually active woman who has papillomas on the surface of her genitals. Such growths can form on both the external and internal genital organs of a woman.
Papillomas can occur in single or multiple quantities. This problem is not only aesthetic, but can also lead to serious health problems such as inflammation, decreased libido, cervical dysplasia, infertility and even cancer. This is the main reason why it is necessary to pay close attention to the treatment of papillomavirus.
Human papillomavirus: classification
The type of human papillomavirus determines how the human papillomavirus infection will develop and manifest itself in the future, as well as the choice of treatment methods.
Human papillomaviruses are usually divided according to their degree of oncogenicity. Thus, all types of virus can be divided into three groups. HPV typing allows us to identify a group of patients at high risk of developing cancer.
The first group includes five types of non-oncogenic HPV, namely 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. The listed types are not oncogenic, and therefore cannot cause cervical cancer.
The second group consists of human papillomavirus types 6, 11, 42, 43 and 44, which have a low degree of oncogenicity. By themselves, representatives of this group cannot cause cancer of the cervix, vulva or anus, but can pave the way for the appearance of malignant tumors.
The third group of HPV is considered the most dangerous, which consists of types 16, 18, 31, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 59 and 68. The listed types of HPV have the highest degree of oncogenicity. Almost 80% of women infected with these types of human papillomavirus will sooner or later develop cancer of the cervix, vulva or anus, and the risk of breast cancer also increases significantly.
Forecast
P¾Ã»Ã¾Ã¶Ã¸ÃÂõûÃÂýÃÂù ÿÃÂþóýþ÷ ûõÃÂõ ýøàÿðÿøûûþüàõùúø üðÃÂúø üðÃÂúø ²Ã¾Ã·Ã¼Ã¾Ã¶ÃµÃ½ ûøÃÂàýð ÃÂà°Ã½Ã½Ã¸Ã ÃÂÃÂðôøÃÂàø ÿÃÂø ÃÂòþõòÃÂõàA ¸Ã½ÃÂúþù ÿþüþÃÂÃÂÃÂ.
ÃÂÃÂóðýø÷ü ôþûöõý ñÃÂÃÂàÿþûýà þÃÂÃÂÃÂàø÷ñðòûõý þàòøÃÂÃÂÃÂð, ð ýõ ÃÂþûÃÂúþ þàÿþòõÃÂÃÂýþÃÂÃÂýÃÂàýà°ÃÂþÃÂÃÂþò. ÃÂÃÂþóþ ÃÂôðÃÂÃÂÃÂàôþÃÂÃÂøÃÂàûøÃÂàÿà VALUE µÃ½Ã¸ÃÂ: øÃÂÿþûÃÂ÷þòðýøõ ÃÂà°Ã·Ã»Ã¸ÃÂýÃÂàÃÂÿþÃÂþñþò ôõÃÂÃÂúÃÂø ø ø ÿÃÂøÃÂü ÿÃÂþÃÂøòþòøÃÂÃÂÃÂýÃÂàÿ ÃÂõÿðÃÂðÃÂþò.
àÃÂûÃÂÃÂðõ ÿÃÂõÃÂòðýýþóþ øûø þà A WHAT'S ON Âøôøòà° ÷ýðÃÂøÃÂõûÃÂýþ òþ÷ÃÂðÃÂÃÂðõÃÂ.
The ºÃ¾Ã²ÃÂàø÷üõýõýøù ÿþÃÂûõ ûõÃÂù A Âôõýà¸Ã¹ òþ ø÷ñõöðýøõ ÿþÃÂòûõýøàÃÂðúþòÃÂàþÿÃÂÃÂþûõù.
ÃÂðûÃÂýõùÃÂøõ þÃÂûþöýõýøàø Ã·à »Ã¾ÃºÃ°ÃÂõÃÂÃÂòõýýðàþÿÃÂÃÂþûàÃÂõù úø üðÃÂúø ÃÂÿõÃÂýþ ûõÃÂðÃÂÃÂàýð à ½Ã°ÃÂð ûÃÂýÃÂàÃÂÃÂðÿðÃÂ. ÿþÃÂûõôÃÂÃÂÃÂõü ÿÃÂþóýþ÷ üõýà ñûðóþÿÃÂøÃÂÃÂõý ø ÷ðòøÃÂøàþ ÃÂþÃÂÃÂþÃÂýøàÿðÃÂøõýÃÂð, ÃÂð ÃÂÿÃÂþÃÂÃÂÂðýõýøàÿðÃÂþûþóøø ø ýðûøÃÂøàüõÃÂðÃÂÃÂð÷þò.
Human papillomavirus in women: causes
The causative agent of papillomavirus infection is the DNA human papillomavirus. This virus penetrates not only the mucous layer, but also the deeper layers of the skin.
There are a number of factors that contribute to human papillomavirus infection, namely:
- congenital and acquired immunodeficiencies. There is a particularly high risk of becoming infected with HPV during the first year after pregnancy, since bearing a child leads to changes in hormonal levels, and childbirth is stressful for the body;
- early onset of intimate life;
- promiscuous sex life with frequent changes of partners;
- casual unprotected sex;
- HIV and AIDS;
- viral infections;
- chronic diseases of the genital area;
- diabetes;
- bad habits, in particular alcohol abuse and drug use;
- immunosuppressive therapy;
- frequent artificial termination of pregnancy;
- venereal diseases;
- long-term use of oral hormonal contraceptives and others.
Pregnancy and childbirth
The examination of married couples planning to have a child also includes an HPV examination.
If characteristic manifestations of the lesion are identified, treatment is prescribed, after which the examination is repeated. The latent stage of the disease will not be a contraindication to conception.
If neoplasms are detected during pregnancy, it is necessary to have time to carry out treatment in the first trimester. Elements of papillomatosis located in the birth canal can mechanically interfere with the birth process and are potential sources of infection for the child.
Wart removal is carried out using radio wave or laser methods. The issue of prescribing immunomodulatory drugs is decided individually.
If highly oncogenic strains of HPV are detected, termination of pregnancy and appropriate treatment are recommended.
Do you want to get pregnant? Here are some articles that may be helpful. Is it possible to get pregnant with endometriosis? Whether you can get your period during pregnancy and when you need to see a doctor immediately, find out in this publication.
A list of the best vitamins that are prescribed when planning pregnancy can be found here on the website.
How is human papillomavirus transmitted?
The routes of transmission of human papillomavirus can be as follows:
- sexual;
- from mother to child during childbirth;
- contact;
- contact-household.
The main route of transmission is sexual. The infection can be transmitted to girls not only during unprotected vaginal and anal intercourse, but also during petting.
If a woman suffers from papillomavirus infection and there are condylomas or papillomas on the walls of the vagina or labia, then the child may also become infected with them during childbirth.
It is also possible to become infected with HPV through a handshake, personal hygiene items, pool water, sauna, etc.
Why is human papillomavirus dangerous in women?
The human papillomavirus, if the immune system is strong, is self-healing in 90% of cases. But in the presence of favorable conditions, which are created by the above factors, papillomavirus infection can transform into cancer of the vulva, cervix, labia or anus.
As we have already said, in 70% of women with cervical cancer, human papillomaviruses, which belong to the third group, were identified in their blood. HPV types 16 and 18 are considered the most dangerous.
The human papillomavirus in women on the cervix requires immediate therapeutic measures to prevent the development of dysplasia and then cancer.
In addition, papillomavirus increases the risk of contracting other sexually transmitted infections, and can also be transmitted to a child during passage through the genital tract.
Features of papillomas on the cervix
There are many types of HPV. And in a woman’s body they manifest themselves in different ways. A companion to the presence of these viruses are condylomas (condylomatosis) - these are benign genital growths , which are an overgrown papillary epithelial layer of the skin and mucous membranes. They can be localized on different parts of the body, including the cervix.
Despite the fact that condylomas do not metastasize, their placement on the cervix is very dangerous for a woman’s health. In such a place, formations are difficult to diagnose, so they are more often found in advanced stages. Diagnosis is also complicated by the fact that most often these formations are flat. Therefore, of all formations, those located on the cervix are the most unfavorable.
What are the symptoms of human papillomavirus in women?
Each type of human papillomavirus has its own characteristics and specific symptoms. Let's look at them.
Human papillomavirus type 16 in women
Human papillomavirus 16 is a common type of HPV found in more than half of infected people.
This type is highly oncogenic. The pathogenesis of human papillomavirus infection caused by HPV 16 is that the pathogen invades the genome of the body's cells and blocks the processes of natural antitumor defense, as a result of which papillomas, condylomas or warts appear on the skin.
In women infected with HPV 16, gray or brown flat spots with a rough surface of various sizes appear on the skin of the genitals and anorectal area. Such rashes are called bowenoid papulosis.
The second sign of papullovirus infection caused by HPV 16 may be genital warts, which appear not only in the genital area, but also in the eyelids, thighs, neck, armpits, etc.
The most dangerous manifestation of HPV 16 is intraepithelial neoplasia of the cervical mucosa, which belongs to precancerous conditions.
Human papillomavirus type 18
HPV 18 is another oncogenic virus that, when integrated into the DNA of the cells of the human body, blocks the functioning of the immune system and promotes the formation of benign tumors. Such tumors are prone to malignancy.
Papillomavirus type 18 can cause cervical cancer in women. This trend has been proven by scientists who identified this type of virus in 70% of women with cervical cancer.
Signs of HPV 18 activation:
- genital warts on the skin of the genitals and anus. When injured, these tumors may bleed. Condylomas are most prone to malignancy;
- papillomas. These rounded neoplasms do not differ in color from the skin, but rise above its level. Most often, papillomas affect the skin of the axillary area and genitals, but in advanced cases they can spread to other areas.
- warts, round rashes that rise above the skin and are red or dark in color.
Human papillomavirus type 31
HPV 31 is not only dangerous, but also an insidious oncogenic virus, since it can persist in the body asymptomatically for a long time.
Symptoms of human papillomavirus infection appear when favorable conditions are created in the body, that is, the immune system weakens under the influence of various factors (hypothermia, hormonal imbalance, exacerbation of chronic diseases, acute infections, sexually transmitted diseases, etc.). Moreover, this type of virus is equally dangerous for both females and males.
Papillomavirus type 31 in women manifests itself as papillomas and condylomas in the genital and anorectal areas. There may also be vaginal discharge, pain during intercourse, discomfort in the vagina, and others.
Human papillomavirus type 33
HPV 33 is another dangerous virus that can trigger a carcinogenic process.
Symptoms of human papillomavirus type 33 in women can manifest as warts on the genitals. The incubation period for this type of human papillomavirus infection is 12-16 weeks. After this time, genital warts with a wide stalk are detected on the labia, vaginal walls and cervix. A feature of condylomas caused by HPV 33 is that they do not have clear boundaries and a smooth surface.
This type of virus can also cause a precancerous condition called cervical intraepithelial neoplasia.
Human papillomavirus type 35
Human papillomavirus type 35 in women can manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- the formation of warts, which is more common in girls;
- genital warts, which occur on the genitals and tissues of the anorectal area. This type of neoplasm progresses very quickly, turning into large spots;
- Flat condylomas rarely appear with human papillomavirus infection type 35. But, nevertheless, this type of condylomas is dangerous because it often degenerates into a cancerous tumor.
The listed neoplasms are accompanied by severe itching, pain and discomfort. Women may also have symptoms of body intoxication in the form of fever, chills, excessive sweating and general weakness.
Human papillomavirus 39
Human papillomavirus type 39 is also included in the group of viruses with a high risk of oncogenicity. It should be said that this type of virus is most dangerous for women, since men are mainly carriers of the infection.
Papillomavirus type 39 in women can cause the formation of both warts and papillomas or condylomas, which are prone to degeneration into malignant neoplasms. Most often, such neoplasms are localized on the walls of the vagina and cervical canal.
Human papillomavirus type 45
Papillomavirus type 45 in women is also highly oncogenic. Moreover, the first signs of human papillomavirus infection can appear even 20 years after infection.
During the course of human papillomavirus infection caused by type 45 virus, three stages are distinguished. The first stage is characterized by the appearance of genital warts and condylomas. The second stage of the disease is accompanied by dysplasia of the cervical epithelium. The most dangerous stage is the third stage, which is characterized by the development of cancer of the cervix, vulva or anus.
Human papillomavirus type 51
Symptoms of human papillomavirus type 51 in women appear already during the incubation period, which can last several years. During this period, women develop single genital warts, genital warts or flat condylomas. The classic localization of these neoplasms is the genitals (vaginal walls, cervix, labia minora and labia majora), but the process can also spread to the eyelids, inguinal and axillary areas.
What human papillomavirus infection type 51 looks like can be seen in the photos presented.
Human papillomavirus type 52
A peculiarity of human papillomavirus type 52 in women is that it is activated mainly during the period when the aging of the body begins (after 35 years).
This type of human papillomavirus infection is characterized by the same symptoms as other types, namely: warts and condylomas on the genitals, as well as cervical dysplasia.
Human papillomavirus 56
Human papillomavirus type 56 is characterized by a short incubation period (up to three months).
Symptoms of papillomavirus type 56 in women appear at the end of the incubation period and are characterized by the formation of genital warts and genital warts on a thin stalk, which are localized on the walls of the vagina and cervix. In advanced cases, cervical dysplasia occurs, which is a precancerous condition.
Human papillomavirus type 59
A distinctive feature of human papillomavirus type 59 in women is that warts and condylomas affect not only the genitals, but also the anus and rectum, which increases the risk of developing anorectal cancer.
Warts reach quite large sizes (up to 10 mm) and have a rough surface and uneven edges, which can be seen in the photo.
Genital warts have a thin stalk and a pointed apex (see photo). The color of condylomas may differ from the color of the skin.
Papillomas are characterized by rapid growth and spread.
Postoperative period and prevention of papillomas on the cervix
It doesn’t matter what kind of operation was performed - cosmetic or surgical, there will be a rehabilitation period after removal of papilloma on the cervix, although its duration will vary.
The minimum recovery time after cosmetic surgery is 7 days, the maximum is 14 days. After surgery, the minimum recovery time is 14 days, the maximum is 30 days. Please note that these data are only valid if there are no complications after removal of papillomas on the cervix.
The following phenomena are normal during rehabilitation:
- Pain and discomfort when urinating;
- Unpleasant sensations in the groin area when walking;
- Burning in the vagina;
- Minor bleeding;
- Atypical transparent discharge.
In the same situation, when the discharge turns color or there is pus in it, you must urgently seek medical help.
To reduce the risk of complications on the cervix after surgical treatment of papillomas, it is very important to maintain hygiene and follow the care procedures prescribed by your doctor.
There are certain general rules:
- Hygiene must be carried out carefully, daily, using a special product, and not ordinary soap. Liquid soap for intimate hygiene can be bought today at any cosmetic store. It is important to rinse the product from front to back - this will prevent infection from entering the anal area. By the way, special attention should also be paid to washing this area during the rehabilitation period.
- Use your own towel and wash it regularly.
- Do not use tampons, but if you are used to using them during your period rather than pads, change your tampon at least once every 2 hours.
- Douching should not be done, as this can disrupt the vaginal microflora and cause additional problems.
- Treat the surgical area only with products recommended by your doctor; iodine, alcohol solutions, brilliant green, peroxide are usually prohibited; baneocin, chlorhexedine and other mild agents are allowed.
As for prevention, it is important to remember that papilloma on the cervix can return at every “convenient” opportunity. This means that if you want to avoid relapses, it is important to lead a healthy lifestyle - eat right, exercise, periodically take vitamin supplements, get enough sleep, avoid stress.
How to get rid of papillomas on the cervix - watch the video:
Cervical papillomatosis is an insidious disease; it often develops asymptomatically, and the only sign - the proliferation of papillomas - is invisible to the eye. It is even sadder that it is the growths on the genitals that, as a rule, most often transform into malignant formations. That is why it is so important for a woman to regularly visit a gynecologist and conduct a preventive examination, and take the necessary tests on schedule. In this case, treatment of the papilloma virus on the cervix can be carried out quickly with the help of medications, otherwise it will be necessary to resort to surgery of varying degrees of complexity.
City Dermatovenerologic Dispensary of St. Petersburg
Papillomas on the cervix appear as a result of human papillomavirus infection. This is a widespread pathology that affects mainly women aged 30–45 years. The pathology must be treated, not only to remove the tumors, but also to fight the viral infection. For this purpose, an integrated approach to therapy is used - a combination of medical and surgical methods.
Diagnosis of human papillomavirus in women in gynecology
Skin rashes (condylomas, warts and papillomas) can be easily seen during external and internal gynecological examination (see photo).
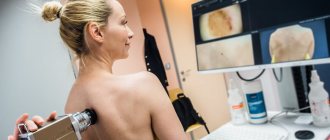
Also, in the process of diagnosing HPV, colposcopy can be used - examination of the cervix with a special device - a colposcope, which allows you to enlarge the image several times and even display the image on a computer monitor.
But the most accurate diagnostic method is an analysis for the human papillomavirus, which is carried out using polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
PCR is used both to confirm the presence of human papillomavirus in the female body and to identify its type.
The “gold standard” for diagnosing HPV is the Digene Test, which determines the number of viral bodies in the body. Knowing the number of viruses in the body, you can estimate the risk of developing cervical cancer.
Also, all patients with suspected HPV are prescribed a cytological examination.
How to treat human papillomavirus in women?
Treatment of human papillomavirus in women can be conservative and surgical.
Drug treatment of human papillomavirus
Tablets against human papillomavirus should have both antiviral and immunomodulatory effects. The following medications are considered the most effective today:
- Viferon;
- Allokin-alpha;
- Epigen-intim;
- Ganferon.
Monotherapy with these drugs is rarely used. Basically, one medicine is combined with another, for example, Allokin-alpha is prescribed systemically, and Epigen-intim cream is prescribed locally. Therapy is also supplemented with immunomodulators, such as Likopid, Immunomax and others.
Since genital warts, papillomas, genital warts and cervical dysplasia increase the risk of developing cancer, they are removed using minimally invasive surgical techniques, which include the following:
- electrocoagulation;
- laser removal;
- cryodestruction;
- chemotherapy;
- removal by radio waves and others.
In severe cases, cervical amputation may be used.
Treatment
Treatment of human papillomavirus infection can be considered optional in the following case.
If the neoplasm is caused by a non-oncogenic strain of the virus, it does not bother the patient, does not interfere with normal sexual activity and is a cosmetic defect.
Only a doctor can confirm the safety of a tumor in a woman and recommend treatment, based on research results.
Read on our project about the necessary research and treatment of varicose veins of the small pelvis. Find out what is the difference between adenomyosis and endometriosis, which disease is the most dangerous.
The main symptoms and reliable treatment of bartholinitis are described in this publication.
Drug therapy
To remove the tumor, external agents are used that destroy the pathologically altered tissue. Additionally, antiviral therapy and drugs that strengthen the immune system are prescribed to reduce the risk of relapse of the disease.
You can get rid of genital warts by the following means:
- Trichloroacetic acid with sodium bicarbonate;
- "Superclean";
- "Solcoderm";
- "Kondilin."
External medications and treatment regimen are prescribed by the doctor. All products are aggressive, they are applied only pointwise to the wart, following the precautions given in the instructions.
Removal
In clinical practice, several methods are used to remove growths of viral origin.
- Laser removal. The method is almost universal and is considered safe, which makes it possible to use the laser even for treatment during pregnancy.
The main disadvantage is the long recovery period, reaching six months.
- Electrocoagulation. The papilloma is exposed to electric current. Removal of the tumor is performed under local anesthesia; it is not recommended during pregnancy.
- Surgical intervention. Usually performed for multiple and very large lesions. After surgery, scarring may form.
- Cryodestruction. Papillomas are treated with liquid nitrogen. Healing occurs within 2 weeks, but there is a possibility of relapse of the disease. Used only to remove external papillomas.
- Radio wave method. It is considered very effective, with minimal risk of disease relapse. Healing occurs within two weeks.
After the warts are removed, the patient is prescribed antiviral and tonic agents.
Traditional methods
You can remove papillomas at home with celandine juice. To avoid damage to healthy tissue, the juice is applied only to the papilloma, after pre-treating the adjacent skin areas with a rich cream.
You can apply aloe or Kalanchoe leaves to the papillomas , fixing them with a band-aid.
A common remedy against skin diseases is castor oil. It is completely safe and has a general strengthening effect. Papilloma is treated 2 times a day until it disappears.
The use of folk experience is permissible when identifying a non-oncogenic strain of the pathogen and must be agreed with a doctor.
Is it possible to remove papillomas yourself or is it better to consult a doctor:
Is there specific prevention of human papillomavirus?
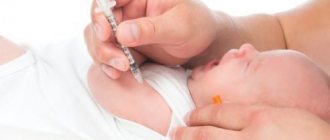
Today in our country two vaccinations against human papillomavirus in women are certified, namely: Gardasil and Cervarix.
These vaccines protect the body from HPV types 16 and 18, which most often cause cervical cancer. In developed countries of America and Europe, these vaccines are included in the vaccination schedule for girls. For example, in Germany, vaccination against HPV is indicated for all girls over 12 years of age. Vaccination is carried out in three stages.
In Russia, the vaccine can be purchased at pharmacy chains. The average cost of the drug is 7,200 rubles.