The article talks about cutaneous types of hemangiomas, which, it turns out, can form not only in children, but also in adults. After reading the information below, you will learn why and when vascular neoplasms appear on the skin in adults. Learn to distinguish capillary formations from cavernous and venous ones. You will learn how to remove small superficial hemangiomas without leaving a trace and painlessly. Get acquainted with traditional medicine recipes that will help relieve swelling and stop bleeding when they are injured.
What is hemangioma?
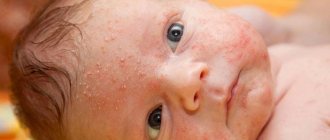
Hemangioma is an abnormal collection of blood vessels on or under the surface of the skin. A vascular tumor looks like a wine or strawberry-colored mole. Often protrudes above the surface of the skin. Appears most often on the face, neck and behind the ears.
Most of these tumors only look painful. Usually they cause discomfort in a person only when they grow in places where they are easy to injure (under the armpits, on the neck, on the scalp).
Note! Skin hemangiomas are benign; complications, such as difficult to stop bleeding, are rare.
Vascular tumors usually appear in infancy, regardless of the sex of the newborn.
After a short period of rapid growth, hemangiomas gradually disappear without treatment. In adults, vascular neoplasms are acquired in nature, because appear throughout life under the influence of external factors, for example, due to excessive sun tanning.
However, up to 40 years of age, hemangiomas are rarely observed. They occur with greater frequency in people of retirement age, especially in people over 70 years of age. Hemangiomas in adults and children are the same type of pathology, but in the first case the formations are most often smaller in size. Many of them grow no larger than flaxseed. However, they occupy large areas of the skin when they begin to grow in groups.
For reference: The presence of hemangiomas in adults does not mean that they can someday transform into a malignant tumor. Cancer cells usually do not form with this type of skin pathology. However, they can bleed, especially if irritated by friction, so some people consult doctors about having them removed.
When does growth most often end and involution begin?
In almost all newborns, hemangioma on the back of the head and other parts of the body appears in the first day after birth and actively grows within six months. Then the development of pathology slows down and stops. Growth stops completely when the baby is 10–12 months old. By the age of six, the neoplasm should resolve.
However, if this does not happen, you should contact your doctor so that he can examine the baby and prescribe a course of treatment.
Causes of pathology
Due to disturbances in the process of formation of blood vessels, mutations occur in the cells of which they are composed. The defective cells are trying to perform their function (to build the walls of a new blood vessel), but they do it incorrectly. As a result, a deformed element is formed, due to which the blood drains and stagnates in the damaged vessels, which leads to the appearance of pink, red and almost black hemangiomas.
There is an assumption that in children hemangiomas arise as a result of minor disturbances that occur in the process of formation of blood branches during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus. Some theories suggest minor anomalies related to genes and the effects of chemical compounds on them. But the causes of hemangiomas in adults are an even greater mystery. Scientists identify the following predisposing factors for their occurrence:
- Diabetes mellitus, liver disease, oncology provoke vascular disorders.
- Vitamin deficiency - a simultaneous lack of vitamin K and ascorbic acid threatens the body with damage to the walls of blood vessels, which is manifested by the occurrence of hemangiomas.
- Ultraviolet irradiation - the skin dehydrates and thins, the vessels dilate, become plethoric (thick), cholesterol plaques form in them, which causes the appearance of vascular pathological formations.
- Hormonal imbalance - hemangioma can form during puberty, in pregnant women and during menopause.
- A decrease in the functions of the hydrolipidic (water-fat) barrier of the skin occurs due to cosmetic procedures (the use of scrubs with coarse particles in the form of salt and pieces of coffee beans).
When studying the above list, it is worth taking into account the fact that the true causes of hemangiomas have not yet been studied. This means that there is no guarantee that a vascular neoplasm cannot fail to appear on the skin of an adult, for example, from exposure to cold or for any other reason.
Forecast for the future
It is noted that the progression of infantile hemangioma continues until the age of one. Then comes a period of regression, and after a few years there is no trace left of the benign formation. Such processes are observed in 6–7% of all cases of the disease.
If the hemangioma has not resolved, but does not grow and does not cause physical or aesthetic distress to the child, doctors choose a wait-and-see approach. Otherwise, active treatment is chosen, which today allows children to be freed from all types of pathology without any problems.
Types of cutaneous hemangiomas
The depth of location, process of formation and appearance of vascular hemangiomas allows them to be divided into three main types:
- Capillary - characterized by a superficial location, consists of endothelium, the cells from which capillaries are formed.
- Cavernous - formed in the subcutaneous tissue from venous and lymphatic abnormally dilated vessels, its size can reach 20 cm in diameter.
- Venous - consists of venous vessels, appears on the lower lip in old people.
Capillary
Other names: infantile, congenital, strawberry hemangioma. It is the most common type of neoplasm that appears above the surface of the skin in children at birth. Most often they can be observed on the skin in the head and neck area. Some congenital capillary hemangiomas disappear on their own before the age of 2 years, some are present on the body up to 5-9 years. In adults, acquired pathology looks like this:
Peculiarity. This hemangioma is soft to the touch. It may have a red or purple color, a smooth surface and clear boundaries. When pressed, the formation becomes lighter. Size from 1 to 10 cm in diameter.
Cavernous
They can occur almost anywhere on the body where there are blood vessels. They are often called raspberry-like because of their bubbly bumps. Unlike capillary types, cavernous ones are not prone to regression (disappearance, reduction).
Peculiarity. They almost always grow to the sides, so if left untreated they can grow, for example, on half of the face.
Rarely does such a neoplasm disappear on its own, and even then not without a trace. In most cases, in the future, cosmetic procedures will still be required to remove traces of its presence on the skin.
Venous
It is less common than the first two types. Most often in older people. The tumor is located on the skin of the face, often on the lower lip, for this reason it is also called a tumor of the senile lips. Ultraviolet radiation provokes the appearance of pathology.
Venous hemangioma can be flat or raised above the skin. The formation is soft to the touch. Its color is usually dark blue or purple. It does not cause any inconvenience to a person other than a cosmetic defect.
For reference: In adults, the most common cavernous-capillary form of formation is called combined hemangioma. The pathology is located in the subcutaneous layers. Formed from superficial and deep blood vessels.
Indications for tumor removal
Typically, your doctor will recommend tumor removal if one of these factors is present:
- The appearance of a tumor on the mucous membrane of the eye, throat, ear. The growth of such tumors can cause harm to the child (difficulty breathing);
- The location of the hemangioma is near vital organs and interferes with their functioning;
- Injury to the tumor, which can lead to bleeding;
- Continued growth of the tumor after the child is two years old;
- Getting infected;
- The disease does not go away after the child is 12 years old.
Differential diagnosis
No special tests are used to diagnose skin hemangiomas. If vascular formations are present, the doctor makes a diagnosis during a visual examination of the patient. But since such anomalies can have different origins, sometimes differential diagnosis is required to clarify the type of pathology.
This process is based on the following points:
- If the formation is congenital, then in order to clarify this factor, its signs are compared with the signs of similar acquired vascular anomalies (pyogenic granuloma, epithelioid nevus, dermoid cyst).
- Using a digital dermatoscope, existing vascular anomalies are analyzed (penetration depth, color, shape).
- The differences between vascular tumors and malignant neoplasms, such as rhabdomyosarcoma, fibrosarcoma, and neuroblastoma, are highlighted.
Congenital and acquired hemangiomas are the most common benign vascular tumors, but they can mimic other types of vascular anomalies. Therefore, in most cases, the diagnosis is made not only by the appearance of the tumor. Taken into account:
- Time of tumor appearance.
- Growth rate.
- Consistency and structure.
Even with these factors taken into account, many other vascular formations can appear very similar to ordinary hemangiomas, especially at an early age, which sometimes makes it difficult to make a correct diagnosis. Therefore, in order to distinguish between them, specialists had to learn to divide pathologies into vascular tumors (formed from the vascular endothelium) and malformations (arteries and veins are abnormally united by intertwined tortuous thin-walled vessels).
Hanging moles are very similar to hemangiomas. To accurately determine the disease, check out this article.
Vascular malformations are divided according to the type of vessel and the rate of blood flow through the vessel. They can be capillary, venous, lymphatic, arteriovenous and mixed. Consist of two or more large vessels. Some malformations are combined and can coexist with capillary and cavernous pathologies. These tumors, like hemangiomas, often appear at birth and increase as the child grows older.
Diagnostic methods
When young parents go to a medical facility, suspecting that their baby has a hemangioma, the child should be examined by three specialists:
- pediatrician;
- surgeon;
- dermatologist.
Venous hemangioma
In the future, if it is determined that not only the skin, but also other systems and organs of the body are affected, the help of ophthalmologists, neurosurgeons and other doctors may be needed. To understand how widespread the tumor is, the following medical tests are done:
- ultrasound diagnosis of tumor;
- radiography, during which the affected area is examined by injecting a contrast agent into nearby vessels;
- computed tomography of the area where the hemangioma is located (vertebral column, head or eye sockets).
Computer tomograph
If the hemangioma has developed as a consequence of some other disease or pathology in the functioning of any internal organ, then it will be necessary to take blood from the child to determine its coagulability and platelet counts.
Drug treatment
Typically, hemangiomas are treated in cases where they cause facial disfigurement or are often injured by clothing. When refusing to remove a congenital hemangioma from a patient, doctors rely on the fact that vascular tumors tend to disappear on their own. While treatment can lead to the appearance of a postoperative scar or cause a side effect from taking medications (decreased immunity).
Removal of hemangiomas can occur using:
- Hormonal therapy. Corticosteroids are injected into the hemangioma to reduce its growth and relieve inflammation (Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone).
- Beta blockers. Drugs such as Timolol gel lower blood pressure and are used 2-3 times a day for 6-12 months to get rid of small superficial hemangiomas.
- Laser treatment. In some cases, the surgeon may use laser treatment to reduce redness and speed up the healing of the hemangioma. The principle of laser therapy is the destruction of blood vessels in the object. But since the rays penetrate only a couple of millimeters into the skin, such treatment will only be effective for superficial flat hemangiomas.
- Regranex healing gel . If there is a chronic ulcer on the hemangioma and it cannot be cured with any other medications, then the patient may be prescribed this drug (typical for diabetics). After which the hemangioma still remains on the skin, but in a healed form. Regranex gel contains becaplermin (a substance that carries a risk of cancer if used repeatedly). Therefore, before using, be sure to talk to your doctor about the existing risks.
- Surgical excision. Surgery is usually performed when the vascular tumor can be excised without causing significant cosmetic harm. If the hemangioma is large or in a sensitive area, such as near the eyes, your doctor may not have surgery. In such cases, cryotherapy (freezing) or a combined type of treatment is prescribed, which combines the use of hormonal or sclerosing drugs with laser exposure.
In the video provided, the surgeon talks about the features of treatment of different types of hemangiomas, as well as in which cases relapses of vascular tumors are possible:
How to treat the disease
Most often, the tumor is not treated in any way; over time, it resolves on its own. But, if the research results have established the danger of the disease (threat of rupture, large size, negative impact on the functioning of organs, as well as cosmetic damage). The choice of one treatment method or another depends on its size, tumor growth rate, structure and condition of the child.
The following methods are distinguished:
- Removal is performed if other methods have not brought any effect, usually if the tumor is located on internal organs. Can be carried out in several stages. The main thing is to remove the hemangioma completely;
- Laser therapy - the result depends on the size and characteristics of the tumor. Sometimes one session is enough, and sometimes 10 procedures are required. This method is considered more gentle and is used for the initial stages of tumor development. This method is not always suitable for children; they may be assigned other activities.
- Cauterization – used to remove small tumors. In this case, either electric current or laser is used;
- Cryotherapy is the treatment of a tumor at a low temperature. Treats simple hemangiomas;
- Sclerosation – injection of a sclerosing drug (alcohol) into the tumor, after which cell growth stops and the hemangioma gradually dies;
- Radiation therapy is the treatment of hemangioma with radioactive rays. This method has been used for a long time and is considered very effective. But there are also disadvantages: it is used only in the case of cavernous hemangioma; up to 6 months of age is strictly contraindicated; Side effects are possible, for example, disruption of the functioning of internal organs.
- Treatment with medications – includes the use of hormones or beta blockers. Hormones prevent further cell growth and promote their death. Beta blockers, a new direction, reduce the pressure in the blood vessels that feed the tumor. This process leads to the death of tumor cells.
Homemade medicine recipes
As a concomitant therapy, you can use the healing properties of effective folk remedies, but under the supervision of a doctor.
Celandine compress for a bleeding tumor
Ingredients:
- Celandine (freshly picked).
- The water is warm and normal.
How to prepare: Grind the stems of celandine into an enamel or glass container and fill with water (1:1). Let stand for 2 hours, this time is enough for the healing juice to come out of the herb. Then strain the mixture.
How to use: Fold the bandage in several layers, soak it in the prepared liquid, squeeze it lightly and apply to the hemangioma for 30 minutes. Then change the compress and repeat the procedure. Treat your skin morning and evening, watch for changes and be sure to see a doctor.
Result: Due to the fact that celandine juice is diluted with water, the compress gently cauterizes the ulcerated vascular tumor, reduces it, relieves pain and inflammation.
Lotion of oak bark and duckweed
Please note that this recipe is suitable for residents of villages where there are small, quiet creeks with duckweed.
Ingredients:
- Oak bark - 1 tbsp.
- Boiling water - 1.5 l.
- Small duckweed - 1 tbsp.
How to prepare: Grind oak bark into an enamel bowl, pour boiling water over it, cover with a lid. Place the mixture on low heat and simmer for 20 minutes. Then add duckweed, remove the broth from the heat and let it brew for 2 hours. Strain.
How to use: Take gauze or bandage, soak in the prepared mixture and apply to the hemangioma for 30 minutes. Repeat the procedure. Carry out treatment in the morning and evening.
Result: Reduces the size of a vascular tumor, has an analgesic and antibacterial effect.
Viburnum ice
Ingredients:
- Viburnum berries - 1 tbsp.
- Cool water - 1 tbsp.
How to prepare: Crush the berries in a mortar, transfer to an enamel container and fill with cold water. Mash the berries thoroughly with your hand again to release more juice. Strain the mixture through cheesecloth and squeeze out the berries. Freeze the resulting liquid in molds.
How to use: Use viburnum ice daily (2 times a day), until complete recovery, in the form of a compress. Apply an ice cube to the vascular formation and hold until it melts.
Result: The product will help get rid of a small superficial hemangioma.
Manifestations
A vascular tumor characteristic of children has the appearance of a flat nodular formation. Its shape can be either round or the most unexpected, and the size sometimes reaches 15 mm. The color of the hemangioma may also differ - from slightly pinkish to bluish. In the latter case, the formation has a higher temperature than the adjacent skin.
The type of tumor may depend on the structure of the blood vessels. Thus, the capillary formation is flat, in rare cases lumpy. The boundaries in this case are clear, and the color is red or bluish. When pressure is applied to the capillary hemangioma, it becomes pale. After some time, the formation restores its original color.
Photo: Vessels with hemangioma
Cavernous tumor is characterized by a bluish color, elasticity and softness. During a child's anguished crying or coughing, it becomes larger and turns a little pale when pressed.
The combined tumor is characterized by the signs described above. The appearance of the mixed formation depends on the tissues complementing the vascular component.
If the location of the tumor is a certain internal organ, its rapid growth occurs. The formation on the bones causes sharp pain.
Photo: Formation of hemangioma on bones
When a hemangioma is injured or gets infected, it takes on the appearance of a boil.
Question answer
What diseases can vascular diseases be signs of?
The most common syndromes are: Kasabach-Merritt syndrome - a rapidly growing capillary tumor that leads to fatal bleeding; Weber's is a disease of the nervous system.
Are vascular tumors inherited?
Medical scientists have concluded that they are transmitted. An example is the following pathologies: angiokeratoma of Mibelli (impaired capillary circulation under the influence of cold); Fabry disease - many small red nodules scattered throughout the body; Louis-Bar syndrome is an immunodeficiency disease; one of the symptoms is persistent dilation of small vessels.
What are the consequences of untimely diagnosis and treatment of ulcerated hemangiomas?
Deep hemangiomas tend to grow into internal organs, as a result of which their functions are disrupted. For example, if a vascular tumor is located near the eye, it can cause vision loss.
Which method is best to choose to remove a flat vascular neoplasm?
The most effective is the use of a vascular laser. The device painlessly and completely removes such tumors. The course of treatment can be 4 - 10 procedures, with an interval of 2 - 2.5 months.
Do hemangiomas on the scalp burn?
Vascular formations on the head are treated with a laser, since after cryodestruction (cauterization with nitrogen), scars remain and hair growth is disrupted.
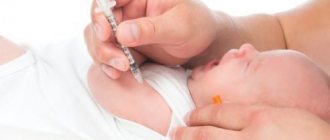
Is it possible to get vaccinated?
Parents who know about the presence of hemangioma on the body of their newborn baby are usually concerned: is it possible to vaccinate? The fact is that there is an opinion according to which vaccinations can provoke the active growth of tumors and even their transition to a malignant state. To say for sure whether vaccines are dangerous for hemangioma, you will need to contact a surgeon and pediatrician who will examine the child.
Vaccination for hemangioma
If the tumor is located away from important organs, does not interfere with respiratory or visual function, and does not grow extremely rapidly, then it can be considered safe for the health of the newborn. This means that vaccinations can be carried out in accordance with the calendar adopted by the pediatrician.
When a hemangioma appears in the eyelid area and does not allow the child to open his eyes, or affects the lip and does not allow the mother to suckle, then you should think about removing it. The same applies to cases of tumor development near the joints, when the child cannot fully move, or near internal organs - such as the liver - since the tumor can compress the baby’s organs. The most dangerous location of a hemangioma is the veins and arteries, which are compressed as the tumor grows and can impair blood flow.
Hemangioma on the lower eyelid of a child
If you want to learn in more detail how to treat hemangioma in newborns, as well as consider the causes and alternative treatment methods, you can read an article about this on our portal.
What to remember:
- Hemangiomas are formed from large and small blood vessels, which is why they have different sizes.
- In adults, the pathology appears as a result of skin injury or after excessive sun tanning.
- Vascular tumors must be treated if they bleed, are constantly exposed to injury, or grow rapidly.
- To treat hemangiomas, along with drug therapy, you can use folk remedies.
- The most effective and safe way to remove vascular tumors is laser therapy.
Recovery period
Rehabilitation after treatment of hemangioma takes different times depending on how large the affected area is and how deep the tumor has grown into the tissue. If the size of the neoplasm is small, then the lesion quickly overgrows, and after healing there are no traces left.
If the pathology is extensive, then the recovery period can be very long: the replacement of the affected tissue with healthy tissue occurs slowly. If the treatment was carried out correctly, then re-development of the pathology is not observed.