Melanoma is a dangerous skin disease of an oncological nature, which develops rapidly, involving healthy tissue in the pathological process. One of the main characteristics of this disease is the spread of metastases to other organs. In oncology, it is generally accepted that metastatic melanoma is an incurable cancer. This pathology begins its development with a mutation of melanocyte pigment cells under the influence of unfavorable factors. Over time, they mix with healthy cells, forming a cancerous tumor. Abnormal cells begin to break away from the tumor, move through the body with the blood or lymph flow, settling in healthy tissues and organs, and then forming secondary tumors.
Description and features of the disease
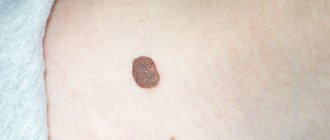
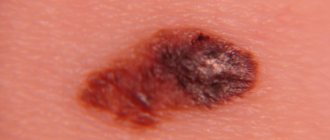
Human skin contains melanocytes. These are the cells that produce pigment that gives color to hair, eyes and the skin itself. The pigment also protects a person from harmful ultraviolet exposure. Foci of accumulation of melanocytes on the skin are called moles or, if we use scientific terminology, nevi. In most cases, they are susceptible to developing into low-quality tumors (melanoma).
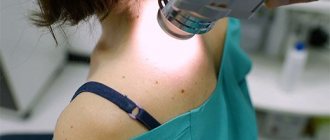
To determine whether a mole is cancerous, you should consult a doctor. He usually looks at the shape of the nevus, its edges, color and diameter, and also asks the patient about the sensations in the area being studied (itching, burning, tingling). If there are any concerns, the specialist should monitor the dynamics: whether any changes occur with the birthmark.
Stages of development of skin melanoma invasion
There are 5 stages:
- neoplasm cells affect only the superficial layer of the skin;
- tumors affect the top layer of the skin;
- melanoma affects the papillary zone;
- invasion of the reticular layers occurs;
- invasion of fatty tissues.
The size of the tumor plays a significant role, because a small melanoma does not threaten human life and health as much as a large tumor. For example, if the tumor size reaches 2 cm, then the survival rate is approximately 70%, and if it is more than 2 cm, then the percentage drops significantly to 50%.
What are the dangers of melanoma metastases?
The primary localization of the disease is extremely diverse: skin, larynx, lungs, digestive system, genitals, etc. However, melanoma of the skin most often occurs in the limbs and trunk, and more specifically, the back. A great danger is its tendency to metastasize, for example to the lungs, and sometimes it is the first and only sign of a person’s disease.
What are melanoma metastases? This is a process called the movement of cancer cells from the primary site to other organs of the human body. It usually occurs in later stages. For this reason, the doctor, before making a diagnosis, must find out whether the identified lesion is primary.
How long do people live with melanoma?
Prognosis for skin melanoma depends on the stage of the disease. To clarify it, an examination is carried out in several stages. It pursues the following goals:
- are there any formations in other parts of the body;
- determine how much the tumor has grown;
- consideration of location relative to lymph nodes;
- determine the exact size of the tumor.
How long do people live with melanoma? The pathology can be successfully cured with surgery at the first and second stages of the disease, if there are no metastases at the cellular level, in the blood vessels and lymph nodes.
Prognosis based on the detection of metastases is unfavorable. In the first stage, they attack the lymphatic system and can be eradicated. Surgery and immunotherapy are prescribed - the drug Interleukin-2, which stimulates the growth of lymphocytes, and Interferon-alpha.
Pathology of the third degree is difficult to treat surgically and conservatively. Statistics indicate a favorable outcome in 25% of all clinical pictures. At stage 4, survival rate decreases significantly, and regression is almost impossible.
The patient’s lifespan depends on the number of affected organs:
- One organ – up to 7 months.
- Two organs – no more than 4 months.
- From three – less than 2 months.
With lentigo melanoma, the lifespan depends on the severity of the oncological process. Under the condition of radial growth, a 100% five-year survival rate was revealed. Against the background of vertical growth, the patient can live for several years. After surgery, only 15% of patients live up to five years.
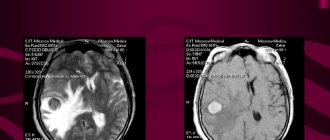
A favorable prognosis is recorded for isolated cutaneous melanoma. With damage to the brain and liver, the clinical picture worsens significantly.
Pathology tends to recur. 10 years after treatment it occurs in 10%.
According to the latest research, the disease can develop 10 years after recovery.
Causes of melanoma metastases
Without suitable treatment, any tumor develops metastases. Some experts are of the opinion that infected cells themselves migrate to other organs and form so-called “dormant foci.” After some time, they become more active and spread further. However, the cause of this phenomenon is difficult to determine. We can only list some of the factors that contribute to the appearance of melanoma metastases. So, these include:
- a large number of small vessels at the site of the initial outbreak;
- localization and structure of the organ with the primary tumor;
- disorders of the body's immunity;
- patient's age. Thus, melanoma with metastases spreads faster in young people than in older people.
Causes of cancer cell metastasis
Hereditary factors and disruption of the hormonal system play a major role in the formation of melanoma. Pathology also often develops due to prolonged exposure to direct sunlight and radiation. Oncologists consider the following points that can provoke the development of the disease with further metastasis:
- age over fifty years, when the risk of developing metastases increases several times;
- the presence of concomitant chronic diseases;
- size and location of the primary tumor;
- germination of a malignant neoplasm into the walls of organs contributes to the spread of metastases;
- insufficient and ineffective treatment of the primary cancer tumor, so it often metastasizes to melanoma in the lymph nodes and then internal organs;
- exhaustion of the body, weak immunity.
Note! The causes and symptomatic manifestations of the pathology depend on many factors. Most often, melanoma forms from a mole, gradually spreading metastases, accompanied by unpleasant symptoms.
Clinical manifestations and diagnosis
Manifestations of metastases are characterized by certain signs and symptoms. All this depends on their location, so it makes sense to briefly consider each organ separately.
The first signs of the disease
According to statistical data, in most patients the tumor spreads to the respiratory system. Thus, metastases in the lungs will be indicated, first of all, by a severe cough that does not go away for a long time. Also signs of metastases to the lungs are shortness of breath and sputum with mucus and blood. In addition, the bronchopulmonary lymph nodes are affected.
In 39%, the tumor penetrates the person’s bones, then he feels severe pain in them. Metastasis is also accompanied by muscle weakness and disorders of several body systems (cardiovascular, digestive). Fractures occur even with mild trauma and impact, and a significant increase in calcium levels is noticeable in a blood test.
When the disease spreads to liver cells, the organ enlarges significantly, the patient begins to feel frequent nausea, and jaundice appears on the skin. The patient also feels pain in the abdomen, weakness, his appetite decreases, and he also loses weight.
If melanoma metastases penetrate the brain, the person first suffers from severe headaches, dizziness and seizures. Short-term memory loss, vision problems, and balance problems may occur. Current statistics show that out of 100 thousand patients, in about 7 patients melanoma metastasized to the brain. The prognosis in such a situation is not very favorable, since in the vast majority of cases, damage to this organ is incurable and quickly leads to death.
Which organs are affected?
Melanoma metastases can spread in two ways:
- hematogenous (or through the blood). In this case, the tumor uses blood vessels to advance. Most often, as a result of such exposure, the lungs, liver, and bones are affected. However, melanoma can also affect other organs.
- lymphogenous. As the name suggests, the lymph nodes of the area where the primary lesion is located are affected. When the disease is localized in the upper extremities, it will be the axillary nodes; if in the lower ones - inguinal. If the torso is affected, the cervical and bronchopulmonary lymph nodes will be affected. With such spread, the primary tumor may not grow, but the nodes themselves increase in size.
Types of distribution
Skin cancer can metastasize by hematogenous or lymphogenous route.
In lymphogenous metastasis, tumor cells penetrate the lymph vessels and then spread through the lymph nodes with the lymph flow. This route of spread is considered the most preferable and most characteristic for melanoma.
Melanomas can also metastasize hematogenously, that is, through the bloodstream, spreading malignant cells to other organs such as the lungs or brain, liver or kidneys, etc.
Experts even identify a separate group of melanomas, which have increased rates of malignancy and a tendency to early spread of metastases through the hematogenous route.
In general, skin cancer metastases are of the following types:
- Nodular type of metastasis, in which secondary formations take the form of multiple different-sized nodes localized in the subcutaneous layer. Such tumors are located at different distances from the primary cancer site.
- Satellites are a rash of many spots that have an appearance similar to the primary tumor. These rashes are usually located in relative proximity to the main lesion.
- The thrombophlebitis-like type is a painful, radially spreading dense formation that has dilated veins and causes swelling of the skin around the melanoma.
- Erysipelas-like metastases – this type of metastasis appears as painful, bluish-red, swollen skin around the primary site of melanoma.
Treatment options for metastatic melanoma
At the first suspicion of a tumor, you should consult a specialist doctor (dermatologist or oncologist). The success of treating melanoma metastases depends on their volume and how well and correctly the diagnosis is carried out. For this purpose, various types of research are used. It can be:
- histological analysis;
- cytological analysis;
- Ultrasound of lymph nodes (for a tumor with metastases to the lymph nodes) and other organs;
- scintigraphy, which involves the intravenous administration of a solution with a radioactive tracer, after which the places where the radiation is more intense are recorded using a camera;
- MRI;
- CT scan.
When diagnosing metastatic melanoma, the use of biopsy should be limited, since it is undesirable to puncture and frequently damage the tumor. This may provoke further development of the disease.
Melanoma is curable when it is detected in its early stages because it then affects only the upper layers of the skin. It is simply cut out surgically, including several centimeters of healthy tissue. If the tumor grew horizontally, the probability of cure is extremely high. There are, however, problems with its vertical location. Then additional immunotherapy, chemotherapy and other types of treatments are required.
If the lymph nodes have been affected, they are usually resected, but the chances of a complete cure are slim. With widespread metastasis of internal organs, doctors give an unfavorable prognosis. The prescribed treatment measures depend on the location of the secondary tumor. At later stages, radiation and chemotherapy are added to surgery. However, the latter cannot be called adequate, since in cases where the situation is too advanced, such an aggressive method can further weaken the patient.
Sometimes metastatic lesions in the bones are treated with medications that contain bisphosphonates so that the human musculoskeletal system is not so fragile. A method of surgical removal of damaged bone is also used: a prosthesis or graft is placed in its place.
After surgery to remove melanoma in the lungs and other organs, you need to be regularly monitored by a specialist: approximately once every six months for the first five years, then annually if the disease has not returned.
The first signs of melanoma
According to statistics, of all cancers, melanoma occurs in 10%. Its first signs:
- the mole has changed in size;
- acquired blurry outlines;
- fluid oozing or bleeding from the surface;
- formation of nodes;
- color change;
- feeling of itching in the area of the mole;
- lack of hair at the site of the tumor;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
The occurrence of apigmented melanoma is a rare phenomenon that carries a danger caused by the asymptomatic course of the disease. There are no pigmented areas on the skin, making diagnosis difficult.
To accurately determine the diagnosis, a histological examination, dermatoscopy, and biopsy are performed. Additional tests: computed tomography, x-ray, ultrasound.
Prognosis and rehabilitation
It is quite difficult to predict recovery from such a disease, since everything, first of all, depends on timely diagnosis and treatment. However, in a situation where metastases have already spread to the lungs, there is almost no point in talking about remission. Most often, treatment is palliative in nature with the goal of prolonging life and relieving painful symptoms. The same thing happens when the disease spreads to the liver.
In general, the situation is that it is better to prevent melanoma than to treat it. And a person who is especially prone to developing this disease (with a large number of moles or with fair skin) must constantly take measures to prevent it.
Even though melanoma is not as common as other types of skin cancer, it is the most dangerous. At a certain stage, this disease begins to spread tumor cells to all organs and systems. However, melanoma with metastases can be cured if detected at an early stage and treated immediately
How can you slow down development?
Genetic predisposition leads to the formation of malignant cells. DNA damage occurs, mutation occurs, and the number of genes changes. The reasons can be chemical, physical, biological.
A recent study in Canada found that the disease could be slowed by adding the MicroRNA 193b gene. It was discovered in human DNA 10 years ago. In the future, these circumstances will help increase the patient’s chances of recovery.
We recommend reading
- Prognosis for recovery when diagnosed with melanoma
- How can melanocytes be restored?
- Preventive measures to prevent melanoma
It is possible to slow down its growth by complete surgical removal under general anesthesia. Local anesthesia may cause cancer cells to spread. If it is impossible to surgically remove all metastases, then chemotherapy is prescribed. Treatment is long-term, and the risk of disease recurrence remains throughout life.
Radiation therapy is used in the treatment of skin cancer. The required dose of radiation is sent to the tumor site. This method is good because radiation does not affect healthy human organs, but affects cancer cells.
At the last stage of melanoma, palliative treatment is carried out. The purpose of such assistance is to alleviate suffering and maintain vital functions. The person dies, but does not experience as much pain.
Metastatic tumor - what is it?
The metastatic nature of a tumor is said to occur when a malignant neoplasm spreads metastases (cancer cells) through blood or lymphatic vessels to other parts of the body, which leads to the development of tumor lesions in other organs. Cancer cells can migrate freely throughout almost the entire body and stop at different points. After such a stop, active division of such metastases begins, which is accompanied by the formation of a metastatic focus.
Methods of treatment and maintenance of the patient
During the formation of a tumor, the doctor prescribes complex treatment: radiation and chemical therapy, immunostimulating drugs, as well as surgery, in which the tumor is pulled out of the body.
People often die from stage 4 melanoma, but treatment is possible. It is used for the following purposes:
- reducing the growth of malignant tumors;
- supporting affected organs and ensuring the vital functions of the body;
- prevention of complications.
The operation is performed under anesthesia and helps eliminate metastases that interfere with a person’s life. Secondary formations are removed along with the tumor after irradiation. Treatment with surgery allows you to reduce the lesions.
Chemotherapy uses medications that support the immune system. Traditional medicine is often used to alleviate well-being after radiation exposure.
Chemotherapy is the main treatment for melanoma. To slow down the disease as much as possible, the drugs Dacarbazine and Temozolomide are used: they temporarily reduce the size of metastases.
Radiation therapy prevents the growth of cancer cells and is used to maintain life and delay death.
If surgery cannot be performed for health reasons, the drug Pembrolizumab is prescribed, which stimulates the body's natural defenses. Thanks to this, the immune system destroys cancer cells and suppresses the growth of new formations. According to doctors, medications help the body cope with the tumor. Clinical trials have shown that radiation therapy doubles patient survival.