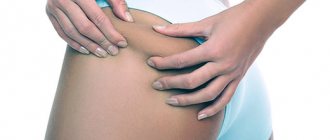
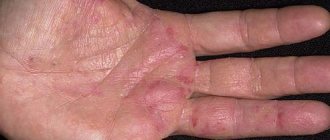
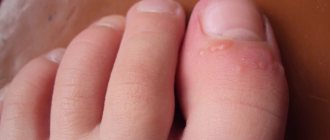
Peeling and redness of the skin on the inside of the hands, which is accompanied by itching and burning, may indicate that a fungus is developing on the palms (mycosis). The infection most often affects older people and children. Let's look at the causes of mycosis of the hands, its initial manifestations and treatment methods in more detail.
Itching and flaking may indicate a fungal infection.
Fungus in children. Causes
Baby fungus appears for various reasons. The main factor is weak immunity.
Provocateurs for this can be:
- frequent colds;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- hormonal problems;
- chronic diseases such as diabetes;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- blood diseases;
- problems with the endocrine system;
- poor quality nutrition with a predominance of carbohydrates and lack of protein, monotony of the diet.
Often the fungus is caused by a lack of B-vitamins, vitamin C, and folic acid.
The fungus can also become infected from other people and objects:
- Candida fungus. Babies can get it from their mother at birth. Less often - from the medical staff of the maternity hospital, who do not comply with sanitary or hygienic rules.
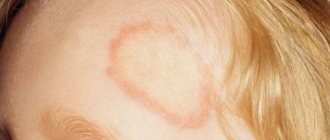
- Ringworm. An older child may get the fungus from a dog or cat. Typically it will be ringworm. You just need to touch the animal. Symptoms will appear within a few days.
- Tinea versicolor. It is transmitted from an infected person through household items and clothing. The fungus is extremely tenacious and can exist in the environment for a long time. These organisms are not very sensitive to temperatures and reproduce in the harshest conditions.
- Children's foot fungus. Often - on the feet. It spreads when wearing someone else's shoes or coming into contact with a contaminated surface. For example, in the pool or in kindergarten. Sometimes mycosis appears due to tight and uncomfortable shoes, which injure the feet and cause them to sweat.
In childhood, fungal infections occur as isolated cases. However, infection also occurs faster. Organisms attach well to children's skin due to the structure of the epidermis. Therefore, it is easier for a child to catch mycosis than for an adult.
Find out more
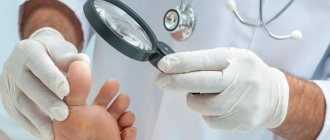
Diagnosis of fungal infection
Initially, fungus on the palms is similar to many dermatological diseases. Therefore, one examination by a doctor is not enough. To determine the presence of an infection and the type of its causative agent, there are several research methods:
- microscopic analysis - a scraping (particles of tissue) is taken from the affected palms and examined for pathogenic microflora;
- examination of the injured areas of the palms under a diagnostic lamp - a Wood's lamp, which shows the presence of a fungal infection;
- cultural analysis - identifying the type of pathogen using bacteriological culture of scrapings.
There are often cases when diagnostics reveals two pathogens at once - dermatophytes and yeast fungi. In this case, several antifungal drugs are prescribed at once.
One way to identify the fungus is cultural analysis.
Fungus in children. Symptoms
The symptom set depends on the fungal variety and location of the lesion:
- Foot. A fungus on the skin of a child's feet affects the feet and toes. Causes small wounds that eventually develop into small ulcers. The skin is itchy. Redness appears. It is difficult for the child to walk due to pain.
- Nail. Nail fungus in a child affects the bed and plate. The nail turns gray and then black. The plate thickens. Peels off. Sometimes the skin around the nail becomes inflamed.
- Ringworm. Affects the scalp and hair. The latter begin to fall out and break off. The scalp itches, turns red and flakes. Scratching causes new wounds to form, which contribute to even greater damage. Sometimes the child's temperature rises.
- Pityriasis versicolor. Usually appears on the back. The skin becomes covered with spots of gray and yellow shades. The latter are peeling off. There is no itching.
- Candidiasis. Affects the oral cavity and genitals. The disease manifests itself in the form of a cheesy coating, which, when wiped off, reveals wounds and small ulcers on the mucous membrane. Children may have a fever, but not higher than 37.5 degrees.
Based on the location of the fungus, it can be superficial or systemic. Superficial does not go further than the skin and mucous membranes. Systemic - affects the entire body and is localized on the internal organs. As a rule, fungus in children (photos on the Internet demonstrate this) is external in nature.
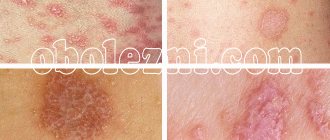
Hand skin candidiasis
Yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida most often affect the palms of women, and dermatophyte fungi in men. The disease affects people whose hands are exposed to a humid environment for a long time - housewives, people working in food factories, confectionery shops, when working with vegetables and fruits, etc. The disease in men is more often occupational.
Rice. 18. Candida albicans fungi under a microscope. Round pathogen cells and filaments of pseudomycelium are visible.
Damage to interdigital folds
The disease begins with the appearance of very small blisters on the skin of the contacting surfaces (usually 3 and 4 interdigital folds). Hyperemia of the transitional fold and maceration are noted. The rejected epidermis becomes white. A hyperemic, shiny, smooth surface is exposed underneath. The boundaries of the lesion are clear, surrounded at the periphery by a rim of exfoliating epithelium, rarely extending to the back of the hand. Subjectively, the patient experiences itching and burning.
Rice. 19. Damage to interdigital folds due to candidiasis.
Rice. 20. Candidiasis of interdigital folds.
Damage to the skin of the palms
This form of the disease is rare and has several forms of manifestation:
- In some cases, the disease occurs as dry lamellar dyshidrosis (superficial ring-shaped, garland-shaped or lamellar peeling is noted). The disease should be distinguished from dyshidrotic eczema.
- The vesicular-pustular form is characterized by the appearance of vesicles and pustules against the background of hyperemia and edema.
- Hyperkeratotic eczema is characterized by the appearance of wide skin furrows of a dirty brown color in areas of keratinized skin.
Rice. 21. Candidiasis of the palms. Dry lamellar dyshidrosis.
Candidiasis of the periungual fold
Prolonged stay in a humid environment and trauma contribute to the development of candidal inflammation of the periungual ridges. The disease begins with hyperemia and edema. The skin becomes thinner and becomes shiny. The nail skin disappears. When pressed, ichor, a crumbly white mass, or a drop of pus may be released. In some cases, the nail plates are affected. Patients are bothered by pain.
Rice. 22. Candida paronychia - inflammation of the periungual fold.
Rice. 23. Candidiasis of the hands (photo on the left) should be distinguished from eczema (photo on the right).
Rice. 24. Interdigital candidiasis (photo on the left) and skin lesions on the hands due to rubrophytosis (photo on the right).
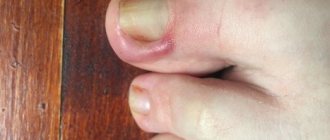
Fungus on children's toes
Fungus on children's toes can spread from the foot or nails (this is not visible from the photo).
In most cases, a child becomes infected with it from another person. The following factors are to blame:
- Wearing someone else's shoes and clothes. If there is a fungus in the kindergarten or one of the family members, the child can easily catch it. Also, you should not put someone else’s socks and tights on your child.
- Wearing the wrong shoes. Tight shoes injure the foot and cause increased sweating. This creates a favorable environment for the proliferation of harmful fungal organisms.
- Walking barefoot. Especially in public places. In the bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool, on the beach, in the garden.
In most cases, the lesion can be treated with topical medications. In neglected cases, use internal medications.
Ointments are considered the most effective. The most gentle are gels. However, before each purchase you should consult your doctor.
Disease prevention
You can prevent the appearance of fungal diseases on the skin of children if you adhere to the following rules:
- Provide your child with individual personal hygiene items, such as a towel, toothbrush, and washcloth.
- If your baby is an infant, you need to take extra care of his hygiene. Try to regularly disinfect pacifiers and toys that he may put in his mouth.
- If you visit a swimming pool, sauna or bathhouse with your child, make him wear his own slippers so that he does not go barefoot. In addition, forbid him to wear someone else's shoes.
- Buy clothes and shoes for your baby only from natural fabrics so that he doesn’t sweat too much, because this will only contribute to the growth of the fungus.
- Regularly disinfect the inside of your shoes.
- Purchase individual tools that you will use to treat your baby's legs and feet.
If you follow these simple rules, your baby will avoid the fate of being infected with fungus, and he will be healthy and cheerful.
Fungus in children. Treatment
Therapy is carried out in a course. Usually - at home and through independent efforts. In advanced cases, you will have to be treated in a hospital. In the case of nail fungus, children are always treated at home.
Medicines used:
- antihistamines;
- hormonal drugs (usually corticosteroids);
- immunostimulants;
- vitamin complexes;
- antiseptic solutions (with boric acid, furatsilin or potassium permanganate - the dosage is prescribed by the doctor);
- antifungal drugs of internal and local types.
First of all, antifungal ointments, pastes and gels are used. They are applied to the affected areas 2-3 times a day. More effective - morning and evening. The composition should include zinc, tar or salicylic acid. The course of ointments is continued for 1.5-2 months.
When the fungus does not go away but continues to spread, tablets are added to therapy. They act on fungal pathogens from the inside. For clarity, you can look at photos of nail fungus in children - they show different degrees of severity of the disease.
In serious situations, they resort to hormonal drugs. But these are extreme measures.
If the fungus has affected the genitals, use suppositories.
If the scalp is affected, the hair in this area is shaved off and the scabs are removed by hand.
In addition to drug treatment, physiotherapy is used:
- laser treatment;
- electrophoresis with the addition of drugs;
- pulsed magnetic therapy;
- Darsonval therapy;
- DMV treatment.
In particularly advanced cases (if the lesion is on the nail), the nail plate is removed by a surgeon.
Forms and stages
The development of infection occurs in several stages:
- First stage . Small spots and lines form on the edges or in the center of the plate.
- Second stage . The spots begin to grow rapidly, which is accompanied by peeling of the nail plate.
- Third stage . Dystrophic deformation occurs, in which the nail crumbles, collapses, and the inflammatory process spreads to neighboring tissues.
Experts distinguish several forms of the disease:
- onychorrhexis. Cracks extend from the free edge;
- psoriatic form. The nail changes color, becomes stained, changes thickness;
- onychomadesis. The cause of development is associated with mechanical trauma, as a result of which a purulent mass accumulates under the nail;
- onycholysis. The nail plate gradually peels off from the free edge and eventually peels off completely;
- hapolonychia. Affected nails soften and begin to deteriorate due to fragility;
- Kaylonychia. Dents form on the plates;
- scleronychia. Thickening of the nails and detachment from the bed to the edge occurs. In addition, they acquire a yellowish or brown tint;
- onychogryphosis. The nail thickens and loses its natural shine, becomes rough with an uneven surface;
- trachyonychia. Scales form on the nails;
- onychoschisis. The surface is covered with small transverse grooves;
- anonychia. This form of the disease is rarely acquired; most often it is congenital.
Treatment with folk remedies for fungus in children
Here's how to treat nail fungus in a child using folk remedies:
- Infusion of celandine. For 20 grams of plant - 1 liter of water. The herb is poured with boiling water and left to cool completely. Afterwards, they are heated to a comfortable temperature and the affected limbs are lowered there. Other parts of the body can be wiped with a cotton pad soaked in the composition.
- Natural honey. For one part honey, add ten parts water at room temperature. The solution is used to make lotions.
- Herbal infusions and decoctions. Sage, oak bark, St. John's wort and chamomile are suitable. Each plant is used separately. They do baths and lotions. For 20 grams of material - 200 ml of boiled water. Leave for 15 minutes.
- Sea salt. For 4-5 tablespoons - 300-400 ml of water. They make baths.
- Mint. Used for feet. 50 grams of freshly picked leaves are poured into 2 small bags. The bags are placed on the legs. On top are socks. Do not take off for 2 hours.
- Tea tree oil. They moisten bandages or cotton pads. Treat affected skin areas.
It is recommended to supplement any therapy with dietary adjustments. The diet will speed up the results.
The menu certainly includes the following components: fresh vegetables (especially green ones), fruits, nuts and seeds, chicken eggs and fermented milk.
Be sure to exclude: sweets and flour, dairy, fried. You can drink tea, but without sugar. It is also worth excluding yeast, both in pure form and as part of dishes. Dairy, sweet and yeast products are food for pathogenic fungal organisms.
Treatment of fungus in children is a long-term measure. Therapy does not stop until the manifestations of the disease completely disappear. Control tests for fungi should also give negative results. They are prescribed by the doctor.
The most effective therapy is complex.
How does infection occur?
The causative agents of the disease are easily transmitted from one person to another. The infected person leaves behind fungal spores along with dead skin particles, which are stored at home for a long time.
A newborn can become infected in utero, an infant through a shared bed. A grown-up one-year-old baby catches the infection by licking objects. Yeast fungus enters the baby's mouth through shared utensils or if the mother licks the pacifier and gives it to the baby.
A baby can become infected with ringworm by touching a sick animal.
City birds, such as pigeons, also spread infections.
At 2 years old, the baby begins to attend preschool educational institutions. In kindergarten, if hygiene standards are not observed, the infection quickly spreads between children.
Schoolchildren acquire the infection by trying on the shoes of a sick person. Fungal spores can remain in winter shoes for a long time; as soon as the immune system malfunctions, infection occurs.
With bruises and cuts, minor injuries increase the risk of infection.
Infection with aspergillosis can occur through inhalation of dust containing fungal mycellosis. You can get sick from it when visiting untreated premises: old baths, bathrooms.