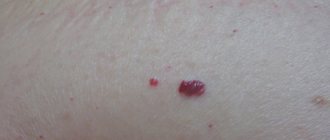
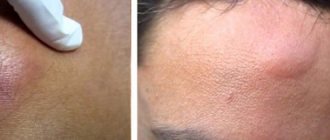
Treatment of red moles is a complex of necessary medical procedures, which is agreed upon with the doctor. Removal of nevi is carried out if there are indications or cosmetic defects on open parts of the body. Red moles are benign formations of vascular origin. With pathological changes in the microvasculature, atypical growth of the capillary network, damage to vascular structures above the surface of the skin, a nodular mole - angioma - appears.
What do red moles mean?
Red moles are benign formations.
In medicine they have a second name - angiomas. They occur as a result of changes in blood vessels. The appearance of red moles occurs throughout a person’s life; in children under seven years of age they can disappear on their own. They practically do not degenerate into a malignant formation. They vary in size, shape, shade. A peculiarity of the formation is that the color changes to a lighter color when pressed.
What causes red moles? They are usually divided according to the type of vessel that caused them. There are capillary, arterial and venous angiomas. Flat and convex nevi on the skin are also noted, depending on the depth of the lesion. Red neoplasms are divided into types depending on what tissue forms them.
Kinds:
- Pineal - convex moles that rise above the skin,
- Flat – moles located in the upper layer of the dermis do not rise above the skin,
- Branched - growths with blood inside,
- Star-shaped - from such pinnacles the divergence of blood vessels is noticeable,
- Nodular - formations with a clear boundary, dark burgundy or purple,
- Cavernous - several formations located in one line behind each other, are often diagnosed on the face.
Large red nevi are called hemangiomas. These growths are quite often subject to various injuries, so they must be removed.
Diagnosis and complications
Red dots are dangerous due to rapid growth and subsequent compression of nearby structures with disruption of their function, which is especially important when hemangiomas are localized in the brain, in the liver, or near the eye.
- Ulceration and inflammation during growth. Some types of red moles undergo reverse development after such complications.
- Bleeding due to injury, especially dangerous with extensive cavernous and combined hemangiomas, as well as tumors located on internal organs, since such bleeding is very difficult to stop.
- Infection (bleeding, ulcerated moles), i.e. the addition of a bacterial skin infection.
With superficial hemangioma, the diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical and histological data. For extensive and deep processes, angiography is performed to determine the connection of the tumor with the vascular network, as well as radiography, which provides accurate data on the size and depth of the vascular tumor.
A specialist must examine the mole, find out the circumstances of its appearance and the symptoms of formation. In some cases, it may be necessary to consult a neurologist, gastroenterologist, or endocrinologist, since such formations may be localized in some internal organs.
If such moles are significant in size or change, the doctor will give a referral for a biopsy. During this study, it is possible to determine whether malignancy (degeneration) of the nevus occurs into a malignant formation.
Expert opinion
Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
The most dangerous are convex red moles that are susceptible to the mechanical effects of clothing, shoes, and jewelry. Red moles on women's breasts are especially often damaged due to friction from the bra. You should also pay special attention to angiomas located on open areas of the body and face that are exposed to ultraviolet rays.
It is these moles that most often degenerate into a malignant tumor. When angiomas are damaged, severe bleeding occurs. After injury, they can increase significantly in size.
Causes of red moles on the body
Red moles on the body (angiomas) are tumors, the occurrence of which is associated with an abnormality in the structure of blood vessels. They can be congenital or acquired.
The occurrence of congenital angiomas occurs even at the stage of intrauterine development of the fetus, under the influence of various factors acting on the body of a pregnant woman:
- infections;
- bad habits;
- ionizing radiation;
- taking certain medications.
The size of congenital angiomas in a child usually does not exceed 10 mm. At primary school age they disappear on their own.
In adults, red moles on the body usually begin to appear over the age of 30-35 years. They occur in approximately 50% of the population. The pathology affects both women and men with equal frequency.
If an adult has red dots on the body like moles, then the reasons for the appearance of such forms of angiomas are:
- abuse of sunbathing or visiting a solarium;
- dysfunction of the liver and pancreas (one of their symptoms is the appearance of bright burgundy moles on the upper part of the body);
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- hormonal changes (pregnancy, menopause);
- increased fragility of the walls of blood capillaries, caused by a deficiency of vitamins K and C in the body;
- lipid metabolism disorders;
- hereditary predisposition;
- some autoimmune diseases;
- skin injuries;
- inflammatory diseases of the digestive system (gastritis, enteritis, colitis);
- hemophilia;
- poor nutrition.
To date, the exact mechanism for the formation of red moles on the body in women and men has not been established. However, taking into account the reasons that cause their occurrence, it becomes clear that red moles, by their appearance (especially multiple ones), signal any disturbances in the functioning of the body or the development of various diseases.
The works of a number of scientists suggest that angiomas should be considered as an intermediate link between a developmental defect and a tumor.
Clinical picture
- The appearance of red, burgundy or purple growths on various parts of the body. If a mole changes color, this is a serious reason to consult a doctor.
- Red body rash on the skin. The appearance of a large number of angiomas in various areas of the skin is an alarming signal indicating a deterioration in general health.
- Asymptomatic course of the disease. The mole does not cause any discomfort other than aesthetic. It should not itch, hurt or in any way affect the person’s general well-being.
Flat
It is located under the skin in the form of a plaque.
By color:
- Pink ones are benign in nature.
- Bright red.
- Crimson.
By vessel type:
- Capillary - most common.
- Venous - have a bluish color.
- Arterial.
If there are a small number of closely spaced moles, this indicates a cavernous angioma, which can be found on internal organs.
Signs that it is time to seek help from a medical facility:
- The color changes over time. The color becomes darker and more saturated. This indicates malignant degeneration.
- The size has increased or the shape has changed. The faster the growth, the faster you need to rush to a medical facility.
- Growing number. In this case, much does not mean good.
- Itching and pain. This occurs due to physical damage, transformation into a tumor, hormonal changes (for example, when carrying a child).
- Bleeding is the most dangerous situation. Large blood losses are possible, since the basis of moles is blood vessels. Most often this happens due to poor placement. An angioma can interfere with comfortable shaving or rub against the edges of the collar, resulting in injury. You should treat the skin area with hydrogen peroxide or rubbing alcohol, apply a bandage and make an appointment with a dermatologist or surgeon.
Quite often, angiomas appear and disappear almost unnoticed by a person. They are located on a closed part of the body, do not hurt, do not change their structure and do not manifest themselves in any way. Then experts recommend just waiting, everything will go away with time.
But if the shape, size have changed, or it spoils the person’s appearance, then the doctor, after a thorough examination, will say whether it can be removed or not.
Treatment of angioma
The method of removing tumors depends on their type and depth of location in the skin. Flat moles are easier to treat than raised moles. In most cases, the removal procedure does not require the use of anesthesia. Sometimes local anesthesia is prescribed followed by the use of anesthetic ointments. After the procedure, a reddish spot forms at the site of the angioma, which soon disappears.
To get rid of simple red dots, which are small in size and have a uniform structure, women are recommended to resort to the following methods for removing angioma:
- Surgical intervention. The main disadvantage is that a scar may remain after removal. Not the best option for women. In addition, this method can only remove small dots.
- Chemical sclerosis. The essence of the method is to inject a special drug around the hemangiomas. It blocks blood flow, nutrition stops and the hemangioma dies.
- Cryodestruction. This is freezing using liquid nitrogen. Again suitable for small formations on the surface of the skin. As a result of freezing, the vessels become brittle and then die.
- Use of carbon dioxide. It is used to cauterize an unwanted spot. But, birthmarks are usually located deep in the skin, so the method may be ineffective. If the treatment was unsuccessful, the mole will increase in size, because it is difficult to burn the base with acid. This method can only get rid of small formations.
- Coagulation. A traceless method that allows you to remove large hemangiomas from the body of women. You will need to use an anesthetic as there will be a thermal effect on the skin. They use infrared, radio wave and other techniques for this.
- If the formations of the red body have a complex structure and are large in size, then step-by-step surgical treatment will be required. In this case, exposure to laser beams will be required. They allow you to leave barely noticeable marks on the skin. Local anesthesia must first be performed. The procedure lasts a couple of seconds. In a day the formation will be covered with a crust. And after a couple of weeks it will disappear.
The specialist will conduct observations for some time after the intervention. He needs to know the level of malignant cells in the affected area. If something happens, action will be taken.
Why are vascular tumors dangerous?
The threatening appearance of angioma often causes concern due to its association with cancer. However, vascular tumors (especially skin tumors) are practically not prone to malignancy.
Unlike angiomas of other locations, skin tumors are not prone to bleeding, but there is an increased risk of injury and infection. This is especially true for tumors protruding above the surface of the skin. Infection is especially dangerous for superficial colorless angiomas, because the entry of pathogenic microorganisms into the formation is fraught with lymphorrhea (leakage of lymph) and the formation of fistulas.
The vast majority of superficial angiomas are unpleasant only aesthetically: a pathological accumulation of vessels can grow along with the development of the child. Lymphangiomas grow more slowly than hemangiomas, but are prone to suppuration and are often painful on palpation.
With a high risk of trauma (located on the palms, head, lips, etc.), especially in infants, vascular tumors are usually removed surgically.
The only type of superficial angioma that causes negative effects by the very fact of growth is a neoplasm located on the eyelids. As the size increases, it can cause protrusion of the eye or a bifurcation of the perceived picture. It is also recommended to remove such tumors.
With age, angiomas may regress and become pale. Often, neoplasms recorded in newborns completely disappear by the age of 7-9 years.
How to get rid of red moles using folk remedies
Traditional medicine offers several ways to remove tumors:
- Dressing;
- Burning;
- Herbal treatment.
Any treatment of red moles on the body must be pre-approved by a dermatologist.
Bandaging
A common way to deal with red raised moles on the body is to bandage the growth. The danger of the procedure lies in the risk of degeneration into a more dangerous form, since the effect is only on the upper part of the tumor formation.
Burnout
Cauterization of tumors occurs through exposure to vinegar essence. The wetting procedure is carried out daily for 2 weeks. If necessary, the manipulations are repeated again after a 14-day break. Between burnings, the mole should be protected with a bandage.
The method is considered reliable; after burning, no traces remain. The disadvantage of the method is its severe pain.
Moles can be affected in less aggressive ways: juice of garlic, lemon, onion, iodine, hydrogen peroxide, soda.
The most painless, but long-lasting method is to lubricate the tumor with oils (linseed, castor). Gradually the mole shrinks and disappears.
Herbal medicine
Herbal medicine is effectively used to combat small red moles on the body. The most common treatment with celandine (tinctures, juice, oil, ointments):
- The fresh plant is cut, the juice from the stem and leaves is applied to the mole 2-3 times daily;
- To make an ointment, baby cream or pork fat is used as a base. The leaves and stem need to be crushed into a paste and the juice squeezed out. Mix 1 part juice and 4 parts base. Apply the resulting ointment to the affected areas daily, 2-3 times;
- Oil based on celandine. It is necessary to take dry raw materials of the plant, add vegetable oil, leave for 7 days in a dark place. Every day, for 30 days, the mole is lubricated three times with the resulting oil.
What happens if angiomas are not treated?
Usually such moles are safe, but with constant mechanical impact or ultraviolet irradiation, they can degenerate into another neoplasm. Red moles are extremely rare, but still sometimes, become the location of skin cancer.
Trying to remove an angioma yourself can cause severe bleeding. If such neoplasms are located near the nose or eye and are large in size, this can lead to impairment of the organs of vision and hearing.
If there are small red stars or spiders on the skin that do not bother or grow, they do not need to be checked. Such neoplasms are a normal phenomenon of skin pigmentation.
What to do if the spots cause itching
In most cases, angiomas do not cause any discomfort. Therefore, if the tumors itch, they may have a different origin. People with this disease usually attribute the appearance of small dots to allergies. And taking antihistamines rarely achieves the desired effect.
The solution for itching is not to treat yourself, but to consult a dermatologist who will make an appropriate diagnosis.
Only a doctor will determine the cause and prescribe the right drug or appropriate course of therapy.
Prevention
- Careful handling of the mole, protection from mechanical influences.
- Drink at least two liters of fluid per day.
- Including foods rich in vitamins E and D in your diet. For example, avocados and olive oil.
- Regular bowel cleansing. You can eat spirulina algae, which removes toxins from the gastrointestinal tract.
- Protect yourself from excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays. This is especially true for white-skinned people with red or blond hair. If you stay in the sun for a long time, you must use sunscreen.
- Moisturize skin as needed.
Red moles on the body are usually not dangerous. They are benign formations. You should consult a doctor only if the angioma causes discomfort or spoils the aesthetic appearance. Modern medicine offers several quick and painless ways to get rid of this disease.
Red spots appeared on the body - what could it be? Chickenpox: symptoms and treatment for children at home Psoriasis: symptoms (photos), causes and treatment Low blood pressure: causes, symptoms, treatment and consequences
Is it worth removing the new growth that has appeared?
Usually, having noticed a red mole on a child’s body, parents immediately begin to think about how to remove this growth. But we note that if the angioma is small and located in a non-traumatic place, you don’t have to touch it - most likely, over time the neoplasm will resolve on its own.
However, a red mole should be removed if it:
- hurts;
- bleeding;
- located in a traumatic area;
- has significant dimensions;
- located on the face (spoils appearance);
- there is a risk of its degeneration into a malignant formation.
Rapidly growing angiomas must be removed. If the neoplasm has changed color, size or shape, this is also an alarming sign , and after examination such a mole is also usually removed.
If the tumor is itchy, resulting in constant scratching, removal is usually also prescribed. Dermatologists also strongly advise removing red moles that appear on the scalp.
The fact is that this arrangement leads to frequent and almost inevitable injury to neoplasms. In this case, removal is usually done using a laser, sometimes with nitrogen.
After removal of the angioma, it is very important not to expose the child to ultraviolet rays for some time. The wound should be covered with a bandage so as not to further injure the vulnerable area and protect it from germs.
IMPORTANT! You should not self-medicate, and do not use any traditional methods of therapy without the knowledge of your doctor. It is especially dangerous to try to remove a mole on your own - this is something that should not be done under any circumstances.