Melanoma is a malignant cancer with a high mortality rate. Develops from moles as a result of exposure to external or internal unfavorable factors. The disease progresses quickly, it is important to notice the degeneration of cells into cancerous ones in the initial stages, and in time to put an equal sign between the words mole melanoma. This will increase the chance of recovery. If you are at risk or have a hereditary predisposition, you should study the differences between a mole and melanoma and regularly conduct self-diagnosis.
How to recognize melanoma: description of pathology
Melanoma is a type of cancer that forms from skin melanocytes or birthmarks. The tumor is aggressive and is fatal in 13% of cases. Most often, the tumor forms in open areas of the skin or is formed from nevi (moles) existing on the body, and sometimes disguises itself as them. Therefore, it is not always possible to immediately determine whether a melanoma or a nevus is located on the skin. In some cases, the tumor can occur in the eye, on the epidermis of the mouth and nose, rectum and vagina.
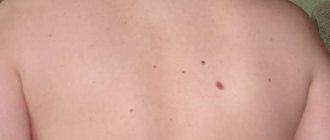
Moles are present on the body of almost all people. They can develop from different layers of the epidermis, so there are several varieties: borderline, intradermal and mixed. The most dangerous are borderline moles, which look like nodules with a distinct black or brown outline and have a dry, smooth surface without hair. The nevus rises slightly above the surface of the skin and does not cause discomfort or pain. It can range in size from two millimeters to one centimeter and is often located in the head, neck, torso, palms and feet. Pathology develops very rarely from mixed and dermal moles.
Note! Especially often, a cancerous tumor (melanoma) degenerates from moles located on the foot, sole and nail growth area, since moles are often injured in these places.
In half of the cases the tumor develops on the legs, in 20% it is observed on the torso and in 10% of cases on the arms. The neoplasm develops quickly; it can grow in several directions: above the skin, along the surface of the epidermis and deeper, growing into the surrounding tissues.
What moles can be removed
Often nevi cause trouble for women when they are in a visible place - the face, neck. Even if they do not bother you, using removal will be the right decision - the appearance will improve significantly. After the procedure, the doctor must send the tissue for histological analysis to decide whether the mole is malignant or not. If the neoplasm is not dangerous, does not bother you, and does not change in size, surgery is not required. What moles cannot be removed? Experts believe:
- there are no contraindications;
- It is important to choose the right excision technique.
You should be careful about skin growths; it is unacceptable to remove them yourself. Only the doctor will determine whether a nevus is dangerous or not and decide what to do with it. You can delete it if:
- injured from clothing - on the neck, in the groin area, under the armpits;
- cause pain when touched;
- are located under the hair on the head and can be damaged when combing or cutting;
- change color, shape, outline;
- significantly increase in size;
- characterized by the presence of burning, itching;
- accompanied by inflammation and bleeding.
Types of pathology or how to distinguish melanoma from a mole
In oncology, there are four types of cancerous tumors:
- Superficial or superficial melanoma is the most common skin cancer. The neoplasm appears as a blue, black, brown or red flat spot with jagged edges. The tumor begins its development in the upper layer of the skin of the head, neck, lower leg, and thigh. At first, these are benign pigment spots that grow in a horizontal direction. Over time, they begin to grow into the subcutaneous and fatty layers and become malignant.
- Lentigo is malignant, characterized by gradual development on the surface of the epidermis. The tumor has the shape of a slightly raised, unevenly colored spot with brown dots. Pathology is observed in most cases on the upper extremities, ears, face, and usually affects elderly people.
- Lentigious acral melanoblastoma develops slightly faster than in previous cases and appears as brown or black spots. This form of pathology is malignant, it develops on the palms, soles and under the nails.
- Nodular melanoma resembles a lump in appearance that grows deep under the skin. The tumor is mostly black in color, it develops rapidly, spreading metastases to internal organs and tissues. This form of pathology is formed from a nevus and is considered dangerous .
Note! The first three types of pathology are distinguished by their distribution on the skin, the fourth type is characterized by tumor growth deep into the skin.
Typically, melanoma develops as a mole in 30% of cases, and in 70% of cases it appears on its own. The neoplasm produces melanin, so its color is in most cases black, but may remain unchanged. In this case, diagnosing the pathology is difficult.
In addition to open areas of the skin, a cancerous tumor can appear on the scalp, on mucous membranes, under the nail plates and palms.
What to do?
All suspicious spots on the skin should not be ignored. Large nevi located in an area of permanent damage can degenerate, so surgical treatment is recommended. It is considered dangerous if melanoma develops after removal of a mole. This may indicate an advanced cancer process.
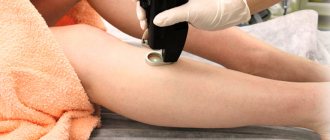
Timely treatment gives the patient a chance to live. It is best to diagnose at the first symptoms, when melanoma is in the upper layers of the skin. In this case, treatment involves removing the formation. This is done using a scalpel, laser or liquid nitrogen. The duration of the operation depends on the size and location of the melanoma, but most often does not exceed 30 minutes. The procedure is carried out using local anesthesia.
If metastases are detected during the diagnostic process, the treatment process becomes significantly more complicated. In this case, surgery alone is not enough, so additional chemotherapy is prescribed. The essence of the scheme is to remove the focus and slow down the process of metastasis. The prognosis of treatment depends on the stage. The mortality rate of patients with late diagnosis is 55% in the first 5 years. If the lesion is inaccessible, a special hardware removal technique is provided.
Stages of development of pathology: how to distinguish melanoma
There are several stages of pathology development, which depend on the area of the lesion, the depth of penetration into the skin, and the degree of spread of metastases. The following grades of melanoma are distinguished:
- Stage zero is characterized by the tumor being limited to the outer layer of the epidermis. The neoplasm does not spread to other areas.
- The first stage is characterized by the penetration of melanoma into the skin, where it temporarily stops developing.
- The second stage is caused by the growth of the tumor to a large size, which can be expressed.
- The third degree of malignancy, in which the neoplasm can have varying thickness and spread metastases to nearby tissues and lymph nodes.
- The fourth degree is characterized by the spread of the tumor to the internal organs, brain and spinal cord.
Note! At the third and fourth stages of development, melanomas are progressive. They metastasize to other areas of the body.
When should you be wary and consult a doctor to rule out malignancy of the nevus?
- changing the shape of a mole from round to asymmetrical
- rapid growth of moles, sizes more than 6 mm.
- the contours of the mole have become uneven, the edges are “ragged”
- change in color of the mole, it becomes uneven or blue-black
- the surface of the mole has become glossy and shiny
- an ulcer spontaneously appeared on the mole
- loss of hair that previously grew from a mole
- the mole has become dense to the touch
- the appearance of “child” elements around the mole
- feeling of itching in the mole area
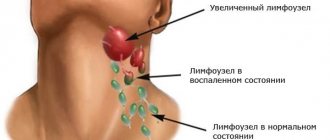
- enlargement of nearby lymph nodes
If you consider yourself at risk, have discovered one of the above signs, or are simply worried about this, make an appointment with a dermato-oncologist. And please never forget to use sunscreen.
Reasons for the development of oncology
Some moles are congenital, others arise during a person’s life under the influence of the following factors:
- hormonal imbalance during pregnancy, menopause, puberty, and when using hormonal drugs;
- the influence of ultraviolet radiation when exposed to sunlight, the use of sunbathing and solariums;
- various damage to the skin.
Exposure to ultraviolet radiation and trauma are common causes of transformation of nevus into melanoma.
There are risk factors that influence the development of pathology:
- genetic and hereditary predisposition;
- strong ultraviolet irradiation, sunburn;
- the presence of more than fifty nevi on the skin.
The presence of several factors increases the risk of developing cancer.
Note! In 40% of cases, the development of melanoma is associated with accidental or intentional trauma to the skin.
Kinds
In principle, all moles can be divided into two large types:
- Pigmented. They arise due to excessive production of melanin in certain areas of the skin.
- Vascular. They appear due to abnormal development or too rapid growth of capillaries (thin blood vessels).
In addition, doctors divide moles into congenital and acquired. The classification of nevi by size is also quite popular; in particular, there are:
- Large and even giant moles (more than 10 cm).
- Medium - no more than 10 mm.
- Small or small - from 0.5 mm to 1.5 mm.
Moles are not divided into categories depending on their location. The fact is that such neoplasms can occur in different parts of the body. They are even found on mucous membranes.
Pigment
There are quite a few varieties of pigmented nevi. Most often, doctors use histological classification to differentiate them. According to it, pigmented moles are:
- Borderline. They are formed by border cells located between the upper and deep layers of the skin. Visually, such moles look like spots with a slightly raised edge. They are characterized by a dark gray or brown color and a diameter of up to 3 mm.
- Epidermal. Such neoplasms are based on epidermal cells. They look like an elevation and have a clearly defined edge.
- Intradermal. Such nevi grow from cells localized deep in the skin. Visually they look like hemispheres, slightly raised above the surface of the epidermis. Painted in dark colors, reaching 1 cm.
- Seborrheic. They look like spots with a rough surface and are flesh-colored.
- Complex. These nevi are based on the deep and superficial layers of the skin. Visually they look like flat tubercles.
- Epithelioid. They are similar in appearance to melanoma, but are not cancer. They are also unable to be reborn.
- Halonevus. Such moles look like a brown spot and are distinguished by the presence of a wide light rim. They can grow or shrink and even disappear, leaving behind a light spot.
- Mongolian spots. Similar neoplasms are recorded in newborns in the area of the buttocks or back. Most often painted blue.
- Blue. Such moles are epidermal; their melanocytes synthesize a bluish-black pigment. Visually, blue nevi look like small nodules.
- Dysplastic. Such nevi are also called Clark's nevi. The neoplasm looks like a single or group growth, is oval or round in shape and has an uneven edge. It is characterized by a red or light color and a diameter of no more than 6 mm. There is a ledge in the central part. A dysplastic nevus, in the presence of a hereditary predisposition, can degenerate into melanoma with a probability of up to 60%, in the absence of a predisposition - up to 20%.
- Papillomatous. Such nevi are considered a type of epidermal nevi. They are characterized by an uneven surface with projections and a brown or pinkish color. Papillomatous nevi are similar to pedunculated papillomas.
- Fibroepithelial. These are quite rare nevi that contain many connective fibers. They are distinguished by softness and elasticity.
- Pink melanocytic nevi. Such moles are more often detected in people with fair skin color and may have a pink or light red color. May be colorless.
- Verrucous. Also known as warty. They look like an elongated dark brown spot. Formed from epidermal cells. Most often they appear in childhood.
Identifying the type of nevus allows you to determine your risk of developing cancer. Some moles require closer monitoring, while others are considered relatively harmless.
Vascular
Vascular nevi have a completely different nature than melanocytic nevi. They arise as a result of the proliferation of cells lining the inner surface of blood vessels, or due to the presence of vascular malformations. Doctors assure that such marks on the body cannot be considered moles in the full sense of the word; rather, the term benign neoplasms is suitable for them. What red nevi on the body may look like:
- Strawberry nevi. This neoplasm looks like a dome over the skin, is oval or round in shape, red in color and has clear boundaries. Strawberry nevus is soft, its surface can be smooth or lobed. Most often, such a neoplasm occurs in newborn babies and grows during the first 4 months of life, and by 5-9 years it disappears without a trace. However, there is a risk of spreading to the subcutaneous tissue and significant increase in size.
- Spider-shaped (stellate) hemangiomas. This tumor is no larger than a match head. Small vessels extend from the red dot, similar to the legs of a spider. Most often, spider-like hemangiomas occur on the face or torso. They appear especially often on the body of pregnant women or patients with chronic liver diseases.
- Capillary senile (cherry) hemangiomas. Such neoplasms can appear in young, mature and old age. They look like bright red flat or raised nodules with a diameter of about 3 mm or more. Capillary hemangiomas can occur in different parts of the body. They are not prone to active growth and usually do not cause any concern to humans.
- Angiokeratomas. Such neoplasms look like dark red keratinized nodules and reach the size of a pinhead. Looks like a wart. Doctors distinguish several types of such neoplasms depending on location, appearance and reasons for their appearance.
Red moles are considered fairly benign neoplasms. The need to remove such marks on the body is considered by the doctor on an individual basis.
Symptoms and signs of melanoma
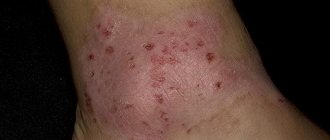
Everyone needs to know what melanoma looks like. The tumor is presented as a dark spot, which rises slightly above the surface of the epidermis. As the tumor grows, it may appear. There are three main symptoms and signs of a mole degenerating into melanoma:
- Dark color.
- Smooth shiny surface, irregular shape.
- Tendency to manifestation and disintegration.
All these signs are caused by the accumulation of melanin in the tumor, skin damage, and the fragility of the tumor. Patients note burning, bleeding, an increase in the size of the nevus, pain, inflammation at the edges of the spot, swelling, peeling and the appearance of crusts and cracks. All this helps to recognize melanoma by appearance.
What types of moles are there?
One person may discover very different tumors. Types of moles are classified according to several criteria. This helps in correct diagnosis in case of changes. They differ in:
- origin – congenital, newly acquired;
- structure – pigmented, vascular;
- place of formation - in depth, on the surface, in the boundary layer;
- raised above the skin - flat - even, protruding as a hemisphere, pedunculated, larger birthmarks;
- potential threats - dangerous, degenerating into melanoma, non-dangerous.
Diagnostics
When examining and interviewing the patient, the dermatologist pays attention to the following points:
- Is nevus congenital or acquired.
- What changes have occurred in the spot.
- Relationship between changes in the structure of the nevus and previous trauma.
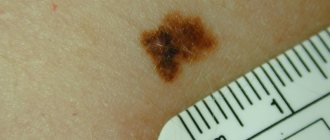
The ABCD technique helps to identify melanoma, which allows you to identify the asymmetry of the tumor, its uneven borders, uneven coloring, and a diameter of more than six millimeters. The doctor may also order additional tests to make an accurate diagnosis.
Note! One of the symptoms of melanoma is its difference from other nevi that are present on the body. Melanoma can appear after accidental or intentional removal of a mole.
Characteristics of melanomas
Melanoma is one of the types of skin cancer. It is she who is called by oncologists “the queen of cancer” for her rapid growth rate and the rate of formation of metastases. It grows under the skin and on its surface in different directions and planes. Once in the inner layers of the dermis, melanoma cells are able to penetrate the bloodstream or lymph, spreading with the bloodstream throughout the body and becoming established in certain organs. This is how metastases (clumps of diseased cells) form and the disease progresses rapidly. Due to the rapid development, the percentage of deaths is quite high.
Among skin cancers, melanoma is the youngest, occurring even in infants and children. The female gender is more susceptible to its manifestation. A birthmark or age spots serve as a base platform, a source for degeneration into melanoma.
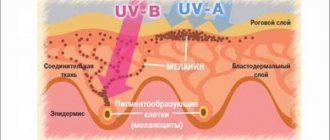
UV rays are considered to be the culprit of skin cancer.
Their influence increases:
- due to the thin ozone layer, the formation of “ozone holes”;
- as a result of people’s high sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation;
- with prolonged exposure to the sun and regular sunbathing;
- with frequent visits to the solarium or hot exotic countries.
Sun exposure and solariums are especially dangerous for people who have many birthmarks on their bodies or a high tendency to pigmentation. You cannot avoid the consequences by covering moles with a band-aid or covering them with a towel: the “greenhouse effect” is harmful, increasing the risk of melanoma.
Sometimes cancer cells form “out of nowhere” for various reasons. On clean, disease-free skin, a dark-colored asymmetrical spot appears, which grows and becomes potentially dangerous. This is usually due to genetic factors and can be traced through the family tree.
What is the difference between a mole and melanoma?
Most often, a person does not monitor the condition of pigmentation or moles that are familiar.
Meanwhile, when a birthmark degenerates, characteristic signs are noticeable:
- changing color to darker;
- lack of uniform color, peeling and loss of clear boundaries of the birthmark;
- redness along the contour of the mole as a result of its inflammation;
- surface growth and compaction;
- formation of dense nodules with signs of necrosis at the base of the nevus;
- irritation of the mole: it itches or there is a burning sensation;
- the formation of cracks and small ulcers, which may result in bleeding.
It is not so difficult to distinguish a nevus from a melanoma if you monitor the condition of the skin. If “metamorphoses” with birthmarks occur, consultation with an oncologist or dermatologist is required. It should be carried out as soon as possible, since the rapid development of melanoma leaves low chances of success.
It is not necessary to look for differences in all of the indicators mentioned. One change, for example, color or shape, is enough for it to become a signal to go to the doctor. An examination is required after visiting hot countries, if the nevus is injured or has significantly darkened.
Types of melanomas
Usually melanoma is a mole in the stage of degeneration.
There are different types of melanomas:
- Lentigo is usually seen in older people on the face or neck, protruding slightly above the surface of the skin.
- Nodular is the most aggressive manifestation of cancer. It is formed by small intertwined nodules that differ in color and volume. Raised above the epidermis and distinguished by shades of dark or purple color.
- Superficial is not much different from a regular birthmark. And since it is difficult to distinguish this type of melanoma, it is the most dangerous because it develops undetected.
- The nail is formed under the nail plate of the big toe. Every 10th melanoma patient has this type of pathology.
In detecting melanoma, the “black sheep” principle applies when one of the moles becomes different from the others in color, shape or other indicators. If an unusual spot is detected, you should undergo a medical examination.
Symptoms and signs of melanoma
How to distinguish malignant growth of cell mass from benign?
There are some signs that answer this question:
- if the nevus is conditionally divided into two parts, then asymmetry is noticeable;
- the birthmark loses its clear boundaries and becomes shapeless;
- the color not only changes, it becomes uneven, interspersed with different shades;
- noticeable rapid growth of the spot and redness at its borders;
- there is a burning and itching sensation.
When a nevus changes, when it begins to differ from a regular mole, the abbreviation ACORD is used (symmetry, edge clarity, color range, size, diameter are examined).
Note: To diagnose melanoma, an examination is carried out once every 3 months. It is advisable to involve another person, since moles are sometimes located in hard-to-reach places on the body. A thorough examination is carried out in the area of the legs, back, and scalp.
Treatment of melanoma
Melanoma is removed using several methods:
- A surgical operation during which a tumor is removed. In frequent cases, healthy tissue is damaged and scarring may occur. This treatment method is the most effective today; it is used to remove dangerous forms of pathology.
- Laser surgery during which the tumor is evaporated, which is localized on the skin of the face and places where strangers can see it.
- Radiosurgery, characterized by the effect of radio rays on a tumor. This method is effective and does not cause injury.
- Cryo-freezing, when the tumor is removed using liquid nitrogen. In this case, scars may appear.
- Electrocoagulation – removal of a tumor with high-frequency currents (cauterization).
Note! Today, doctors most often use surgical removal of a cancerous tumor with the possible use of radiation and chemotherapy.
Melanoma is an extremely malignant skin tumor
Melanoma is an extremely malignant type of skin cancer. Pathology accounts for 1 to 2% of all diagnosed neoplasms in the world. Unfortunately, in recent years, doctors have observed a systematic increase in the incidence of melanoma. Also, people in the age group of 30-50 years are increasingly becoming victims of this disease, which was less common until now.
Every year in Russia more than 2.5 thousand cases of melanoma are diagnosed, of which 3-15% are so-called familial melanomas, inherited in genes. Thanks to genetic tests, melanoma can be detected at an early stage.