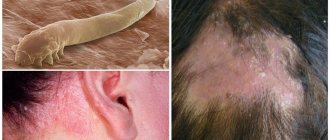
The most dangerous form of skin cancer, which develops rapidly and can metastasize to other organs, is called melanoma; the initial stage of the disease is difficult to diagnose.
And, unfortunately, it very quickly turns into more severe and dangerous ones. The earlier melanoma is diagnosed, the better the prognosis for treatment. Human skin performs a number of important functions: barrier, thermoregulatory, respiratory, metabolic, secretory. Various benign neoplasms may be present on the skin, which can degenerate into malignant ones. Melanoma is considered a dangerous type of cancer, as it develops rapidly and can affect not only the skin, but also the skeletal system, internal organs and the brain.
Usually the disease develops from birthmarks, so it is very important to know what skin cancer looks like in order to be able to identify it in the initial stage. It is during this period that treatment of melanoma can end successfully.
More about the disease
Among all cases of skin cancer, melanoma is diagnosed in only 1-4% of people. However, dermatologists and oncologists around the world are sounding the alarm. Melanoma, which you will be introduced to by the photos in our today's publication, is the most aggressive form of cancer, and the trend towards increased incidence is rapidly growing.
Treatment
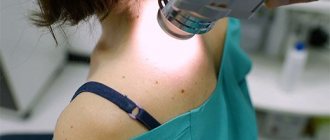
Melanoma is first diagnosed by visual inspection and palpation. Then dermatoscopy is performed, which helps to study the nature of the tumor in more detail, as well as take material from the affected area of skin for further biopsy. Also, research methods such as MRI and CT are used to determine the diagnosis.
After a multidisciplinary diagnosis, oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe treatment according to the severity of the disease. In the early stages, as a rule, complex treatment is prescribed based on the patient’s medical history. Late stage melanoma involves radiation and hormonal therapy, and a course of painkillers is prescribed. Chemotherapy is not used in this case due to the immunity of melanoma to chemotherapy drugs. Surgery after detection of an oncological process is performed quite rarely, as it can lead to metastasis of the lesion to other organs.
To prevent malignancy of a mole, you should undergo regular examinations by a dermatologist. It is recommended to remove not only moles that are suspected of malignancy, but also pigmentation that is prone to frequent trauma or located in places where there is frequent contact with sunlight. There is a list of requirements that must be met during mole removal surgery:
- avoiding direct mechanical trauma to the mole;
- performing surgical incisions exclusively within healthy tissue;
- application of a tourniquet above and below the operated tumor to prevent migration of cancer cells through the bloodstream.
The most common methods for removing moles in the initial stages are:
- destruction with liquid nitrogen - removal of a birthmark by exposure to very low temperatures. The procedure is effective only if the moles are superficial;
- laser vaporization - vaporization of a mole by exposure to a laser beam. It is considered the most effective procedure, it allows you to remove several benign formations at a time, provided the size of the moles is no more than 2 mm;
- electrocoagulation - evaporation of a mole using electric current (the procedure is fraught with relapse of the disease).
When do you need to see a doctor urgently?
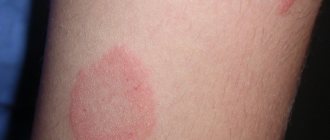
Not all photos allow you to understand which moles are dangerous and cause melanoma. Of the moles already present on the body, a tumor of this type develops only in 30% of all cases. Therefore, the similarity of symptoms with signs of skin melanoma in the photo is not yet a reason for urgent consultation with a specialist. An urgent, high-quality diagnosis is necessary if a pigment spot appears where it used to be, or if a mole begins to bleed, itch, or grow very quickly.
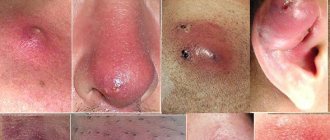
MELANOMA PHOTO
0. The first entry is mine.
Melanoma on the back.
Diagnosis: T2M0N0 - RF. Breslow 0.9 mm. Clark III, 3 mitoses - Israel
Treatment of melanoma. Part I
Melanoma on the hand.
Diagnosis: T1aN0M0. Breslow thickness 0.55 mm.
Treatment of melanoma. Biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes. Review
Melanoma. Photo. Breslow 0.68 mm.
Melanoma and pregnancy
Melanoma on the thigh.
Diagnosis: T3aN0M0 stage 2, Clark 2, Breslow 2 mm.
There is no review for this photo (and whether there will be one is unknown). Photo taken with a dermatoscope. You look at it and see a completely normal mole...
Melanoma on the thigh.
Diagnosis: Clark 3, Breslow invasion 2 mm (after histology revision in Israel, 1.2 mm). In the photo, the result of removal and the prerequisites for further extensive plastic surgery.
Melanoma. Treatment in Israel . May 2014. Review updated January 2021
Melanoma on the foot.
Diagnosis: stage IIa – pT3aN0M0R0, level 5 invasion according to Clark, thickness according to Breslow 4 mm (after revision in Israel 4 according to Clark) . In the photo, melanoma before and after surgery.
Treatment of melanoma in the Russian Federation and Israel. Review. Photo . September 2014 – August 2021
Melanoma on the shoulder. Photo.
Diagnosis: T3bN0(0/7)M0, Breslow 3.9, with focal ulceration.
Treatment of melanoma. Keytruda. Story. Photos. Prices.
Metastasis of melanoma in the groin area without an identified primary lesion TxN2M1.
Photo.
But in this photo there is just a nevus.
There was a suspicion that it was melanoma, but histological examination showed the opposite:
Melanoma on the thigh. Series of photos.
Diagnosis: 0.75 mm, level 2 according to Clark. Number of mitoses: 4 / sq. mm.
Treatment in Israel. Melanoma. Sentinel lymph node biopsy
Melanoma on the neck.
Diagnosis: Nodular melanoma, 6 mm, pt4a, level of invasion according to Clark - IV, without ulceration, everything is clear in the margins, 6 mitoses per 1 mm.
Treatment of melanoma in Israel. Biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes. Review. Prices. Photo.
Melanoma of the abdomen.
Diagnosis: Melanoma, 1.8 mm, 4 levels according to Clark, 9 mitoses per sq/mm.
This case is also associated with the patient’s pregnancy. Treatment in Israel. Biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes. Review
Melanoma on the hand.
Diagnosis : Nodular melanoma T2aN0M0,st.1b , which after a trip to Israel turned into T3aN1aM0 , because metastasis was discovered in the sentinel lymph node.
Treatment of melanoma in Israel. Biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes. Review.
Mixed pigmented nevus
But this neoplasm in the photo turned out to be not melanoma , but it turned out that it was a mixed pigmented nevus with grade 2 lentiginous melanocytic dysplasia. in combination with intradermal abscess.
Melanoma on the chest.
Thickness 7 mm. Mitotic index 8 mitoses per sq/mm. Sentinel biopsy was performed. A metastasis of 0.9 mm was detected.
Treatment of melanoma in Israel. Review. Prices. Photo
Melanoma on the shoulder
with a diagnosis of Melanoma of the skin of the left deltoid region T2aN0M0 stage IIA. Histological conclusion: Melanoma without ulceration 2 mm, II level of invasion according to Clark, without signs of agnio- and perineural invasion. Pronounced number of tumor-associated lymphocytes.
Melanoma on the back
with a diagnosis of Nodular melanoma of the skin, Breslow thickness 4.25, level 4 invasion, 11 mitoses. A concomitant disease is hemophilia. There is no photo of the mole. Only the results of the operation.
Treatment of melanoma in Israel. Story. + photos of results
Not melanoma, but a mixed nevus with an area of desmoplastic blue nevus
Such things need to be removed, because you can easily miss “that very moment”
Asymmetric nevus. How to avoid getting treatment in Israel
Not melanoma yet. Nevus on the eyelid 1.5 x 3 cm. Removal and plastic surgery in Israel
Interesting review and result of the operation
Treatment in Israel. Mole removal. Review
Melanoma on the shoulder with signs of regression. Photo.
Review of treatment in Israel. When performing a biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes, three sentinel lymph nodes were identified. All are clean.
Amelanotic melanoma
2 mm Breslow (originally 4 mm), Clark III. A sentinel lymph node biopsy was performed. Operated by Professor Chaim Gutman
Treatment of melanoma. Latvia-Israel. Photo of non-pigmented melanoma
Pigmentless melanoma blue nevus on the hand. Photo
Amelanotic melanoma or not? Histological epic
Melanoma. Breslow 0.5, Clark 2, no ulceration, 1 mitosis. Photo
A very interesting story from a propaganda point of view (even unique, I would say).
Melanoma and pregnancy. Another story
Melanoma on the shoulder. Photo. Breslow 4.5, Clark 4, 1 mitosis.
A story about the treatment will appear later. Quote “She was a little paler and not as prominent, she turned red after we did cytology at the hospital. There was no mole or anything else in this place. It looked more like a pale pimple." History of treatment in Israel here
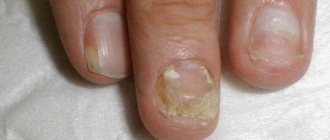
Subungual melanoma. Breslow 7, Clark III, Photo
About how melanoma was discovered, how it was treated and what is happening today. About standard errors of histology and so on, and so on, and so on.
Subungual melanoma (photo). History, 3 surgery, histology, adjuvant therapy
Subungual melanoma (photo of the beginning and result of the operation). Breslow 1.25, Clark IV.
Subungual melanoma. Identification, development, result. Photo
Amelanotic melanoma on the toe. Photo
May 2017
Two dermatologists prescribed two different ointments, and now it looks like this (October 2017).
27 Melanoma was suspected, but it turned out to be: Combined papillomatous nevus with focal lentiginous melanocytic dysplasia grade 1.
28 Melanoma and dermatofibroma. Photo. It is very clearly shown that on your own you will not be able to distinguish a malignant neoplasm from a benign one.
Photo of melanoma on the back. Breslow 0.6 without mitoses.
Sentinel lymph node biopsy is not indicated. History: Treatment in Israel. Mole removal
Unusual melanoma. In the photo it looks like a wen, but in reality:
Mixed desmoplastic melanoma without mitosis with a typical epithelioid component 5 mitoses/mm2, Clark grade V, Breslow thickness - 7 mm.
History: Rare melanoma or history of one wen
Melanoma on the knee. Long story, lots of photos.
Melanoma, thickness 0.8, Clark III. A sentinel lymph node biopsy was performed. No metastases were found.
History: Treatment of melanoma in Israel
They suspected a keratoma, but it turned out to be squamous cell skin cancer. Photo.
Keratoma, or the story of one pimple. About how important it is to do a histological examination.
Photo of melanoma in situ
Review of treatment in Israel. Rather, it’s not even about treatment, but about adventure.
Melanoma on the leg. Photo. Breslow 22 mm, Clark V.
Treatment of melanoma in Russia. 4 stories
34A. Melanoma on the lower back. Photo. Histology
Breslow 1 mm, Clark III. Description in the post for photo No. 34
A melanoma cell detected in a lymph node. Photo.
Breslow 4 mm, Clark III. Treatment in Israel. One melanoma cell, or why biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes
Photo of melanoma on the buttock.
Brelow 0.7 mm, Clark III invasion. There are no mitoses, no ulceration, and no perineural or intravascular invasion. Melanoma. And again histology
Photos of blocks and glass. This is what melanoma looks like prepared for histological examination
Photo of malignant melanoma on the back
Malignant melanoma arising in a nevus with severe dysplasia. Radial growth phase. Breslow 0.12 mm, Clark II. - this is already the result of a revision in Israel. Diagnosis in Kyiv - Breslow 0.35 mm Clark II.
Melanoma on the shoulder. Photo.
It grew for 36 years and became more active after the patient had an accident and broke it. Melanoma, or the history of the evolution of a mole
Squamous cell skin cancer. Photo.
At first glance, this is the most melanoma. But first impressions are deceiving. This is squamous cell skin cancer (squamous cell carcinoma). Histologically confirmed
Photo of melanoma with strange histology
Melanoma, superficial spreading form, Clarke invasion I.
When reviewing histology in Moscow, it turned out that this is a borderline spindle cell nevus of Reed
Melanoma metastasis. Photo.
The result of a biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes not performed on time. /vse/nabolelo/melanoma-istorii/melanoma-recidiv-v-limfouzly-klinicheskij-sluchaj/
Melanoma is not on the back. Photo
Pigmented epithelioid cell melanoma without ulceration. Breslow less than 1 mm, Clark III, 3-4 mitoses per sq/mm.
Melanoma on the ankle. Photo
Breslow 0.6 mm, Clark IV, two mitoses per sq. mm.
Photo of melanoma on the wrist
Breslow 1.5 mm, Clark II, radial growth phase, 1 mitosis per sq mm
Melanoma on the skin of the chest on the right. Photo
Histology (end of 2021). Nodular melanoma with ulceration, with invasion into the papillary reticular layer of the dermis according to Clark. Breslow thickness is not included in the document.
Melanoma on the ear (on the pinna). Photo
Removal of melanoma and biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes in Israel. Breslow thickness 0.65. Treatment of melanoma in Israel review . First review of 2021
Melanoma. Metastasis to the postoperative scar. Photo
Result of cessation of targeted therapy (Tafinlar + Mekinist)
Melanoma on the temple (temporal region). Photo
Photo of the melanoma itself and the scar from the initial excision. Home histology: 0.7 Breslow, II Clark, no ulceration or mitosis. Revision in Israel 0.8 Breslow and III-IV Clark.
Melanoma on the temple. Treatment in Israel
Melanoma. Subcutaneous metastases of melanoma. Photo
A mole was removed without histology. The results are in the photo and in a short story
I thought it was melanoma, but it turned out to be a blue nevus. Photo
Combined two-component melanocytic nevus of the skin of the left hand, represented by an association of a blue nevus and a complex functional-dermal nevus.
Melanoma on the abdomen. Photo
Melanoma on the right side of the abdomen. Breslow thickness 0.8 mm, Clark III. There are no mitoses or ulcerations.
Diagnostics
Melanoma is diagnosed by a dermatologist and oncologist using a special magnifying glass and sometimes additional broad-spectrum diagnostic tools. For dynamic monitoring, the doctor takes a photo of what the melanoma looks like and, along with all the characteristics, including size, enters it into the patient’s personal medical history.
Forecast for life
The prognosis for melanoma depends on the time of detection and the degree of tumor progression. When detected early, most melanomas respond well to treatment.
Melanoma that has grown deeply or has spread to the lymph nodes increases the risk of recurrence after treatment. If the depth of the lesion exceeds 4 mm or there is a lesion in the lymph node, then there is a high probability of metastasis to other organs and tissues. When secondary lesions appear (stages 3 and 4), treatment of melanoma becomes ineffective.
- Survival rates for melanoma vary widely depending on the stage of the disease and the treatment provided. In the initial stage, cure is most likely. Also, cure can occur in almost all cases of stage 2 melanoma. Patients treated in the first stage have a 95 percent five-year survival rate and 88 percent ten-year survival rate. For the second stage, these figures are 79% and 64%, respectively.
- In stages 3 and 4, the cancer has spread to distant organs, resulting in a significantly reduced survival rate. The five-year survival rate of patients with stage 3 melanoma ranges (according to various sources) from 29% to 69%. Ten-year survival is achieved in only 15 percent of patients. If the disease has progressed to stage 4, then the chance of five-year survival is reduced to 7-19%. There are no 10-year survival statistics for patients with stage 4.
The risk of melanoma recurrence increases in patients with a large tumor thickness, as well as in the presence of ulcerations of melanoma and nearby metastatic skin lesions. Recurrent melanoma can occur either in close proximity to the previous site or at a considerable distance from it.
Cancer prevention
In the photo above you could see melanomas of various types - nodular, superficial spreading, lentigo. Any tumor of this type is a consequence of exposure to excessive amounts of ultraviolet radiation. Protect your skin from the sun, avoid tanning beds, and the chances of developing the disease will be close
WE RECOMMEND YOU TO WATCH:
Relapse
Most relapses of melanoma occur when the primary cancerous tumor is significantly thick. Subtle malignant neoplasms are less likely to lead to the return of the disease. Causes:
- local recurrent lesion;
- inflammatory process in the lymph nodes;
- distant metastases.
Provoking factors include:
- weakened immune system;
- patient's age;
- poor-quality surgery to remove the primary tumor.
The vast majority of relapses appear after several years (7–10). They are rarely shown before 32 months. In exceptional cases earlier.
What to do if melanoma recurs?
The appearance of any symptoms of local relapse is a reason to resume treatment. Depending on the area of occurrence, volume and pathology of metastasis, as well as the age and health of the patient, the doctor prescribes a treatment method. Surgery is highly effective in removing a tumor. In this case, both the tumor itself and the tissue surrounding it in the range of 5−7 cm are excised (the coverage area depends on the size of the formation). Additional methods that can stop the growth, suppress or destroy cancer formations are:
- chemotherapy;
- x-ray radiation;
- radioimmune therapy;
- immunotherapy.
The first three methods are combined with surgical excision and enhance the destruction of metastases. The course of application depends on the degree of development and chronicity of the disease. Immunotherapy helps in maintaining the body’s protective function to independently fight cancer and resist other negative consequences. Synthetic medications and special equipment are used to carry out such treatment methods.
To reduce the risk of melanoma reoccurring, patients should undergo regular medical examinations. The scar should be constantly examined by a surgeon or oncologist. In addition, specialists interview the patient to obtain information regarding the presence of any manifestations and sensations.
These diagnostic measures should be carried out regardless of the presence or absence of clinical signs. Since most patients are at increased risk of relapse, systematic monitoring by the attending physician is required to prevent the appearance of a secondary formation.
Main symptoms of the disease
The appearance of metastases in the human body is observed after cancer cells penetrate the circulatory system, the following symptoms appear:
- open wounds and ulcers form in the affected area;
- the skin becomes gray;
- bumps appear under the skin;
- lymph nodes increase in size;
- the person begins to cough frequently;
- migraines appear;
- There is a sharp weight loss.
Diagnostic measures
If a dark spot occurs, you should contact a specialist who will conduct an examination and determine the severity of the manifestation.
If a person suspects that melanoma has developed under the nail, it is important to go to the hospital as soon as possible. The doctor will conduct a survey of the patient, during which they will find out how long ago the dark mark on the nail appeared and whether the patient is worried about additional signs
Then the doctor resorts to dermatoscopy, during which the doctor examines the neoplasm using a magnifying glass
In this case, the specialist pays attention to the uneven borders of the tumor, asymmetrical shape and heterogeneous shade. If the entire melanoma is located directly under the nail plate, this complicates the diagnostic process
To confirm the preliminary diagnosis, a biopsy of the affected tissue is performed, after which a histological examination begins. In addition to the nail tissue, examination of the lymph nodes may sometimes be necessary. To confirm or refute metastasis, the patient is sent for an ultrasound or computed tomography scan of the internal organs.
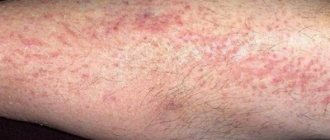
Reasons for development
The main cause of malignant degeneration of melanocytes is considered to be ultraviolet irradiation , both natural and artificial. Melanin is a substance that is “responsible” for the color of human eyes, hair and skin. The production of melanin is closely related to the action of UV rays and the functioning of the hormonal system.
The normal process of melanocyte division is disrupted by:
- intense UV irradiation,
- hormonal changes in the body due to illness or natural causes (pregnancy, menopause),
- immunodeficiency states . Melanoma does not provoke an adequate immune response in the patient's body. Low immune status facilitates the development of malignant tumors;
- injury to nevi.
Note! For the occurrence of melanoma, it is not the frequency or duration of exposure to the sun that is critical, but the intensity of insolation. Even a single burn of the skin in childhood can initiate a malignant process in an adult under certain conditions.
Risk factors for developing melanoma
- Hereditary predisposition . Melanoma is inherited by close relatives in a dominant manner. If there have been cases of skin cancer in your family, then you are at risk;
- The presence of a large number of moles or birthmarks;
- Bright skin;
- Nevi in places that are subject to regular mechanical stress (squeezed, rubbed, crushed);
- History of sunburn
Note! The exact reason why a malfunction in the DNA of melanocytes occurs cannot be determined. It is believed that a combination of several unfavorable factors leads to malignant processes.
Photo 2. The appearance of melanoma is primarily associated with increased UV radiation. Source: Flickr (Fábio Petry).
Complications and consequences
Although melanoma is a lesion of pigment cells, it can spread to other tissues or even organs. This process is called metastasis.
Complications of melanoma appear gradually. First, it spreads hematogenously throughout the human body. Through blood vessels, affected cells can travel anywhere from the brain to the liver or even bones. Another route of spread may be the lymphatic system. In this case, the lymph nodes are at risk.
Surprisingly, despite these complications of melanoma, which, in general, are known to many, there are still very often attempts to carry out treatment on their own.
⛔