Atheroma is an epidermal cyst, which is a spherical formation. Appears due to blockage of the sebaceous gland duct. The disease was assigned the ICD-10 code “170.9”. A cavity under the skin occurs in different places, for example, atheroma behind the ear is not uncommon. Most often it is purely an aesthetic problem, but it can also be complicated by purulent inflammation. That is why, if such a growth is detected, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist or surgeon and, if necessary, remove the tumor.
Appearance, location and symptoms
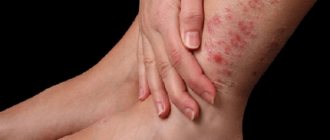
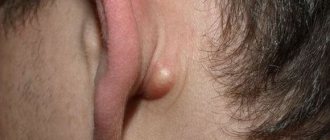
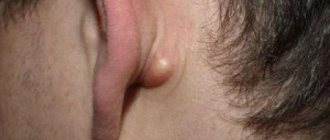
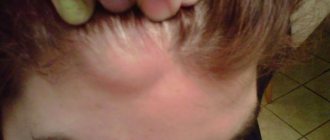
Externally, atheroma of the postauricular area resembles a rounded lump with clear contours measuring 5-40 mm. It is formed when the sebaceous gland is blocked. In the blocked duct of the gland, a small cyst first forms, which is gradually filled with fat and dead epidermal cells, which is why it enlarges. The contents of the cyst resemble a white or yellowish cheesy mass. Over time, the tumor may become inflamed, and then additional symptoms are observed:
- pain when palpating;
- swelling and redness of the skin;
- hardness of subcutaneous atheroma;
- purulent discharge;
- burning, itching behind the ear.
In addition to the space behind the ears, such defects are often localized on the earlobes and in the upper part of the ears. In this case, upon visual inspection, a dense ball hanging from the lobe or from the auricle is noticeable. Atheroma of the lobe is no different from behind the ear - it can also become inflamed and grow, causing the following symptoms: pain, redness of the skin, swelling, itching, burning. It is extremely rare that such defects are found in the ear canal or deeper in the ear.
Possible complications
If atheroma of the lobe develops for a long time without proper treatment, it can become infected, during which pain occurs, and the skin in the affected area darkens. Gradually suppuration occurs, resulting in the development of an abscess. In this case, timely elimination of the cyst is very important, otherwise the infection can penetrate the circulatory system and the entire body becomes infected.
We recommend reading Hemangioma in newborns - types, treatment, diagnosis
Complications such as inflammation of atheroma can lead to very significant consequences, even death. If such a neoplasm of the skin of the ear occurs, you cannot delay treatment, but you should immediately seek medical help. Only timely and adequate therapy will help prevent such complications and maintain your health. A small atheroma can be eliminated in one session by a surgeon, without leaving any marks or scars on the affected area.
Causes
The main cause of atheroma is the inability to remove lipoid substances from the sebaceous gland due to its sealing. Such cysts form more often in people prone to sweating, acne and seborrhea.
Also, atheroma of the auricle is often provoked by piercing the ears (piercing) with a low-quality instrument in unsterile conditions.
Additional factors that provoke the growth of atheromas are:
- poor hygiene (then the sebaceous gland duct may become clogged with dirt);
- hormonal imbalances;
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- skin injuries;
- hyperhidrosis (pathological excessive sweating);
- negative influence of surrounding environmental factors;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- genetic predisposition.
Atheroma in a child’s ear can form due to a sharp decrease in immunity due to acute and chronic infections.
Prevention
Surgical intervention does not cause pain in the patient, but it is important to eliminate the causes of the pathology after its completion. Without this, the likelihood of subsequent relapses is high.
Experts recommend spending time on prevention:
- maintain personal hygiene;
- promptly replace and wash linen;
- eliminate factors that provoke excessive sweating;
- cleanse the skin in a timely manner using scrubs, masks, peeling;
- purchase only high-quality cosmetic products;
- get rid of problems that cause metabolic disorders.
To eliminate the possibility of relapse, you should follow your doctor's recommendations. An important condition for the effectiveness of treatment is the timeliness of seeking medical help. But you shouldn’t self-medicate.
No similar articles found.
Health risks
Atheroma itself cannot harm health, unless it greatly increases in size and becomes noticeably noticeable, but only if it does not become inflamed and does not fester. Suppuration is possible when infected with bacteria. In this case, the growth turns red, enlarges, hurts, and itches. Purulent inflammation can spread further to adjacent tissues of the parotid region and provoke sepsis - a general infection of the body by microbes that have entered the bloodstream.
Due to suppuration of an ear cyst in a child or an adult, when it turns into an abscess, a fatty phlegmon can form. It often connects to the blood vessels that supply the brain with blood and can introduce an infection into the bloodstream that quickly travels directly to the brain. Purulent inflammation of the brain can be fatal.
It is extremely rare that atheromas on the ears degenerate into malignant tumors. Much more often they cause hearing impairment, especially when atheroma is observed in the auricle. This is why it is so important to go to the hospital to see a surgeon and dermatologist immediately when atheroma is detected.
Diagnostics
If skin formations are detected on the earlobe or in the auricle, the diagnosis of atheroma is carried out by a dermatologist or surgeon. First of all, the doctor conducts an external examination, determines the exact location and size of the tumor.
To confirm the diagnosis, patients are prescribed additional tests:
- ultrasonography;
- x-ray of the skull;
- audiometry - measurement of hearing sensitivity to sound waves of different frequencies;
- a smear from the auricle with further cytological examination;
- otoscopy of the ear.
Treatment methods for ear cysts are determined only after receiving the results of all studies performed. In most cases, patients undergo surgery to remove the tumor. When diagnosing atheroma of the auricle, therapy should begin without delay, otherwise this disease can lead to serious hearing impairment.
How are epidermal cysts differentiated?
At the hospital, a specialist will first conduct a diagnosis. He will examine and palpate the neoplasm behind the ear, try to find the excretory duct to make sure that it is atheroma of the ear, or rather, to differentiate it from other diseases:
- furuncle;
- lymphadenitis;
- lipoma
If the doctor cannot diagnose atheroma by appearance, then he will refer you for additional tests, namely a histological examination of the contents of the tumor. Only after confirmation of the diagnosis is treatment prescribed.
Advantages of visiting our clinic
If you need removal of atheroma using the radio wave method in a clinic in St. Petersburg, then you can safely contact us. Our clinic employs highly qualified specialists with extensive experience who can competently diagnose and prescribe effective treatment. During their work, our ENT doctors use the most modern equipment to treat atheroma. We try to find an individual approach to each patient in order to take into account the characteristics of his body as much as possible. Our center employs highly qualified surgeons who can successfully remove atheromas without the risk of relapse. So, by contacting us, you can enjoy the following benefits:
- Consultation with a doctor with extensive experience.
- Competent diagnostics.
- Correct prescription of treatment.
- Treatment of atheroma is carried out using the most advanced technologies and modern equipment.
- Individual approach to each client and polite treatment.
- Favorable prices.
In addition, our center also employs pediatric ENT doctors , during whose appointments your children will not be afraid. You can find out more detailed information about how atheroma is removed using the radio wave method, prices and much more by contacting our employees by phone.
How to treat ear atheroma
The main method of treating atheroma is its surgical removal. If it is inflamed, then before the operation the doctor may prescribe medications to eliminate the inflammatory process.
At home, many people prefer to treat atheroma on the ear with folk remedies, but this is not the best option, since traditional therapy, if used incorrectly, will not correct the situation, but will only do harm.
It is better not to experiment and coordinate any of your actions with your doctor, even if you want to try folk remedies.
Local preparations
Treatment of earlobe atheroma when it is inflamed is carried out primarily with folk remedies and medications for external use. Systemic medications (tablets and injection solutions) are prescribed only in advanced cases. Effective local medications for the treatment of atheroma are:
- Ichthyol ointment;
- ammonia;
- Vishnevsky ointment;
- antimicrobial ointments Levomycetin, Tetracycline.
You need to treat the tumor with ointments 3-5 times a day, and make lotions with ammonia as follows: moisten cotton wool generously, apply it to the sore spot of the ear, wrap it with a warm cloth on top, and hold it for as long as possible.
Among the folk remedies to get rid of atheroma in the ear, you can try:
- Compress from coltsfoot. Tape a few fresh leaves to your ear and keep it there overnight. Repeat the procedure until the inflammation stops.
- A compress made from a film that lines the inside of chicken egg shells. Carefully separate the film from the shell and apply it to the tumor. When it dries out, change it.
- Fat ointment. Melt the lamb fat, cool and smear the tumor 6-8 times a day.
- Garlic compress. Grind a head of garlic, mix with vegetable oil (2 tablespoons), rub the product into the tumor three times a day.
Conservative treatment methods will relieve inflammation, but will not be able to remove atheroma completely, since the sebaceous gland cyst is prone to recurrence - it grows again in the same place. To get rid of atheroma forever, you will have to remove it surgically.
Radical removal methods
Removal of atheroma on the ear is carried out in three ways:
- standard surgical way - using a scalpel;
- laser;
- radio waves.
Standard surgery is the most affordable option. Under local anesthesia, the skin is cut and the contents of the atheroma are removed, then the cavity is treated with special antimicrobial drugs and sutured. When removing small tumors, sutures are usually not applied, since the cysts are elastic, so they can be reached even through a small hole.
Laser therapy is used to remove only small atheromas on the ears and consists of evaporating the tumor, namely the capsule along with its contents, and cauterizing its bed. Thanks to this, relapses are prevented. The operation is quick, painless, minimally traumatic, and leaves no traces. The laser immediately seals the blood vessels, so there is no bleeding after surgery. The rehabilitation period lasts no more than a week, after which the patient can begin normal life. The only drawback of this treatment method is the high cost: 6,000-20,000 rubles. for the operation.
Radio wave therapy has a similar effect, only a radio knife is used instead of a laser. During the operation, the contents and membrane of the cyst are destroyed by radio waves. This procedure is more affordable than laser; its price starts from 2000 rubles. Its disadvantages are contraindications: the presence of pacemakers or prostheses in the body. The advantages of this method are the same as the previous one: no blood, no scars, quick recovery, painlessness, almost 100% guarantee of no relapse.
How to relieve inflammation of atheroma at home
Inflammation of the sebaceous gland in the ear can be relieved with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with local and general action. For this purpose the following are usually used:
- Nimesulide;
- Paracetamol;
- Ibuprofen;
- Diclofenac.
But it is better to immediately go to the hospital if the cyst becomes inflamed for a full examination and individual therapy. Self-treatment at home can only make things worse: the symptoms will be muffled, but the inflammatory process will not stop and will turn into purulent inflammation.
Symptoms of pathology
Epidermoid cysts and atheromas have similar clinical manifestations. often called primary atheromas . Unlike tumors of the ear canal, postauricular cysts that have grown up to 5 mm or more are easier to notice due to the following signs:
- the spherical bulge is mobile and absolutely painless (which distinguishes it from boils and other inflammatory processes in the subcutaneous layers);
- the surface of the skin is smooth, without any changes (redness or vascular network);
- the contents of the capsule can be visible through the skin - a yellowish or grayish tint;
- The cystic cavity is elastic to the touch, of moderate density.
Cysts behind the ear can reach 2–5 cm and are prone to aseptic (without the formation of pus) and purulent inflammation.
If pathogenic flora penetrates into the cavity through the bloodstream or due to external damage, inflammation develops with the formation of purulent contents. This process is accompanied by:
- significant redness and swelling (the cyst increases sharply in size);
- throbbing pain and itching;
- local increase in temperature (in the ear area).
With low immunity, spread of inflammation to the lymph nodes or prolonged ignoring of signs of suppuration, the general condition worsens - the temperature rises, weakness and headache appear, nausea and vomiting are possible.
Next, there are two possible options:
- the cyst opens on its own - then, at best, it scars, at worst, the cavity becomes re-infected, now only from the outside, and a non-healing wound appears at the site of the cyst;
- the cavity is not opened , its contents are replaced by dense fibrous tissue (the nature of the tumor changes).
Both cases will require surgery.
Tumor-like neoplasms in rare cases can create the basis for benign or malignant tumors.
Treatment prognosis and likelihood of relapse
Atheroma behind the ear and in other places is prone to relapses, but with the right approach to treatment they are almost 100% preventable. Fragments of the cyst can provoke a relapse (the reappearance of similar structures in the same place) if they remain inside when it is removed. The likelihood of relapses also depends on the patient, who must follow preventive recommendations to prevent them:
- cure concomitant diseases (chronic, thyroid pathologies affecting hormonal levels, dermatological, etc.);
- follow a diet - more vegetables, less fat, flour, sweets, completely eliminate alcohol, soda, chemical products;
- strengthen the immune system (lead an active lifestyle, toughen up, take vitamins);
- Maintain hygiene and keep your body clean at all times.
Only by following these recommendations will it be possible to avoid cyst recurrence and further negative consequences.
Description
The shape of the formation is oval or round. Sizes range from pea to fist size. Atheroma can protrude sharply above the surface of the skin or be immersed in the subcutaneous tissue. Tactilely, it is most often soft and elastic. Formations of dense consistency are less common. Occurs in both children and adults. It often appears in newborns and infants up to one year old, most often on the head.
The cyst shell is connective tissue lined with epithelium. Inside the capsule there is a white curd-like mass consisting of cholesterol, fat, detritus, and horn cells of the epidermis. When infected, the color of the contents changes from white to brown, and there may be an admixture of blood.
Atheroma grows slowly, over the years, and can be either single or multiple. Location: any part of the body with growing hair, most often the skin of the face (usually below the mouth), head, neck, back, intimate area, nipple.
Epidermal cysts are characterized by secondary changes - calcification, suppuration, malignancy (malignancy). When suppuration occurs, hyperemia, pain, swelling occurs, an increase in temperature, both local and general, is possible, and it is possible that the contents of the capsule may burst out.
The sebaceous gland is an organ located in the epidermis of animals and secretes a secretion (sebum), the main function of which is to protect the skin from microbes. Sebaceous glands are found on almost the entire surface of the human body with the exception of the palms and soles. Atheroma can occur anywhere. But more often it appears in places where sebaceous glands are most concentrated - on the cheeks, chin, scalp, behind the ear.