Separation of the nail from the nail bed on the foot is a pathology that may indicate a bacterial, viral or fungal infection. Most often this happens when hygiene rules are not followed after visiting public places with high humidity. In addition, detachment can begin due to severe vitamin deficiency, chronic diseases of internal organs and after nail injuries. You can get rid of this problem with the help of medications and folk remedies.
Why does the nail move away from the nail bed on the foot?
If the nail moves away from the nail bed on the foot, then this phenomenon in medicine is called onycholysis. This disease is one of the most common types of nail dystrophy. It is based on a lack of oxygen supply to the tissues, and the degree of destruction of the nail depends on the severity of this process. Onycholysis can affect one nail plate or several. It can be triggered by infectious and non-infectious factors. The last of them include:
- injury or compression of the nail plate;
- contact with household chemicals and aggressive substances;
- use of low-quality varnishes and other coatings.
Onycholysis can result from prolonged contact with water, detergents, alkalis, solvents and bleaches. This disease can be caused by artificial nails, the use of low-quality gel polish, acrylic or shellac, which contain formaldehyde. Abuse of manicure and use of sharp objects is also one of the reasons for nail detachment.
Some endogenous processes can cause disturbances in the supply of nutrients to the nail plate. The main ones are:
- taking tetracycline antibiotics and fluoroquinolones;
- chronic diseases of the cardiovascular, digestive and nervous systems;
- avitaminosis;
- dermatological diseases - eczema, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, lichen planus.
Often, deformation, splitting and peeling of toenails indicates that the body lacks vitamin A, E and B2. This pathology may indicate a lack of iron in the body and iron deficiency anemia. With diseases such as atherosclerosis, varicose veins, Raynaud's disease, flat feet, problems with the nail plates are possible.
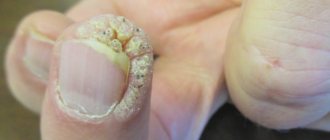
The main and most common cause of onycholysis is infection with a dermatophyte fungus. Infection with streptococci and staphylococci can lead to the problem of peeling nails, but then a pronounced inflammatory process is observed. Most often, onycholysis is found on the big toe; with fungus, the spread of infection begins from the little toe.
Other diseases
If detachment of the nail plate on the fingers is a consequence of the development of a general disease, it is important to undergo extensive diagnostics, find out the diagnosis and complete the full course of treatment prescribed by a specialized doctor.
There is no point in using local therapy without treating the underlying disease.
When a fingernail begins to peel off after antibiotic therapy, it is first important to restore the intestinal microflora.
This therapeutic tactic will improve the absorption of micronutrients that are actively involved in the growth of nail plates.
Treatment methods
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to establish the true cause of nail detachment, and only a dermatologist can do this. It is mandatory to take a test to detect a fungal infection, since it is the main cause of onycholysis. If the test results are negative, and the doctor cannot make an accurate diagnosis, then a full examination of the patient is carried out to identify the disease that could cause the detachment of the nail plates.
If onycholysis is a consequence of a somatic disease, then an examination by a specialized specialist is required, who will select an individual course of treatment. After eliminating the root cause of this pathology, the condition of the nail plates will return to normal. If onycholysis occurs due to antibacterial therapy, all efforts must be directed toward restoring the intestinal microflora.
Nail detachment caused by injury is most responsive to treatment. The treatment method depends on the degree of damage to the nail. In the marginal variant of the disease, as the nail grows, carefully cut it off and protect the fingers from any injury. To eliminate the risk of infection, an antibacterial patch is applied to the nail. If the affected area is large, it may be necessary to remove the nail plate surgically, apply a bandage, and use antibacterial agents.
If a hematoma forms under the nail, treatment tactics will depend on its size. If it is small in size, no additional action is required. A large hematoma must be removed as a blood clot will interfere with therapy.
When a fungus is detected, treatment includes taking antimycotics for internal and external use, which are selected on a strictly individual basis. Fungus therapy is long-term and can last up to a year. For bacterial infections, antibiotics are indicated. Eczema and psoriasis require treatment with corticosteroids. If the cause is an allergy, immunotherapy is prescribed.
As a restorative therapy, a gelatin solution is used: 1 tablespoon up to 5 times a day for 3 months. Additionally, medications containing iron, calcium and vitamin complexes are prescribed. Every day, to enhance blood circulation, you need to carefully massage your fingers at home, with special emphasis on your nails. Movements should be as careful and soft as possible.
Drug therapy
The choice of drugs depends on the diagnosis. If the nail plates break or peel off due to a fungal infection, the treatment will be long and complex. The therapy will necessarily include drugs for external and internal use. The most effective are the following tablets:
- Ketoconazole.
- Terbinafine.
- Fluconazole.
- Griseofulvin.
The specific dosage and duration of treatment is prescribed only by a mycologist - a doctor specializing in fungal diseases. Many antimycotics have a large number of contraindications and are prohibited for children and pregnant women. Local medications are used up to 4 times a day for several months every day. These include:
- Mikospor.
- Loceril.
- Itraconazole
- Ketoconazole.
- Batrafen.
- Lamisil.
- Amorolfine.
Exoderil is most effective against fungal infections. The drug is available in the form of a solution or cream. It is applied 2 times a day, and the duration of treatment depends on the speed of recovery of the nail plate.
For streptococcal or staphylococcal infections, heliomycin ointment or syntomycin emulsion is used. These drugs are applied to the bed at the site of nail detachment and to the skin 2 times a day. For bacterial infections, Vishnevsky ointment and Levomekol, which contain castor oil, xeroform and tar, are effective. They are recommended to be used in the form of compresses, which are applied for several hours.
For onycholysis, Solcoseryl ointment is often used, which improves blood circulation and has regenerating, membrane-stabilizing and antihypoxic properties. During treatment, the affected nail is cut off as it grows back.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies is effective only if the disease is not caused by a bacterial or fungal infection. Olive oil is helpful for onycholysis. To do this, add a couple of drops of lemon juice to a tablespoon of oil, apply the mixture to your nails before bed, let it absorb and put on socks. The procedure is performed 1-2 times a week. You can replace olive oil with tea, sea buckthorn or castor oil.
For peeling nails, special medicinal baths that can be done at home are useful. To prepare them, use a solution of soda, potassium permanganate or table salt. Therapeutic baths can be made using medications - a solution of thymol (1-2%) and chrysarobin. After such procedures, the feet are dried and ointment or cream is applied. The duration of use of the baths is from 4 weeks.
Gelatin baths have a strengthening effect. To prepare them, pour 1 tablespoon of gelatin with water and leave for 40 minutes. After this, the solution is placed on low heat until the gelatin is completely dissolved and cooled. Nails are immersed in the bath for 15 minutes.
Baths based on chamomile and pine needles are effective. To do this, add 1 tablespoon of dried plants to a glass of boiling water, let them brew for half an hour, then filter. The resulting decoction is diluted with boiled water in a 1:1 ratio. Keep your feet in this bath for 30 minutes.
To strengthen nails, use a solution of 60 ml of water, a tablespoon of salt and the juice of one orange, 5 drops of iodine. You need to keep your fingers in the specified mixture for at least 15 minutes. Kombucha gruel has similar properties. To prepare it, the mushroom is peeled from the film and crushed, after which it is applied to the affected areas 3 times a day.
Nutrition
Throughout therapy, it is recommended to adhere to a dietary diet. This is especially important if the cause of nail detachment is a fungus. To stop the spread of infection, it is recommended to exclude foods high in cholesterol, trans fats and glucose from the diet. It is important to adhere to the following recommendations:
- Avoid foods high in sugar.
- Introduce plant fiber and slow-digesting carbohydrates into your diet.
- The main side dish should be raw or boiled vegetables.
- Limit consumption of meat and dairy products.
- Avoid coffee, alcohol and soda.
- Between meals, take herbal tea or mineral water.
- Introduce a ban on confectionery products.
Despite the large number of prohibitions, you will not have to feel hungry. The diet can include:
- Vegetables and fruits.
- Berries.
- Cereals.
- Seafood.
- Vegetable oils.
- Nuts, flax.
- Rye and wheat bread.
- Porridge.
- Eggs.
- Legumes.
In the first days of the diet, heaviness and bloating occur in the abdomen. This phenomenon indicates adaptation in dietary changes. To cope with unpleasant symptoms, it is recommended to add seasonings to your diet that promote the production of digestive enzymes.
Fungal infections
Treatment of fungal infections deserves a separate description. It is always complex.
It is necessary to simultaneously carry out local therapy and take oral antifungal drugs.
A course of local therapy consists of taking baths with potassium permanganate, salt and soda.
Affected legs or arms are treated daily with a 5% chrysarobin solution or a 2% tinol solution.
Any antifungal ointment is applied at night.
As the affected plate grows, it is trimmed. The ointment is rubbed in until the nail is completely renewed.
Instead of ointment, females are allowed to use nail polish with an antifungal composition.
Local treatment lasts almost a month, during which pathogenic microorganisms can penetrate the bloodstream and spread throughout the body.
Therefore, doctors include oral administration of special drugs in therapeutic regimens.
There are many of them, the most effective tablets are:
- "Griseofulvin";
- "Fruconazole";
- "Terbinafine";
- "Ketoconazole".
Since the course of taking such drugs is long, since almost each of them has a highly toxic formula, taking antifungal agents must be carried out under the supervision of the attending physician.
Onycholysis photo
Self-medication for fungal infection of the plates is unacceptable.
Features of therapy in children
It is important to monitor the condition of the skin around the nails in children. A small wound can cause a bacterial or viral infection. Particular concern should be shown if the baby’s nail darkens and peels off from the bed.
The causes of onycholysis in children are similar to those in adults. The differences lie in treatment tactics - for bacterial and fungal infections, if possible, it is necessary to limit yourself to local drugs and abandon systemic ones.
The course of treatment for fungal infection is at least 3 months. Every day, antifungal ointment is rubbed into the nails and affected areas of the skin. The most popular drugs that can be used for children are:
- Clotrimazole.
- Ketoconazole.
- Lamisil.
For bacterial infections, antibiotics are prescribed. The choice of drug depends on the baby’s age, weight and the presence of concomitant diseases. In case of extensive damage, the nail plate is removed, but this procedure is carried out only in a hospital setting. Throughout therapy, it is important to organize proper nutrition and, if necessary, take multivitamin complexes.
Symptoms of onychomadesis
Since the development of the clinical picture is rapid, not all patients have time to determine the onset of the disease. From the moment the first changes appear until the nail completely detaches, it can take from several days to a month.
Symptoms before plate separation:
- one or two nails on the toes and hands become white or yellow, in rare cases the nail becomes bluish or black;
- the shape changes to the point of bizarre, unnatural, but sometimes the plate simply thickens, longitudinal or transverse grooves appear;
- the skin under the nail may become inflamed, but this only happens if there is a bacterial infection (even with a fungal infection, inflammation is usually not observed);
- with inflammation, the surrounding skin turns red, the person suffers from pain and discomfort;
- with onychomadesis fungus, it is accompanied by itching and burning.
Next, the nail begins to tear away from the base, but with a traumatic cause, detachment can also start from the distal end. With psoriasis, separation occurs completely without pain on the free side. After removing the nail, the bed becomes exposed, so it can become directly infected. If bacterial or fungal infection of the nail matrix is not prevented, the plate may never grow.
Prevention
To protect yourself from a disease such as onycholysis, you need to follow simple recommendations. These include:
- Wear shoes made from natural materials.
- Change socks every day.
- Do not wear tight and uncomfortable shoes.
- Dry your feet thoroughly after contact with water.
- Protect your nails from injury.
- Eat properly.
- Do not take antibiotics unless prescribed by a specialist.
- Treat chronic diseases.
- Carefully follow the rules of hygiene.
To determine what caused the disease, you need to visit a specialist and get tested. Self-medication for this disease can only aggravate the situation and cause complete rejection of the nail plate.