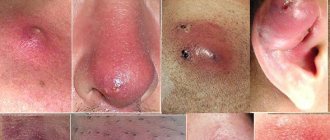
Onychoschisis is a dystrophic change in the nail plate, which results in transverse splitting of the nail into leaf-shaped plates.
Onychoschisis does not pose any danger to the life and health of the patient, but it creates a noticeable cosmetic defect, disfiguring the nails. The following nail diseases can also be classified as a cosmetic defect: onycholysis, trachyonychia, melanonychia, etc.
Structure of the nail plate
The nail plate is a hard derivative of the skin, the remains of the claws that human ancestors once had. The nail has a body and a root. The root is hidden under a layer of skin, a periungual ridge, and vessels and nerves are connected to it. The nail grows from the root side.
The body of the nail is represented by a plate consisting of several layers of keratin - a dense protein. This protein is produced by keratinocytes, which form the bulk of the skin. In addition, the keratin plate contains dead cells, and between the layers of protein there is a small amount of water and fat.
General description of onychodystrophy
Onychodystrophy is a pathology characterized by damage to the nail plates, nail bed and fold. This disease is also accompanied by metabolic and nutritional disorders, which leads to changes in the external and internal state of the nail part and nearby tissues.
Deformation of the nail plate is noted, its thickness increases, color changes, peeling occurs, strength is lost, and the nail crumbles. It begins to take on an unsightly appearance , which causes not only aesthetic discomfort, but also physical pain. This disease can occur due to a genetic disorder or through infection from an infected person.
The symptomatic progression of this disease manifests itself in various changes in the condition of the nails, taking into account the cause of the disease . The following types of onychodystrophy are classified:
- Onychorrhexis is a dystrophic change that results in the formation of cracks in the nail surface in the longitudinal direction. Initially, the change appears from the free edge, with a further increase in the affected area to its base.
- Onychoschisis is a pathological condition that results in the separation of the nail surface in the transverse direction into several independent plates, starting from the center of the nail. In this case, there are no inflammatory processes. This disease does not pose a threat to life and health. It only causes a cosmetic defect, which entails visual discomfort.
- Onychomadesis is a condition characterized by rejection of the nail at the base. An inflammatory process is likely to occur. Typically, the cause is traumatic injury.
- Onycholysis is a pathology during which there is a disruption in the connection of the nail bed with the nail, which leads to complete or partial detachment of the plate. As the pathology develops, the affected nail changes its natural color to a yellowish-brown tint.
- Hapalonychia is a softening of the dense nail structure, which ensures its complete destruction.
- Koilonychia is the formation of a saucer-shaped depression in the middle of the nail plate. Moreover, its natural structure and color are preserved.
- Anonychia is the complete absence of a nail. It is one of the symptoms of abnormal development. It is divided into acquired (in the form of complications of the course of some fungal diseases) and congenital (hereditary cause) pathologies.
- Trachyonychia is a condition during which the structure and color of the nail plate changes. Signs of delamination are likely to appear.
- Scleronychia is a disease accompanied by the following symptoms: the nail becomes dense, brown or yellow, growth slows down, and the bed becomes detached from the plate.
- Onychogryphos - characterized by signs of changes in color and shape, the presence of lumpiness and roughness, and an increase in the thickness of the nail plate.
- Platonychia is defined as a deviation from normal development, accompanied by a lack of natural convexity. In this case, the nail becomes smooth.
Causes of onychoschisis
The etiology of onychoschisis is varied, but its essence is damage to the nail plate by any external factors:
- Mechanical injury. Incorrect manicure technique, using rough brushes and nail files, and biting the nail lead to gradual delamination of the plate. Constant hitting of the keys also leads to damage to the integrity of the nail plate. Therefore, onychoschisis is typical for pianists, typists and people who constantly work at a computer.
- Chemical substances. Varnishes, acetone and its derivatives, household chemicals, solvents affect the fatty component of the nail, dissolving it, which leads to delamination. The alkalis that are used in production have a particularly strong effect on the nail. Therefore, onychoschisis is often an occupational disease.
- Biological agents and systemic diseases. Often, it is a fungal infection that leads to the destruction of the nail plate. Onychoschisis may be a consequence of psoriatic nail damage.
Prevention of deviation
As a rule, people suffering from onychoschisis simply do not treat their nails carefully enough.
The best means of prevention is to take care of your nails and prevent their contact with household chemicals.
Here is a list of recommendations that reduce the load on the nail plate:
- Eliminate metal files and replace them with glass ones;
- Work with chemical reagents and household chemicals only with gloves;
- Reduce the risk of injury to the nail and nail bed. In relation to programmers and musicians, it is better to cut your nails short than to walk proudly with onychoschisis. You need to understand that when struck, the entire nail suffers, and not just the protruding part;
- If onychoschisis is accompanied by any skin disease, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment, because a mechanically damaged nail is more susceptible to fungal and bacterial infections;
- The diet should be balanced and contain sufficient amounts of vitamins B, E, D and A.
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner and follow these simple measures, onychoschisis goes away without a trace in the vast majority of cases.
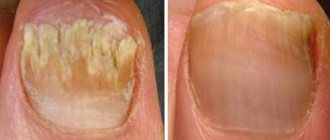
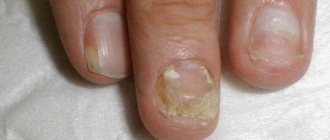
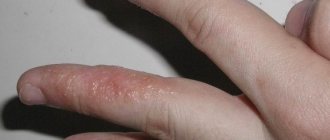
Symptoms of onychoschisis
The nail plate breaks in the transverse direction. In this case, only the regrown area is involved in the process; after cutting, the nail appears healthy. Often the shade of the nail changes, becoming gray or off-white. This happens due to changes in the thickness and transparency of keratin, as well as due to the high density of foreign protein in the fungal cell wall.
Usually the nail beds of the II-IV fingers are involved in the process. The skin and other tissues around the affected areas are not affected.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of onychoschisis are separation of the nail plate. The nail splits into several layers in the transverse direction. Sometimes there is a change in the color of the nail, it becomes off-white or gray.
Most often, onychoschisis is observed on the second, third and fourth fingers. Only the regrown section of the nail is split, that is, if the nails are cut short, they look quite healthy, but as they grow, the plate splits into several layers. Nails with onychoschisis become increasingly brittle and brittle. The soft tissues surrounding the nail are not affected by onychoschisis.
How to treat onychoschisis?
Treatment of onychoschisis depends on the etiology of the process. Fungal infections require long-term therapy with local or systemic antifungal drugs. Immunomodulatory therapy, vitamin and mineral complexes (vitamins A, E, calcium, phosphorus and others) are prescribed.
Systemically applied:
- Retinol preparations. Vitamin A plays a direct role in the formation of skin cells and keratin. The product is used for a long time, at least 6 months. Dosages depend on the drug and the regimen, but retinol is often prescribed 30 drops every 12 hours.
- Cyanocobalamin, or vitamin B12. Every other day, 200 mcg of the substance is administered intramuscularly. Course – 1 month.
- Edible gelatin is a source of fats and amino acids to strengthen the nail plate. Use a 10% solution of the product for 3 months, half a glass 4-5 times a day.
Local treatment consists of using salt or oil baths with the addition of vitamin solutions. In addition, phonophoresis of vitamins A and E is prescribed for the damaged nail. Physiotherapy is carried out in courses of 10 procedures with breaks of 6-8 weeks.
Treatment
Massage is used to treat onychoschisis.
Treatment of onychoschisis must be comprehensive; the technique is selected individually, taking into account the reasons that provoked the development of the disease. The main goal of treatment is to strengthen the nail plate and restore nutrition to the tissues surrounding the nail. As a rule, treatment includes the use of medications (systemically and locally), physiotherapy, and massage.
To improve tissue nutrition, patients with onychoschisis are prescribed vitamin and mineral supplements, dietary supplements, which include amino acids and unsaturated fatty acids, since these substances act as the “building material” for the nail plate. General strengthening and also sedatives are useful to strengthen the immune system and stabilize the emotional background.
As a systemic treatment the following is prescribed:
- A long course of retinol, which must be taken 30 drops twice a day for at least 6 months.
- Cyanocobalamin injections. A single dose is 200 mcg, the course consists of 30 injections, it is recommended to perform them every other day.
- Ingestion of a solution (10%) of edible gelatin. The course of administration is 3 months, the daily dose is half a glass, divided into 4-5 servings.
Local therapy for the treatment of onychoschisis involves the use of baths with the addition of sea salt and essential oils.
If the crack in the nail plate is minor, it is recommended to apply an antibacterial patch and use a gentle regime for the affected finger. If the splitting of the nail is deep, then the distal (extreme) section of the affected nail is removed, followed by applying a bandage with an antiseptic.
Physiotherapy for onychoschisis consists of phonophoresis using preparations of vitamins A and E, since these vitamins help strengthen the nail plate. Physiotherapy is carried out in courses of 10-12 procedures with a break of 1.5-2 months.
Treatment with folk remedies
Salt baths for onychoschisis. Salt strengthens nails well; it is better to use sea salt for baths, but you can get by with regular salt, which is found in every kitchen. To carry out the procedure, you need to take half a liter of warm water and a tablespoon of salt. Keep your nails immersed in salt water for 20 minutes, then wipe thoroughly and apply nourishing cream or oil to the nail plates.
There are many folk recipes that strengthen nails and can help in the treatment of onychoschisis. However, we should not forget that without eliminating the cause of the disease, it will be impossible to achieve success in treatment.
Beeswax is also used to treat onychoschisis.
For onychoschisis, a mask made from natural beeswax helps well. It can be purchased at honey fairs or at specialized retail outlets. A small amount of wax needs to be melted to a liquid state (it is better to do this in a water bath). After the wax has cooled to a temperature of about 40 degrees (it will be hot, but not scalding), you will need to immerse your fingers in it so that the nails are completely covered with wax. After 15 minutes, remove the “wax thimbles”.
Sea buckthorn oil is very useful for nails; it can also be used to treat onychoschisis. Simply rub the oil into the nail plates. If you don’t have sea buckthorn oil, you can take olive oil and add a little lemon juice to it.
Vitamin composition for the treatment of onychoschisis. To prepare the ointment, you need to purchase vitamins A, D and E in ampoules. You need to take one ampoule of vitamin E and three ampoules of vitamin A and D, mix their contents and add 20 grams of olive oil or any nourishing nail cream. Rub the resulting composition into sore nails every day for three weeks.
Treatment with folk remedies
It is not recommended to treat onychoschisis at home. The procedures can only be used as auxiliary techniques to the main therapeutic measures, because they do not eliminate the causes of the process, and in case of fungal infection they can lead to the spread of the pathogen to healthy nails and soft tissues.
- Salt baths. A tablespoon of preferably sea salt is dissolved in 500 ml of warm water. Soak clean hands in water for 20 minutes. Afterwards, carefully dry your hands, then lubricate your hands, especially your nails and periungual ridges, with hand cream or oil.
- Beeswax mask. Dip the phalanges of your fingers and nails into the melted and hot, but not scalding, wax. Pull your hands out and hold the formed wax caps for 15 minutes. Repeat the procedure daily until a new nail grows.
- Sea buckthorn oil. Rub oil on damaged nails in the morning and before bed for six months.
Onychodystrophy
There is no comprehensive generally accepted classification in modern dermatology. In our opinion, the most convenient is to divide onychodystrophies according to the reasons for their occurrence, with an emphasis on the specifics of clinical manifestations. There are congenital onychodystrophies, as a result of gene mutations and the transmission of hereditary predisposition, and acquired onychodystrophies, a heterogeneous result of trophic disorders. Congenital onychodystrophies are clinically manifested by the following types:
1. Onychomadesis - manifests itself in the form of rapid separation of the nail from the bed from the distal edge, most often as a result of injury or inflammation; genetic predisposition to pathology is inherited.
2. Koilonychia - a hereditary predisposition to a spontaneously occurring oval depression in the center of the nail plate.
3. Anonychia - congenital absence of the nail plate, transmitted from generation to generation.
4. Platonychia – a congenital pathology in the form of an even, flat nail.
5. Micronychia - congenital short, small nail plates on the hands, less often on the feet.
6. Hippocratic nails - a hereditary anomaly with convex nail plates, “drum fingers”.
Acquired onychodystrophies can be independent nosologies or an integral part of a symptom complex of somatic pathologies, dermatoses, visually manifested in the form of changes in the nail plates. The first group (isolated diseases) includes:
- Onychoschisis is a dystrophic division of the nail across into several components without inflammation;
- Bo's transverse grooves (manicure onychodystrophy) - a rainbow-shaped depression in the nail from edge to edge, the most common type of onychodystrophy;
- Median canaliform onychodystrophy - a distinctive feature is the “herringbone symptom”: a central crack - the trunk, from which grooves-branches extend, is a consequence of injury;
- Onycholysis - loss of connection with the nail bed while maintaining the integrity of the latter with slow detachment of the nail due to injury or infection;
- Onychogryphosis - hyperthickening and curvature of the nail due to age;
- Leukonychia is an abnormal coloration of nails as a result of matrix dysfunction. It can be dotted (small spots of different diameters), stripe-like (the appearance of one wide or several narrow whitish stripes transverse to the axis of the nail - Mührke’s line), total (with whitish spaces over the entire surface of the nail), partial (half of the nail is white, the rest is unchanged );
- Hyperpigmentation - occurs as a result of the accumulation of hemosiderin and melanin. Manifests itself as yellow nail syndrome (consists of a triad of symptoms: onychodystrophy, somatic pathology, disease of the lymphatic system); drug pigmentation (occurs as a result of the use of tetracycline antibiotics, resorcinol, cosmetic varnishes); subungual dystrophy (characterized by longitudinal hemorrhages in the subungual space due to injury to the nail bed).
Acquired onychodystrophies, as part of other diseases, can be presented in various forms. Thus, onychorrhexis - dystrophic separation of the nail along - is considered one of the signs of lichen planus, eczema, and psoriasis. Longitudinal grooves in the nail, resulting from a lack of iron, protein or folic acid, may indicate disorders in the cardiovascular system, rheumatoid arthritis. Mie lines - white stripes across the nail - are a symptom of arsenic poisoning. Scleronychia - extreme hardness of the nail and hapalonychia - a very soft nail that breaks off, are a symptom of endocrine disorders. Trachyonychia - a cloudy, rough, flaking, "sandy" nail - usually occurs with immunodeficiency. “Thimble” onychodystrophy - the surface of the nail is mottled with impressions resembling a thimble, accompanies psoriasis.
Causes of onychorrhexis of nails
The nail plate consists of several layers of keratin, between which lie fat molecules and a small amount of water. Keratin is produced by skin cells from the lower part of the plate - the matrix. The matrix is surrounded by a dense network of capillaries and nerves responsible for its trophism. It is the malnutrition of the nail plate that leads to onychorrhexis.
Onychorrhexis is characteristic of the following diseases:
- Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerotic damage to the inner wall of blood vessels prevents the flow of nutrients into the matrix, which leads to splitting of the nail. This process is typical for older people.
- Autoimmune diseases (vasculitis, Raynaud's syndrome and others). Immune complexes damage the cell wall of their own blood vessels, which leads to disruption of nutrition and keratin formation.
- Fungal infections. The pathogen develops deep in the layers of the nail plate, which leads to inflammation, destruction of its structure and peeling.
- Nail psoriasis. This process is caused by a defect in the formation of the nail plate.
- Endocrinological disorders (diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis) are also the cause of splitting of the nail.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. With pathology of this profile, the formation of red blood cells that carry oxygen is disrupted, which leads to a decrease in the nutrition of the nail matrix.
- Injury to nails during manicure and the use of cheap varnishes and acetone-based solvents, contact with chemicals.
- Mental disorders. Psychological trauma leads to malnutrition of the nail. In addition, with some mental illnesses, patients wash their hands more than 50 times a day, which adversely affects the development of the nail plate.
Treatment of nail onychorrhexis
Therapeutic procedures are carried out in three main areas:
- Treatment of the underlying disease that caused the splitting of the nail.
- Strengthening and improving nutrition of the nail plate.
- Prevention of repeated episodes of pathology.
Thus, treatment depends on the etiology of onychorrhexis. Medicines are prescribed by a doctor, who also determines individual treatment periods. Strengthening measures include prescribing multivitamin complexes, salt baths and baths with essential oils. Physiotherapeutic treatment (phonophoresis) is also prescribed.
Treatment of onychodystrophy
The grooves themselves that form on the nail plates do not require drug treatment, since this problem is more of a cosmetic nature than a medical one. Therefore, the proposed methods for getting rid of grooves include a set of measures to care for sore nails and the skin of the hands.
If the nail defect is caused by a certain disease, the diagnosis of which can only be revealed through a comprehensive examination, then its elimination entirely depends on the healing of the disease itself that provoked such a symptom.
Diet for illness
So, if you notice grooves on your nails, the first thing you should do is add a variety of minerals and vitamin-containing foods to your daily diet. Or even take a course of pharmacy vitamins.
Track your nutrition by including nuts, fish in your diet, and eat more vegetables and fruits. Stop eating unhealthy foods: fast food, smoked and fried foods, alcohol. Drink up to 2 liters. liquids per day: juices (preferably freshly squeezed) and water.
Hygiene
The second thing to do is to pay increased attention to nail hygiene:
- Get your manicure done regularly, starting with polishing your nails with a special sanding file and ending with applying a protective varnish (any cosmetologist will recommend the series and brand of a suitable product).
- Treat your hands with lotion daily after each hand wash, and apply a moisturizer to your nails.
- Before going to bed, do not neglect a manual massage of your hands and fingers using a lotion based on jojoba oil and vitamin E, which improves skin condition.
These methods are also used as preventative nail care. It is advisable to entrust the nail polishing procedure to a manicurist in a well-established cosmetology clinic or professional salon.
Care
If you don’t have funds in your wallet for a set of manicure measures, don’t despair. Here are some tips that you can follow to help you sand and polish yourself:
- Sand each nail in one direction (from right to left or from top to bottom). This way you will not damage the integrity of the plate.
- Removing a large layer of nail tissue is not recommended, as this can lead to inflammation of the epithelium and bleeding.
- All hangnails and scratches on the nail formed during polishing should be carefully polished.
- After completing the procedure, wash your hands and apply protective nail care products.
Don't expect the grooves to disappear after the first sanding. Carry out a session no more than once a week so that your nails have time to recover. And remember that hand hygiene and a balanced diet are the key to the beauty of your nails and skin.
Signs and symptoms
The nail surfaces are called horny formations, which consist of many plates of a porous base, due to this, metabolism and nutrition occur in them. The nail itself consists of keratin fibers , which contain cysteic acid; strength depends on it, and a healthy appearance and elasticity depend on the amount of fat cells and water between the plates.
An insufficient amount of these components leads to onychodystrophy. Deformation of the nails begins - a very common problem that should be regarded not as a defect related to the cosmetic field, but as a serious pathology of onychomadesis, the treatment of which requires immediate treatment.
The course of the disease is accompanied by the following symptoms: longitudinal and transverse grooves appear on the plate, depressions and spots of different colors and sizes form in the center of the nail surface. Nails become rough. The shape changes, the nail surface becomes saucer-like. The nail begins to bend.
The formation and growth of the nail part begins from the root. This area is called the matrix, and it is the heart of the nail. The presence of many vessels in this part contributes to increased blood supply, which determines the attractive pink tint of the nail. During an injury of any nature of origin and intensity, circulatory disorders or inflammatory phenomena in the matrix, the process of formation of the nail plate may be completely absent or begins to slow down.