A furuncle is one of the manifestations of purulent-inflammatory diseases, characterized by damage to the hair follicles, a number of adjacent soft tissues and sebaceous glands.
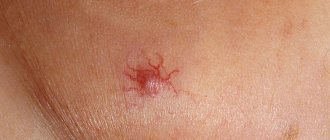
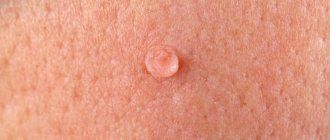
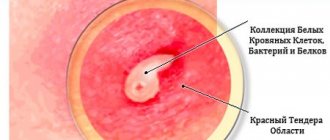
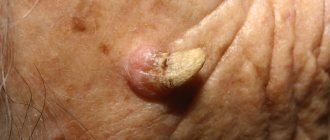
A furuncle is a formation on the surface of the skin in the form of a dense painful node, the diameter of which can be several centimeters, on average it does not exceed 3 cm. In the central part there is a necrotic core, which is covered with a pustular formation.
Gradually, the abscess begins to soften, and in the area of the rod, the presence of an abscess with an area of fluctuation can be determined. When the pustule ruptures, necrotic contents will drain from the cavity and it will become free. In the area of the boil there will remain a focus with developed inflammation.
The boil, whose code is defined as L02, can be divided into several types.
In the modern classification according to ICD-10, codes are defined for boils in accordance with their anatomical location:
- face L02.0;
- neck L02.1;
- body L02.2;
- buttocks L02.3;
- limbs L02.4;
- other parts of the body L02.8;
- with unspecified localization L02.9.
Description
Furunculosis.
This is a purulent-necrotic disease of the hair follicle and perifollicular connective tissue. The primary inflammatory element is the inflammatory node, which forms around the hair follicle. The main cause of furunculosis is staphylococcal infections. A typical dermatological picture, signs of inflammation in a clinical blood test and the results of bacteriological culture of skin discharge make it possible to diagnose furunculosis without much difficulty. Patients with furunculosis are treated by a dermatologist.
Complications of carbuncle
The danger of the disease lies in the spread of inflammatory, purulent-necrotic processes to neighboring anatomical and physiological structures with the formation of a lesion in them. The list of negative consequences of pathology includes such conditions as:
- soft tissue abscess;
- phlegmonous lesion;
- inflammation of bone structures;
- phlebitis, which can be combined with blockage of a vessel by a blood clot;
- infection of the meninges – observed when there is a carbuncle on the face;
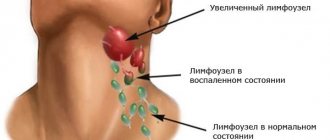
- inflammatory process in the lymph nodes or vessels;
- periadenitis;
- septic lesion.
Some of the above nosologies can lead to general intoxication of the human body with subsequent death. To avoid such consequences, it is necessary to promptly seek highly qualified medical help.
Causes
The cause of furunculosis is staphylococcal microflora, which, under the influence of various factors, is activated and provokes a purulent-inflammatory process. In the presence of immunodeficiencies, short-term exposure to exogenous factors is sufficient for the development of furunculosis. The presence of foci of chronic infection, diabetes mellitus, hypovitaminosis, errors in diet, chronic intoxication, both independently and in combination, can provoke furunculosis. With localized furunculosis, skin trauma, local hypothermia and contamination are the main reasons for the introduction of staphylococci into the follicle.
Prevention
The following are preventive measures:
- Normalization of lifestyle, including proper nutrition and physical activity aimed at maintaining immune strength.
- Compliance with hygienic measures aimed at eliminating the growth of pathogenic flora and normalizing protective forces.
- Timely elimination of excessive sweating and excessive work of the sebaceous glands.
- When pyoderma rashes appear, it is necessary to identify the underlying cause and timely treatment of the skin to remove microbes.
- Correction and treatment of somatic pathologies, chronic infections, malignant neoplasms.
- Self-treatment of a boil, as well as removal of purulent formations in the face and nearby vessels, is not allowed.
- Timely consultation with a specialist and treatment of boils, taking into account the determination of sensitivity to antibacterial agents.
Symptoms
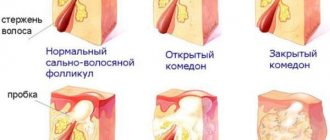
At the initial stage of the disease, a small purulent-inflammatory infiltrate forms around the hair follicle, which resembles folliculitis. After a few days, the entire hair follicle is involved in the inflammatory process. With furunculosis, unlike folliculitis, not only the follicle is affected, but also the adjacent sebaceous gland and surrounding connective tissue. Clinically, the elements of furunculosis rashes resemble a cone-shaped congestive-hyperemic node rising above the surface of the skin. As the focus of inflammation forms, soreness, swelling and pain of a pulsating or jerking nature increase. If furunculosis affects the follicles of the face and neck, the process is accompanied by extensive swelling around the infiltrate. On the 3rd, 4th day, a fluctuation zone begins to form in the center of the infiltrate - when you press on such an element of furunculosis, a springy movement of purulent masses in the follicle cavity is felt, and around the hair there is a small focus of purulent tissue melting and the formation of a fistula. After the elements of furunculosis are opened, a small amount of thick pus is released, which has accumulated on the surface and a small ulcer is formed. At the bottom of the ulcer you can see a greenish necrotic rod; the presence of such a rod is a diagnostic symptom for furunculosis. After a few days, the rod is rejected along with a small amount of blood and purulent masses. After the rod is rejected, the inflammatory phenomena of furunculosis begin to decrease. The affected area becomes less painful when touched, and tissue swelling subsides. After the elements of furunculosis resolve, a deep crater-shaped ulcer is formed with remnants of pus and necrotic masses, which are gradually rejected or form chronic furunculosis. The ulcer is filled with granulation tissue and a retracted scar is formed; the depth and size of the scar depend on the size of the necrosis zone in the center of the boil. Furunculosis has no favorite localizations, but more often elements of inflammation occur on the forearms, face, back of the neck, buttocks and thighs, that is, where areas of problematic skin prone to oiliness are located. If the elements of furunculosis are isolated, then the patient’s general well-being does not suffer, the body temperature remains normal, and the patient leads the same lifestyle. When furunculosis affects the area of the nasolabial triangle, the wings of the nose, and the area of the external auditory canal, even with isolated rashes, body temperature rises, symptoms of intoxication and headaches are observed. The skin on the face becomes purple, tense, swelling and pain are pronounced. The work of facial muscles, the high risk of injury to elements of furunculosis during shaving and washing, attempts to squeeze them out on your own can lead to thrombophlebitis of the facial veins and to the dissemination of staphylococcal infection into internal organs and tissues. Due to the characteristics of venous blood flow on the face, facial furunculosis in some cases leads to meningitis and meningoencephalitis. Sepsis with the formation of multiple abscesses in the internal organs is one of the most severe complications of furunculosis. In the acute course of furunculosis, many boils of the same stage of resolution are present on the skin. Untreated acute furunculosis, the presence of immunodeficiencies and neglect of personal hygiene rules lead to chronicity of the process. The chronic course of furunculosis is characterized by the presence of boils of varying degrees of resolution; at the same time, on the skin there are granulation changes in the elements and recurrent boils, the process in which is activated several times a year or more often. With localized furunculosis, individual areas of the skin are affected, while with disseminated furunculosis, the process becomes widespread. Furunculosis of the extremities, especially when the elements are located near the joints, is complicated by regional lymphadenitis. Sometimes with furunculosis complications such as glomerulonephritis are possible. Leukocytosis.
Types of boils
The inflammation often spreads, affecting several bulbs. It can occur in various areas of the body. According to the location of the boil, ICD 10 codes were assigned:
- on the face L02.0;
- on the neck L02.1;
- on the body L02.2;
- on the buttocks L02.3;
- on the limbs L02.4;
- on other parts of the body L02.8;
- without specifying the place of formation of L02.9.
Diagnostics
Clinical manifestations, the presence of a fluctuation zone, and the presence of signs of an infectious process allow a diagnosis to be made. In a clinical blood test, there is a noticeable increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left and pronounced leukocytosis. Cultural diagnostics confirms the staphylococcal nature of the disease. Together with cultural diagnostics, the sensitivity of the microorganism to antibiotics is determined. Accurate identification of the pathogen also helps to identify the source of infection; for example, nosocomial infection often manifests itself in the form of pyoderma and furunculosis.
Complications of carbuncle
The danger of the disease lies in the spread of inflammatory, purulent-necrotic processes to neighboring anatomical and physiological structures with the formation of a lesion in them. The list of negative consequences of pathology includes such conditions as:
- soft tissue abscess;
- phlegmonous lesion;
- inflammation of bone structures;
- phlebitis, which can be combined with blockage of a vessel by a blood clot;
- infection of the meninges – observed when there is a carbuncle on the face;
- inflammatory process in the lymph nodes or vessels;
- periadenitis;
- septic lesion.
Some of the above nosologies can lead to general intoxication of the human body with subsequent death. To avoid such consequences, it is necessary to promptly seek highly qualified medical help.
Treatment
Treatment of furunculosis should be carried out by a dermatologist. Self-medication with Vishnevsky ointment can lead to the spread of the process and to phlegmon, since Vishnevsky ointment is used only after the purulent capsule has resolved at the granulation stage. Squeezing out the rods during furunculosis with your hands or using vacuum cans leads to premature opening, when nearby areas of healthy skin are contaminated with pathogenic microflora, and part of the rod remains inside and thereby leads to a chronic process. During the treatment of furunculosis, it is necessary, if possible, to limit or completely eliminate water procedures, but with extensive furunculosis, slightly warm baths with potassium permanganate disinfect the skin. As hygienic procedures, they resort to wiping healthy skin with non-aggressive antiseptic solutions - salicylic alcohol or furatsilin solution. Great attention should be paid to personal hygiene; minor scratches and cuts are treated with a solution of brilliant green; frequent changes of underwear and bed linen are required. Excluding fatty, spicy foods from the diet and containing foods rich in vitamins and protein help improve tissue regeneration. At the stage of maturation, the skin around the elements is treated with antiseptics, injecting the affected area with a solution of novocaine with antibiotics relieves pain and prevents the spread of the purulent process to healthy tissue. Electrophoresis with antimicrobial drugs helps prevent complications of furunculosis in the form of abscesses and phlegmon. After a fluctuation zone has been identified, crystalline salicylic sodium is applied to the center of the furunculosis elements and fixed with a dry bandage. Such applications have a keratolytic effect and promote accelerated rejection of the rod. In case of abscessive furunculosis, opening of the boil under local anesthesia and removal of purulent-necrotic masses is indicated. After self- or forced opening, the wound is thoroughly washed with 3% hydrogen peroxide and bandages with proteolytic drugs, syntomycin and erythromycin ointments are prescribed. The dressings are changed every other day, and after the process enters the granulation stage, Vishnevsky's liniment and ichthyol-based ointments are used for better healing. Ultraviolet irradiation and UHF therapy are used in doses at all stages of furunculosis. Internal antibiotics are used in cases of chronic furunculosis and abscess formation of elements. In the presence of general diseases, exhaustion of the patient and reduced immune status, antibiotics are prescribed in the form of intramuscular injections. To increase the body's resistance, gamma globulin and ozone therapy are used, vitamin therapy, autohemotransfusions, UVOC and restorative drugs are prescribed. Prevention of furunculosis consists of maintaining personal hygiene, timely treatment of pustular diseases, treatment of systemic diseases and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
How does suppuration occur?
The pathological process begins with the penetration of infection into the tissue. Staphylococcus aureus usually leads to the appearance of a boil in the ear. These bacteria cause purulent inflammation. First, an infiltrate forms, which looks like a compaction. If treatment is not started at this stage, then after 2-3 days suppuration begins with tissue necrosis. This lasts about 3-5 days. Then the abscess breaks out either independently or during treatment, and recovery occurs. After this, gradual healing of the skin occurs over the course of a week.
Additional facts
Ear furuncle, or localized otitis externa, is a relatively common pathology. It accounts for 15-18% of the total number of otolaryngological diseases. According to statistics, limited external otitis occurs with a frequency of 3-6 cases per 1000 population. In etiology, the most significant factors are skin damage and immunodeficiency, which cause 50-60% of all cases of the disease. The pathology is equally common throughout the globe. It is observed somewhat more often in males than in females. Mostly young and middle-aged people are affected – from 18 to 45 years old. Complications occur in 2-5% of patients.
Pathogenesis
The initial, infiltrative stage of boil development is accompanied by penetration of pathogenic microflora into the mouth of the sebaceous gland/hair follicle, which leads to the formation of a pustule. The latter contains a large number of neutrophilic leucites, pathogenic bacteria and fibrinous threads. Next, infectious agents spread deep into the follicle, provoking inflammatory changes with the further formation of infiltrative masses and zones of necrosis - this is how the transition to the abscess formation stage occurs. The tissues adjacent to the affected area undergo purulent melting and form purulent exudate, which accumulates under the epidermis, surrounding the follicular ostium. After some time, the accumulation of a large volume of pus leads to rupture of the epidermis and the release of contents, including a purulent core and dead hair. The resulting defect is filled with granulation tissue, and over time a keloid scar forms at the site of the lesion.
Phlegmon
Phlegmon is a diffuse inflammation of tissue (subcutaneous, intermuscular, retroperitoneal, etc.).
Cellulitis is caused by both aerobic and anaerobic (usually non-clostridial) microorganisms. According to the nature of the exudate, phlegmons are divided into serous, purulent and putrefactive. The difference between phlegmon and an abscess is the absence of a pyogenic membrane, which ensures a fairly rapid and extensive spread of the purulent process. Clinically, phlegmon is determined by all signs of inflammation.
In case of serous form of phlegmon, conservative treatment is allowed; other forms are treated according to the general principles of treatment of surgical infection.