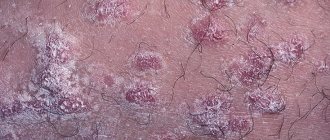
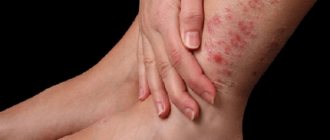
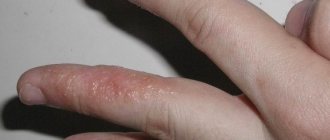
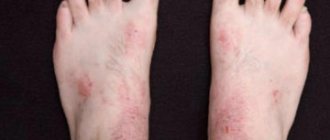
Symptoms
Psoriasis on the legs brings the patient great inconvenience and pain, because the skin on the surface of the limbs is very itchy and covered with cracks, the subcutaneous layer is gradually filled with intracellular fluid, which causes swelling.
The disease selects places on the legs that are more involved in movement and bending: feet, heels, knees and hips. The pathology is dangerous for humans because its course is a change of 2 states: exacerbation of the disease and its remission.
Each period of the disease has its own symptoms:
- Initial stage. Minor signs of pathology are observed, they are rarely paid attention to. These are small pimples that gradually enlarge, merging into psoriatic plaques, and are covered with light scales.
- Exacerbation stage. During this period, plaques grow rapidly and an inflammatory process occurs, accompanied by severe itching. The skin begins to crack, and the cracks become covered with new blisters, which quickly transform into flaky plaques. The plaques also harden just as quickly. Plaques on the feet cause suffering, as they are subjected to mechanical action while walking and standing.
- Stationary stage (rest of the disease). The disease does not develop, but it does not go away, the skin peels off, the plaques itch.
- Remission stage. The disease subsides: the rash, plaques and pigmentation disappear.
The symptoms of the disease make it possible to determine the stage of its course.
Physiotherapy
To eliminate psoriasis on the feet and other parts of the legs, physiotherapeutic procedures are recommended as an addition to complex therapy. But they cannot be used in the acute stage; physiotherapy is indicated only for the stationary stage of the disease and during remission.
The most effective methods:
- Electrosleep.
- Ultraviolet irradiation.
- PUVA therapy.
- Magnetotherapy.
- Laser therapy.
- Ultrasound treatment.
- Laser photochemotherapy.
- Cryotherapy.
- Plasmapheresis.
- Darsonvalization.
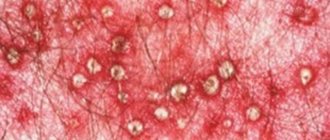
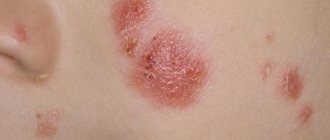
Photo
Below you can see what the initial and other stages of the disease look like in the photo.
Proper diet
Any treatment will be ineffective if you do not follow the nutritional rules. You are allowed to eat low-fat fish, meat, sour milk, porridge, whole grain bread, cottage cheese, and cheese. Prohibited:
- smoked products;
- alcohol;
- eggs;
- animal fats;
- baking;
- sweets;
- soda;
- fast food;
- citrus;
- spicy seasonings;
- ice cream.
Pathology
Psoriasis is a systemic pathology that affects up to 5% of the world's population. The disease involves the skin, joints and a number of internal organs. Scientists point to several concepts for the development of the disease:
- infectious-immunological;
- genetic;
- neuroendocrine;
- exchange.
They argue that changes during the course of the disease occur in the gastrointestinal tract, nervous, cardiovascular and urinary systems. The musculoskeletal system is most negatively affected.
The pathology is characterized by a violation of the “structure of the dermis, cellular activation and local infiltration of the skin by inflammatory cells.”
In general, the disease significantly changes a person’s quality of life: productivity and the desire to communicate in society decrease, and apathy and stress often set in. From a medical disease it develops into a social problem.
Average degree of damage
In this case, the patient is haunted not only by psoriatic rashes, but also by itching and burning of the problem area. In addition to drug treatment, the following is prescribed:
- phototherapy;
- plasmapheresis;
- cryotherapy;
- PUVA.
It is also recommended to take internally and use external retinoids, which contain vitamins A.
From what and for what reasons does it appear?
In modern medicine, no relationship has been established between the occurrence of a disease of a complex nature and gender, age, structural features of the body and the presence of past illnesses. But long-term observations of the development of psoriasis made it possible to identify risk factors for the development of the disease:
- Frequent injuries to the extremities, especially the toes. Improper foot care: dry foot skin, poor-quality cosmetics, excessive hygiene.
- Heredity.
- Changes in the hormonal levels of the body.
- Stressful conditions, psychological and emotional overload.
- Infectious diseases.
- Intoxication syndrome.
- Metabolic disorders (including those associated with thyroid dysfunction).
- Phlebeurysm.
- Decreased immunity.
- Lipid metabolism disorders.
- Allergy.
- Long-term use of medications.
- Disruption of the central nervous system.
In addition to the listed factors that provoke the onset of the disease, there are reasons associated with the change of seasons:
- Summer psoriasis occurs due to exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
- Winter psoriasis - from severe frost.
There is a form of psoriasis, the causes of which have never been established: the disease manifests itself all year round and does not have any of the factors for its development.
Choice of medications
In the initial stages, you can get by with more gentle medications. Dermatologists usually recommend ointments with a non-hormonal composition. The most popular of them are:
- Ichthyol;
- Tar;
- Naftalan.
They are able to eliminate inflammatory processes and play the role of antiseptics. These compositions have significant contraindications, so they can only be used according to the indications of a specialist. What drugs are we talking about:
- Salicylic acid, Cygnoderm. These compounds are capable of destroying the stratum corneum. They are classified as keratolytics. A characteristic property of these substances is the ability to exfoliate and resolve plaques.
- Antipsoriasis, Akrustal. They contain solid oil. These products have a regenerating, that is, restorative effect on the skin of the feet, softening it.
- Psorkutan. It contains an active form of vitamin D, which inhibits cell division. Due to this, the degree of inflammation and peeling is reduced.
If these medications fail to cope with the progression of the disease, switch to corticosteroids. They are used to treat the surface of defects. What groups are distinguished here:
- Low activity compounds. These include Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone. They act on the surface of the epidermis and are suitable for the initial manifestations of the disease.
- Moderately active. They combine Betamethasone, Decoderm. What ointments are advisable to use on rough areas of the skin, for example, the soles and knees.
- Highly active. These are Ultraveit, Galciderm, Dermovate. They must be prescribed when all previous classes of medications have failed to stop plaque enlargement.
It also happens that external dosage forms do not cope with the symptoms. In this case, you need to connect the tablets. The following drugs are considered the most effective:
- Cyclosporine. It suppresses the immune system and its activity in the body.
- Methotrexate. Does not allow epidermal cells to grow too much.
- Acitretin and Accutane are tablets from the group of retinoids, that is, derivatives of vitamin A. They are a necessary component for the regeneration of dermal cells.
Varieties
Depending on the location and manifestations of the disease, several types of psoriasis on the legs are distinguished.
| Type of psoriasis | Features of the course of diseases and |
| Ordinary (plaque) | Gray or silvery plaques form on the skin of the feet, legs and knees, which grow quickly and form large lesions. |
| Pustular generalized (exudative) | A severe form of the disease in the lower leg: feet and legs (less commonly, knees). Bubbles appear - not dry, but filled with reddish liquid. They often open, and there is a risk of a slight inflammation that can quickly develop into a purulent wound. |
| Plantar pustulosis | Localized on the soles of the feet. It is characterized by the appearance of purulent blisters, which are constantly opened during the mechanical action of walking. |
| Psoriatic onychodystrophy | A non-infectious form of the disease associated with damage to the toes. Manifests itself in the pathology of the nail plates.
|
| teardrop-shaped | Occurs due to a previous streptococcal infection. It appears as a large number of small rashes on the skin of the limb, red in color. Location: knees. |
| Psoriatic arthropathy | Internal form of the disease. Knee, hip joints and connective tissues are affected. The toes and joints become swollen. The patient experiences severe pain and is often immobilized. The disease leads to disability. |
| Inverse | Localized on the inner side of the thigh. Presents almost non-flaky pale pink smooth spots. |
| Psoriatic erythroderma | It flows from the groin area to the feet. It is characterized by intensely itchy rashes with peeling skin, swollen lymph nodes and swelling. |
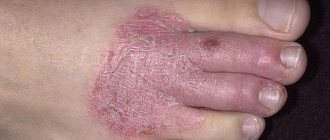
| Psoriasis on the feet | Constantly bleeding cracks form on the soles, blisters form on the heels and near the toes. Sweat and friction cause severe itching. |
Psoriasis on the feet
The feet can be affected by any type of disease. Treatment of this area is the most difficult, since many people need to wear shoes all day long and walk.
In children, foot psoriasis is a very serious disease. In this case, the entire localization surface turns red. Because of the pain, it is often impossible to touch it.
The skin of the feet is susceptible to fungal infections. Fungus on the feet causes complications of psoriasis.
For therapy, it is very important to treat the skin of the feet with antiseptics and constantly moisturize it.
You can look at photos of psoriasis on your feet to become familiar with the symptoms.
Treatment
Due to the complex concept of the development of the disease, its treatment is complex. It is important that all methods of therapy are aimed at reducing the symptoms of psoriasis and alleviating the suffering of the sick person.
In addition to an integrated approach to treatment, there are a number of rules, following which you can reduce the risk of worsening the patient’s condition:
- Thorough but not excessive foot hygiene.
- Timely replacement of underwear (socks, tights).
- Shoes that do not restrict movement and do not chafe the skin.
How to treat using traditional therapy?
This therapy involves the use of anti-inflammatory and regenerating ointments, gels and topical medicinal creams.
For psoriasis, the following types of ointments are used:
- Non-hormonal agents: Salicylic, Ichthyol, Sulfuric, Zinc, Naftalan ointments, Kartalin, Daivonex, Psoriaten, Calcipotriol, etc. Ointments relieve itching, regenerate and disinfect the dermis, and resolve exudates. They have virtually no side effects, except for individual intolerance.
- Hormonal agents: Triderm, Belosalik, Advantan, Hydrocortisone, Fluorocort, Flucinar, Prednisolone, Lokoid, etc. Gels quickly relieve the symptoms of the disease: relieve swelling and inflammation, reduce itching, restore and regenerate the dermis. But they have side effects: they disrupt metabolism, discolor the skin, and can lead to infection.
Systemic medications
Therapy based on the use of drugs orally is called systemic.
It involves taking the following medications in the form of tablets or solutions intramuscularly or intravenously:
| Product name | Action |
| Antihistamines: Zyrtec, Claritin, Suprastin, Diazolin | Relieves itching and inflammation |
| Antibiotics (penicillin group) | Fights purulent rashes |
| Enterosgel, Polysorb, activated carbon | Removes toxins |
| Diprospan | Used for advanced, severe forms. Quickly relieves symptoms, but has many side effects |
| Sandimmune | Quickly eliminates inflammation. But due to high toxicity, it is used only in a hospital under the supervision of a physician. |
| Methotrexate | Stops the development of the disease. Contraindications: kidney and liver diseases |
Physiotherapy
A good addition to the treatment complex are physiotherapeutic procedures, which are carried out only during inpatient treatment or remission.
The most effective are the following procedures:
- Light therapy of the legs - ultraviolet irradiation (recovery in 80% of cases).
- Cryotherapy – cold treatment for 1-6 months.
- Plasmaphoresis is the transfusion of your own blood after ultraviolet irradiation.
- Puva therapy is the use of psoralens, which increase sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation.
In addition to the methods listed above, traditional physiotherapy procedures are used:
- electrosleep;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- darsonvalization.
Psychological methods
Since the development of psoriasis is presumably stimulated by a negative psychological and emotional state, various psychotherapy techniques are used in treatment:
- Psychological training to identify the causes of stress.
- Teaching the patient the ability to get out of conflict and stressful situations, suppress anger and irritation, and develop self-confidence.
Complete elimination of negative factors leads in most cases to recovery or long-term remission.
Folk remedies for use at home
To enhance the therapeutic complex of treatment, folk remedies are widely used:
- Ointments against the disease:
- based on propolis and butter;
- Vaseline and crushed fresh celandine.
- Blends:
- from honey and glycerin;
- from medical grease, honey and baby cream;
- from Kalanchoe juice, honey and eucalyptus oil.
- Compresses:
- from grated raw potatoes;
- with apple cider vinegar.
- Decoctions of string, celandine, licorice and oregano.
- Birch tar.
Herbal products are gentle and have no side effects.
Systemic drugs
For moderate and severe disease, systemic medications are prescribed in the form of tablets and injection solutions.
It is recommended to treat psoriasis on the legs under the supervision of a doctor using the following medications:
- Antihistamines help cope with itching and reduce the inflammatory process (Zyrtec, Suprastin, Telfast, Claritin, Diazolin, etc.).
- If suppuration is present, antibiotics from the group of penicillins or cephalosporins are prescribed.
- Enterosgel, Filtrum-sti, Polysorb, activated or white carbon and other enterosorbents have a detoxifying effect.
- Diprospan in the form of an injection solution is used to treat severe forms of the disease. This is a hormonal drug that has a rapid therapeutic effect, but at the same time causes many side effects.
- Sandimmune is an immunosuppressant that helps quickly eliminate inflammation. The drug is highly toxic, so it is used only in a hospital setting under the watchful supervision of doctors.
- Methotrexate in the form of tablets and injection solutions is an analogue of folic acid that stops cell division and the spread of the psoriatic process. The drug cannot be used for pathologies of the kidneys and liver.
- Infliximab is indicated for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis.
- A solution of sodium thiosulfate cleanses the body of waste and toxins, has an anti-inflammatory effect, and restores immune defense.
Preventive measures
By following preventive measures, you can prevent the occurrence and development of the disease.
Prevention recommendations:
- lead an active lifestyle, play sports;
- sunbathing;
- wear comfortable, loose shoes, be sure to walk barefoot (at home, in the garden);
- monitor the condition of your nails: keep them clean, treat them with products that prevent the development of fungus;
- treat feet with antiseptic agents;
- follow a diet (no smoked meats, sweets and alcohol).
If psoriasis has become your problem, do not despair, because, knowing the symptoms and causes of the disease, you can begin treatment on time. But only an attentive attitude to the pathology and patiently going through all the procedures will help curb its unpleasant symptoms. Hello!
Prevention of psoriasis on the legs
Psoriasis currently has no cure, but after treatment it is important to delay the time of relapse for as long as possible. Treatment is sometimes expensive, as the cost of many drugs is quite high. But by following preventive measures, you can extend the time of remission by years.
- It is important to monitor your diet, exclude alcohol, tobacco, and allergy-causing foods. It is recommended to include vitamins D and A in your diet.
- Eliminate various psychological stress.
- In summer and winter, protect your skin from exposure to the sun and frost.
- Cleanse, nourish and moisturize the skin.
- Use natural remedies for preventive measures under the supervision of a doctor.