Causes of skin pathology in children
Psoriasis in a child can occur under the influence of various factors. The root causes of this pathology have not been fully studied, but the factors that provoke improper cell division have been established quite accurately. Reasons that provoke the occurrence of psoriasis in children:
- Genetic predisposition. A relationship has been identified between parental psoriatic rash and the appearance of symptoms of this pathology in the future in the child. In this case, only the type and characteristics of the skin that are favorable for the development of this disease are inherited.
- Autoimmune pathologies. Rashes are formed against the background of a strong immune reaction, which provokes destabilization of cells and leads to their improper division.
- Psychological destabilization. The load on the child’s immature nervous system leads to autoimmune disorders.
- Parasitic infestations and infectious microflora. The development of psoriatic rash is observed with long-term use of medications that are prescribed to relieve the inflammatory process.
- Pathologies in the functionality of the endocrine system. The main function of the endocrine glands is to maintain the hormonal balance of the growing organism. Hormonal imbalance can cause disruptions in the functioning of not only the skin, but also the entire body.
- Balanced diet. Nutrition problems can cause anemia, disruptions in electrolyte balance, and disturbances in the functionality of metabolic reactions in the body. Due to the appearance of these pathologies, favorable conditions for the development of psoriatic rashes may form.
It is impossible to accurately determine the causes of psoriasis in children.
Prevention of exacerbations of the disease
The following rules and recommendations should be observed in everyday life:
- monitor the child’s hygiene;
- When bathing, use gentle products and soft washcloths;
- avoid hypothermia and overheating of the baby;
- buy clothes made from natural fabrics;
- exclude foods that may cause allergies from the child’s menu;
- avoid protracted illnesses;
- strengthen children's immunity;
- Treat cuts and cracks correctly.
If you suspect an exacerbation of the disease, you should immediately contact a dermatologist. Timely and correct treatment will ensure long remission of the disease. Older children should be taught that psoriasis is not contagious and will not limit their daily activities. Teenagers need to be given moral support.
How does psoriasis begin in children?
Depending on the progressive course of childhood psoriasis, several stages are distinguished:
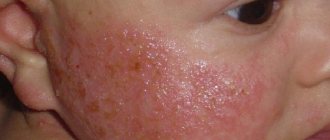
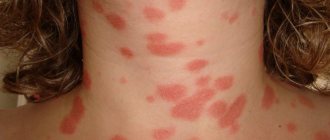
- Initial. Symptomatically manifests itself through the formation of rashes in the folds and the appearance of hyperemia. Psoriatic rash spots can merge with each other. They are often diagnosed on the face, genital area or buttocks. After a certain period of time, the rash begins to actively peel off, which is the main difference between psoriasis and other dermatitis.
- Progressive. When this phase of development of psoriatic rashes occurs on the child’s skin, an increase in the affected area is observed, followed by the spread of pathology to the head area. Scaly formations are found only in the center of the spots. With psoriasis diagnosed in children at an early stage, mild peeling is also possible. If the scaly layer is removed, bleeding and the presence of a terminal film are observed. This period lasts on average about 2 or 3 months.
- Stationary. At this stage, the formation of additional affected areas stops and the formation of peeling continues.
- Regressive. This phase of the development of pathology is accompanied by a decrease in dead zones and the spread of white spots in the affected areas begins.
The first signs characterizing the presence of psoriasis in children include:
- obvious enlargement of lymph nodes;
- the appearance of severe itching;
- formation of thickening in the area of psoriatic rash;
- elevated temperature levels in a child;
- the appearance of pigmentation, which begins with pink shades and reaches scarlet;
- pronounced swelling of the skin surface.
Psoriasis in adolescents manifests itself with almost the same symptomatic picture as in children. A provoking factor for the development of the disease is hormonal imbalance in adolescent patients.
What ECZEMA looks like in the initial stage: detailed PHOTOS in the article - coin-shaped eczema.
What is guttate psoriasis, why it occurs, how it manifests itself in children and adults, principles of treatment and prevention, see here - guttate psoriasis.
How parapsoriasis differs from psoriasis, forms of parapsoriasis and principles of therapy, treatment at home, read here - treatment of parapsoriasis.
Subtypes of childhood psoriasis
Psoriasis has several types. They are distinguished by the nature of symptoms and localization of the rash:
- Diaper subtype. Formed in babies up to one year old. The rash usually appears on the buttocks. It is difficult to diagnose the pathology due to the similarity of symptoms with irritation. Photos of psoriasis in infants clearly demonstrate the situation.
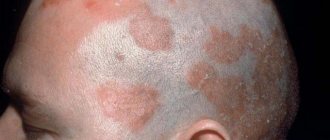
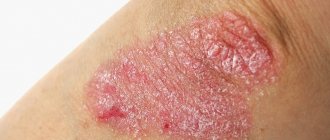
- Plaque-like. Or ordinary. The most common not only in children, but also in adults. Reddish spots are visible on the skin, slightly rising above the general surface. The spots gradually grow in area and become covered with silvery, easily detachable scales. May appear in different areas. However, more often - in the fold areas. It is also often possible to notice psoriasis on a child’s head.
- Teardrop-shaped. The formations are small and drop-shaped. It often develops into plaque psoriasis, but may simply disappear over time. Between the ages of 4 and 5 years, this subtype usually appears due to a streptococcal infection.
- Generalized. Appears quickly and unexpectedly. Affects large areas of skin. The formations are pustular and painful. May cause complications in the form of pathologies of the heart and kidneys.
- Pustular. Appears at the age of 7 years. It rarely happens before this age. The skin swells and becomes covered with blistering formations with liquid inside. Often the disease occurs in conjunction with inflammation of the lymph nodes. Photos will demonstrate these signs of childhood psoriasis more clearly.
- Erythrodermic. It is formed due to improper thermoregulation of the body. The rash affects large areas and is very flaky and itchy. Over time, the skin peels off. This type of psoriasis can cause death. Especially for kids.
- Psoriasis of the flexor surfaces. Formed in fold areas. The formations are smooth and convex. There is no peeling.
- Nail psoriasis. Formed on the nail plates.
- Arthropathic. Affects joints. Muscles lose mobility, joints and fingers swell.
In addition, psoriasis is divided depending on the time of year when it appears. In children - usually in winter and late autumn. Due to different forms of psoriasis, symptoms and treatment in children may differ slightly.
How does psoriasis manifest in children?
Symptoms of psoriasis rashes in children have a similar course:
- hyperemia of the skin;
- a feeling of pain and severe itching in the affected areas;
- the appearance of plaques or rashes;
- bleeding is observed under the upper keratinized layer;
- Infants develop oozing.
Often there is not only the development of one psoriatic disease, but also the addition of an additional secondary infection.
The symptomatic picture of childhood psoriasis also depends on the type of disease. The main variants of the disease are presented in the table.
| Form of psoriatic rash | Symptomatic manifestations |
| Diaper | Externally, the symptoms are especially similar to dermatitis, which makes it difficult to diagnose this disease. The pathology spreads in places under the diaper, these are the buttocks and groin area. Psoriasis in newborns begins with the formation of weeping areas of the skin. |
| Plaque form | Accompanied by the appearance of plaques with clear boundaries, which are accompanied by pigmentation. As the disease progresses, an infiltrate may form under the keratinized layer. Affects the elbows or knees, and can sometimes spread to the scalp. |
| Guttate psoriatic rash | It is characterized by the formation of tubercles with pigmentation that resemble drops of a red hue. The spread is very fast. With prolonged development without proper treatment, self-elimination occurs or the pathology transitions to a plaque-like form. |
| Pustular | The disease is accompanied by the formation of papules with purulent contents or liquid inside. Additional symptomatic manifestations include swelling, hyperthermia and itching. With prolonged development, the appearance of erosive areas is observed, followed by the addition of pathogenic microflora. The pathology may spread to the entire surface of the skin. Affects schoolchildren and older age groups. |
| Erythrodermic | A striking distinctive symptom is the loose structure of the upper layer of skin, which is accompanied by infiltration. Sometimes there are areas with blood. It can affect fairly large areas of the skin surface. The development of pathology is accompanied by headache, itching and hyperthermia. In case of acute intoxication, immediate hospitalization of the patient is necessary. |
| Seborrheic form | The rash provokes a pronounced feeling of itching and is characterized by peeling. Externally, the exfoliated areas resemble flakes. |
| Arthropathic type | It is a manifestation of psoriatic arthritis in children. It affects not only the skin, but also joint pain or swelling in this area. |
In young children, manifestations of psoriasis can be observed in various parts of the body:
- on the buttocks;
- in the groin area, especially in places in contact with the diaper;
- in the lumbar area;
- affects the armpits;
- scalp skin.
Procedural treatment
Treatment of psoriasis is a combination of processes. In addition to drug treatment, it is advisable to undergo procedures such as:
- Physiotherapy – plasmapheresis and ultraviolet treatment. Prescribed by a doctor after examination.
- Vitamin therapy. A child’s body with psoriasis is weakened and needs high doses of vitamins. Particular emphasis is placed on vitamin complexes with a high content of vitamin D.
- Cryotherapy. Can be replaced by swimming in cool (350C) water. To do this, just lie in a bathtub with cool water for 10-15 minutes 1-2 times a week.
- Phytotherapy. It is beneficial to brew and drink chamomile tea. It is also advisable to bathe the child in warm water with the addition of salt and infusions of soothing herbs, such as chamomile or St. John's wort.
What does psoriasis look like in children?
Childhood psoriasis has certain external symptoms, which depend on the type of disease and are presented in the table.
| Type of psoriatic rash | External manifestations |
| Plaque-like | One of the common forms of the disease. It manifests itself through the formation of hyperemia on the skin, which is accompanied by a feeling of itching and peeling of the stratum corneum. The diameter of the spots is quite variable. |
| teardrop-shaped | The impetus for the development of pathology is given by mechanical damage to the upper layer of the skin. In this case, tubercles of various red shades form at the site of the lesion, which after a while begin to peel off and itch. Externally, this type of psoriasis resembles allergic reactions. |
| Pustular | With the development of this pathology, the formation of blisters filled with liquid is observed on the body. If they burst, open inflammations form. |
| Generalized | This disease is rarely observed in children, but it has serious consequences. Development occurs with sudden damage to large areas of the skin |
| Erythrodermic | The progression of the disease occurs with detachment of the affected areas. The disease can be fatal. |
| Arthropathic | Externally, swelling of the fingers or toes is observed. Later, muscle or joint pain appears. |
The stages of development of psoriatic rash are also characterized by various external manifestations, namely:
- The progressing stage occurs with the appearance of red areas that itch and peel. Often the spots quickly enlarge and spread over the skin. Soon cracks form and bleed. In severe cases, the child may experience an increase in body temperature, lymphadenitis, and severe swelling.
- The stationary stage is characterized by a decrease in areas of peeling and a cessation of the spread of the rash.
- With the regressive type, resorption of the rash and the appearance of depigmented areas are observed.
Psoriasis in children can spread to the scalp; seborrheic type of rashes especially often affects this area. To successfully treat psoriatic rash in a child, a comprehensive diagnosis is necessary.
Treatment methods
Before you begin to treat psoriasis, you need to find and eliminate the cause of its appearance:
- stress;
- infection;
- allergies;
- and etc.
Further treatment depends on the characteristics of the child’s body and the stage of the disease.
Medications for psoriasis can be divided into several categories.
| 1. | Topical steroids | The main active ingredients in such drugs are hormones. The use of topical steroids makes it possible to achieve a quick and long-lasting effect. But if the recommendations for use are not followed or if there is individual intolerance, there is a high risk of developing skin atrophy or withdrawal dermatitis. Not recommended for children. May cause Cushing's syndrome, growth retardation, and other serious problems. | Betamethasone, Lokoid, Dermovate, Flucinar Celestoderm-B |
| 2. | Non-hormonal agents | The main active ingredient is active zinc or calcipotriol (synthetic vitamin D3). Preparations with calcipotriol are allowed for children over 6 years of age, and those based on zinc - for children over 1 year of age. Zinc-containing preparations are highly effective and safe. They can be applied without restrictions to any, even sensitive facial skin and to affected areas of any area. | Calcipotriol - “Calcipotriol”, “Davonex”, “Daivobet”. Zinc – “Zinocap”, “Skin-cap” |
| 3. | Products for external use | Each drug has its own nuances and limitations for use. Some may cause allergies, excessive dry skin or kidney problems. | Salicylic ointment, Lanolin cream, Fluorocort, Prednisol ointment, sulfur-tar and others. |
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of psoriatic rash occurs after a comprehensive examination by a dermatologist, who will pay attention to the psoriatic triad:
- slight elimination of the upper keratinized layer is observed;
- after removing the stearin stain, a terminal film is formed;
- bloody dew under the terminal layer.
Psoriasis in an infant can develop without the formation of a terminal film in the form of weeping. An accurate diagnosis can be determined after testing:
- general blood analysis;
- urine test;
- coprogram;
- HIV test;
- study of scrapings in a histological section;
- enzyme immunoassay;
- analysis of a smear from the mucous membrane for flora.
Psoriasis in infants can develop rapidly and with complications, so timely and high-quality diagnosis with all of the above studies is necessary.
What provokes psoriasis, what psoriasis looks like on the hands and how it begins, see here - psoriasis of the palms.
Where to treat psoriasis, treatment with radon baths, naftalan therapy. Read about treatment of psoriasis with mud and leeches here - naphthalan therapy.
Types of phototherapy, what are its advantages, complications and side effects. See the features of treatment using phototherapy in children here – https://psoriazweb.ru/lechenie-psoriaza/lechenie-psoriaza-fototerapiej.html
How is psoriasis diagnosed, besides external signs?
Of course, at first, the disease is diagnosed with an external examination, through which a specialist determines the area of focal lesions and the degree of neglect of the disease. But external examination is far from the only method of diagnosis.
Psoriatic triad
The psoriatic triad represents a number of symptoms characteristic of this disease. Based on them, the doctor can make a diagnosis. These symptoms include the following:
- Stearic stain. This symptom is characterized by increased peeling. This is due to the fact that dried epidermal cells become loose and cannot linger on the surface of the skin. Peeling flakes look a lot like dandruff.
- Terminal film. This symptom is characterized by the covering of the papule with a thin film, which comes off very easily when rubbed. If you remove all the scales from the plaque, you can see this film with the naked eye.
- Pinpoint bleeding. This symptom can be detected after the film is removed. With the appearance of pinpoint bleeding, one can observe the beginning of the rapid growth of plaques and their merging together.
Based on a number of these signs, you can accurately diagnose psoriasis.
Laboratory tests for differential diagnosis
After the specialist makes a visual examination, he directs the patient to undergo laboratory tests, which take place in several stages. The patient will need to submit the following material for testing:
- Scraping from the site of skin lesions. Differential diagnosis is carried out using the results of histological examination. For a superficial scraping, scaly material is removed from the plaques, and for a deep scraping, droplets of blood are collected from the papules.
- Blood donation. A blood test is mandatory in diagnosing psoriasis. With a prolonged course of the disease, a low level of hemoglobin and an increase in the number of leukocytes can be detected in the material.
- Analysis of urine. Skin ailments often occur with metabolic disorders; analysis of the material helps to get an idea of the state of the water-salt balance in the body. The detection of sedimentary salts in the urine indicates a severe course of the disease.
Laboratory tests will help make a more accurate diagnosis and determine the stage of the disease. Based on the diagnostic results, individual therapy is selected.
Principles of treatment of psoriasis in children
Complete recovery from psoriasis cannot be achieved with treatment in children. The main goal of therapy is to increase the duration of remission and quickly relieve the main symptomatic manifestations during periods of disease progression. For the treatment of psoriatic rashes the following are used:
- eradication of provoking factors;
- sedative medications;
- antihistamines;
- desensitizing drugs;
- a full range of vitamins and minerals;
- if necessary, it is possible to use hormonal drugs;
- medicinal baths;
- physiotherapeutic measures;
- climatotherapy.
It is necessary to treat the disease in children at the first manifestations. Often, psoriasis that has spread to a child’s head looks like dandruff, and only after a long time do specific symptoms appear.
Drug therapy
It is necessary to treat psoriasis in infants with the help of topical medications, these include:
- salicylic acid;
- Kartalin;
- Akrustal;
- Zinc ointment.
In children over 2 years of age, hormonal therapy may be prescribed for the treatment of psoriasis based on:
- Hydrocortisone.
- Flumethasone;
- Flucortolone;
- Prednisole.
Additionally, complex medications are taken that will support the immune system at a high level and various vitamin complexes.
Diet
It is also possible to achieve long-term remission with the help of dietary nutrition. In this case, exclude from the diet:
- fried foods;
- fatty meats;
- butter;
- sweets, including chocolate;
- strawberries and all citrus fruits;
- dairy products with a high percentage of fat.
It is also necessary to reduce salt in the diet. Following a proper diet will significantly alleviate the symptomatic manifestations of psoriatic rash.
Psoriasis in children is often perceived by parents as allergic manifestations or dermatitis. However, it is impossible to miss time to treat this pathology, since it is in the initial stages that it is easiest to cure.
How to treat yourself at home?
If the disease is severe and accompanied by complications, then the patient is treated in a hospital.
Pathology at the initial stage of development can be dealt with at home. Traditionally, medications are used. If you approach the problem in a comprehensive manner, then psoriatic rashes will begin to go away quickly. Therefore, in addition to pharmaceutical drugs, physiotherapy and alternative medicine methods are used.
It is important to adhere to a certain diet. Therapy depends on the stage and severity of the disease
Drug therapy
To treat guttate psoriasis, doctors recommend drug therapy. It allows you to quickly transfer the disease into remission. For this purpose, drugs of different therapeutic effects are used.
Drug therapy includes oral administration:
- antihistamines;
- vitamins;
- antibiotics;
- hormonal drugs;
- immunomodulators;
- cytostatics.
Additionally, ointments and creams with anti-inflammatory, moisturizing, antiallergic, exfoliating and regenerating properties are prescribed.
For example, Triderm, Travokost, Naphthalene ointment, Dermovate, Kartalin, Daivonex, Psorilom, Cygnoderm, Sophora. Ointments based on corticosteroids are widely used: Advantan, Hydrocortisone, Belogent, Beloderm, Lorinden.
Infliximab is prescribed when ointments and creams are ineffective. This remedy has immunosuppressive properties.
For severe skin disease, doctors prescribe the antibiotic Azitrox. If the pathology is accompanied by an inflammatory, infectious process, then Clarithromycin is used.
Latest generation antibiotic Azitrok
It is recommended to take vitamin complexes that include D3: Calcitrin, Maxacalcitol, Tacalcitol. These drugs have proven effective in the fight against psoriasis.
They are recommended to be taken in combination with ultraviolet irradiation. To support pH balance and detoxification, NSP products are used: Chlorophyll, Black Walnut, Nature Lax, Loklo, Red Clover.
Treatment of guttate psoriasis with folk remedies
Traditional methods are also used to treat pathology. As monotherapy, alternative medicine recipes are effective at the initial stage of the disease. In severe cases, they are used in combination with drug therapy.
Effective alternative medicine:
- Pour the leaves of the string with alcohol and leave for several days. Add lanolin and Vaseline. Mix and apply the resulting creamy mass to the affected skin;
- Mix eucalyptus oil (30 g), honey (10 g), Kalanchoe extract (10 g) and leave for three days. Wipe the skin areas affected by psoriasis with the composition;
- mix lycopodium (2 g), celandine (5 g), honey (2 g), grease (60 g) and lubricate the rash three times a day;
- Combine celandine (10 g), one protein, rosehip branches (30 g), oak bark ash (30 g), mix, leave for 3 weeks in a dark cupboard at room temperature. Apply the finished composition to psoriatic plaques;
- combine celandine tincture and red wine in equal parts. Wipe the skin twice a day.
These remedies are used until the psoriatic plaques disappear. It is useful to take herbal baths based on a decoction of string, celandine, and chamomile. These plants relieve inflammation and soothe the skin.
Traditional healers recommend drinking linden and mint tea. Sea buckthorn oil also helps to cope with the disease. They lubricate the affected areas of the epidermis. At the same time, it is taken orally, a teaspoon in the morning on an empty stomach.
It is useful to treat the affected areas with sea buckthorn oil
Monastic tea helps well with the teardrop type of psoriasis. This collection contains plants that relieve inflammation, itching and promote recovery. The product is hypoallergenic and improves blood circulation.
The patient should take only those medications prescribed by the doctor. The use of traditional methods should be discussed with your doctor. Self-medication can only worsen the condition.