What is a subcutaneous mite
Before you begin treatment, you need to carefully understand what demodicosis is.
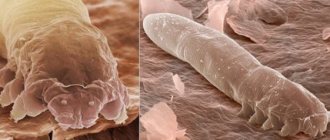
Demodicosis or acne is a chronic disease that causes the activity of subcutaneous mites. This parasite, measuring about 0.4 mm, can live in the sebaceous glands and follicles of humans. Its body is elongated, translucent, covered with a shell of scales.
The dense shell protects the parasite, making it resistant to various chemicals . The average lifespan of a subcutaneous tick is about 60–120 days.
There are two types of parasites:
- Demodex brevis. Lives in the sebaceous glands associated with the follicles.
- Demodex folliculorum. It is found directly in the follicles located over the entire surface of the head, including in the front part.
The subcutaneous tick moves actively at night because it does not tolerate sunlight well. It feeds on bacteria, dead cells, and products produced by the sebaceous glands.
According to scientists, ticks under the skin are found in 90% of the population and, as a rule, do not cause any inconvenience to the carrier. However, when favorable conditions occur, the parasite begins to actively multiply, penetrating into the deep layers of the skin and maintaining its vital activity due to dead cells, as well as the sebum produced by the glands.
At this stage, the disease becomes noticeable - redness of the skin and peeling appear.
Diagnosis
Regardless of what kind of symptoms appear, it is necessary to consult a doctor. It is impossible to diagnose the disease on your own; an examination of the patient is required, a scraping is taken from the skin and studied in a laboratory setting.
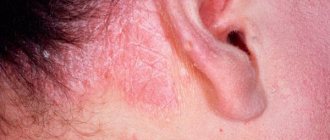
In most cases, skin parasites affect areas of the skin on the face. A person can easily confuse the first manifestations with ordinary acne and think that it is just pimples. The use of incorrect medications only aggravates the condition, the disease develops and complications appear on the facial part of the body.
In subsequent stages, the oval of the face may become deformed, the size of the nose will increase, and severe swelling will be observed.
When the hands are affected, purulent rashes appear on the outside. Infection of these areas is quite rare, and infection is often associated with the use of fatty cream by an already infected person. Such symptoms are confused with eczema and dermatitis, which should not be allowed.
Damage to the legs and chest by the subcutaneous parasite occurs in very rare cases; most often these areas are affected by the scabies mite. In addition, a rash on the skin in these areas may be associated with a moose flea bite. Each individual case requires its own individual treatment.
The parasites do not affect the back and buttocks; any signs in these areas may indicate the development of eczema, allergies, or tick-borne dermatitis.
Remember, the earlier the disease is correctly diagnosed, the easier it will be to cure it. The development of the disease causes complications that will be quite difficult to cope with. In severe, advanced forms, treatment can take years, and sometimes complications caused by the disease lead to irreversible processes.
Symptoms of the disease
Most often, demodicosis affects the skin of the eyelids, forehead, cheeks and even the external auditory canals. The parasite can also settle in the hair of the chest, head, and back. Women are susceptible to this disease more often than men.
The following symptoms of demodicosis can be distinguished::
- skin itching, which intensifies at night.
- The appearance of a large number of acne, pustular formations, and rashes.
- Peeling of the epidermis.
- The formation of tuberous growths that are felt upon palpation.
- Inflammation and redness of the eyes.
- Appearance of a grayish tint on the skin.
- Active hair loss (including eyelashes).
- Active work of the sebaceous glands, oily skin shine.
- Pore expansion.
- A cluster of white scales at the base of the hair.
- In advanced cases, the shape of the nose becomes deformed, it swells, and increases in size.
There are three stages of disease development:
- prodromal period (initial stage). At this stage, localized redness of the epidermis and the appearance of a minor rash are noticeable, which is not a cause for concern. At this stage, treatment shows maximum effectiveness and leads to a quick and complete recovery.
- Erythematous period. The rash and redness are pronounced and cover large areas of the body. At this stage, the disease responds quite well to treatment.
- Papulopustular stage. At this stage, the skin becomes covered with nodules, from which ulcers subsequently form. Self-medication at this stage does not give the expected result and requires the intervention of a specialist.
- Hypertrophic stage. At the last stage of the disease, the skin becomes covered with numerous nodules, large ulcers, and bumpy growths. At this stage, demodicosis is difficult to treat even under the supervision of specialists.
Most often, these symptoms can be observed in older people, less often in young people, and even less often in children. This is due to increased oily skin in adulthood and significant accumulation of sebum.
Clinical picture
The main symptom of subcutaneous mites on the face is the presence of vulgar acne. The human skin is very thick, it shines in the sun (especially in the area of the cheeks and nose). Its color is unnatural, most often pale gray.
The pores begin to expand, which is noticeable to the naked eye. They secrete a large amount of sebaceous secretion, making the skin look oily all the time. At night, a person usually experiences severe itching, which significantly impairs the quality of rest.
Primary skin rashes can be presented in the form of papules, pustules, microabscesses and acne. During their formation, the skin turns red and swells. The vascular pattern often intensifies, sycosis and folliculitis develop.
If there are scars, scratches or knots on the patient’s face, it is customary to talk about secondary elements. In severe cases, the nose becomes deformed. The skin over it is replaced by scar tissue, and the volume of the organ also increases. Externally, the nose resembles a red plum. In this case, the doctor makes another diagnosis - rhinophyma.
When the first signs of active tick activity appear on your face, you should consult a dermatologist. He will carry out all the necessary diagnostic measures. Then the specialist will draw up the most effective treatment regimen for subcutaneous mites on the face.
An ophthalmologist treats the pathology if Demodex multiplies in the eye area. In this case, the symptoms are as follows:
- Redness and swelling are noticeable along the edges of the eyelids.
- Eyelash loss for no apparent reason.
- Copious and frequent lacrimation.
- You can notice purulent crusts on the eyebrows.
- Redness and dryness of the conjunctiva.
- The skin around the eyes begins to peel.
- Increased sensitivity to light.
- Presence of barley.
As mentioned above, demodicosis can affect not only the face, but also the torso and scalp. In this case, the skin also turns red, thickens, and forms vulgar pimples, which are very itchy at night.
Ways and causes of infection
It is not difficult to understand how demodicosis is transmitted. Acne mites come out from the sebaceous glands along with sweat and sebum, so it is easy to pick them up by using shared towels, dishes, or trying on clothes in a store. Ironwort acne is transmitted from person to person through a handshake or even a simple touch.
If favorable conditions exist, the subcutaneous parasite will begin to actively multiply; in their absence, the disease will not develop, and the person will remain a simple carrier.
It is not so important to know where the subcutaneous mite comes from and the causes of demodicosis. It is much more important to remember what factors can trigger the disease.
Among them may be:
- weakened immunity caused by prolonged, severe stress or prolonged use of antibiotics.
- Gastrointestinal diseases, including heavy consumption of coffee, alcohol, fatty foods, spicy seasonings.
- Hormonal diseases and disorders of the endocrine system.
- Use of other people's things, abuse of solarium, bathhouse, sunbathing.
- Regular use of low-quality cosmetics.
- Excessive sweating and active fat production.
Once in favorable conditions, females tend to lay eggs in the deep layers of the skin (up to 20–40 eggs per follicle). After three days, new individuals appear from them, which feed, reproduce, die and decompose in the layers of the epidermis. Waste products, accumulating, cause a severe allergic reaction.
Proper nutrition
In order for therapy to bring the most positive effect, it is necessary to reconsider your diet. Spicy, sweet, salty and fatty foods should be excluded. You cannot use semi-finished products, smoked meats and preservatives. The consumption of carbohydrates is also limited.
Meals should include a large amount of vegetables and fruits, cereals and dairy products. Also, during treatment, alcohol consumption is prohibited, and smoking should be stopped. Attention should be paid to a healthy lifestyle and taking vitamins, since it is very important to restore the body’s protective functions.
Diagnostics
At the initial stage, the symptoms of demodicosis can be easily confused with acne or allergies. Therefore, it is better not to self-medicate; before determining the cause of the disease, it is better to immediately start with diagnosis.
Before visiting a dermatologist, you should not use any antibacterial drugs and treat demodicosis on the back and other parts of the body with medicinal agents for 24 hours.
To diagnose demodicosis, scrapings are taken from different places . If the number of detected subcutaneous individuals exceeds 5 pcs. per 1 cm2, the disease is considered confirmed.
Of course, if demodicosis was detected on the legs, but not on the sternum or arms, the entire surface will have to be treated, regardless of location. The spread of subcutaneous mites in the absence of treatment is a matter of time.
Signs of illness
After the mite is activated, the skin becomes oilier, shiny, and the pores become enlarged. Rashes, pimples and ulcers may appear. The number of red spots gradually increases, they become lumpy. Some patients notice swelling of the skin.
When a person is a carrier of the subcutaneous mite, symptoms may be completely absent. Only under certain circumstances will the number of parasites begin to increase.
If the mite parasitizes the eyelashes, whitish scales are visible at their base. Gradually, hair loss, redness of the eyes, watery eyes and severe itching are noted. Lack of treatment leads to the formation of crusts and constant discomfort. The patient becomes nervous and generally feels unwell.
How to get rid of subcutaneous mites
Treatment of demodicosis is a complex undertaking. The victim must not only treat the affected areas externally, but also take antiparasitic agents internally. To obtain a long-term effect, it is necessary to exclude factors that provoke the development of the disease.
It is impossible to say clearly how long demodicosis can be treated. It all depends on the treatment used and the degree of neglect of the disease. At the initial stage, improvement may occur within a week, at the last stage - only after several months.
There are several main areas of treatment for subcutaneous mites.
Drug treatment
The most effective remedies for subcutaneous mites include::
- pills. Metrogyl and Trichopolum tablets are considered effective broad-spectrum antimicrobial drugs. To calm irritation and relieve redness, doctors prescribe antihistamines Suprastin, Zyrtec, Zodak. As additional therapy, agents are prescribed to strengthen the immune system.
- Ointments, gels, creams. Sulfur ointment has a pronounced therapeutic effect. It stimulates the regeneration of the skin and helps eliminate subcutaneous parasites, but has a pungent, unpleasant odor. Benzyl benzoate and permethrin ointment are effective against subcutaneous mites. The active substance of the drugs is able to penetrate the chitinous membrane of the parasite, destroying it.
Of course, before treating demodex with medications, you should consult a doctor to determine the optimal dosage and make sure there are no contraindications.
Antiparasitic drugs
In addition to the listed ointments and creams, a number of antiparasitic and medicinal drugs are used as an adjuvant for the treatment of subcutaneous demodex mites:
- Aerosol "Spregal". Spray on the body before bed, apply to the face using a cotton pad. The main active ingredient has a detrimental effect on both subcutaneous mites and laid eggs.
- Cream-gel "Dexomed Phyto". It has an antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, cleansing effect, it refreshes and soothes damaged skin.
- "Demazol". Accelerates skin regeneration, reduces inflammation caused by demodex mites.
- "Chlorhexidine." Inexpensive antiseptic drug with a wide spectrum of action.
- "Azogel". Restores the functioning of the sebaceous glands due to the azelaic acid included in its composition. It has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects.
- "Crotamiton." Used after a shower, relieves irritation, destroys parasites.
It should be noted that the listed drugs are used as part of complex therapy. If they are used as an independent means of treatment, the effect produced will be short-lived.
Antibiotics
These drugs are used as adjuvant therapy when ulcers appear. The demodex mite will not die from the effects of antibiotics, but the development of a secondary infection will be prevented. Thus, the process of healing and tissue regeneration will accelerate.
Antibiotics have quite a few disadvantages. They contribute to a decrease in immunity, disruption of the kidneys and liver, destroy beneficial microflora in the intestines, and provoke allergies.
Therefore, antibiotics are used only in advanced cases, when effective treatment of demodicosis is of paramount importance and the benefit brought by the medicine exceeds the harm caused.
Vascular strengthening agents
Such remedies cannot cure demodicosis. The purpose of the drugs is to strengthen the walls of the capillaries so that they cannot be damaged by subcutaneous mites. A treatment regimen for demodicosis using vascular strengthening agents should be developed by a doctor.
As additional support measures, you can use:
- ascorbic acid;
- fat-soluble vitamin E, which increases the strength of blood vessel walls;
- vitamin P, which reduces capillary fragility.
The use of vascular strengthening agents will remove redness of the skin.
Application of medicinal cosmetics
The use of professional cosmetics helps eliminate external signs of the disease. The main task of such preparations is to moisturize the skin, reduce sebum production without drying the surface, and relieve irritation. Also, cosmetics against demodicosis have a sunscreen effect.
Before getting rid of subcutaneous mites using medications, you can undergo a number of cosmetic procedures.
Deep peeling
To treat the skin, trichloroacetic acid is used, which dissolves the upper keratinized layer of the epidermis. Within a week, the scales with dead parasites and their metabolic products peel off and are replaced by new, healthy cells.
Demodicosis in humans can go away after deep peeling in the initial stages of the disease. If the parasite has penetrated into the lower layers of the skin, into which the acid does not penetrate, the procedure must be combined with drug treatment (only after consultation with your doctor).
Cryomassage
You can get rid of demodex in the upper layers of the skin using low-temperature treatment. During the procedure, the specialist uses a roller soaked in liquid nitrogen. As a result, the top layer of skin freezes and dies. The damaged epidermis peels off and a new layer is formed to replace it.
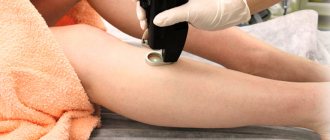
Laser removal
The procedure involves treating the body surface with directed light rays. Before being cured of demodicosis using laser treatment, you must undergo thorough preparation: stop using cosmetics for a week, exclude fatty foods, as well as foods that can cause allergies.
The course of maintenance therapy may include 5–15 sessions and be repeated 2–3 times a year, depending on the severity of the disease . Laser therapy not only gets rid of acne, it relieves swelling, increases blood circulation, and has an anti-inflammatory and decongestant effect.
Treatment
Treatment for scabies should be prescribed by a doctor only after examination, diagnosis and only on an individual basis. Often therapy occurs with the use of sulfur ointment and benzyl benzoate.
These drugs are quite effective, low cost and do not cause allergic reactions. But there is also a drawback, an unpleasant odor and stickiness. The course of treatment also includes taking antiallergic drugs. Quite often, baths using potassium permanganate are prescribed.
Getting rid of demodex will be much more difficult. In this case, therapy consists of complex treatment. Antimicrobial ointments are used, for example, ichthyol or benzyl benzoate. Antibacterial drugs are also used, for example, Colbiotsin, Demalan, immunomodulators, antibiotics, antihistamines.
Folk remedies
In the early stages, it is possible to treat demodicosis at home. Since subcutaneous mites are mainly localized on the head, various masks have a positive cosmetic effect.
The following remedies can be used for treatment:
- Yellow clay. It has an antimicrobial effect, whitens and nourishes the skin. The clay should be diluted with water to the consistency of sour cream and left overnight.
- Laundry soap. Has an antimicrobial effect. It needs to be grated, dissolved in water, whipped into a fluffy foam and left to dry.
- Solid oil. It is mixed with birch tar and olive oil in equal proportions and applied to the skin.
Herbal decoctions have antiparasitic properties, albeit to a lesser extent than medications. Suitable for preparing compresses or lotions: celandine, tansy, yarrow, wild rosemary, wintergreen, knotweed. Mint, oak bark or string will help relieve inflammation. Herbal infusions can also be used for daily washing.
Folk remedies are effective only in the initial stages of infection. It should also be noted that masks may be incompatible with other types of treatment.
What is demodicosis? Reasons for the development of the disease
- Decreased immunity (even local) in humans. The causes may include frequent infectious diseases, immunodeficiencies and blood diseases (leukemia).
- Diseases of the digestive system. This factor leads to endogenous (internal) poisoning of the body and, as a consequence, to contamination of the ducts of the sebaceous and sweat glands with toxins.
- Pathology of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis).
- Exhaustion of the nervous system – frequent, repeated nervous experiences and stress.
- Taking hormonal drugs internally or using them externally in the form of creams and ointments.
- Using cosmetics that are not suitable for your skin type. For example, they dry it out too much or, conversely, make it greasy.
- Eating disorders (irregular meals, abuse of spicy foods, large amounts of coffee and alcohol).
- Tobacco smoking, drug use.
- Excessive insolation (sunbathing, visiting solariums, saunas).
Answers to popular questions
A person who has been diagnosed with demodicosis immediately has a lot of questions. Let's try to answer some of the most popular ones.
People are interested in what a tick looks like under a person's skin . Due to the small size of this parasite, it is extremely difficult to detect on the surface. It can only be seen through a microscope. It is completely different from its forest counterparts and looks more like a worm, thanks to its elongated body.
Many people ask whether demodicosis is contagious in humans. Yes, this disease is contagious. A sick person is a carrier of the subcutaneous tick. He can transfer it along with hygiene products, personal belongings, and even through accidental touch.
Also, many people worry whether demodicosis has complications. Although this disease is not fatal, it is very unpleasant. If it is started, the victim’s skin will have pronounced cosmetic defects: lumps, ulcers, acne.
In addition, the disease provokes scratching of the affected areas, which can lead to infection of the surface and the formation of ulcers. If the subcutaneous mite reaches the eyelids, the eyelashes will begin to fall out, the eyes will hurt, itch, and a feeling of “sand” will appear.
All questions you may have can be asked to the dermatovenerologist by writing them down the day before your appointment. Having received complete answers to them, you can get a complete picture of what is happening.
What temperature is detrimental to demodex mites?
Demodicosis is a disease caused by the active reproduction of the subcutaneous demodex mite. A person of any age and gender suffers from two types of similar parasites, each of which is resistant to adverse environmental conditions. At what temperature does Demodex die? There is a popular belief that ticks disappear at certain temperature changes (from low to high temperatures). In order to understand this issue, it is necessary to study the structure and characteristics of the life cycle of a particular parasite. What kills demodex?
Have you been trying to get rid of PARASITES for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to get rid of parasites by taking every day...
Read more "
A type of dangerous subcutaneous tick
The size of such parasites ranges from 0.1 to 0.4 millimeters, so small microorganisms cannot be seen with the naked eye, especially since they live under the skin. Types of dangerous subcutaneous parasites for the human body:
Any type of subcutaneous mite exists by feeding on keratinized particles of human skin and the parasite does not survive inside the human body.
Features of the life cycle of the subcutaneous mite
Once they reach a person, the parasite eggs begin a new life cycle. Stages of development of Demodex in the human body:
This type of parasite can develop on eyelashes
The life cycle on the body of a healthy person is 14 days. Outside the body, the parasite continues to multiply and survives for up to two days. In an environment deprived of high humidity, the viability of the parasite persists for up to a month. Suitable conditions for demodex to live are a fatty environment in which the mite feeds for a long period of time. The optimal temperature for active reproduction of subcutaneous mites is 35-40ºC. A sharp drop in ambient temperature to -10ºC causes the parasite to go into torpor until more favorable conditions appear. The critical and maximum temperature at which demodex dies is 52ºC.
Symptoms of demodex reproduction
The clinical manifestation of demodex reproduction is difficult to ignore. Symptoms that a special mite has appeared in the subcutaneous layer of a person:
An advanced disease continues for weeks, even years, and is accompanied by worsening problems of the general condition of the skin. Demodectic mange does not go away on its own, but contributes to the formation of bumps on the face, followed by loss of eyelashes and hair. Self-medication is also fraught with serious consequences.
Fighting subcutaneous mites
At what average ambient temperature does a demodex mite die? Getting rid of the parasite is only half of the treatment for demodicosis. Restoration of the skin and subsequent prevention are also important. To combat subcutaneous mites, acaricidal agents are used in the form of solutions or emulsions. Medicines that destroy demodex include metronidazole and ornidazole. Complex therapy helps you return to a healthy, full life in a short period of time.
Is it contagious?
Anyone can get demodicosis, because mites live in any body.
There is a danger of contracting the disease in two ways:
- upon contact with a patient (by touching the skin, through kisses);
- through household items (using other people's towels, clothes, hygiene products, etc.).
It is quite easy to catch a “foreign tick” during a period of decreased immunity, exacerbation of chronic diseases, after surgery or childbirth. In these cases, the body is weakened and therefore vulnerable to the perception of harmful microorganisms.
Should I remove a tick after a bite?
In terms of first aid, definitely yes. But you need to get it out correctly, and if you don’t know how, then it’s better not to risk it (Figure 10). The fact is that by sharply pulling out the body, you can damage its integrity. And subsequently, part of the head or proboscis will remain in the skin, which leads to inflammation of the affected area. Even if you carefully pull it out, there is still a chance that small chewing particles will remain in the skin, which can cause a purulent abscess.
Figure 10. You need to remove the tick very carefully
To get the parasite out, you can treat the damaged area with any substance that does not allow air to pass through, for example, oil, then wait a few minutes and even if the pest does not come out on its own, it will become easier to unscrew it. You should grab the parasite as close as possible to the bitten surface with tweezers, a loop of strong thread, or clean fingers with proper dexterity. Holding it strictly perpendicular to the surface, you need to rotate the body of the arthropod around its axis and remove it from the skin.
For educational purposes, you should make a request online for tick bites - photos on human skin. The main thing is not to confuse local redness with the consequences of a lesion. In this case, you will already be faced with the result of incorrect self-medication. In the vast majority of scenarios, go to the hospital immediately and for sure.