STD
Symptoms of syphilis
Syphilis is an infectious disease. The causative agent is Treponema pallidum. It penetrates through mucous membranes or lesions on the skin. There are many ways of transmitting the disease.
Syphilis on the skin, as statistics show, affects more than 20% of the world's population. Moreover, the numbers are not indicative, because many patients simply do not seek help from a medical institution. This leads to an increased risk of infection.
- Ways of infection with syphilis
- Primary syphilis
- Secondary syphilis Incubation period
- Roseola
- Papules
- Shepherds
- Leucoderma
Spots on the body
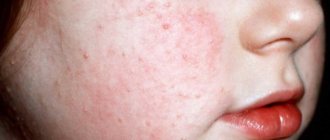
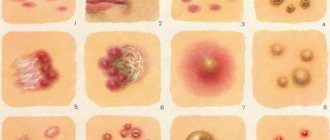
As treponemas multiply, certain changes occur in the body. The appearance of a rash on the skin is the most common symptom. First of all, spots appear. First, the patient notices a change in skin color in some places. They become a rich pink hue, and as syphilis progresses, they increase the affected area and provoke general malaise.
Skin manifestations of syphilis are classified in order to determine how long the treponema remains in the body. The spots should be distinguished from other rashes. The surface of the skin does not change. Syphilis spots cannot peel off; they are randomly located throughout the body. The upper layer of skin is damaged, so they do not have a large depression.
Congenital syphilis
With congenital syphilis, which appears some time after birth, the appearance of secondary syphilides can be observed on the skin. However, with the development of this form, skin manifestations are especially pronounced.
Papular syphilide - the main symptoms are presented in the form of infiltrates on the skin. The skin becomes thicker, swelling and redness appear. In pathological places, the skin is damaged, leaving small cracks. Even after everything heals, scars will remain, which are subsequently impossible to get rid of.
Another typical manifestation of congenital syphilis is syphilitic pemphigus. Small bubbles appear on the skin, inside which there is a transparent liquid, their size is about two centimeters. Common locations are the soles and palms.
The bubbles do not increase in size, and therefore do not merge with each other. The disease affects not only the skin, but also internal organs, and the child’s condition worsens.
Pimples
A few weeks to a month after infection, acne will begin to appear on the patient's face, body and mucous membranes.
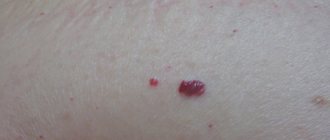
At the stage of primary syphilis, a hard chancre appears; outwardly it looks like a red spot. A nodule then forms and eventually becomes an ulcer. The cartilaginous bottom varies in size from 1 mm to 2 cm. A week after the appearance of pimples, they thicken and the lymph nodes enlarge.
During secondary syphilis, acne spreads throughout the patient's body. Most of them will be observed on the face. The spread of the rash occurs when the blood contains a large number of treponemas and they begin to affect tissues and internal organs.
New pimples will appear on the body for several months, consuming more and more of the skin's surface.
With secondary syphilis, pimples are brown in color and round in shape. They are located chaotically and have clear boundaries. The formation of abscesses indicates that syphilis is progressing successfully.
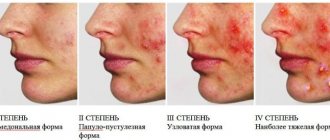
At the tertiary stage of syphilis development, the infection affects the nervous system and the condition of vital organs. Pimples become large bumps, they are mainly located on the forehead, head and nose.
Pimples during syphilis will not itch or peel; they have a dense consistency, as well as a reddish or bluish tint. There is no pain during touching, but squeezing the rash is extremely dangerous, as it will aggravate the person’s condition. Without taking antibiotics and selecting complex therapy, acne will not go away.
Tertiary syphilis
Rashes characteristic of tertiary syphilis form on the skin several years after infection. However, in medicine there are also cases where they appeared after 10 or more years. This is often due to the fact that the disease was not treated correctly.
Possible routes of infection
Syphilis of the skin at a late stage manifests itself as follows:
- gummas and tubercles on the skin;
- formation of small spots.
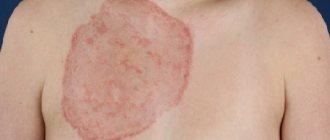
Such elements are not contagious. Gumma are dense nodules, up to 3 centimeters in size, protrude slightly above the surface of the skin, there is no pain. Gradually the skin over them becomes purple.
In rare cases, gummas open, and large ulcers remain in their place. The edges are tight, there is no pain, the bottom is lined with dead tissue. The ulcers may not go away for many months. After recovery, a rough scar remains. If ulcers do not form, the gummas heal on their own, and a subcutaneous scar remains in their place.
As for tubercular syphilide, tubercles up to one centimeter in size remain on the skin, the color is bluish-red. When ulcerated, deep defects remain on the skin, with a crust on top. Such symptoms may not go away for many months.
The video in this article explains in more detail what symptoms bother patients.
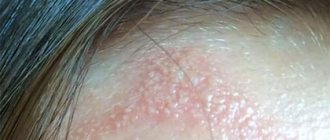
Papules
Papular rashes are pale pink in color and round in shape. They should not exceed 1 cm in diameter. At first, the syphilis rash has a smooth surface and is slightly shiny. As treponemas develop, the papules begin to peel off and become denser to the touch.
Mostly the rashes are located on the palms, legs and genitals. In the presence of concomitant diseases, the rash begins to itch. Due to constant discomfort, a person cannot lead a normal lifestyle, sleep disturbances and changes in the nervous system occur.
Patient examination plan
Before curing syphilis in the hand area, you need to make a correct diagnosis. For rashes on the lower extremities, the following diseases must be excluded:
- scabies;
- furunculosis;
- vasculitis;
chicken pox;- rubella;
- measles;
- lichen;
- lupus;
- acne;
- ecthyma;
- impetigo.
To confirm the diagnosis you will need:
- examination of the skin and visible mucous membranes;
- dermatoscopy;
- RW analysis;
- anticardiolipin test;
- coagulogram;
- general clinical tests;
- serological studies.
The pathogen can be identified by examining a scraping taken at the site of the rash or the patient's blood. For syphilis, dark-field microscopy is informative. Gram staining is not performed. The doctor must assess the condition of the internal organs. For this purpose, CT, MRI, ultrasound, radiography, angiography, lumbar puncture and electrocardiography are performed.
Leucoderma
White lesions occur during secondary syphilis.
They are observed 6 months after infection with syphilis. The rash remains on the body for several months. In the presence of concomitant diseases or poor immunity, this period increases to a year. Treponema is not found on affected areas of the skin, so antibacterial therapy does not affect leucoderma. Pale areas of skin during syphilis are observed in the neck area. Also, manifestations of syphilis can be found in the armpits, legs and arms. First, the patient develops yellow spots, then the process of discoloration begins within them. Patients do not experience itching, peeling or pain.
Leucoderma appears during a relapse of syphilis. Medicines do not affect its development, so the spots remain even after treatment. If a rash is detected, the patient should consult a doctor as soon as possible, since they may cause changes in the cerebrospinal fluid. Therefore, the physician will need to monitor the patient during treatment of the syphilitic infection and for several months after its completion.
Treatment methods
Syphilis on the mucous membrane or on the skin takes a long time to cure. In the secondary stage, therapy can last for several years in a row. For the entire period of treatment, it is necessary to avoid intimacy, especially if the infectious period is still ongoing. Preventive treatment is indicated for all family members.
If syphilis develops, you should not self-medicate or use traditional methods; this is not only ineffective, but also dangerous. Moreover, with syphilis, cure is determined not by the disappearance of symptoms, but by what laboratory tests show. In many cases, treatment takes place in a hospital.
The most effective treatment method is the administration of a water-soluble solution of penicillin. The medicine is administered once every 3 hours for 24 days. The causative agents of the disease are sensitive to antibiotics, and this is especially true for penicillin.
However, if effectiveness is not achieved, other drugs may be prescribed: macrolides, teracyclines, etc. In addition to taking antibiotics, you need to take vitamins, as well as medications to maintain immunity. Instructions for taking pills are issued strictly by the attending physician.
All family members should be careful. The patient must use his own items: dishes, bed linen, etc. A favorable prognosis with treatment is possible, but only if therapy was started in a timely manner.
Roseola rash
Roseola is observed in 70% of people suffering from syphilis. The rashes are round spots with jagged edges. The color of roseolas varies from pale pink to crimson. Doctors point out to patients that spots of different colors can occur even on one area of the body. When you press on the roseola, the stain completely disappears.
Roseolas do not merge with each other and do not peel off during the progression of syphilis. In terms of their relief and consistency, the spots should merge with the skin. The diameter of roseola does not exceed 2 cm. The rashes change color during cool weather, they become more saturated in color.
The rash can be located on the stomach, back, chest and mouth. Without drug treatment, the rash persists for 3 weeks. In the mouth, the rash will be clearly visible as it takes on a blue tint. The appearance of the oral cavity can be confused with a sore throat if the other symptoms of syphilis are not taken into account. Simultaneously with roseola, ulcers appear in the mouth; they are located on the vocal cords and larynx, causing the patient to lose his voice.
Recurrence of roseola rash occurs within 3 years after infection with a venereal disease.
Condylomas
Condyloma is a benign tumor that appears on the skin as a wart. Patients seeing them do not take the necessary measures, believing that the papilloma virus is simply developing in the body. Treponemas can provoke the formation of condylomas during the secondary stage of development of the disease.
Condylomas appear in places where friction constantly occurs or the skin regularly comes into contact with liquid.
This may be the area of the armpits, anus or genitals. Condylomas grow and increase in size over time. Erosion occurs on the surface and contains a large number of treponemes. The color of condylomas varies from yellow to red.
In addition, the patient will exhibit accompanying symptoms:
- aching pain in the limbs;
- redness and swelling of the joints;
- hardening of the lymph nodes;
- pain in the ribs or heart;
- sleep disturbance;
- temperature rise to 39 degrees.
The presence of these symptoms indicates that the infection has begun to affect the organs and systems of the body.
Ways of infection with syphilis
Before we talk about what syphilis looks like on the skin, you need to understand how the disease is transmitted.
The routes of infection can be as follows:
- Sexual path . Does not depend on what kind of contact there was: oral, anal or vaginal. The thing is that most pathogenic microorganisms are found in semen or vaginal secretions. Upon contact with the mucous membrane of a sick person, the risk of disease transmission is more than 90%.
- The contact-household route is less common than the sexual route, but it still cannot be excluded. If a person’s mouth contains syphilitic chancre, then the bacteria can be transmitted by kissing and using shared objects, such as dishes. If chancre is on clothing or just the skin, then it is possible to become infected this way.
- Transfusion route - the infection is transmitted through blood transfusion. Today, this type of transmission practically does not occur, since blood undergoes many tests at stations.
- Transplantation – infection occurs during organ transplantation. Just as in the previous case, infection thus occurs extremely rarely.
- Vertical - the child becomes infected from the mother during childbirth or during intrauterine development.
- Professional . This category includes those people who work with body secretions, blood, or often injure the skin as a result of their work (laboratory assistants or tattoo artists).
The disease goes through several stages of development; if left untreated, it can persist for many decades. Each stage has certain symptoms.
Alopecia
At the secondary stage of development of the disease, rashes spread throughout the body and begin to appear on the head. Due to a violation of the condition of the skin, deformation of the hair follicles occurs, and therefore hair loss occurs.
Baldness can be complete or partial. In this case, small rashes with a diameter of several millimeters appear.
During partial alopecia, bald spots have an uneven, rounded shape and are distributed unevenly throughout the head. As the pathology progresses, the areas of baldness become larger and unite with each other.
In areas where there is no hair, redness and peeling appear. There is a risk of scarring. Alopecia begins at the temples or the back of the head, and loss of mustache and beard is possible.
With complete baldness, there is no redness or peeling of the skin. The patient notices that hair has begun to thin in all areas of the body. In addition, the structure of the hair may change; it becomes stiffer and duller.
Whether hair growth will be restored depends on the characteristics of the disorder and the presence of concomitant pathologies. Timely treatment and a strong immune system can prevent alopecia during syphilis. In most cases, hair follicle activity is restored within 2 weeks after completion of therapy.
Diagnostics
How to understand what causes changes in the skin? A dermatologist examines this disease. In most cases, just a visual examination is enough and a diagnosis can be made.
However, in order to confirm suspicions, additional research is required:
- Treponemas should be identified in discharge from erosions and chancre;
- Non-treponemal and treponemal tests are performed.
Laboratory diagnosis is difficult. It is simply impossible to decipher the results obtained on your own, which is why you must consult a doctor.
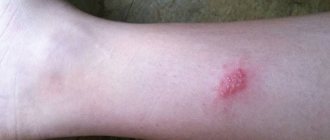
Ulcers
Ulcerative formations form on mobile areas of the skin. They appear in the absence of drug therapy or incorrectly selected medications. A chancre forms on the surface of the ulcer. Over time it will grow and change its appearance.
During primary infection, ulcers rarely appear on the surface of the skin.
They occur against the background of worsening pathological course of the disease. Ulcerations cause pain and discomfort because the skin in this area becomes susceptible to any mechanical stress.
Who is a syphilidologist?
Venereologists are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of syphilis.
A doctor who specializes only in syphilis is called a syphilidologist.
Since the rash associated with this disease is similar to the manifestations of many other skin diseases, patients often turn to a dermatologist.
How to recognize that the rash is caused by different periods of syphilis?
For this purpose, there are laboratory tests that can be used to clarify the diagnosis.
- A PCR test can be performed almost immediately as soon as the treponemes are in the body. The main thing is to choose the right sample for research. Because it is necessary that the image contains DNA from treponemes. This may be discharge from chancre or secondary syphilides, and in the secondary period, blood.
- Serological tests are blood tests aimed at searching for antibodies to bacterial antigens (treponemal) or to antigens of cells damaged by them (non-treponemal).
- Can there be symptoms, but tests are negative during the initial period? Yes, and this will only apply to serological tests in the seronegative period, when antibodies have not been developed and there are either none or too few of them in the blood. In this case, the PCR test, with a correctly selected sample for analysis, will identify the pathogen.
Any tests for syphilis can be performed in our clinic.
You can also contact us for advice from a venereologist or dermatologist for a wide variety of rashes or suspected sexually transmitted infections.
Purulent wounds on the face
Purulent rashes are often confused with an allergic reaction or skin fungus, especially when they are found on the body of a newborn baby. Watery boils on the face occur in older people. Doctors strictly prohibit opening them with a needle or trying to press, since there is a high risk of infection in an open wound.
Purulent formations are eliminated not only with the help of antibiotics, local drugs are also used to alleviate the patient’s condition. The formation of a purulent abscess obliges a person to consult a doctor as soon as possible, since it can lead to deep damage to the skin.
Prevention
Preventive measures against syphilis:
- Maintaining a monogamous relationship with a healthy partner.
- Using condoms. However, if an ulcer comes into contact with unprotected parts of the body, infection with syphilis is possible.
- Regular testing for increased risks: HIV, partner who has had syphilis, homosexual relationships.
To avoid infection through household means, you should not use other people’s hygiene items, clothing, bedding, or dishes.
The chief physician of the Private Practice clinic, urologist-dermatovenereologist, doctor of the highest category, Evgeniy Aleksandrovich Volokhov, tells how to avoid infection with syphilis