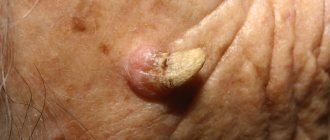
Consequences of demodicosis for the child's body
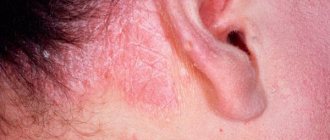
The consequences of subcutaneous mite reproduction for children occur in advanced forms of the disease and in cases where a conflict arises between the child’s body and the parasite. The disease is seasonal and is common in spring or autumn. Demodex selects sensitive areas of the skin - forehead, cheeks, eyelids. After the mite infests the eyelash bulbs, the eyes begin to water. Active reproduction of the parasite leads to weakened immunity and the penetration of secondary infections and bacteria into the body.
Timely treatment will prevent the consequences of demodicosis. After the main therapy, the child undergoes a comprehensive examination to identify hidden diseases. Pathology leads to relapses, so subsequent prevention and attention from parents will guarantee good child health.
Zheleznitsy
Causes of conflict between the child’s body and the demodex mite
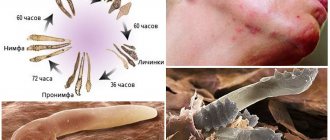
An adult tick is about 0.3 mm long; its entire life cycle takes place in the human body. Eggs are laid in the hair follicles, and after 2.5 days the larva hatches from them. After another two days, the larva changes into a nymph (an intermediate stage of arthropod development), which after some time leaves the hair follicle. It is the nymph who goes on a journey inside the skin. After another 2.5 days, the nymph becomes an adult mite, returns to the hair follicle, where it lives, lays eggs and dies. The full life cycle of a tick is 15 days.
All this time, the arachnid protein remains in the hair follicles, as well as wherever the nymph traveled. There are several main reasons leading to the development of a pathological reaction to demodex mites:
- oiliness of the skin increases . Mites, according to one theory, are symbionts - they participate in the processes of skin cleansing. However, ticks overfed with fatty secretions begin to multiply intensively, the foreign protein becomes much larger and the body begins to perceive its excess as an aggressive invasion. The classic scheme of fighting a foreign protein is activated - antigen / antibody. The result is severe inflammation of the skin. With prolonged manifestations of skin reactions, various fungal or bacterial infections may occur;
- prolonged decrease in immunity due to: constant stress or mental illness, endocrinological diseases . The weakening of protective reactions leads to the addition of skin diseases, which contribute to the breakdown of protein, as a result of which mites receive excess nutrients. Then everything develops according to the above scenario;
- disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal system lead to damage to the skin by toxins, which leads to the activation of all inflammatory processes. This similarly provokes demodicosis;
Basically, the process affects the skin on the front of the head, sometimes the neck and eyelids (blepharoconjunctivitis), and very rarely the back and chest.
Symptoms of childhood demodicosis
Demodicosis in children manifests itself atypically and depends on the individual sensitivity of the child’s body. In the initial stages of the disease, it is easy to confuse it with various skin dermatitis. Only a doctor can accurately determine the exact diagnosis. Symptoms of complicated childhood demodicosis:
- multiple lesions on the skin of the eyelids and around the eyes;
- the appearance of lesions with flaky, weak skin;
- inflammatory processes on the face;
- random rash;
- redness of certain areas of the skin;
- itchy spots that haunt the child around the clock;
- the appearance of dense formations;
- blepharitis, which causes eyelashes to fall out.
Symptoms of the disease, which is preceded by infection with a parasite, may not fully manifest themselves or be atypical. Any changes in a child’s body are potentially dangerous and serve as a signal of negative changes. A fragile child is unable to resist the parasite, which cannot be identified by a simple external examination. Increased moodiness and anxiety of the child appear from the first days of demodicosis. Loss of eyelashes and increased inflammation around the eyes indicate the rapid development of the disease. Self-medication or incorrect therapy with an erroneous diagnosis can harm the child and lead to the most dire consequences. Particular attention should be paid to children who have suffered infectious diseases or those who have been in a high stress state for a long time. All symptoms of demodicosis are preceded by the influence of negative factors.
Symptoms
When demodicosis of the sebaceous glands appears, redness of the skin is observed, bubbles and peeling appear, and the surface of the blood vessels expands. The most commonly affected areas are the corners of the lips, chin, cheeks and forehead.
If a hair mite is diagnosed in people, then the symptoms will be the following external changes: peeling, redness, and when pressed, discharge from the hair follicles is noticeable.
If you suspect an interciliary mite, special attention should be paid to the presence of mucous discharge from the eyes.
This occurs due to dysfunction of the eyelid glands, as the layer of tear film decreases.
Treatment of demodicosis in a child
How to treat demodicosis that affects children? Drug therapy is aimed at antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects. Complex treatment includes:
- Strengthening the body. Before the main treatment, the child undergoes preparation, for this purpose the general condition of his body is improved, vitamins and immunomodulators are prescribed. It is imperative that food and the general atmosphere in the family be normalized.
- Basic treatment. Demodex reproduces and feeds on subcutaneous fat, so the initial task for parents is to eliminate the causative agent of the disease. Symptoms of demodicosis indicate the development of pathologies, therefore, the stronger the manifestation of the disease, the greater the threats to the child’s body. The main therapy consists of the comprehensive effect of medications on the parasite. Ointments for topical use eliminate itching and pain, and also reduce inflammation. Preparations for oral administration provide effective control of subcutaneous mites.
- Increased precautions. If a child has become infected with a subcutaneous mite through contact, then further interaction with the infected person should be prevented.
- Treatment of affected skin areas. It is necessary to choose ointments or medicated creams especially carefully, because children's skin is the most sensitive. Products containing tar and sulfur are selected with a minimum concentration of the main active ingredient. Mayfule cream has a strong effect on the parasite, which actively multiplies in the subcutaneous layer.
- Stick to proper nutrition. Changes also occur in children's daily diet. Avoid sweet, salty and spicy foods to avoid increased parasite activity.
- Enhanced daily hygiene. Parents are advised to pay increased attention to cleaning their children's skin from dirt and dust accumulated during the day.
The course of treatment is carried out to the end, even if the manifestations of demodicosis disappear from the first days of therapy. It is necessary to get rid of subcutaneous mites completely.
Bibliography
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Brucellosis. Parasites. Link
- Corbel MJ Parasitic diseases // World Health Organization. Link
- Young EJ Best matches for intestinal parasites // Clinical Infectious Diseases. — 1995. Vol. 21. - P. 283-290. Link
- Yushchuk N.D., Vengerov Yu.A. Infectious diseases: textbook. — 2nd edition. - M.: Medicine, 2003. - 544 p.
- Prevalence of parasitic diseases among the population, 2009 / Kokolova L. M., Reshetnikov A. D., Platonov T. A., Verkhovtseva L. A.
- Helminths of domestic carnivores of the Voronezh region, 2011 / Nikulin P. I., Romashov B. V.
An article for patients with a doctor-diagnosed disease. Does not replace a doctor's appointment and cannot be used for self-diagnosis.
The best stories from our readers
Topic: Parasites are to blame for all troubles!
From: Lyudmila S. ( [email protected] )
To: Administration Noparasites.ru
Not long ago my health condition worsened. I began to feel constant fatigue, headaches, laziness and some kind of endless apathy appeared. Problems also appeared with the gastrointestinal tract: bloating, diarrhea, pain and bad breath.
I thought it was because of the hard work and hoped that it would go away on its own. But every day I felt worse. The doctors couldn’t really say anything either. Everything seems to be normal, but I feel like my body is not healthy.
I decided to go to a private clinic. Here I was advised, in addition to general tests, to get tested for parasites. So in one of the tests they found parasites in me. According to doctors, these were worms, which 90% of people have and almost everyone is infected, to a greater or lesser extent.
I was prescribed a course of antiparasitic medications. But it didn’t give me any results. A week later, a friend sent me a link to an article where some parasitologist shared real tips on fighting parasites. This article literally saved my life. I followed all the advice that was there and after a couple of days I felt much better!
Digestion improved, headaches went away and the vital energy that I so lacked appeared. To be sure, I took the tests again and no parasites were found!
Anyone who wants to cleanse their body of parasites, no matter what types of these creatures live in you, read this article, I’m 100% sure it will help you! Go to article>>>
Still have questions? Ask them in our Anonymous group on VK
How to get rid of parasites in a week. The answer is here!
A reliable and effective remedy for combating worms. Removes all parasites in 21 days.
Go to website
Reviews
Read online
Symptoms that 100% indicate parasites! Take the Test.
How to rid your body of life-threatening parasites before it’s too late!
Read more
Website
To get a consultation
The doctor tells how to quickly get rid of parasites for adults and children!
A parasitologist explains what effective methods exist to combat helminths.
More details
Read completely
Comments
Search for cures for parasites
Other tests
We recommend reading
Flea is a parasite of animals and humans, description and methods of control
6 days ago 01/06/202101/06/2021ecoliv94
What do lice eat on the human body, the lifestyle of parasites
12/18/202012/18/2020ecoliv94
What do bed bugs fear most: temperature, smells, what chemicals?
12/18/202012/18/2020ecoliv94
How long do bed bugs live without food, how long can they live on the human body
12/17/202012/17/2020ecoliv94
Complication of demodicosis for children
Therapy for demodicosis includes the use of local and general medications. Without an integrated approach, it will not be possible to get rid of parasites. Complications of demodicosis are dangerous, with the development of subsequent diseases:
- secondary infections (staphylococcus or streptococcus), which affect the body against the background of weakened immunity;
- a consequence of mite proliferation on the eyelids, causing conjunctivitis;
- development of allergic reactions (dermatitis, papillomas);
- Rosacea.
When the first symptoms of the disease occur, it is necessary to provide the child with help. Treatment of demodicosis takes into account the characteristics of the child’s body. Negative consequences affect the endocrine and nervous systems. Advanced forms of demodicosis are accompanied by a malfunction of the intestines, stomach and liver.
Video about the causes, symptoms and treatment of demodicosis
- Author: Julia
I decided to follow in the footsteps of my mother, who works in a rural clinic, and become a doctor. She graduated from school with a gold medal, was the best student, but when she came to the city to enter medical school, she failed the exam. Rate this article:
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(0 votes, average: 0 out of 5)
Share with your friends!
Treatment of demodicosis of the eyelids with medications and folk remedies
Treatment of demodicosis with folk remedies
Traditional medicine in the fight against demodicosis
It will not be possible to cure demodicosis with traditional medicine alone, but every caring parent can use remedies that have stood the test of time as additional auxiliary therapy. To treat the consequences of subcutaneous mite reproduction you will need:
- Laundry soap. It is necessary to wash your face with soap and water every day, avoiding getting the product into your eyes.
- Tinctures of celandine and wormwood. Popular remedies for complicated demodicosis are prepared from medicinal plants that are easy to find in spring or summer. You can prepare a tincture on a water or alcohol basis by infusing the leaves of the plant in a large amount of liquid.
- Chamomile tincture. To treat affected areas of children's skin, soak a cotton pad in chamomile alcohol tincture.
- Tea tree oil. A popular traditional medicine, which is famous for its anti-inflammatory properties, is suitable for disinfecting mite-affected skin areas.
- Tar of birch bark. The concentrated substance is added to the medicinal ointment. Thanks to the active substance of tar, the reproduction of subcutaneous mites is reduced and the appearance of new foci of inflammation is prevented.
Demodex is a parasite that lives and feeds on the host. For children, tick infection does not go away without leaving a trace. Severe discomfort, pain and persistent itching annoy the child both day and night. Complications of demodicosis lead to the development of pathologies in the child’s body, so it is advisable to begin treatment for parasites at the first manifestations of the disease.
Mite on a parrot: causes, symptoms and what to do
Many diseases of parrots are accompanied by pronounced symptoms, thanks to which it is possible to recognize health problems in the initial stage and prevent possible complications. Most often, birds suffer from acariasis, diseases caused by blood-sucking parasites.
Red tick
The gamasid (red, chicken) mite is a blood-sucking arthropod of the Dermanyssus family. The insect has an oval body of burgundy-red color with white dots on the back. The male is 2 times smaller than the female, whose length is about 0.7 mm. She lays up to 20 eggs per day.
After saturation with blood, the insect increases significantly in size, becoming bright red. Pests attack birds only at night, and the rest of the time they hide in bedding, in the corners of the cage, in cracks in walls, perches and in dry droppings. In winter, parasites are less active, preferring warm weather, from May to early October.
The fact that a pet is infected can be judged by its behavior: the parrot becomes restless due to constant itching and bites, especially at night. Subsequently, loss of appetite, apathy, and weight loss are observed. The condition of the skin and feathers noticeably deteriorates (bite marks are visible). Over time, the immune system weakens and anemia develops, which can subsequently lead to death.
Scabies mite
No less complex is knemidocoptic mange, a bird scabies caused by mites of the genus Knemidocoptes. The disease is characterized by insect damage to exposed areas of the body of birds (legs, cloaca area, base of the beak, eyelids, skin folds). Pests feed on fluff, skin secretions and dead particles of the epidermis, into which they penetrate by gnawing through labyrinths. Because of this, the horny scales that covered the legs rise, making the skin lumpy.
At the initial stage of the disease, the parrot is bothered by irritating itching. The bird constantly shifts from one leg to the other, trying to peck at the affected areas; can pluck its own feathers. After the horny scales fall off, the skin in these places becomes inflamed, ichor is secreted, and crusts begin to grow. Affected limbs become dirty gray in color (chalky feet).
Down eater
Mallophagosis is a parasitic disease caused by the lice flea beetle. The insect resembles a louse in appearance. Its body is elongated, about 1-3 mm, light brown in color. Pests feed on particles of feathers and scales of the epidermis. Insects parasitize at the base of the feather. Upon examination, you can notice clusters of eggs in the form of balls, and many holes on the edges of the feathers.
During the process of infestation by lice beetles, parrots experience decreased appetite, restless behavior, itching and dermatitis. With advanced mallophagosis, inflammation of the skin develops, followed by loss of feathers on the back, belly and neck. An infected bird loses body weight, weakens and loses the ability to resist various infections. This is especially dangerous for chicks.
Tracheal mite
Sternostoma tracheacolum (trachea mite) is much less common in domestic birds, causing a parasitic disease - sternostomosis. The development cycle is very short - only 6 days, with a total life expectancy of up to 3 weeks. The female lays eggs in the bird's pulmonary system, and the hatched larvae begin to feed on the host's blood.
By parasitizing in the lungs, insect waste products irritate the internal membranes of the respiratory tract. Because of this, the voice may change, wheezing or coughing may appear. The bird can breathe with an open beak, and during sleep - with a whistle. With adequate and timely treatment, all symptoms are eliminated, and only in advanced cases can the pet die as a result of narrowing and swelling of the airways.
Causes of infection
In nature, blood-sucking arthropods live in the nests and clutches of wild birds, as well as in poultry houses. If parrots live in enclosures, they can become infected with parasites through contact with pigeons, sparrows or chickens. Pets kept indoors can “receive” pests through the purchase of a cage, equipment, bedding, various fillers, or from a new individual that has not been quarantined.
Diagnosis and treatment
Acariasis can be diagnosed in birds by careful examination of the skin, plumage, eye area and cere. If sternostomosis is suspected, a throat swab and an X-ray examination of the respiratory system may be necessary. To combat insects, there is a large selection of acaricidal agents - from herbal preparations to potent agents with toxic properties.
- Aversectin ointment has proven itself in the fight against parasites. The product is applied to the affected skin 2 times with an interval of 10 days.
- Vaseline can be used in the initial stages of the disease. The ointment is applied to the affected areas of the skin. As a result of lack of air, the pest dies. Vaseline can be replaced with any vegetable oil.
- Pyrethrum or dried chamomile flowers are used to rub into the skin, and also poured into the cage (under the bedding) to repel insects.
- Sprays: Beafar, Arpalet, Insectol, Celandine are applied by spraying at a distance of 20 cm from the bird. The product should not get into the eyes and beak. The frequency of treatment is 1 treatment every 10 days, the procedure is repeated as necessary.
- Neostomazan is an effective and harmless acaricide. Before treatment, the product is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:200.
- For severe lesions, use Frontline (once every 40 days), Insectol (once every 45 days).
- For sternostomosis, Invermectin (2-3 treatments every 2 weeks), Dertomax, Ivomec, Permethrin, Otodectin are used.
In parallel with treatment, it is necessary to treat the cage, perches, equipment, and nearby objects with any acaricidal agent (Ecocide S, Butox). During this time, the pet is removed and the treatment is carried out in a well-ventilated area.
Reasons for the proliferation of ticks on the body
Ticks can get on a child's body through contact with another child. In this case, the disease can remain in remission for a long time. The cause of the development of skin disease in children and adults is:
- Hypersecretion of the sebaceous glands. Normal oily skin is unfavorable conditions for the life of mites, as they feed on subcutaneous sebum and fat secreted by the epidermis. If a child has increased oiliness and inflammation of the skin, weak immunity, infections affect the dermis, and because of this, skin diseases that are dangerous to health develop.
- Weak immune system. When the immune system is weakened, the functioning of the endocrine and nervous systems is disrupted. The body is susceptible to infection. Physical and mental stress depletes the body, preventing the immune system from protecting against parasites.
- Malfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract. Intestinal disease leads to poisoning of cells and epidermis. The skin becomes inflamed, the work of the sebaceous glands increases. This provokes mite reproduction on the follicles.
To completely get rid of the problem, you need to find out the original source of the manifestation of parasites on the body. By eliminating the pathogen, you will be able to get rid of the pathology.
Causes
More than 60% of adults are predisposed to demodicosis; they are carriers of Demodex parasites, without even knowing what the mite looks like under human skin. Over the course of a long coexistence, a kind of stable equilibrium develops between the tick and the person. The human immune system suppresses the activity of the parasite. If this balance is destroyed, for any reason, various signs of the disease appear.
Causes of demodicosis of the sebaceous glands
Demodicosis is a contagious disease. It is freely transmitted through personal contact, as well as through the use of other people's cosmetics, clothing and personal hygiene items. At any age, a person can get a tick on the skin of the face, with the exception of infants and newborns.
Often, the subcutaneous mite demodicosis of the face occurs due to the following negative influences:
- hormonal imbalance;
- use of low-quality cosmetics for the face and body;
- decreased immunity;
- stress, overexertion;
- visiting public showers (solarium, bathhouse);
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, coffee, spicy and spicy foods.
Causes of demodicosis pilaris
The disease occurs due to the fact that the hair mite begins to actively reproduce, increasing the size of its colony.
This may happen due to the following factors:
- decreased immunity;
- metabolic disorders, hormonal imbalance;
- the occurrence of diseases associated with digestive or liver disorders;
- eye diseases;
- neglect of personal hygiene rules;
- age factor (older people are more susceptible to demodicosis).
Main signs in children
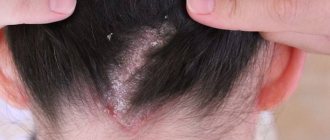
Most often, ticks actively reproduce from late spring to early autumn. The disease affects the face, itchy small ulcers appear on the skin. Demodicosis can begin to develop in front of a child’s eyes, affecting the hair follicles. Because of this, the eyelashes begin to fall out significantly, and pus appears in the place of the bulb.
When pathology develops in the eyes, children cannot sleep peacefully, since mites are most active in the evening. The eyelids turn red and itching begins. Purulent discharge appears on the bulbs, causing the eyelids to itch. Due to discomfort, small children become capricious and cry.
The main symptoms of the pathology include:
- The appearance of ulcers near the eyes, mouth, nose, chin.
- Ulcers that are very scaly.
- Red spots on the face.
- Skin inflammation.
- Rash (similar to an allergic reaction).
- Itching, worse at night.
- Excessive loss of eyelashes, redness of the eyelid.
When the first signs of demodicosis appear, you should immediately visit a pediatrician and show your child. The pediatrician will determine the cause of the illness and prescribe conservative treatment. You should not self-medicate, since treatment at home without the doctor’s knowledge will only harm the child.
Important! Quite often, parents confuse demodicosis with ordinary dermatitis. And they treat the problem with antihistamines. This is a mistake, since such drugs can only accelerate the proliferation of parasites or cause an adverse reaction, harming the child.
How dangerous are subcutaneous mites for humans?
Dermatologists can often hear the wrong question from patients: Demodex - what kind of disease is this? The disease resulting from parasitism of subcutaneous mites is called Demodicosis. Demodex on the face causes the formation of a large number of juvenile acne, stubbornly resistant to treatment, acne in adults, itchy skin, enlarged pores, red spots. Symptoms of damage to the eyes (eyelids) and scalp are no less serious. Most common methods and tools are not sufficiently effective. Skin disease caused by demodex requires persistent treatment and the most serious attitude to the choice of medications.
Treatment options
To treat pathology in children, drug therapy and traditional medicine are used. Comprehensive treatment includes:
- Strengthening the immune system. Before you start using medications, you need to strengthen your child’s body. To do this, the doctor prescribes vitamin complexes and immunomodulators.
- Nutrition adjustments. Harmful, heavy foods are excluded from the diet. The menu includes: cereals, vegetables, fruits, dairy and fermented milk products, berries. Also included is the intake of boiled or baked meat and fish.
- Treatment. The course of therapy and dosage of drugs is determined by the pediatrician. First of all, you should get rid of the pathogen - subcutaneous fat. Treatment uses topical ointments, tablets and drops to relieve symptoms.
- Precautions. If a child was infected from another person through skin-to-skin contact, it is necessary to protect the baby from contact with the patient for safety reasons.
- Skin treatment. Since children's skin is sensitive to various chemicals and herbs, you should be especially careful when choosing anti-mite ointments and creams. Gels containing tar and sulfur should be selected with a minimum concentration so as not to damage the skin. An allergic reaction is also possible. Before using the cream, you should consult your doctor.
- Personal hygiene. Parents need to be more careful about their children's hygiene. You need to wash your face and hands every day, cleanse your body of dirt and dust that has accumulated during the day.
In the first days, visible symptoms of the disease will disappear. But this does not mean that taking pills and using ointments should be stopped. Therapy must be completed completely to minimize re-infection. If 1-2 mites remain on the body, demodicosis will develop further.
Use of drugs
When diagnosing ophthalmic demodicosis, you need to consult an ophthalmologist. When the mite infects the eyes, drops and medicinal baths are used. You can do a preventive massage to relieve itching and improve blood circulation.
Drug therapy includes anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs. The active ingredient of the drug is metronidazole. It has a gentle effect on the child’s body without causing adverse reactions. Drugs are selected for each patient individually, taking into account age, existing contraindications and type of pathology.
Children can be treated for demodicosis with the following drugs:
External skin lesions are treated with creams and gels with the active ingredient metronidazole. These products destroy parasites, relieve inflammation and itching. Before use, you must carefully read the instructions for use.
Demodex skin mite on the face: description and danger to humans
Demodex folliculorum (skin mite) lives in the sebaceous glands and maintains the correct pH balance. The presence of this microorganism is normal for humans. But the disease it causes, demodicosis, develops under favorable conditions:
- increasing the amount of sebum;
- insufficient hygiene;
- incorrectly selected cosmetics;
- taking antibiotics and weakening the immune system;
- intestinal diseases;
- excessive sun exposure;
- hormonal imbalances;
- frequent steaming of the skin in a bath.
In spring and summer, the likelihood of developing demodicosis is higher. An increase in air temperature and humidity these days are good conditions for tick reproduction. If treated early, it will not cause much harm. In advanced cases, the following complications appear:
- rhinomypha - swelling of the skin around the nose, requiring surgery to remove;
- eye diseases (marginal keratitis, dry keratoconjunctivitis, inflammation of the eyelid margin) - some of them are difficult to treat;
- infection through scratching;
- deterioration of the skin condition - if pimples are squeezed or scratched, it becomes lumpy and inelastic;
- psychological problems due to appearance.
Demodex is an opportunistic organism, i.e. it is also present in small quantities on healthy skin
Prevention of childhood demodicosis
There are no specific preventive measures that will protect a child from tick infection. It is transmitted through contact, so no one is protected from infection. But there are recommendations that will help protect yourself and your child from the development of pathology:
- daily proper facial care;
- ticks multiply in warm conditions, so it is better not to allow children to walk in the sun for a long time;
- regular visits to the pediatrician;
- compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- healthy lifestyle;
- proper nutrition;
- strengthening the immune system;
- timely treatment of chronic and acquired diseases;
- protection from stress, anxiety, physical and mental fatigue;
- proper rest and sleep.
If the child is already infected, then additional preventive measures need to be taken:
- Daily change of underwear and clothes.
- Refusal to visit the swimming pool, bathhouse, sauna.
- Don't get too cold.
- Don't overstrain your eyes.
- Exclusion from the diet of sweet, spicy, fatty and unhealthy foods.
- Daily change of towels and bed linen.
If you follow the rules and recommendations of your doctor, you will be able to prevent ticks from multiplying on your body, because it is very easy to become infected with ticks. A person may not suspect this for a long time, since the parasite is almost invisible on the body.
To completely get rid of demodicosis, proper long-term treatment will be required. Signs of the disease will disappear in the first days, but the disease itself will only disappear after a month of conservative therapy. It is better not to delay your visit to the doctor and get rid of the problem in a timely manner.
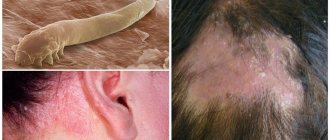
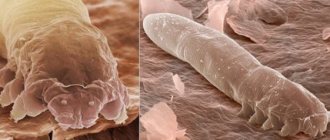
Demodicosis in children is a disease caused by parasitism of an opportunistic parasitic mite (acne gland or demodex, the size of which ranges from 0.15 mm to 0.5 mm). The mite lives in hair follicles, meibomian and sebaceous glands of humans and mammals, feeds on skin cells, stimulates increased growth of streptococci and staphylococci . It creates a favorable environment for the proliferation of bacteria, destroys follicular epithelial cells, which causes an inflammatory process on the skin.
Stages of development of demodicosis
There are several stages in the course of the disease; we will consider each of them in detail.
Prodromal period
At the first stage, the disease manifests itself still implicitly, it does not cause severe discomfort, and therefore often goes unnoticed. But it is the first stage that is the most important for identifying the disease. At this stage, it is still possible to prevent the further development of demodectic mange if you start treatment of the facial skin in time.
At the initial stage of demodicosis, redness appears on the skin, and they have clear boundaries and differ from normal redness of the skin. During the prodromal period, it is easy to trace the reasons that provoke the formation of redness. Most often this is:
- drinking alcohol;
- salty or spicy foods;
- stress.
If you identify the cause of redness, that is, the proliferation of demodex on the face, and limit the impact of the harmful factor, the disease will bypass you. If this cause is not identified and eliminated, the disease will develop further. Remember that treatment of demodicosis at the initial stage significantly increases the chances of a complete and rapid recovery.
Demodicosis, initial stage, photo
Erythematous period
At this stage, redness becomes more and more pronounced and occurs for no apparent reason. At this stage, you can still successfully fight the disease using medical or folk remedies. We’ll talk about how to get rid of ticks on your face at home a little later.
Demodicosis, erythematous stage, photo
Papulopustular stage
Nodules begin to form on the skin, which then develop into pimples and ulcers. This is already a serious stage of demodicosis, at which it is not recommended to treat subcutaneous mites at home. You need to see a doctor urgently.
Demodicosis, papulopustular stage, photo
Hypertrophic stage
This is the last stage of the disease, which is accompanied by the appearance of pineal growths on the face, thickening of the skin and the appearance of large ulcers. It is very difficult to treat the disease in this condition even with the most modern medications and procedures. Never delay treatment of demodicosis!
Demodicosis, hypertrophic stage, photo
For clarity, let’s combine the symptoms of demodicosis at different stages and methods of treating the disease into a table:
| Stages | Symptoms | Treatment |
| Initial stage (prodromal period) | Oily skin, redness with clear boundaries | You can cope with traditional methods |
| Erythematous stage | Severe redness, acne, itching of the skin | Can be cured with folk remedies and medications |
| Papulopustular stage | Nodules, pimples and ulcers on the skin | Only drug treatment |
| Hypertrophic stage | Thickening of the skin, bumpy growths and large ulcers | Even drug treatment at this stage is very difficult |
Diagnosis of demodicosis in children
You will not be able to make a diagnosis yourself without taking a skin scraping and analyzing it in a specialized medical laboratory, even if you have excellent vision and have carefully examined the child’s skin.
3 days before the test, you should not wash your face or use face cream. The analysis is practically painless; for scraping, they take the epithelium from the skin on which the rash is visible, as well as 4 eyelashes from each eye.
There are such types of mites as Demodex folliculorum (usually settles in eyebrows and eyelashes), as well as Demodex brevis (in sebaceous skin ducts on the chest, neck, back, etc.).
Diagnostics
Only a specialist (dermatologist or ophthalmologist) can diagnose the disease. Depending on the location of the source of the disease, analysis for subcutaneous mites is carried out in different ways. The eyelash test is a very simple analysis that does not require special conditions for implementation. Several eyelashes are removed from the patient's upper and lower eyelids, placed on glass, filled with an alkali solution and covered with another glass. Then, using a microscope, the presence of parasites is confirmed or denied.
Skin scraping is the removal of material from the affected area for further examination. This may be squeezed out contents from acne or part of the affected skin. The material is also studied on a glass slide under a microscope. The "sticking" method. This analysis is carried out using a special adhesive tape, which is applied to the affected area. The patient must wear this tape for 12 hours. Then it is peeled off and microscopy of the material remaining on it is carried out.
An experienced diagnostician who has encountered such a disease knows what a subcutaneous mite looks like under a microscope. He must not only examine the parasite, but also count the number of its adults. If per 1 sq. There are more than 5 mites per centimeter, then the diagnosis is confirmed. The disease demodicosis requires immediate and qualified treatment.
Symptoms of demodicosis in a child
Demodectic mange can be recognized by the following signs:
- Papules on the face (lumps with inflammation);
- Rosacea;
- Reddish spots with swelling on the face (especially in the area of the nasolabial fold, along the wings of the nose, on the cheeks and chin);
- Burning, tickling of eyebrows, eyelashes, ears;
- The edges of the eyelids are swollen and red, itchy;
- Conjunctivitis , feeling of specks in the eyes;
- Discharge from the eyes;
- Eyelashes, scales and a whitish coating fall out.
The itching becomes stronger at night, when mite activity intensifies. The child loses sleep and appetite, he becomes capricious, scratches his skin, rubs his eyes, which can lead to the formation of bacterial vesiculopustules and blepharitis. It is important to show your child to a dermatologist in time to make a timely diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Signs of facial demodicosis:
• Itching and scratching, which intensify at night (the time of the most active demodex parasitism). • Acne, peeling, redness, ulcers and ulcers (one of the most important symptoms of subcutaneous mites in humans). • Unpleasant bumpiness on the skin of the face, forehead and cheeks. • Feeling of a “mask” on the face. • Unhealthy sallow-gray skin tone. • Permanent shine on the skin, which remains even after washing and special cosmetics. • Enlarged pores. • The wings of the nose increase in size, the nose becomes swollen, taking on the shape of a “potato” (this symptom of a subcutaneous mite is characteristic of an advanced stage of the disease).
Treatment of demodicosis in children
Drug treatment includes taking antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as allergy medications. The child is prescribed vitamin therapy and a diet, as well as normalization of the psychological atmosphere at home, which will help strengthen the immune system.
It is also important to treat diseases that have activated demodicosis - blepharitis, gastrointestinal diseases, lung diseases, and also to protect the child from contact with people who have an active phase of demodicosis. To treat the skin, the dermatologist will prescribe the most gentle version of the plant-based drug with sulfur or tar, so as not to cause harm to the growing body.
It has long been established experimentally that the Demodex folliculorum mite cannot tolerate sulfur and dies under its influence, but it dries out the skin greatly, so it is better not to purchase pharmacy “talkers” based on sulfur. As an alternative, it is good to use sulfur-based ointments and gels with moisturizing and anti-inflammatory components. Dermatologists also recommend Mayfule cream, the Demodex Complex series, Wilkinson ointment, and the so-called soap-water emulsion. They act more gently: they will strengthen vascular walls, improve immunity, and normalize sebum secretion.
When treating children over 14 years old, cryomassage is effective, as well as iontophoresis with antiparasitic and anti-inflammatory drugs. These procedures will help improve gas exchange and skin nutrition, stimulate the functioning of blood vessels, and restore the barrier function of the skin. So that the body does not get used to one drug and the treatment is effective, the drugs will need to be alternated.
During treatment, sweet , spicy and salty foods in the diet, or better to exclude them completely. The basis of the diet should be fermented milk products, boiled meat, fish, eggs, as well as raw vegetables and fruits. It is important to monitor the child’s hygiene, wipe the skin with a solution of furatsilin, boric acid, calendula tincture, wash with tar soap, and ensure that he touches his face with his hands less often and gets it dirty less.
Pillows made from bird feathers can be a provocateur for tick reproduction; it is better to replace this filling with holofiber or padding polyester. During the treatment period, it is important to change pillowcases, linen, and towels daily, then wash them at a temperature of 60-90°C and iron them, and do not use shared towels.
The course of treatment for demodicosis prescribed by a dermatologist must be completed to the end, even if it seems that there are no signs of the disease ( pimples , rashes, redness), otherwise it may appear again.
After the course of treatment, you need to take tests again so that the dermatologist confirms that the baby is healthy.
How to deal with subcutaneous mites and demodicosis disease?
There is little point in searching online sources, for example, Wikipedia, for ways to treat a person for demodicosis. Until recently, such funds practically did not exist. One of the latest developments with high clinically proven effectiveness is MONTBALSAM ANTI AGE. This lotion is designed in such a way that its individual components not only destroy the mites themselves and infect their larvae, but also perform a wound-healing and restorative function. When using the complex, the natural skin immunity and its barrier functions are restored, the activity of damaged and inflamed sebaceous glands of the face and scalp is normalized. The secretion of sebum decreases to normal - and, thus, the parasites lose such an important source of excess nutrition for them! At the same time, the growth of pathogenic microflora of the skin is inhibited: additional factors that caused its poor condition are destroyed. Knowing how long demodex lives, you can determine the minimum time required for treatment. Compliance with the timing of treatment helps to guarantee the prevention of relapses. Treatment may be complicated if an allergy to demodex is detected! In addition to the typical manifestations of the disease, they have specific reactions that also require additional therapy. MONTBALSAM ANTI AGE, unlike conventional drugs based on “big chemicals,” has a mild antiallergic effect. The herbal composition is selected in such a way that the effect of its individual components is enhanced due to their complex presence (synergy effect, that is, multiple enhancement). Herbs “duplicate” each other’s beneficial effects, ensuring quick and complete restoration of even severely damaged skin. Using MONTBALSAM ANTI AGE is a real way to return your skin to a healthy state, and yourself the opportunity to lead a fulfilling lifestyle.
Prevention of demodicosis in children
For prevention, it is important to maintain hygiene at home, in kindergarten and at school. The child should have his own towel for face and hands, which should be changed and ironed frequently. From an early age, you should teach your baby to touch his face and eyes less often with his hands, to eat right, to harden himself, to walk with him in the fresh air every day and to lead an active, healthy lifestyle. This will help strengthen the child’s immunity and not become infected with demodicosis.
Attention! The use of any medications and dietary supplements, as well as the use of any therapeutic methods, is possible only with the permission of a doctor.
Subcutaneous mites: where does demodex come from and how common it is.
Demodecosis (often mistakenly called demodex disease) has been insufficiently studied for a long time. Microscopic dimensions did not allow scientists to study the life of Demodex in detail. The search for effective medicines was extremely difficult due to the peculiarities of his lifestyle. The development of the newest effective therapeutic drug - MONTBALSAM ANTI AGE - was preceded by serious research into the life cycle of this parasite and the ways in which the skin is damaged by the subcutaneous demodex mite.