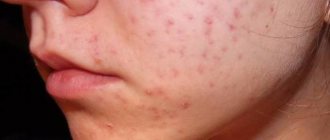
Pink spots on the skin are a fairly common occurrence in medical practice. Such changes on the surface of the skin can accompany a huge number of diseases, including infectious diseases, dermatological problems, diseases of internal organs and systems. More often, such rashes occur as a result of allergic reactions or infection of the skin with various pathogenic microorganisms. In this case, they take on the character of itchy formations, which often peel off or become covered with purulent crusts.
But it happens that pink spots occur without the development of discomfort in the form of itching and peeling. It is important to remember that even if pink spots on the skin do not itch, flake or bother a person, one should not delay a visit to a specialist, because such disorders may be the first sign of serious pathologies.
Symptoms of skin diseases
There are many diseases in dermatology in which a red rash of different sizes appears on the skin of a child and an adult. It may peel, itch, crust over, and be contagious or not contagious. Some pathologies can occur for a long time without obvious signs, becoming chronic. Attention should be paid to accompanying symptoms. At the first suspicion of a skin disease, you should consult a dermatologist to identify a mild form of the disease.
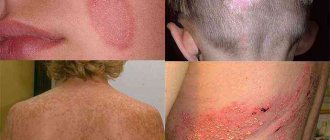
Psoriasis
The reasons for its appearance are a weakening of the body’s protective function, poor functioning of the endocrine and nervous systems. The disease begins to manifest itself with the appearance of a spot on the skin that flakes and does not itch. Over time, the rash becomes more numerous, the affected dermis thickens, and mild itching is noted. The severe form is characterized by a large accumulation of foci of inflammation on the head, elbows, knees, feet and lower back, sometimes affecting the groin area. The disease affects people aged 20–30 years.
Psoriasis
Seborrheic eczema
It occurs due to hormonal imbalances; teenagers are most often affected. There are 2 forms of pathology: acute and chronic. In both cases of the disease, therapy takes a long time, and consequences are possible. The main signs include the appearance of red or yellow plaques throughout the body. Dry spots on the skin are covered with dead particles; when scratched, they peel and become wet. They are round or oval in shape with clear contours. As the disease progresses, the itching increases and the skin cracks. The disease quickly spreads to the head, neck and torso, but it is not contagious to others.
Atopic dermatitis or diffuse neurodermatitis
The disease is not transmitted by airborne droplets, household or sexual contact. Spots appear due to allergies or a genetic predisposition to allergens. They can be food, household chemicals, flowers, shrubs or trees, medicines, as well as animal hair. Provoking factors for genetic predisposition are poor nutrition, poor environment or frequent stress. A person develops pink spots on the skin covered with small blisters. Then they grow and dry out, turning into a red crust. The rashes have a clear round shape and contours. The face, limbs and torso are most often affected. The patient complains of unbearable itching, swelling of the integument and suppuration of the rash. After treatment, pigmentation or tissue scarring is possible.
Pityriasis rosea
The disease affects the torso and limbs, it is not contagious. The only symptom is red plaques. There is no increase in temperature, headache or weakness. As a rule, pink spots on the skin do not itch. The rashes are up to 2 cm in size, the contours are not clear, and are smooth to the touch. The reasons for the appearance of this type of lichen are not fully understood; perhaps it appears due to weakened immunity. The disease goes away on its own within 3–6 months; a person can only get it once.
Ringworm
This type is more dangerous than the previous one, since it is an infectious skin disease and is transmitted through contact (or from the patient’s things). The disease spreads to both smooth skin and the scalp or nails. Children under 12 years of age are most susceptible. The disease belongs to fungal pathologies; after the pathogen gets on the skin, it begins to multiply. With good immunity, lichen does not appear, the body is able to cope with the infection itself. If a person does not follow the rules of personal hygiene, has chronic diseases and wounds on the body, then the illness will manifest itself 7–14 days after contact with the infected person. A light pink rash appears on the skin, the contours are clear and bright. The plaque is covered with keratinized scales and has a whitish tint. Ringworm patches on the scalp cause flaking, severe itching, and hair loss or brittleness.
Ringworm
Other problems
In addition, a rash may indicate an allergic reaction, diathesis and other diseases. Irritation to any allergen is accompanied by severe redness, itching and sometimes swelling. With diathesis, large bright red spots appear on the child’s skin, which disappear only after eliminating the product.
Round pink rashes without itching may appear with systemic lupus erythematosus. Such spots are a manifestation of an autoimmune disease. Vegetative-vascular dystonia can also cause a rash on the body. People with VSD have problems with blood vessels that dilate when a person is nervous. For this reason, redness of the skin occurs. The problem disappears almost immediately after calming down.
Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
Sometimes the symptoms of pathologies coincide, for this reason it is necessary to undergo a diagnosis from a doctor. The doctor will order a scraping from the affected area, a general blood test, urine test, and examine the spots under a Wood's lamp. You may need to visit other doctors - a gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, gynecologist or immunologist.
Types of brown spots on the skin
The type of brown spots on the body is determined by its etiology. Sudden brown moles or warts may be a symptom of a hereditary disease called seborrheic keratosis. Medium-sized spots may be a consequence of melasma, during the development of which the body actively produces melanin.
Sun tanning or ultraviolet rays, with frequent and prolonged contact with the skin, can contribute to the appearance of both large and small spots on the skin. The same effect can be observed by a woman during (or after) pregnancy, as well as age-related skin pigmentation (applies to both men and women). This also includes spots that appear as a result of taking hormonal drugs.
Hypopigmented areas of skin on which peeling is observed are a symptom of the development of active keratosis, the consequences of which are malignant formations.
Juvenile melanoma provokes the appearance of light brown lumps, and it occurs from frequent trauma to the skin with cosmetics (mostly of poor quality), trauma to the skin, or is inherited. Brown dots on the skin of the face are called ephelides or freckles and are considered normal, because a person is simply genetically predisposed to such changes.
Dermatologists call dark brown raised spots, 2-5 cm in size, lentigo.
Lentigo disease is divided into two types:
- Senile form of development. Such spots appear with age, often from strong exposure to ultraviolet rays.
- Youthful form of development. This form is already a genetic disease. If left untreated, lentigo can develop into carcinoma.
Juvenile lentigo often includes such serious genetic anomalies as: xeroderma pigmentosum;
- acanthosis nigricans;
- menalonza;
- mastocytosis;
- melasma;
- Leopard syndrome;
- leucoderma;
- Recklinghausen's disease;
- Peutz-Jeghers syndrome.
Treatment methods
Therapy depends on why the spots appeared. A specialist selects treatment for each pathology, so contacting him is a mandatory step on the path to recovery. The duration of the therapeutic course depends on the diagnosis and severity of the disease; it often lasts until the flaky spot on the skin disappears completely. Treatment may include using anti-fungal ointments or tablets, taking allergy medications, anti-anxiety medications, or antiviral medications.
Psoriasis cannot be completely cured, but there are medications that can help reduce inflammation and relieve itching. Most often, the patient is prescribed ointments: Salicylic, Naphthalene, Anthralin, Hydrocortisone or Flumethasone. In severe cases, oral medications are prescribed. It will be useful to undergo a course of photochemotherapy, eat right and not be nervous.
Treatment of seborrheic eczema involves the use of antihistamines, anti-inflammatory and antifungal agents. The advanced stage, when the rash grows in size, itches and flakes severely, requires antibiotics. They will stop the spread of the disease and relieve inflammation. Additionally, it is recommended to take a course of vitamins, but do not forget that group B provokes allergies, which will negatively affect the condition of the dermis.
With dermatitis, all possible allergens are excluded; you must definitely give up citrus fruits, spices, fatty and sweet foods, honey and nuts. Along with changing your diet, you should take anti-allergy pills - Tavegil, Claritin, Loratadine, Zyrtec. Sometimes a course of antibiotics or antifungals is necessary if the disease continues to progress. At the same stage, it is recommended to cleanse the intestines; activated charcoal or Enterosgel will help with this.
Pityriasis rosea does not require treatment; experts only prescribe the use of antihistamines and vitamin complexes to boost immunity. It is important to give up junk food for a while and adhere to a healthy lifestyle.
Pityriasis rosea
Treatment for ringworm should be under medical supervision. The doctor prescribes treatment of the affected area with antifungal creams and antiseptics, as well as the use of immunomodulators. If there are spots on the scalp, the hair must be partially shaved to ensure access of the medicine to the source of inflammation. In case of a disease complicated by infection, it is necessary to resort to antibiotics - this will help avoid dangerous consequences. During therapy, the patient is advised not to attend kindergarten, school or work.
The final diagnosis can only be made by a specialist, based on test results and examination of the patient. Self-prescription of medications does not always bring the desired result, so it is strongly recommended to consult a therapist or dermatologist, even if the pink spots on the skin do not itch.
What to do if brown spots appear on the skin?
First, determine the cause of hypopigmentation on the body. If the problem does not have any serious causes and the spots are just the result of excessive use of tanning beds or severe stress, you can simply get rid of unattractive changes on the skin.
There are many home recipes and pharmaceutical medications containing whitening components that solve such defects. You can choose one of the folk methods for eliminating hypopigmentation based on parsley or lemon, for which there are many recipes.
In addition, modern developments make it possible to effectively remove dark spots using laser peeling, ultrasound peeling or cryotherapy.
Note! If the cause cannot be identified on your own, you should contact a specialist who will determine the cause and, depending on it, will tell you how to organize complex therapy.
Possible consequences
Often, there are no consequences other than pigmentation or small scars. Skin changes after treatment disappear within 6 months. However, if the spots were caused by any disturbance in the functioning of the internal organs, then complications may develop. These include:
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- liver diseases;
- deterioration of metabolism;
- stroke;
- renal failure.
Timely consultation with a doctor and treatment will help you avoid the consequences. Compliance with all the specialist’s instructions guarantees a speedy recovery. For prevention, it is recommended to eat right, avoid stressful situations and heavy loads. After treatment for infectious diseases, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations and, if a pink spot appears on the skin again, begin therapy immediately.
You can ask your question to our author:
Causes of brown spots on the skin
There is also no need to panic right away; often this is just the body’s reaction to factors beyond a person’s control. But hypopigmentation can also be caused by more serious health problems.
First, you need to understand what could affect such skin changes as melasma (excessive melanin deposits).
Causes of melanin deposition:
- features of the genotype (phenotype);
- age-related changes after 50 years;
- hormonal disruptions or changes (pregnancy, postpartum changes, menopause);
- excessive stress on the psyche (trauma, stress, strong feelings);
- prolonged exposure to direct sunlight;
- exposure to certain medications;
- allergy;
- malfunctions of the stomach, liver, thyroid gland;
- infectious diseases;
- worms;
- presence of tumors;
- exposure to chemicals or ultraviolet rays;
- Itsenko-Cushing syndrome (excessive production of hormones by the adrenal glands).
Let's celebrate! If a person remembers that he has not taken any medications, has not used new cosmetics or hygiene products, is not pregnant and is still far from menopause, and works in an office and not a chemical shop - you should listen to your health and consult a doctor first. see a dermatologist.