Causative agents of pustules on the labia
The causative agents may be:
- viruses;
- mushrooms;
- bacteria.
Most often, pustules appear when bacteria penetrate the skin.
This symptom can be caused by specific or nonspecific microflora.
Most often, it is nonspecific infections that cause the formation of pustules of the labia minora.
These are bacteria that live on the skin.
They usually do not cause inflammatory processes.
Primarily because they are not able to penetrate the skin.
But if the skin barrier is broken, this becomes possible.
Bacteria enter there and initiate inflammatory processes.
As a result, a pustular rash appears.
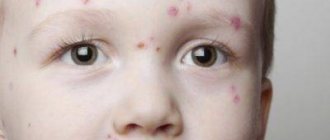
Pustules on the labia minora are usually small in size.
They are red in color and located on the edematous mucosa.
Inside there is a white thick mass.
Pustules may resolve on their own.
They open if they are large.
Sometimes they just dry out and gradually regress.
The main causative agents of nonspecific inflammatory processes are:
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- other types of staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- coli;
- Proteus;
- pseudomonas;
- enterobacteria.
Sometimes pustular skin lesions occur against the background of sexually transmitted infections.
They can be provoked by candida, herpes, and syphilis.
Often several pathogens are observed at once.
After infection with a sexually transmitted infection, secondary bacterial flora can join.
As a result, ulcers form.
Methods of treatment and prevention
There is no one general cure for boils. Therapy is based on destroying the bacterial infection and alleviating the symptoms of the disease. Analgesics and medications containing ibuprofen help relieve fever and inflammation. Antibiotics are used to fight harmful microbes. Self-medication can be dangerous, since many medications have contraindications for use and cause a lot of side effects. Therapy of the intimate zone is predominantly local in nature.
Ointments
Ointments
Ointments that have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and healing properties have proven themselves well.
The following popular drugs can be distinguished:
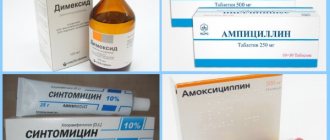
- "Heparin". It has an antiseptic and antimicrobial effect. Indicated for drawing out purulent masses.
- "Syntomycin". It has no side effects and does not cause irritation to the mucous membrane of the intimate area. Antibacterial complex external remedy is effective against ulcers, boils, acne. The antibiotic included in the composition destroys pathogenic microorganisms. Novocaine gives an anesthetic effect.
- "Ichthyol". Affects the maturation of boils. It is applied pointwise, since the ointment can cause irritation of the mucous membranes.
- "Levomekol". Has a restorative and antibacterial effect.
- "Baneotsin". An antimicrobial agent containing two antibiotics that enhance each other’s effect on boils when applied topically.
- "Clotrimazole". The medicine has no contraindications. Effectively copes with pathogens that cause suppuration.
- "Zinc". Healing agent. Used on the genitals after boils have broken out. The ointment is approved for use during pregnancy.
- "Vishnevsky ointment". The drug can relieve pain, clean wounds of varying depths, and relieve inflammation.
Prevention
Prevention
To prevent the formation of ulcers, you need to follow some recommendations:
- You need to choose the right underwear. It is better to take clothes from breathable materials with natural fibers without synthetics.
- A daily hygienic shower is required.
- Depilation should be carried out extremely carefully. Cuts and injuries often become the cause of infection.
- Strengthening the immune system should be carried out systematically. An organism deprived of protection is unable to resist.
- You should eat a varied diet. Include foods rich in vitamins and elements, fresh vegetables and fruits in your diet.
Frequent recurrence of furunculosis indicates the presence of health problems. Doctors' recommendations include undergoing a full examination to find out the reasons.
When are pustules on the labia contagious?
If a woman has an abscess on her labia, this does not mean that she is contagious.
If the pathology is caused by nonspecific flora, then it is not sexually transmitted.
But there are cases when pustular lesions are provoked by sexually transmitted diseases.
Then they are transmitted through sexual intercourse.
Determining “by eye” the exact cause of the appearance of ulcers is not always within the power of even an experienced doctor.
This requires laboratory tests.
Accordingly, if you see ulcers on a woman’s labia, you cannot know for sure whether she is contagious or not.
At least until she goes to the doctor and gets the necessary tests.
If it is determined that there are no sexually transmitted infections, the patient will be able to have sexual activity without the risk of infecting her partners.
Types of acne
There are almost as many types of rashes as there are their causes, but the main ones include the following.
White pimples
They appear after hair removal (the so-called irritation, which goes away on its own over time) or after wearing synthetic underwear. Another reason for the appearance of such seals is the critical temperature (too cold or too hot), that is, after hypothermia and overheating.
Subcutaneous
These are peculiar tubercles that do not cause pain or discomfort. They may appear due to a congenital feature of the sebaceous glands. Such pimples may themselves change in size, but this is absolutely normal and nothing to worry about.
If subcutaneous pimples are caused by blockage of the sebaceous glands, then they can be dangerous and require removal in a non-inflamed state. Sometimes such ulcers on the genitals indicate a low ability of the immune system to protect itself from pathogens.
Reds
They are usually very painful and have a distinct red color. They are caused by various diseases of the endocrine system or hormonal imbalances, which are often observed in women during menopause or in young girls whose bodies are just beginning to mature.
They can also appear from severe stress. But please note that red pimples can be common teenage acne, which will not cause any harm if it is not accompanied by pain.
Colds
They appear due to hypothermia, which makes them vulnerable to viral diseases and does not exclude their transformation into dangerous ulcers. Do not neglect treatment, as blood poisoning is possible.
Watery
If the pimples are watery and have a sharp end, then they may be papillomas, which are the result of the papilloma virus or a decrease in the activity of the immune system.
If the pimples look like a bubble and fluid flows out of them, then it is herpes.
All types of rashes have a different nature, so in order to identify the real nature of the pimples on the labia, you must definitely go to the hospital.
Folliculitis on the labia
One of the most common causes of pustules is folliculitis.
This pathology is usually caused by staphylococci.
Less common are folliculitis of other etiologies:
- pseudomonas;
- herpetic;
- gram negative;
- fungal;
- syphilitic;
- parasitic.
The disease is usually caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
Inflammation is possible only in those places where there are hair follicles.
They are present on the labia majora.
This often creates optimal conditions for bacterial growth.
Causes of infection of hair follicles by staphylococci:
- mechanical trauma (during hair removal or shaving);
- increased skin moisture (the result of sweating, vaginal discharge);
- rubbing with linen;
- trauma during sexual intercourse.
Folliculitis can be superficial or deep.
Superficial ones are more common.
In this case, the inflammation does not spread below the funnel of the bulb.
Such pustules heal without scarring.
It is worse when the folliculitis becomes deep.
It's called sycosis.
Then there is a considerable risk that the disease will develop into something more than just pustules.
Pathology can provoke boils, carbuncles of the labia majora.
Sometimes phlegmon develops and abscesses form.
These are severe purulent inflammations that require surgical treatment.
After healing, scars remain.
What is a boil
Staphylococci and streptococci usually cluster around the follicles. Any wound or crack in this place facilitates the penetration of a pathogenic microorganism into the hair follicle. In intimate places, abrasions often form, where under certain conditions diaper rash forms. All this creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. An increase in their number contributes to the development of the inflammatory process, which ends in the formation of pus. Any rash near the vagina or on the penis is a big problem that needs to be addressed immediately.
Etiological factors
There are internal and external factors that cause the activity of staphylococci and streptococci. The former cause a decrease in immunity, the latter contribute to the penetration of infection deeper into the body.
The defense system can be weakened by:
- congenital immunodeficiency,
- surgical operations,
- severe systemic diseases (oncology),
- endocrine pathologies: diabetes mellitus, dysfunction of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands,
- increasing testosterone levels in the female body,
- excessive sweating,
- long-term use of antibiotics, cytostatics, immunosuppressants,
- vitamin deficiency that arose against the background of poor nutrition.
The following can provoke infection into the hair follicle:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules,
- promiscuity,
- hypothermia,
- overheat,
- chronic fatigue,
- lack of a clear work and rest schedule,
- bad ecology,
- work associated with the constant presence of dust, dirt, aggressive chemicals,
- constant stress and overexertion,
- wearing tight underwear,
- poorly performed depilation,
- bad habits.
Doctors pay attention to the fact that furunculosis of the vulva often results from complications of bartholinitis, genital herpes, and sexually transmitted diseases. Pathogenic bacteria can penetrate deep into the hair follicle growing in the perineum, with the blood flow from the source of infection. Superficial ulcers can form anywhere where hair grows. In men, they are most often localized on the pubis, scrotum, and around the penis. In women, a boil appears on the small or large lip, around the anus.
Boils on the labia
This term refers to acute purulent inflammation of the hair follicle, which spreads to surrounding tissues.
This is usually a complication of folliculitis caused by staphylococcus.
A dense knot forms in the skin.
It is warm to the touch, hyperemic.
The labia where the boil appeared becomes swollen.
The result of the merger of several boils can become a carbuncle.
Subjectively, throbbing pain is felt.
General symptoms are also possible.
But they appear only with multiple boils.
In this case, fever and malaise occur.
Initially, a small dense knot forms on the labia.
Then it increases to 1-2 cm.
A necrotic core appears.
On top it is usually covered with a pustule (abscess).
Fluctuation (fluctuation of fluid) is noted under the necrotic core.
Over time, the abscess opens.
A cavity opens under the rod.
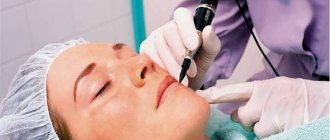
Laser removal of boils in intimate places
Surgery using laser action allows you to remove suppuration quickly, painlessly and without the risk of traditional complications:
- subsequent soreness of the skin area;
- repeated suppuration;
- bleeding;
- scarring of tissue with the formation of a scar.
The laser is used to open the tumor and for subsequent wound treatment (debridement). The procedure does not involve drainage or suturing. Healing after surgery takes no more than a week, leaving no scars or other cosmetic defects.
Advantages of using a laser to remove purulent formation:
- high-quality results from the first use;
- elimination of the source of inflammation without the risk of relapse;
- minimal level of injury;
- no pain during the procedure;
- short recovery period;
- The treatment does not involve the formation of scars or cicatrices.
Removing a boil in the intimate area using a laser is convenient, fast and effective. In Moscow, the technique helps patients in solving a rather delicate and complex problem. The choice in favor of a laser becomes a justified decision, since the procedure is characterized by minimal pain and no risk of recurrence of suppuration.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine can complement or, in some cases, partially replace drug therapy.
Here are a few recipes for treating ulcers on the labia:
- In order to speed up the ripening of the boil, apply an aloe leaf cut lengthwise to it, fix it with a bandage and hold it for 3 - 4 hours. You can apply agave several times during the day.
- Applying a baked onion will help speed up the breakthrough of the abscess - the cut onion is placed on the affected area overnight.
- A compress of dried calendula flowers mixed with ghee is applied to the affected area for 2 to 3 hours.
- To draw out pus from a boil, you can make compresses with laundry soap - rub it on a grater and mix with water, then soak a napkin in the mixture and apply it to the abscess. The duration of the procedure is from 6 to 8 hours.
- Lotions made from medicinal herbs have an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect. To do this, prepare an infusion of calendula, string, chamomile, sage, thyme and apply it to the boil for 30 - 60 minutes.
Bartholinitis on the labia
Bartholinitis is called inflammation of the Bartholin gland.
It is located in the vestibule of the vagina, at the base of the labia majora.
The pathology is of infectious origin.
Most often there are several pathogens.
The outcome of the inflammatory process can be the formation of a retention cyst or abscess.
A cyst forms when the gland duct is blocked.
Then secretion accumulates in it, stretching the walls.
If suppuration occurs, an abscess forms.
Pus accumulates inside, the wall is formed by a pyogenic capsule.
The onset of the disease is usually acute.
Pulsating pain appears in the area of the labia majora.
The pain intensifies with palpation, defecation, and walking.
Sexual intercourse becomes impossible.
Body temperature can rise to 38 degrees or more.
An abscess on the labia majora can open spontaneously.
In this case, the pus is poured out, and the wound heals with the formation of a scar.
What can't be done with a boil?
Regardless of the stage of the pathological process, sexual activity is prohibited for the entire duration of therapy. Otherwise, the risk of relapse increases.
Since this formation is a source of infection, you should only touch the affected area with clean hands. After the treatment procedure, you must wash your hands with an antibacterial agent to prevent infection from entering the body.
Opening a boil yourself (picking or squeezing) is strictly prohibited. The skin in the groin area is very delicate; many capillary vessels pass through here. If the abscess is not completely squeezed out, the infection can enter the blood. This entails inflammation of the venous tissues.
Also, do not scratch or scratch the damaged area. If the abscess has opened on its own, it is necessary to carefully treat the wound, remove its contents and apply a bandage. It is recommended to repeat antiseptic procedures until the pimple is completely healed. To reduce the inflammatory process, you can take antibiotics. Medicines must be prescribed by a doctor after testing for pathogenic flora.
Pustules on the labia due to STDs
Sometimes sexually transmitted infections cause the appearance of pustules.
Their pathogens can provoke a rash on their own.
In other cases, the cause is the addition of accompanying bacterial flora.
Ulcers can occur when:
- herpes;
- syphilis;
- candidiasis;
- HPV;
- molluscum contagiosum.
All of these infections are contagious.
They are transmitted through sexual intercourse and close household contact.
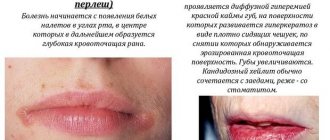
Pustules on the labia with herpes
Herpetic infection itself does not manifest as suppuration.
This is possible in the case of the addition of secondary bacterial flora.
The incubation period lasts about 1 week.
Then a tingling sensation appears in the area of the labia majora.
After 1-2 days, bubbles with liquid form on the reddened skin.
It's transparent.
After a few days it gradually becomes cloudy.
In some cases, a bacterial infection is associated with a herpetic infection.
The blisters become infected with bacteria that are present on the skin.
This is an opportunistic flora.
In this case, you can see that what is inside is not clear liquid, but pus.
This complicated form of the disease is more severe.
There is pain and symptoms of intoxication increase.
After resolution of inflammatory elements, scars may remain.
They appear when the skin of the labia is deeply damaged.
Molluscum contagiosum on the labia
This is a viral infection that is sexually transmitted.
It is not hazardous to health.
But it causes certain inconvenience to a woman.
Nodules form on the labia.
They look ugly and interfere with normal sex life.
In appearance, these nodules resemble pustules.
The similarity is enhanced by the presence of a pasty white mass inside.
It looks like purulent discharge.
The developing elements of the rash are painless.
There are no significant signs of inflammation.
Without treatment, pustules on the labia exist for quite a long time.
They can last up to six months.
With reduced immunity – even longer.
Against the background of HIV, pustules never disappear at all.
But you can remove them if you wish.
What to do if you jump during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, the mother's body is weakened due to the fact that all the necessary nutrition is given to the child. Because of this, immunity is significantly reduced, and the body cannot cope with the infection.
Boils on the genitals are a common occurrence in women during pregnancy. The pathogen already present in the body turns out to be stronger than the woman’s immunity, which manifests itself in the form of boils in the intimate area.
Be careful when treating. It is recommended to use only those drugs that will not affect the development of the child. They also adhere to strict dosages of medications.
Candidiasis on the labia
A fungal infection can provoke the formation of ulcers only in severe cases.
As a rule, vulvovaginal candidiasis manifests itself:
- red spots;
- white coating on the labia;
- papules.
A severe course is possible due to immunodeficiency.
Including HIV-infected patients.
Then painful pustular elements often form.
They occur simultaneously with spots, cracks, erosions, papules and other rashes.
The affected area may not be limited to the labia alone.
Candidiasis develops as an exogenous or endogenous infection.
The disease can occur after sexual intercourse with a man who is a carrier of candidiasis.
In other cases, candida is already on the woman’s labia.
The disease manifests itself due to decreased immunity.
Causes of rashes in women
Rash and single pimples on the female genital organs definitely cannot be considered a variant of the norm. Such symptoms should be a reason for an unscheduled visit to the gynecologist. Possible reasons for its appearance include:
- Natural factors, for example, incorrectly selected underwear or improper hygiene.
- Aggression of various parasites.
- Inflammatory processes in the hair follicles or glands.
- Viral diseases, such as herpes.
- Fungal infections.
- Benign neoplasms.
- Dangerous diseases, for example, syphilis, etc.
It is quite difficult to determine on your own what caused the alarming symptoms. To make a correct diagnosis, various laboratory tests are usually performed.
Why did white dots appear in the crotch?
White dots, similar to small pustules, often appear on the labia majora due to:
- Wearing uncomfortable underwear, particularly tight or too tight underwear.
- The occurrence of the greenhouse effect when using synthetic underwear.
- Insufficient hygiene.
- Individual reaction to hygiene products, for example, intimate hygiene gels, pads, etc.
- Shaving. In this case, pimples may appear on the skin in places where hairs grew due to infection entering the tiny wounds.
White pimples on the labia can cause severe discomfort: they ache and itch. If the cause of their appearance is not corrected, they can lead to a widespread inflammatory process.
Red spots or blisters on intimate organs
Red spots may well appear when pustules burst, arising against the background of the reasons we described just above. But sometimes the appearance of blisters in the perineum can be explained by other factors:
- Bites of skin parasites, which can be picked up during sexual intercourse or when visiting a swimming pool (sauna, etc.). It is very difficult to see them with the naked eye, but the bite sites are easily visible - they look like itchy red spots or blisters.
- Allergic reaction. Red spots or blisters that look like nettle stings are a common sign of allergies. In the area of intimate organs, in particular on the labia minora or majora, it can be caused by cosmetics, pads, latex, local contraceptives, etc. Manifestations of allergies usually itch noticeably and also lead to some swelling of the epidermis.
Red spots on the labia minora and majora may well appear due to various sexually transmitted diseases. In such a situation, they are constantly irritated by abnormal secretions. But with such diseases, other symptoms still come to the fore - the discharge itself, itching and burning, etc.
Single painful inflammation
If a single painful pimple appears on the labia, it may be a manifestation of a developing boil - an acute inflammatory process in the hair follicle, sebaceous gland, and surrounding connective tissue. This condition is most often caused by bacteria, and it can develop after injury (for example, received while shaving). You can suspect the development of a boil by:
- Severe painful sensations.
- The formation of a red and swollen area, similar to a large pimple.
- The appearance of a purulent head at the top of the pimple (after 2-3 days).
- Deterioration of general condition and increase in temperature (not always).
Typically, a boil on the labia opens on its own and then heals. But due to its special location, such a pimple can lead to the spread of infection, so it is better to treat it under the supervision of a doctor.
Inflammation of the Bartholin gland
A large internal pimple at the entrance to the vagina may be a manifestation of the inflammatory process in the Bartholin gland. This common disease is also known as bartholinitis. As you know, the Bartholin gland is a steam gland and is located at the very entrance to the vagina. Its inflammation can be provoked by injuries, surgical interventions in the area of the external genitalia, immune disorders, wearing tight underwear, etc. The causative agents of the disease can be a variety of pathogenic microorganisms. You can suspect the development of bartholinitis based on the following symptoms:
- Redness of the labia minora near the vagina.
- The formation of a small nodule (internal pimple), up to the size of a pea.
- Swelling of mucous membranes.
- The appearance of a slight burning sensation, which is subsequently supplemented by moderate pain. When suppuration occurs, the pain becomes especially pronounced.
- A slight increase in temperature - up to 37.5 ° C, with suppuration - higher.
- Discomfort when walking.
You can cope with non-purulent bartholinitis using conservative therapy - it is only important to consult a doctor in time. But if the disease is accompanied by suppuration, surgical intervention is performed.
Blisters on the genitals
If pimples on the labia look like blisters, their development is most likely due to the activity of the herpes virus. This disease is considered quite contagious; unpleasant symptoms can appear after sexual contact with a sick person or due to the banal transfer of the virus from the mucous membranes of the lips to the intimate organs (with insufficient hygiene). Genital herpes is accompanied by quite striking symptoms:
- Burning, itching and swelling in the intimate organs.
- The appearance of bubbles filled with liquid contents. They subsequently burst, dry out, form crusts, and eventually fall off.
- Enlarged lymph nodes, manifestations of intoxication.
The danger of herpes is that once infected, there is no way to completely eliminate the virus from the body. Subsequently, the disease can recur, and the risk of repeated manifestations can be reduced only through proper treatment and targeted strengthening of the immune system.
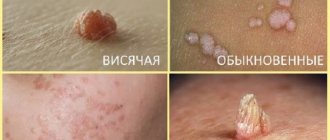
Causes of painless rashes
New growths may appear on the female labia that look like pimples, but do not cause any particular discomfort. Such elements may be:
- Manifestations of HPV - human papillomavirus. This disease is considered quite common; it can be contracted through direct contact, as well as through blood. The activity of the virus in the presence of predisposing factors (decreased immunity, microtrauma, etc.) leads to the appearance of condylomas on the genitals. Such neoplasms look like small flesh-colored growths of unequal size. Condylomas have a soft structure; as they grow, it is clear that they are located on a thin stalk. They can occur not only on the labia, but also in the vagina, as well as on the skin near the anus, etc. Such neoplasms can be injured, and they are also dangerous from the point of view of malignancy - the development of cancer.
- Benign neoplasms, in particular fibroma, myoma, lipoma, fibromyoma, hemangioma, myxoma, lymphangioma or hidradenoma. Such tumors in the initial stage of development may look like small formations. They are often mobile and do not cause pain or discomfort, but can grow. When enlarged, benign tumors cause significant discomfort and cause a sensation of a foreign body.
- Vulvar cancer. This is a fairly rare type of cancer, which is most often diagnosed in older women. However, there is a risk of developing such cancer in younger representatives of the fair sex. Possible manifestations of cancer include painless spots, pimples, lumps, and changes in the normal color of mucous membranes or skin. As the tumor progresses, it can cause discomfort - cause pain, burning and itching, as well as ulcerate and bleed.
Most diseases of the external female genitalia respond successfully to conservative treatment. The development of dangerous diseases, in particular cancer, can be prevented through regular preventive examinations with a gynecologist.
Balls under the skin
Sometimes an incomprehensible formation on the labia looks like a subcutaneous moving ball. This may look like this:
- Subcutaneous pimple. Sometimes the inflammatory process in such a formation is not very active, so the neoplasm does not cause any discomfort. A pimple may go away on its own after some time, or it may begin to hurt and require targeted treatment.
- Vulvar fibroma. Such a neoplasm can be located in the thickness of the labia majora, where it is less often found in the vestibule of the vagina. This benign tumor grows slowly and most often does not cause discomfort.
- Vulvar fibroids. Such a tumor consists of muscle fibers. Its typical location is the labia majora. Myoma has a dense elastic consistency and is not connected to surrounding tissues.
- Lipoma. This tumor consists of fat cells. It can appear on the labia majora, and is also sometimes detected on the pubis. This neoplasm has a soft structure and rounded shape.
Doctors usually insist on surgical treatment of benign tumors in the genital organs, especially if they increase in size and begin to cause discomfort. But sometimes it is enough to observe small tumors without taking any active action.
Rash with white coating
The appearance of pimples with a white coating on the genitals suggests the activity of thrush, a fungal disease caused by Candida fungi. With this disease, rashes are a secondary symptom; other health problems come to the fore:
- Itching in the external genital area.
- The appearance of abundant white discharge with a specific cheesy structure.
- Painful sensations during sexual intercourse and urination.
Plaque in the form of a whitish rash is found only on the mucous membranes. It does not occur on the skin of the labia majora.
Formations for syphilis
Despite the wealth of information available about sexually transmitted diseases, doctors occasionally have to deal with syphilis. In women, this disease can manifest itself as a special rash on the labia. In particular, with primary syphilis, a characteristic hard chancre can form on the intimate organs - a deep, painless or practically painless ulcer. She has:
- Smooth side surfaces, smooth bottom and smooth edges.
- Correct round shape.
- Dense structure.
The chancre does not increase in size. Its appearance may be accompanied by swelling of the labia. Subsequently, such a formation disappears without a trace, after which the secondary stage of syphilis begins.
White pimples in Fox-Fordyce disease
Fox-Fordyce disease is a specific skin disease, which is characterized by the appearance of small nodular rashes of different localization. Most often it is found on the genitals, pubis, and around the breast nipples. Sometimes the rash also appears in the armpits, and also near the navel. The rashes look like nodules:
- Oval shape.
- Flesh color.
- Matte-shiny color.
Such elements of rashes are located near the follicles of the apocrine glands and sebaceous ducts. The disease is usually accompanied by severe itching and causes severe scratching. This disease is typical for women, but is sometimes diagnosed in men. But its manifestations should not be confused with the so-called Fordyce granules - light pimples (sebaceous glands), which usually look like pimples on the penis and can appear in a boy during puberty. Such neoplasms do not cause discomfort and do not require targeted treatment.
To date, the causes of Fox-Fordyce disease have not yet been studied, so therapy is mainly symptomatic and aimed at suppressing severe itching.
Black spots in the perineum
The appearance of black spots on the labia is a rather nonspecific symptom. This symptom can be observed when:
- Shaving when hairs begin to grow back or ingrown hairs appear.
- Formation of comedones - classic blackheads. On the skin of the labia, such a nuisance can occur as a result of wearing tight synthetic underwear, as well as due to insufficient hygiene and a tendency to excessive sweating. Sometimes blackheads appear due to hormonal imbalance. Comedones can turn into full-fledged inflamed acne, so it is better not to ignore them.
- Activation of the HPV virus. Sometimes condylomas that appear on the genitals do not have the classic flesh color, but look like small convex dark dots.
A single black dot on the labia may also represent a pinpoint hemorrhage or a common mole. Such marks do not pose any threat to health, but nevi on intimate organs require close attention and careful handling - they should not be injured by chemicals, razors, etc.
There is a risk that the detected neoplasm is a parasite, a mite, that has burrowed into the delicate skin. In such a situation, you need to immediately contact doctors to remove it and provide appropriate assistance.
Pimples in the vagina
It is worth noting that rashes that appear only in the vagina are extremely rare. Typically, such symptoms are complemented by the appearance of rash elements on other parts of the genital organs, in particular on the labia, and are caused by the above factors. Isolated rashes may be a manifestation of:
- Various infectious diseases. In this case, they are supplemented by corresponding symptoms - itching, burning, and the appearance of incomprehensible discharge.
- Human papillomavirus.
- Primary syphilis.
- Benign or malignant tumors.
If you discover any unknown neoplasm in the vagina, you should see a doctor as soon as possible. Self-diagnosis and self-medication can lead to extremely unpleasant consequences.
Why might a pimple appear on the clitoris?
Rashes of such atypical localization are extremely rare. The rash usually appears on the labia, near the urethra and the clitoris, but rarely involves the clitoris itself. The appearance of such symptoms may be explained by:
- The appearance of an abscess due to insufficient hygiene, wearing tight and synthetic clothing, etc.
- Mechanical irritation.
- Formation of papilloma (manifestation of HPV).
- Manifestation of genital herpes (the pimples subsequently spread to other areas of the genital organs).
Any tumors on the clitoris cause great discomfort and greatly affect the quality of life. But the doctor will tell you how to neutralize the discomfort as soon as possible.
Causes of rashes in girls
Rashes on the genitals can appear even in young children (up to one year). Most often, these symptoms are explained by:
- Insufficient hygiene.
- Allergies to diapers or detergents used.
- An allergy to food, in which case the rash spreads to other areas.
- Mechanical irritation. In particular, the rash may appear after playing in the sand in shorts.
It is worth noting that rashes on the genitals in girls can be caused by other factors, in particular, fungal or bacterial infections, etc. Therefore, if you discover unpleasant symptoms, you should contact a pediatrician and pediatric gynecologist. This will help avoid serious problems with the health of the girl’s reproductive system in the future.
HPV on the labia
Infection with papillomavirus is not accompanied by the appearance of ulcers.
The disease is manifested by the formation of painless growths on the labia.
Usually there are no signs of inflammation.
Subjectively, only itching can be felt.
Sometimes these growths become infected with secondary bacterial flora.
Then small pustules appear in their place.
The risk is higher if a woman injures papillomas.
This may happen during the process:
- sexual intercourse;
- hygiene procedures;
- attempts to independently remove formations.
After treatment, the pustules disappear.
But the condylomas remain - they have to be removed with a laser or liquid nitrogen.
Pustules on the labia with syphilis
Syphilitic infection has local manifestations only in the primary period.
In secondary and tertiary cases, not only the labia are affected, but almost all organs and tissues are affected to one degree or another.
After infection with syphilis, there is an incubation period.
After a month, erosion appears.
The labia are one of its most common locations.
In the natural course of the disease there is no suppuration.
The erosion is dense to the touch, painless, covered with a gray coating.
But sometimes secondary bacterial microflora is involved in the infectious process.
In this case, the following changes occur:
- an abscess forms at the site of erosion;
- erosion can turn into an ulcer with purulent plaque at the bottom and necrotic masses;
- the site of inflammation becomes painful;
- lymph nodes become inflamed and painful.
What it is?
A boil is a skin infectious disease. It is characterized by inflammation of the tissue and hair follicle with the formation of pus.
Reference! The disease begins in the hair follicle, after which it spreads to nearby tissues and leads to their inflammation and subsequent necrosis.
A boil is a skin blister with pus inside. It has the shape of a cone, a diameter of two millimeters, red or purple in color, and is often confused with a pimple. The appearance of a single boil is typical, but cases of multiple furunculosis have been identified. The skin around the bubble becomes inflamed and swollen.
When opened, the film covering the pus is easily separated. After the contents leak out, you can see a necrotic rod inside, similar to a stick of pus and going deep into the skin. The wound is an inflamed red ulcer. Often dead hair is found among the pus.
When localized on a woman’s genitals, a boil can affect:
- labia majora - where hair grows;
- labia minora - at the base;
- mucous membrane - at the entrance to the vagina.
Tests for pustules on the labia
To find out the true reason for the formation of pustules on the labia, you need to see a doctor and get tested.
The cause needs to be known in order to choose an effective treatment.
It will help avoid complications by preventing further development of diseases.
As you already understand, there are many reasons for the formation of ulcers.
They can be caused by nonspecific bacteria or pathogens of sexually transmitted infections.
Sometimes these are not only bacteria, but also fungi or viruses.
The treatment regimen depends on what pathogens are detected.
After all, different infectious agents are destroyed by different drugs.
The following tests are prescribed:
- microscopic examination of a smear from a rash;
- PCR for sexually transmitted infections;
- bacteriological culture of flora.
The listed studies in most cases make it possible to establish the etiology of pustular lesions of the labia.
Microscopy may reveal fungi (candida, dermatophytes), coccal or rod microflora.
If sexually transmitted diseases are suspected, PCR is performed.
They do tests for herpes, HPV, and other infections if indicated.
The material is inoculated onto a nutrient medium.
Colony growth is then monitored, microorganisms are identified and tested for resistance to various antibiotics.
To diagnose syphilis, they take ulcer discharge or blood to determine antibodies in it.
Treatment of a boil
A boil or boil on the labia goes away on its own in 5-7 days. You can speed up the healing process of an abscess on the genitals using ointments or surgery.
The most effective and safest method to get rid of an abscess on the genitals is to consult a surgeon. The doctor will open the suppuration, remove the contents of the cavity and necrotic core, as a result the problem will go away faster. If nothing is done, it will take about a week for the abscess to mature and open, and a week for tissue regeneration. If you consult a doctor, the recovery period will be reduced to one week, since there is no need to wait for the abscess to spontaneously open.
Before removing a boil on the pubis and genitals, the doctor will treat the skin around the abscess with an anesthetic drug. After the anesthesia injection, the patient will not feel pain. Then an incision is made using a scalpel and the contents of the cavity are removed with a special tool. Afterwards, the cavity is treated with an antiseptic, ointment is applied and covered with a bandage. The doctor will also give recommendations on what medications should be used to speed up skin regeneration.
Ichthyol ointment helps to speed up the process of boil ripening at home. The drug is generously applied to a gauze compress, which is then applied to the ripening abscess for several hours. The compress is changed 3-4 times a day. This treatment is carried out until the abscess matures and a rod becomes visible on its surface.
When purulent contents have formed, you can either go to the doctor or continue treatment at home. By turning to a surgeon, the patient will save herself from having to endure discomfort for several more days, since it takes time for the boil to open on its own.
If a home treatment method is chosen, treatment of the abscess continues with antibiotic ointment. Levomekol is well suited for this, as it effectively acts on gram-positive microorganisms that provoke suppuration. The ointment is applied to a gauze compress, avoiding contact with the mucous membrane. The compress is applied to the abscess and covered with a bandage on top. The procedure is repeated several times a day.
When the boil opens, it is important to promptly remove the pus using a cotton swab so that it does not get on the mucous membranes of the genital organs and provoke the development of inflammation.
At each stage of treatment, antiseptic treatment is required. To do this, use a solution of Chlorhexidine, which is generously moistened with a cotton swab and applied to the boil for a few seconds.
To speed up the healing of the wound at the site of the boil, it is necessary to use antibacterial ointments. They are applied directly to the wound, and then cover the affected area with a bandage or plaster.
For large boils on the labia and pubis, it is recommended to consult a specialist to prescribe medications. Large inflammation sometimes needs to be treated with antibiotic tablets that have a systemic effect on the body.
Under no circumstances should you try to open a boil on the labia yourself; this can lead to infection of the genitals and the development of bacterial damage to the external genitalia.
Treatment of pustules on the labia
Different treatment regimens are used, depending on the pathogen identified.
Treatment can be conservative or surgical.
In most cases, it is possible to limit oneself to conservative therapy.
Drug treatment is used locally and systemically.
Local usually complements oral medications.
Only for mild pustular skin lesions can they be used without systemic antimicrobial agents.
Drug therapy
Treatment of the pathology usually depends on the symptoms and complications that accompany the boil and the cause of the inflammatory process. Many women seek help from a doctor late, trying to cope with the abscess on their own. In this case, surgical intervention is usually required.
Levomekol and Ichthyol are used as methods of conservative therapy. These ointments are used to relieve inflammation and swelling. Based on the results of the analysis to identify the pathogen, the doctor prescribes antibiotics (Dicloxacillin, Tetracycline, Erythromycin). The course of treatment is no more than two weeks.
Pustules on the labia: what to anoint
Local medications are prescribed differently, depending on the situation.
Most often, pustules on the labia are of staphylococcal etiology.
In this case, mupirocin and fusidic acid are used topically.
Antibiotic ointments may be used.
Their active ingredients are tetracycline and erythromycin.
Antiseptic solutions and sitz baths are used.
In case of herpes infection, acyclovir cream is used topically.
It is prescribed in addition to systemic therapy.
For fungal diseases, clotrimazole or miconazole cream is used.
How to properly treat a boil
Before touching the abscess, as well as after touching, you must wash your hands well with soap or some other antibacterial agent.
If, after touching the formation, you are faced with the process of preparing food, you must wash your hands very thoroughly so as not to introduce infection into the food.
During the course of this disease, carefully monitor hygiene. Shower regularly.
During removal of ulcers, local anesthesia is used. After opening, a swab with an antiseptic is applied. In order for the wound to heal faster, the doctor may prescribe UHF, irradiation with infrared light, or electrophoresis.
Local treatment includes compresses that soften purulent formation, reduce pain symptoms and promote rapid maturation of the boil. After applying the compress to the abscess, you must apply a dry, clean bandage in the form of gauze. The boil cannot be squeezed out; you need to wait until it opens on its own. This type of wound care is carried out until it is completely healed.
At the first manifestation of a boil, you must go to the hospital; you cannot self-medicate. Because self-treatment can only worsen the condition. To avoid this disease, it is necessary to monitor the hygiene of the genital organs. Depilation of the intimate area should be carried out correctly and carefully. Lead a healthy lifestyle, eat well and strengthen your immune system.
Pustules on the labia: what pills to take
In case of severe inflammatory processes, systemic therapy is prescribed.
For sexually transmitted infections it is almost always used.
Herpes is treated with acyclic nucleosides.
Acyclovir, famciclovir or valacyclovir are used.
For candidiasis, fluconazole is prescribed orally, and sometimes itraconazole.
In the case of superficial staphylococcal folliculitis, you can limit yourself to local treatment only.
But with sycosis, furunculosis or carbuncle formation, systemic antibiotic therapy is required.
It is also necessary for bartholinitis.
Antibiotics are prescribed internally.
These can be cephalosporins, tetracyclines, macrolides.
If the formation of pustules is caused by syphilis, penicillin is prescribed by injection.
In the primary period, drugs of medium or high duration are used.
Benzathine or procaine penicillin is prescribed.