Young children are more susceptible to fungal diseases due to underdeveloped immunity. Ringworm is most often diagnosed in preschool children. The disease is classified as highly contagious. The danger is that fungal spores are very resistant to environmental influences and can remain active for 1.5-2 years, therefore, if one child from a group is infected, it is imperative to notify the management and urgently introduce a microsporia quarantine in the kindergarten .
Ringworm may require quarantine
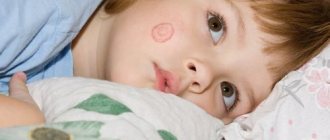
Manifestations on the head
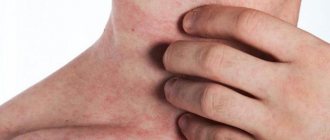
The first symptoms of the disease appear as a rash on the head, eyebrows or along the eyelash line. The rash appears as isolated pink or reddish spots, separated from healthy areas. The diameter of the neoplasms is approximately 3.5 cm. A ridge formed by bubbles can be observed around the spot. After just a few days, the hyperemia in the inflamed areas disappears and peeling begins. The fungus feeds on keratin, a protein that promotes hair growth. Fungal spores fill the follicle, forming a dense dome, which interferes with the normal nutrition of the hair, so at the site of the rash, it becomes fragile and begins to break off. A mild form of microsporia in children may look like a severe manifestation of dandruff that appears suddenly. At the site of the inflamed areas of the skin, mild or severe itching may be felt, which causes discomfort. The child becomes whiny, capricious, and sometimes has sleep disturbances. When affected by the microsporum fungus, symptoms of intoxication, fever, increased temperature, and inflammation of peripheral lymph nodes may be observed. This complication is called scab; it is quite dangerous and difficult to treat. In children with allergies, the manifestations of microsporia will be more pronounced. Infection with the microsporum fungus is fraught with the appearance of an erythematous-edematous form. This type is characterized by severe burning, itching, the appearance of a purulent infiltrate, and swelling. The surface of the new growths is covered with small bubbles, which often pour out, leading to the formation of a hard crust.
Ringworm causes severe itching and discomfort
Forms of microsporia
The types of microsporia are classified taking into account the depth of skin damage, the prevalence of lesions, the method of infection, and the course of the disease.
Superficial
The surface layer of the skin is affected, on which red scaly spots appear on the body and head, where the hair breaks off, forming bald spots with short stumps.
Exudative
Affects the deeper layers of the epidermis. Bright red spots are visible on open areas of the body, on the surface of which small bubbles with liquid inside form. There is weeping and itching. Serous discharge permeates the skin scales, they stick together, forming a dense crust. Underneath there is erosion, similar to a burn.
Infiltrative-suppurative
Affects the skin to its full depth. It usually appears on the scalp as a raised, dense, painful infiltrate, which gradually softens with the formation of purulent contents. When you press on the node, pus is released from the openings of the hair follicles. Accompanied by fever, intoxication, and enlarged lymph nodes. At the site of the infiltration, a scar or areas devoid of hair are formed.
Sometimes it takes the form of kerion Celsi (honeycomb of Celsus), when the pus flows like honey from a honeycomb, thick and light yellow.
Chronic
Another name is recurrent. It develops with untreated or undertreated microsporia, when the fungus makes itself felt again.
Anthroponotic and zoonotic
If a child becomes infected from an animal, then this form of microsporia is called zoonotic. It is the most common. Anthroponotic is much less common. It is transmitted from person to person or through the patient’s belongings.
Atypical forms
They run smoothly and disguise themselves as other skin diseases. Their classification is based on similarities with other diseases.
- Trichophytoid microsporia. Forms many small, vague foci without signs of inflammation. The hair is broken off close to the head. Gradually covers the entire hairline with the formation of bald areas. Often becomes chronic.
- Seborrheic causes severe hair loss and flaking of the skin with the formation of many scales resembling dandruff.
- Rosacea-like appears on the body in the form of pink spots with clear boundaries and slight peeling, reaching very large sizes.
- Psoriasiform. Reminiscent of psoriasis - plaques covered with silvery scales.
Diagnosis
As soon as parents suspect lichen, it is necessary to go to an appointment with a local pediatrician. He is involved in treatment together with an infectious disease specialist and a dermatologist. Neoplasms are examined under a Wood's lamp. In a darkened room under the light of the device, they acquire an emerald color. In addition, a scraping is prescribed. Skin, hairs, and follicles from the affected areas are used as biomaterial for research. Such studies must be carried out at least 5 times. So that the doctor can see the full picture, it is necessary to take blood and urine tests. In case of deviations from the norm, they are retaken once every 10 days.
Biochemical blood tests are performed to exclude oncology and autoimmune diseases (lupus erythematosus).
The study is carried out before starting treatment and again after a month. If the diagnosis of ringworm is confirmed, the pediatrician is obliged to inform the management of the preschool institution and the SES about a possible outbreak of the disease and demand that the group be quarantined.
Wood's lamp will help make the correct diagnosis
According to SanPiN, within 3 days a notification must be submitted to the Federal Budgetary Healthcare Institution and its branches, territorial skin dispensary organizations about the identification of a patient with ringworm diagnosed for the first time. When each new case appears, it is considered as being initially diagnosed. In a preschool setting, patient information must be included in the Infectious Disease Reporting Register. This is a mandatory document maintained in all educational institutions. It is necessary to control the number of patients and record the exchange of information between healthcare organizations.
Activities in kindergarten
Microsporia in children: quarantine in kindergarten, events, timing will be discussed below.
- The patient is isolated until hospitalization or until the child is taken home. Disinfection is carried out urgently. It is necessary to remove all the patient’s clothes, bedding, toys, and remove carpets.
- The child is not allowed to attend kindergarten, swimming pools, or various clubs until recovery is confirmed. The absence of fungus must be proven 3 times by blood tests and by examination under a Wood's lamp.
- To ensure maximum isolation, the patient is allocated a separate room; personal items belonging to him must be removed from general use.
- During the first 3 days after reporting a patient with ringworm, preschool medical workers should examine the entire group of children who have been in contact with the patient. Regular inspection should be carried out until final disinfection measures are taken. Observation is carried out 1-2 times every 7-10 days for 3 weeks using fluorescent lamps. A prerequisite is to maintain an observation sheet in which the data of each medical examination is entered.
Routine disinfection must be organized by the health authority that diagnosed the disease. Preventive measures until hospitalization or until the child is taken home are organized by the kindergarten.
Treatment of microsporia in children
Prescription of drugs against microsporia occurs only after visiting a doctor. If the lesion is localized on smooth skin, topical medications are prescribed. This includes ointments, creams, solutions and sprays. Treatment continues until the symptoms of the pathology completely disappear.
When the scalp is affected, the treatment regimen looks different. The patient is prescribed complex therapy, including taking antifungal medications and topical medications.
Microsporia therapy:
- if the epidermis is damaged, it is necessary to shave the hair from this area once a week. You can also use special patches. This will prevent further spread of the infection;
- if lichen occurs on the head, it also needs to be shaved. The procedure must be repeated 2 times a week until complete recovery;
- Use special shampoos to wash your hair. They should contain ketoconazole or selenium sulfide. You can also use regular tar soap for hygiene purposes.
Recommendations for parents
All parents who have been in contact with a patient with lichen, or those who are just about to go out into the garden after a long illness, must be informed about the possibility of infection. Parents of contact children should take preventive measures:
- wash all the clothes the child was wearing at high temperatures;
- disinfect the apartment with antiseptics;
- go to an appointment with your local pediatrician, find out about further actions, ask to prescribe immunotherapy.
Those who have just suffered from an infectious disease are advised to refrain from visiting kindergarten until the situation stabilizes, because a child with weak immunity risks getting sicker than others. Usually, groups in kindergartens are not closed, and responsibility for the choice to drive or not to drive the child is placed on the parents. If you do not want your child to become infected, ask the doctor for a certificate until the epidemic ends. The doctor is obliged to issue such a document and has no right to refuse you.
Prevention of ringworm
Since lichen is highly contagious, its prevention is given a special place. In order to avoid infection you must:
- avoid wearing wet shoes and clothes;
- wash regularly. Once a week you can use a special fungicidal soap;
- avoid wearing other people's clothes and shoes;
- use only personal hygiene items. You should not dry yourself with someone else’s towel or take someone else’s washcloth;
- do not wear other people's hats;
- reduce contact with sick people;
- do not pet homeless animals;
- maintain and strengthen the immune system.
Microsporia of the scalp in children is a rather unpleasant disease. To avoid infection, you must follow simple recommendations. If you suspect the development of lichen, you should make an appointment with a dermatologist.
Diagnosis
Microsporia is diagnosed by a qualified dermatologist. The specialist collects the patient’s medical history and also examines his skin and hair. The presence of microsporia is indicated by the following symptoms:
- lesions on smooth skin with a diameter of 0.5 to 3 cm, with a white scaly center and reddish bumpy edges, usually up to 3 pieces in one area;
- affected hair, looking like circles up to 5 cm in diameter with crusts or tubercles along the edges; brittle hair that breaks off at a height of 4–6 mm from the head, and the remaining part is covered with a white film;
- peeling of the skin, mild itching.
For both adults and children, the disease causes virtually no physical discomfort, so it is not detected immediately. The incubation period lasts from 5 to 7 days.
At this time, the disease can be transmitted from an infected person to family members or students of the same group, so it is imperative to diagnose not only the patient , but also those around him.
To accurately determine the nature of the lesion, three methods are used simultaneously:
- Wood's lamp. In a darkened room, when using a Wood's lamp, the affected areas of the skin and hair are highlighted with a greenish tint. This method is used to identify lesions in humans and animals. Sometimes it allows you to identify lesions that have not yet become visible to the human eye, since the spores have so far only slightly affected the skin or hair.
- Microscopic examination. A scraping of skin or hair is taken for examination. Under a microscope, spores are detected, their location and quantity. This helps confirm the preliminary diagnosis.
- Cultural research. It is necessary to accurately establish the type of pathogen, since some dermatomycosis is very similar in symptoms to microsporia. For 3 days, scrapings taken from the patient remain in a nutrient medium in which the fungal colony quickly multiplies. After 3 days, it turns out to be so enlarged that doctors are able to carefully examine it and determine the type of fungus.
Diagnosis of the disease
Making a diagnosis for this disease is not difficult. In most cases, an external examination and instrumental examination are sufficient. In order to make an accurate diagnosis, you need to determine the presence of a fungal infection and separate it from other similar diseases.
Most often, the following methods are used to diagnose microsporia:
- a scraping is taken from the patient’s skin to determine the presence of fungus;
- examination of the skin and hair under a Wood's lamp, in the light of which they turn green if there is an infection;
- The cultural method allows you to determine the type of pathogen and select the correct therapy.
Often, examination using a Wood's lamp and a microscope is sufficient to make a correct diagnosis..
Requirements for quarantine for the prevention of deprivation in kindergarten
In preschool and school institutions, after detection of a patient, quarantine is established . The patient is sent home or to a special institution for treatment, and the rest of the children are necessarily examined by a dermatologist.
Employees of the institution are required to notify the sanitary and epidemiological station about the situation so that measures can be taken to reduce risks.
During the quarantine period, children must stay at home and not visit playgrounds, public institutions and classes. They can spread the disease.
Every 5 days, a dermatologist is required to check the condition of kindergarten students (the same group in which the patient studied).
If we are talking about a permanent kindergarten, from where children cannot immediately go home, quarantine is also prescribed. Basic Rules:
- remove all soft toys and carpets;
- hard toys must be washed in warm water and soap once a day, in nurseries - twice a day;
- children eat in a separate room, they should not visit public places (canteens, shared bathrooms and toilets, playgrounds);
- children are provided with lockers where they put their outerwear; all lockers must be numbered and signed;
- Other personal items (toothbrushes, combs) are also numbered; teachers ensure that they are used strictly by the owner;
- at the end of each day, mattresses and bed linen are disinfected or vacuumed;
- bed linen and clothes of children in quarantine are washed separately from the linen of children from healthy groups.
Order on microsporia at school
› Medicine
Microsporia is a fungal disease that affects the skin and hair follicles. It may be caused by various fungi of the genus Microsporum: zoophilic or anthropophilic.
Zoophilic diseases are transmitted from domestic animals , mainly cats. Anthropophilic ones get on the skin through contact with people and objects touched by an infected person.
This lesion is easily transmitted between people and can break out in epidemics. If microsporia is detected in educational institutions, quarantine is introduced according to SanPiN standards.
Diagnosis
Microsporia is diagnosed by a qualified dermatologist. The specialist collects the patient’s medical history and also examines his skin and hair. The presence of microsporia is indicated by the following symptoms:
- lesions on smooth skin with a diameter of 0.5 to 3 cm, with a white scaly center and reddish bumpy edges, usually up to 3 pieces in one area;
- affected hair, looking like circles up to 5 cm in diameter with crusts or tubercles along the edges; brittle hair that breaks off at a height of 4–6 mm from the head, and the remaining part is covered with a white film;
- peeling of the skin, mild itching.
For both adults and children, the disease causes virtually no physical discomfort, so it is not detected immediately. The incubation period lasts from 5 to 7 days.
At this time, the disease can be transmitted from an infected person to family members or students of the same group, so it is imperative to diagnose not only the patient , but also those around him.
To accurately determine the nature of the lesion, three methods are used simultaneously:
- Wood's lamp. In a darkened room, when using a Wood's lamp, the affected areas of the skin and hair are highlighted with a greenish tint. This method is used to identify lesions in humans and animals. Sometimes it allows you to identify lesions that have not yet become visible to the human eye, since the spores have so far only slightly affected the skin or hair.
- Microscopic examination. A scraping of skin or hair is taken for examination. Under a microscope, spores are detected, their location and quantity. This helps confirm the preliminary diagnosis.
- Cultural research. It is necessary to accurately establish the type of pathogen, since some dermatomycosis is very similar in symptoms to microsporia. For 3 days, scrapings taken from the patient remain in a nutrient medium in which the fungal colony quickly multiplies. After 3 days, it turns out to be so enlarged that doctors are able to carefully examine it and determine the type of fungus.
Requirements for quarantine for the prevention of deprivation in kindergarten
In preschool and school institutions, after detection of a patient, quarantine is established . The patient is sent home or to a special institution for treatment, and the rest of the children are necessarily examined by a dermatologist.
Employees of the institution are required to notify the sanitary and epidemiological station about the situation so that measures can be taken to reduce risks.
During the quarantine period, children must stay at home and not visit playgrounds, public institutions and classes. They can spread the disease.
Every 5 days, a dermatologist is required to check the condition of kindergarten students (the same group in which the patient studied).
If we are talking about a permanent kindergarten, from where children cannot immediately go home, quarantine is also prescribed. Basic Rules:
- remove all soft toys and carpets;
- hard toys must be washed in warm water and soap once a day, in nurseries - twice a day;
- children eat in a separate room, they should not visit public places (canteens, shared bathrooms and toilets, playgrounds);
- children are provided with lockers where they put their outerwear; all lockers must be numbered and signed;
- Other personal items (toothbrushes, combs) are also numbered; teachers ensure that they are used strictly by the owner;
- at the end of each day, mattresses and bed linen are disinfected or vacuumed;
- bed linen and clothes of children in quarantine are washed separately from the linen of children from healthy groups.
SanPiN for school
The same measures are being taken in secondary schools as in preschool institutions. Quarantine is established, children are regularly examined by a dermatologist .
An SES worker is involved. Based on his decision, final disinfection of upholstered furniture, walls, floors and ceilings, as well as other things, is carried out.
Final focal disinfection eliminates fungal spores and makes the premises safe for children and working personnel.
Microsporia mainly affects children from 5 to 12 years of age. Starting from puberty, the structure of sebum changes, as well as the composition of hair. As a result, the disease becomes harmless for older schoolchildren, with the exception of weakened girls.
How many days does quarantine last?
Quarantine is established for a period of 3 weeks (21 days) to 45 days. The exact timing depends on the nature of microsporia.
The bestial form remains active for no longer than a month, which is why quarantine is set for 21–30 days . But anthropophilic can be dangerous for up to 45 days, and the quarantine period is set accordingly.
Recommendations for parents
During the quarantine period, children are sent home, where they must be kept subject to a number of restrictions. Quarantine should be taken calmly .
It is advisable to immediately explain its importance to the child and reassure him in order to avoid psychological problems. Parents need to accept three things:
- Quarantine is a measure necessary more for those around them than for the child himself. Therefore, even if parents are sure that a preschooler or schoolchild is healthy, they should not take him out into public places. During the incubation period, symptoms of the disease may not be noticeable, but the spores remain active and are transmitted to others.
- A child also poses a potential danger to household members, especially children, pets and weakened women. It is necessary to limit the contact of a potentially sick person with the listed groups.
- All instructions issued by a dermatologist or an employee of the sanitary-epidemiological station, including the requirements for ongoing disinfection, must be followed unquestioningly.
During the quarantine period, you need to provide the child with a separate place and separate things that will not come into contact with the things of other family members.
A separate sleeping place, cutlery and dishes, and toys are provided. Clothes are collected in a special bag and washed separately.
Conclusion
Microsporia is an unpleasant disease, but its appearance should be taken calmly.
Despite complex treatment, quarantine and the need for disinfection, parents need to remain calm and follow the instructions of doctors.
In this case, the quarantine will end successfully for the child, his family, and the educational institution.
Source: https://nekurim.info/info/prikaz-po-mikrosporii-v-shkole/
SanPiN for school
The same measures are being taken in secondary schools as in preschool institutions. Quarantine is established, children are regularly examined by a dermatologist .
An SES worker is involved. Based on his decision, final disinfection of upholstered furniture, walls, floors and ceilings, as well as other things, is carried out.
Final focal disinfection eliminates fungal spores and makes the premises safe for children and working personnel.
Microsporia mainly affects children from 5 to 12 years of age. Starting from puberty, the structure of sebum changes, as well as the composition of hair. As a result, the disease becomes harmless for older schoolchildren, with the exception of weakened girls.
BU KHMAO-Yugra "Surgut City Clinical Clinic No. 4"
The “Thank you, Doctor!” campaign dedicated to the celebration of Medical Worker Day starts in Ugra
On May 23, 2021, at the Health Center for the adult population of the Surgut City Clinical Clinic No. 1, the
World AIDS Day of Remembrance
What you need to know about HIV
May 12 – International Nurses Day
Employees of the Surgut City Clinical Clinic No. 4 congratulated the veteran of the Great Patriotic War on Victory Day
Opening hours of the Surgut City Clinical Clinic No. 4 May 9, 2021
Recommendations for parents
During the quarantine period, children are sent home, where they must be kept subject to a number of restrictions. Quarantine should be taken calmly .
It is advisable to immediately explain its importance to the child and reassure him in order to avoid psychological problems. Parents need to accept three things:
- Quarantine is a measure necessary more for those around them than for the child himself. Therefore, even if parents are sure that a preschooler or schoolchild is healthy, they should not take him out into public places. During the incubation period, symptoms of the disease may not be noticeable, but the spores remain active and are transmitted to others.
- A child also poses a potential danger to household members, especially children, pets and weakened women. It is necessary to limit the contact of a potentially sick person with the listed groups.
- All instructions issued by a dermatologist or an employee of the sanitary-epidemiological station, including the requirements for ongoing disinfection, must be followed unquestioningly.
During the quarantine period, you need to provide the child with a separate place and separate things that will not come into contact with the things of other family members.
A separate sleeping place, cutlery and dishes, and toys are provided. Clothes are collected in a special bag and washed separately.
DERMATOVENEROLOGY. NET
INSTRUCTIONS FOR DISINFECTING AND ANTI-EPIDEMIC MEASURES FOR FUNGAL
Approved by the USSR Ministry of Health on January 10, 1950.
Each patient with a fungal disease is registered by the sanitary-epidemiological station at his place of residence, place of work (in child care institutions, hairdressing salon, bathhouse) or study. This is done for the purpose of organizing anti-epidemic measures, including disinfection.
Disinfection at the patient’s home (current and final)
A. Routine disinfection Its task includes:
1. Establish a regime that prevents the spread of the disease.
2. The patient must have a separate bed, comb, washcloth, sponges, towel, etc. There is a separate place for storing the outer dress and headdress.
3. Dirty laundry is collected in a pillowcase (bag) and stored separately.
4. When washing, the laundry is first soaked for 1 hour in a 1% activated chloramine solution at room temperature (5 liters per 1 kg of laundry) (10 g of chloramine per 1 liter of water). Immediately before disinfection, ammonium sulfate is added to the solution.
5. The child is not allowed into the child care facility or to communicate with other children in the apartment itself. An adult patient is not allowed into children's and communal institutions (baths, hairdressers). A sick mother should wear a headscarf, wash her hands frequently, and have separate household items. Washing in the bath is prohibited.
6. The room where the patient is located is damply cleaned daily with rags, which, upon completion of cleaning, are boiled for 15 minutes or soaked in a 5% solution of chloramine or a 1% activated solution for 1 hour.
7. A cap with ties under the chin is placed on the affected head. Nails are bandaged. Bandages that are removed are burned.
B. Final disinfection.
1. Things that have been personally used by the patient (bed linen, clothing, bedding and clothing) are subject to disinfection. Hats
They are burned. Valuable hats are disinfected in steam-formalin chambers.
2. Disinfection of things is carried out as follows:
A) Disinfection is carried out using the steam method at a temperature of 110-111°, pressure 0.5 atm. for 1 1/2 hours or at a temperature of 118-120°, at a pressure of 1 atm. within 1 hour.
1 m3 of chamber is designed for 40-50 kg of clothes (7 sets of clothes).
B) Disinfection using the steam-air method is carried out in chambers at a temperature of 98° for 45 minutes. Up to 8 sets of clothes are provided per 1 m2.
C) Disinfection using the steam-formalin method is carried out at a temperature of 58-59°, formalin consumption is 250 cm3 per 1 m3, exposure is 21/2 hours. Formalin is introduced into the chamber using a nozzle at a temperature of 55-56 ° on the external thermometer. The beginning of exposure is considered from the moment the formalin administration ends. Leather and fur items are disinfected only using the steam-formalin method.
Routes of infection
Penetration of the infection occurs through contact with a carrier, which can be another person, object, or animals that are already infected with the fungus. There are several types of spores, which determines how they spread among people. There are three main species of Microsporum depending on the main host:
- Zoophilic fungi. The main carriers are cats, dogs and other animals.
- Anthropophilic. People become the main carriers.
- Geophilic. The main habitat is soil, where they remain viable for several months
Symptoms
There is a general clinical picture for all types of microscopy, but there are also individual signs of each type of disease, which become characteristic features of the disease. Common symptoms include the following:
- Red spots. One of the first signs of the development of pathology is the appearance of lesions on the scalp and body. When localized on the scalp, spots may also appear in the area of the eyebrows and eyelashes. When they appear on smooth skin, lesions can be found on any part of the body.
- Whitish small scales. After a few days, the spots become pink and fade. Whitish scales begin to form on the surface, and there are many of them. They can be mistakenly taken on the scalp for dandruff, and on the body as the first signs of psoriasis in a child.
- Severe itching. In some cases, areas of peeling are accompanied by this symptom. When a child scratches his head, parents at first think that it is lice. Microscopy is often confused with eczema or another type of dermatitis. This is not a mandatory sign; the disease can proceed without it.
- Increase in body temperature. It is not observed in all patients, but may be present.
- Enlarged lymph nodes. This symptom is observed only in some babies on the neck.
Skin microsporia
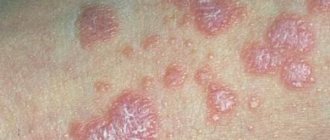
Depending on the type and stage of the pathology, certain symptoms may develop, which simplify the diagnosis of the disease. Microsporia of smooth skin in children and newborns most often occurs in a superficial form. Signs include the following manifestations (see photo):
- The first to appear is a red spot (focus) of a round or oval shape. It has clear boundaries and rises slightly above the skin.
- Then the lesion begins to increase in size, becoming even denser and slightly swollen. A roller appears along the radius of the spot, which consists of bubbles and crusts.
- In the center of the lesion, the inflammatory process decreases. The area limited by the roller becomes pink and covered with scales.
- Sometimes microsporia re-enters the site of primary infection. Another lesion appears inside the old ring. This form is often found in anthroponotic microsporia.
- As a rule, 1-3 such lesions form on the surface of smooth skin. If the spots are close together, they may merge. Lesions without an active infectious process do not cause discomfort in most cases. If an inflammatory process is observed, the child experiences itching and pain.
- In newborns and children under 3 years of age, the disease often has an erythematous-edematous form. The lesions are swollen, red and with obvious inflammation, with very few scales.
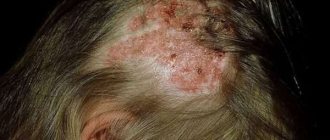
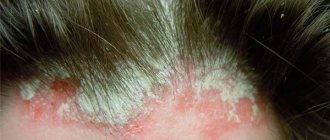
Microsporia of the head
Ringworm on the scalp most often appears between the ages of 5 and 12 years. In older adults, this pathology is very rarely observed, because the hair follicles are capable of producing acid that kills the causative agent of the disease. Fungal infection is more often diagnosed in children with red hair; the disease occurs with the following symptoms:
- Areas of peeling appear on the dermis, ring-shaped scales form at the roots of the hair, they surround the hairs along the entire perimeter.
- After 1 week, hair loss occurs. Loss of pigmentation occurs, hair becomes brittle, brittle and very dull. As a result, they break off, leaving only a short “hedgehog” of about 5 mm.
- The remaining fragments of hairs are covered with a fungal coating of spores. The skin in these places is dense and moderately red, covered with numerous grayish scales.
These are common symptoms that appear in this form of pathology, but there are also atypical options. The following types of disease are distinguished:
- Infiltrative form. The lesion rises above the rest of the skin. It has a red appearance, swollen, hair breaks at the level of 4 mm.
- Suppurative form. There is a strong inflammatory process, the spot is dense and thick. Bluish-red nodules with pustules form on the surface, which release pus when pressed.
- Exudative. There is severe swelling. Redness, small blisters at the site of infection. The scales stick together due to the inflammatory fluid, and a crust forms that covers the spot.
- Trichophytoid. A large number of small lesions appear on the skin, they peel slightly. The spots do not have clear contours, obvious inflammation, hair breaks at the level of 2 mm.
- Seborrheic. Hair thinning is observed in some areas of the head. In these places, the scalp with yellowish scales is visible. If you peel them off, you will end up with broken hair roots.
Medicines for internal use
Treatment of microsporia of the scalp includes taking a number of medications. They are selected by the doctor based on the stage of the disease. Its causative agent and the individual characteristics of the child’s body. Medicines for ringworm include
- Lamisil;
- Terbizil, etc.
A course of treatment is impossible without topical medications. Used to treat the scalp and body skin
- Isoconazole;
- Exifin;
- sulfur ointment, etc.
Causes
The main source of infection are dogs and cats. Penetration of spores occurs not only through direct contact of a child with a sick animal, but when touching objects that have fur or scales on them. The fungus continues to live in the soil for another 1-3 months. Infection can only occur through contact; probable sources of microsporia can be:
- objects touched by the patient (person or animal);
- sick people;
- sick animals;
- the soil.