Angiomas are neoplasms on the skin that look like red moles. These growths are considered to be benign. The appearance of moles is usually associated with disturbances in the circulatory or lymphatic system. Angioma can form on the body throughout a person’s life, however, having appeared in childhood, such moles can subsequently completely disappear. Let's find out why red moles appear on the body and how to deal with them.
Angioma refers to benign tumors, the structure of which is represented by lymphatic or blood vessels
What is angioma
Angioma is a benign vascular tumor that appears as a result of the transformation of blood vessels. The neoplasm can be of different sizes and shapes; its appearance resembles a regular mole, but is red in color. The localization of angiomas also differs and depends on the individual characteristics of the woman’s body.
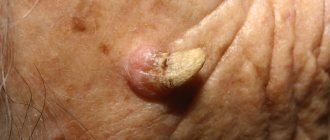
Angiomas on the body
In addition, the mole may be flat or raised above the surface of the skin.
Reasons for appearance
Angiomas on the body (the causes in women may be related to physiological and pathological factors) appear in patients of different ages. The greatest number of cases of their occurrence was recorded among people from 20 to 45 years old.
The main causes of tumor formation are the following:
- Disturbances in the functioning of the vascular system, when small capillaries in the skin change and form a nodule.
- Diseases of the lymphatic system that provoke the accumulation of lymphatic vessels under the skin.
- Hormonal imbalance as a result of stress, overwork, treatment with potent drugs, during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
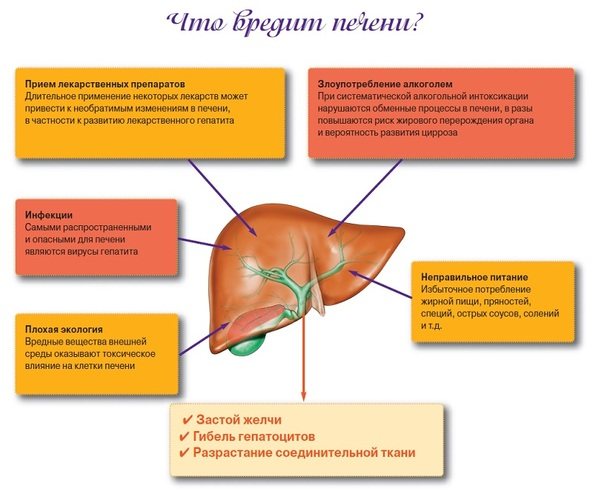
- Liver diseases of varying severity, provoking changes in blood vessels.
- Genetic predisposition to the appearance of such neoplasms.
- Self-administration of hormonal drugs.
- The presence of malignant tumors in the body becomes a cause in exceptional cases.

In women during menopause, all processes in the body change. This can also lead to angioma, but the likelihood is not as high.
Treatment and diagnosis of cavernous angioma
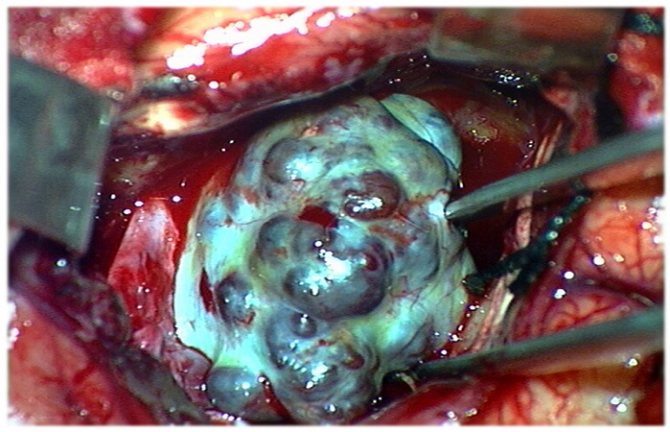

Most cavernomas do not require active treatment. All that is needed is dynamic observation over a long period of time. Surgery may be required if symptoms occur, which are usually caused by bleeding into the brain tissue surrounding the cavernoma.
In case of repeated hemorrhages detected on CT or MRI, hospitalization in a neurosurgical hospital is necessary with further decision-making on surgical intervention.
Because cavernomas are clearly demarcated from surrounding tissue and surrounded by glia, their surgical removal is a relatively simple task. Control of blood loss is also quite simplified, since blood flow in the pathological vessels is slower than what would normally be expected when excision of well-perfused tissue.
Despite the fact that cavernous angiomas are visualized using computed tomography (CT), this method is not the method of choice: the fact is that the identified signs in a CT study may correspond not only to cavernous angioma, but also, among other possible options, poorly differentiated tumor.
The sensitivity of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is much higher, due to its higher contrast resolution, as well as its greater ability to image flowing blood and its breakdown products.
The combination of different MRI pulse sequences has largely solved the problem of misdiagnosis or under-detection of cavernous angiomas, since these lesions have quite specific features on MRI.
CT and MRI can be used for follow-up of patients with already diagnosed cavernous angiomas, especially in cases where there is a risk of hemorrhage.
Although the MR image of cavernous angiomas does not predict the occurrence of bleeding, MRI is the method of choice for long-term follow-up of patients with cavernous angiomas, as well as for the evaluation of family members of the patient who are at risk of having such malformations.
In addition, MRI is extremely useful in planning surgical intervention, as it allows you to assess the size of the formation, its boundaries, and thus determine the type of operation and surgical approach. With classical angiography, most cavernous malformations are not visualized, and even when signs are detected, they are extremely nonspecific.
If the lesion develops in combination with other vascular malformations, which occurs in approximately 30% of patients with venous malformations, then its MR characteristics become much more complex and less specific.
In such patients, angiography may be useful to further clarify the diagnosis. Brain scanning using CT and MRI in most cases allows one to clearly distinguish a cavernoma from other brain formations, including tumors of varying degrees of malignancy.
However, in some cases, differentiation of these formations represents a diagnostic problem, the solution of which requires extensive experience. In this regard, the ability to attract a highly qualified diagnostician is critical.
In addition, high-quality interpretation of CT and MRI images provides a solution to other diagnostic problems: exclusion of surrounding cerebral edema, identification of the severity of hemorrhage, description of details affecting the operability of the cavernoma.
If you are in doubt about the diagnosis, you should consult a radiologist from a leading center specializing in brain pathology. A second opinion from such a diagnostician can be very valuable in the differential diagnosis of angiomas and other pathological conditions.
Source: teleradiologia.ru
Types of angiomas and locations in women
Experts divide angiomas into several types. The first classification involves the identification of 2 species, taking into account the structure, into monomorphic and polymorphic. The first type is a tumor formed as a result of mutation and accumulation of one type of cell. The second type is a tumor formed by several types of cells, usually growing to large sizes.
Taking into account the form of the neoplasm, doctors also distinguish several varieties:
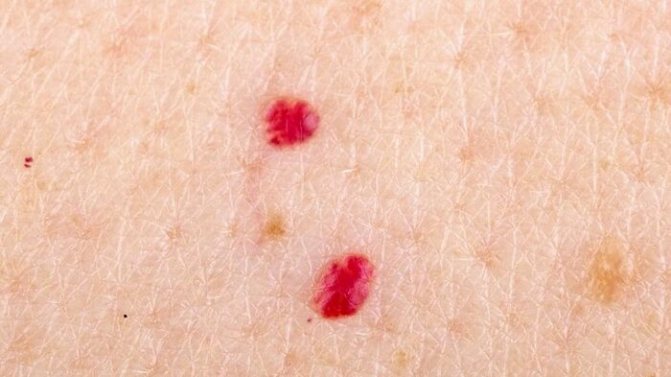
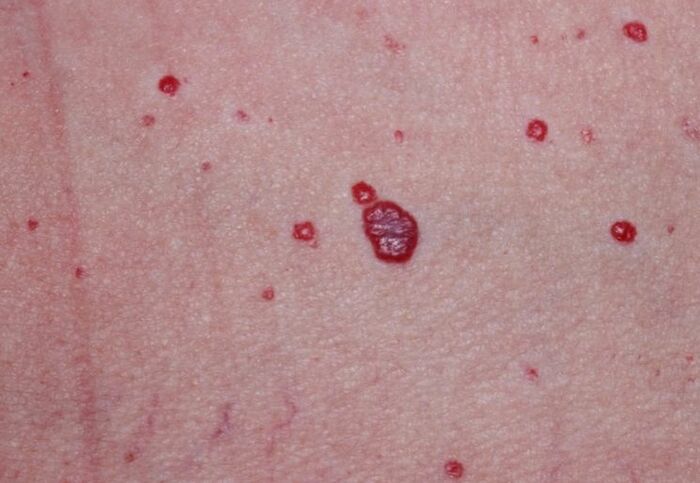
- A simple one is formed as a result of the accumulation of capillaries. Externally, such a mole looks like a small red spot, located on the body or mucous membranes; when pressed, its color becomes less bright. Usually the patient does not pay attention to the stain, since it does not bother and is not damaged by clothing.
- Cavernous angioma is usually medium or large in size, raised above the surface of the skin, and burgundy in color. When you touch it, you can feel a local increase in temperature. In most cases, inside the formation there are cavities filled with thrombotic masses, so when damaged they protrude out and provoke bleeding.
- The branched type of tumor is considered dangerous. It consists of a plexus of blood vessels; upon close examination, you can see a barely noticeable pulsation. Around the neoplasm there are vessels located close to the surface layer of the skin; they visually increase its size and nourish the changed cells.

The location of angiomas on the body also differs. In women, they can be localized on the back, inner and outer surfaces of the shoulders and forearms, abdomen, chest, and neck. Less commonly, neoplasms appear on the legs, head, and genital area.
Types of neoplasms
There are several classifications of angiomas. They are distinguished by shape, cause of appearance, tissue composition and type of vessels that provoked the problem.
Thus, according to their shape, neoplasms are divided into pineal, nodular, branched (arachnid) and flat. Pineal angiomas are characterized by a convex shape; they rise noticeably above the skin. Nodular angiomas are usually small in size. Outwardly, they resemble small red dots. However, they do not have branches from the capillaries - a characteristic vascular network. It is characteristic of branched (arachnid) angiomas, which in appearance can actually resemble a spider with many legs. Finally, flat angiomas resemble ordinary moles in appearance.
Content:
- Types of neoplasms
- Reasons for appearance
- Methods for removing angiomas
Based on the reasons for their appearance, formations are divided into hemangiomas and lymphangiomas. Hemangiomas are a manifestation of blood vessel pathology, and the cause of lymphangiomas is a disruption in the functioning of the lymphatic system. They are diagnosed less frequently than hemangiomas and are point formations.
As for hemangiomas, they are divided into capillary, which are bluish-purple or bright red spots, as well as cavernous (cavernous) and punctate. Cavernous hemangiomas can acquire very significant sizes. These are soft tubercles that change shape when pressed. As a rule, they appear on the skin of the face, in the groin, and in the armpit area. Punctate hemangiomas are characterized by miniature sizes, and in appearance they resemble tiny red dots, similar to an injection mark.
Are red moles on women's bodies dangerous?
Angiomas on the body (causes in women can provoke the formation of several moles at once) are benign growths, and therefore in most cases do not pose a threat to a woman’s health. However, this is a tumor that, under certain circumstances, can develop into a malignant one.
Red moles become dangerous when they are constantly damaged during hygiene procedures or when injured by clothing. In addition, there is a high risk of cell degeneration with regular exposure to chemical compounds present in cosmetics. Sun rays also have a negative effect on angiomas, so they can provoke cell degeneration.
The danger of cutaneous hemangioma on the hands of an adult


Hemangiomas themselves are not life-threatening. They do not metastasize and do not degenerate into malignant neoplasms, however, if they actively grow, serious complications can arise:
- infection of hemangioma when it is injured. In such cases, the risk of secondary infection increases, which leads to suppuration;
- blood loss - develops when the growth is damaged. Stopping such bleeding is quite difficult, especially if several vessels are damaged;
- poor blood clotting - develops against the background of an increased influx of platelets and proteins - clotting factors. Over time, their number decreases, which entails dangerous bleeding in the event of injury to the growth;
- aesthetic discomfort - the presence of a tumor-like process on the hands or fingers always attracts the attention of others, so a person tries to hide the growths and experiences constant mental stress.
Hemangiomas in children or adults always require the close attention of doctors - specialists in the field of dermatology, surgery, and oncology. Particular attention is paid to rapidly growing tumors or those that first appeared in adulthood. Timely diagnosis and properly selected treatment will allow you to get rid of the formation on your hands and eliminate possible risks and complications.
Do red formations go away on their own?
When a single and small formation appears on the body, there is a possibility that it will disappear on its own after a certain period of time. However, this doesn't happen very often. In most cases, angioma remains on a woman’s body for life or until it is removed using one of the known methods.

If the tumor is large and bothers the patient, you should not expect it to disappear on its own.
Photos
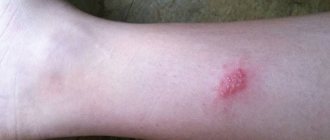
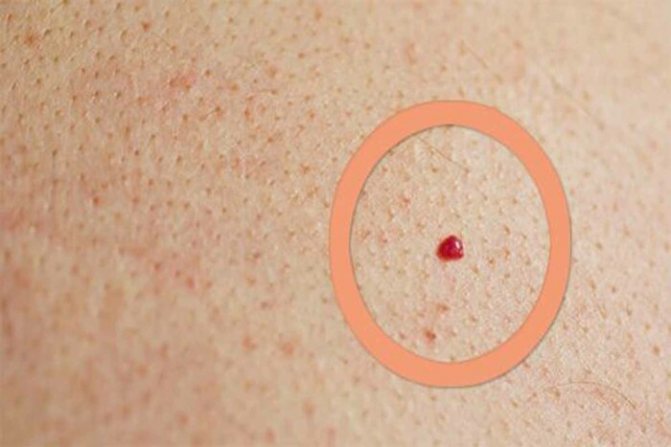
Cherry angioma
Cherry angioma, as shown above, is not a cause for concern or treatment.
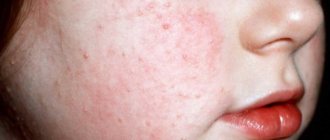
Multiple angiomas

Contact your healthcare professional if multiple angiomas appear at once.
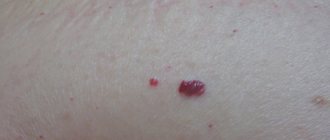
arachnoid angioma
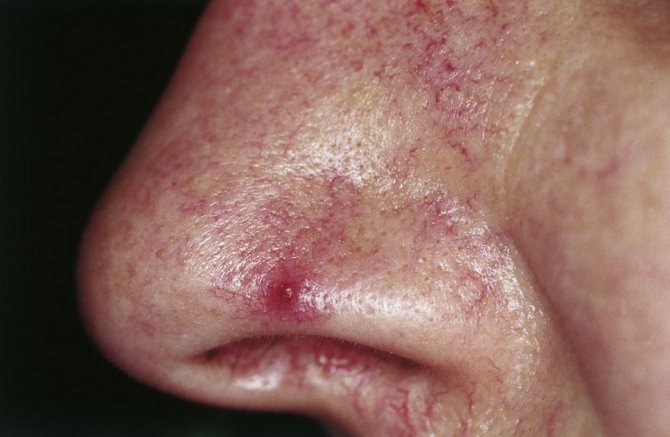

Spider angiomas can cause complications and should be examined further by a doctor. People often confuse them with cherry angiomas.
Is it possible to remove angiomas, in what cases?
Red growths are allowed to be removed, but the decision is always made by a dermatologist during examination and examination. If the mole does not bother the patient and is located on an inconspicuous or hidden area of the body, it is not removed, but the patient must regularly visit a doctor who will monitor the condition of the angioma.
If the patient regularly feels discomfort, the mole hurts, bleeds, quickly increases in size, is constantly injured by clothing, its removal using one of the hardware methods or surgery is indicated.
Prognosis and prevention
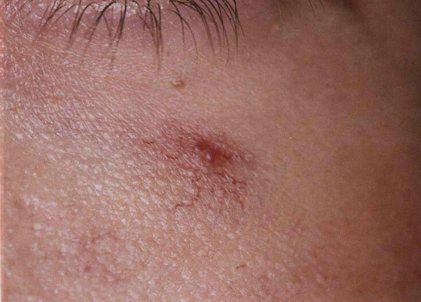

The prognosis for stellate angiomas is good, education does not affect health and life expectancy. However, such marks located on open areas of the body can cause significant discomfort due to changes in appearance.
Prevention of congenital angiomas has not been developed. To prevent the appearance of stellate angiomas and hyperkeratotic seborrheic keratosis in later life, you should avoid excessive sun exposure. You should sunbathe only in the morning or evening; if you need to stay in the sun for a long time, you need to use sunscreen.
Diagnosis of angiomatosis
If a single angioma or multiple neoplasms are detected on the body, a woman is advised to consult a specialist. He will conduct a full examination and determine whether the mole needs to be removed.

| Method | Description |
| General examination and interview of the patient | The specialist examines the neoplasm, the skin around it, and determines the time of appearance of the mole |
| Clinical blood test, biochemical blood test | Analyzes make it possible to identify abnormalities in the internal organ systems that could cause angiomas |
| MRI | This type of diagnosis is not always indicated; it is most often required when identifying signs of a tumor of internal organs. During the procedure, the specialist can see even a small tumor |
| Biopsy | It is prescribed for pain, discomfort and rapid growth of a mole. The doctor takes a sample of material that is examined in the laboratory |
After receiving the results of the examination, the doctor will determine whether removal is necessary and the best method suitable for the patient. Sometimes an additional ultrasound examination is required to identify diseases of the internal organs, as well as studying the woman’s hormonal levels by taking a blood sample and sending it to the laboratory.
Contraindications
Despite the effectiveness of all methods used for removal, there are also certain restrictions when the operation cannot be performed.
First of all, the removal procedure may be contraindicated for any immune system disorders. In addition, it is better to refrain from surgery if you have diabetes, hypertension, herpes virus, heart pathologies, or kidney failure.
Also, some types of surgical intervention are not allowed when the development of oncological processes in internal organs and tissues is detected. Refusal to remove an angioma is also advisable if the patient has a history of cancer.
In addition, gynecologists do not recommend getting rid of vascular formations during pregnancy. This is explained by the fact that against the background of hormonal imbalances, when one tumor is eliminated, the appearance of new growths can be provoked.
Surgical removal
Angiomas on the body (the causes in women in many cases are related to internal processes in the body) are successfully removed surgically in a hospital. Typically, this method is used when moles are located in closed areas of the body and are small in size. Neoplasms on the face are not excised in this way; large angiomas are also removed using another method.
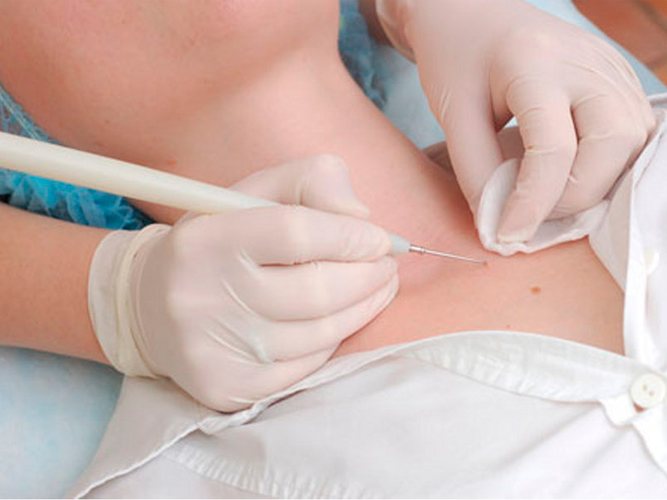

The procedure can be carried out on an outpatient or inpatient basis and takes place in several stages:
- Medical staff prepares the patient and clears the area of skin where the excision will be performed. Usually the patient is positioned horizontally.
- The mole site is treated with antiseptic solutions several times.
- After this, a local anesthetic is administered, for example, Novocaine 0.5%. The amount of product is determined individually.
- Using a disposable scalpel, the surgeon excises the angioma within the healthy tissue, at the same time washes the wound and stops the bleeding.
- After excision, the wound is treated several times and packed with gauze soaked in 10% saline solution.
- A sterile bandage is applied on top.
If the manipulation is successful, the patient is allowed to go home after 3-4 hours. She will have to come in every day for dressing changes. For the first 2-3 days, do not apply ointment to the wound, but change the bandage, and apply a tampon with saline solution directly to the affected tissue.
After this, the specialist prescribes a healing and antibacterial ointment, for example, Levomekol. It is also applied under a bandage, which is changed daily. The patient is prohibited from removing the bandage on her own and lubricating the wound with anything. The bandage is removed when the edges of the wound are pulled together and a thick crust appears on its surface.
The patient is then allowed not to come for a dressing, but to independently treat the area around the wound with a solution of brilliant green until it is completely healed and the crust is removed. Healing usually takes from 7 to 14 days, depending on the characteristics of the woman’s body. The cost of the procedure in clinics starts from 1000 rubles.
Laser removal
The laser removal procedure is considered the most preferable option for the formation of angiomas. It is suitable for excision of moles on the face and other parts of the body, and is used for tumors of various sizes and shapes. The manipulation is carried out on an outpatient or inpatient basis.
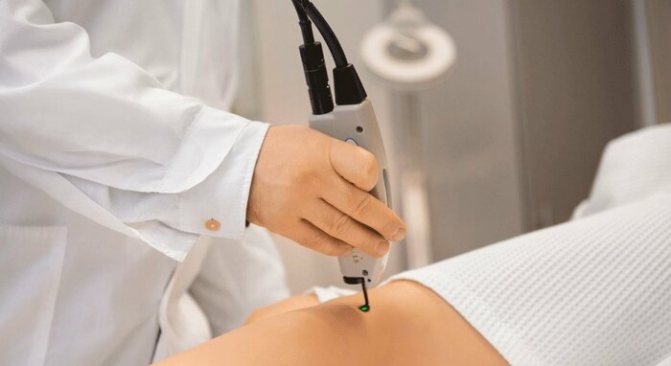

The patient is placed on the couch, the part of the body with the mole is freed from clothing, and the site of treatment is numbed. Lidocaine or Novocaine is used for pain relief. After this, the specialist takes the handle of the laser device and directs the beam to the tumor.
To remove a medium-sized mole, you will need from 2 to 5 sessions, depending on the depth of its germination. This is due to the fact that the laser beam excises the angioma layer by layer and is not able to immediately affect all layers. If the tumor is located deeply, a scar remains after the manipulation.
After the last session and complete excision of the mole, a wound remains, but it does not bleed, since the laser immediately cauterizes the vessels.
The wound can be lubricated with Solcoseryl or Methyluracil ointment. These drugs stimulate healing. Typically it will take 7-10 days for complete recovery. The price of the procedure depends on the size of the tumor, starting from 2000 rubles. per session. Healing ointments may only be used after consulting a doctor.
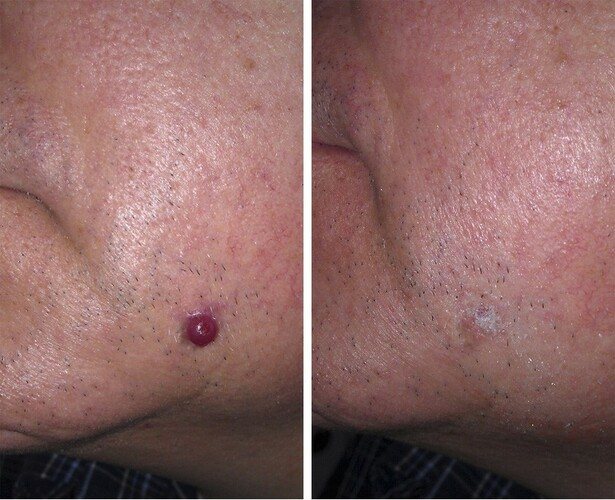
Cauterization
Angiomas on the body often cause serious discomfort to the patient. The reasons for women may be different, but only a doctor can tell you the best method to combat the problem. Often the cauterization procedure is effective. For this purpose, a high-frequency electric current is used, which is directed to the formation zone using a special apparatus.
The process of preparing for manipulation is standard. The patient undergoes an examination, the doctor appoints a day for the manipulation. The patient must be in a horizontal position and standard local anesthesia is used. The specialist directs the handle of the device to the area of the mole, the electric current acts on it layer by layer, which leads to tissue necrosis and simultaneous coagulation of blood vessels.

1-2 procedures are enough to completely get rid of the formation. Sometimes more sessions are needed if the angioma is large and deep. After removal, a small wound remains at the site of the mole. Experts recommend not to damage delicate tissues and not to use drugs for healing. After 3-5 days, a brown crust forms on the wound site.
After this, it is allowed to treat the affected area with brilliant green. After 10 days, a small trace of removal remains. Sometimes a scar forms if the angioma was deep. The cost of removal in different clinics is approximately 2000-3500 rubles. depending on the size of the mole.
Cryodestruction method
Cryodestruction is a procedure in which the neoplasm is exposed to liquid nitrogen at the lowest possible temperature; it is approximately -170-1900C. This allows you to freeze the changed cells and provoke their death.
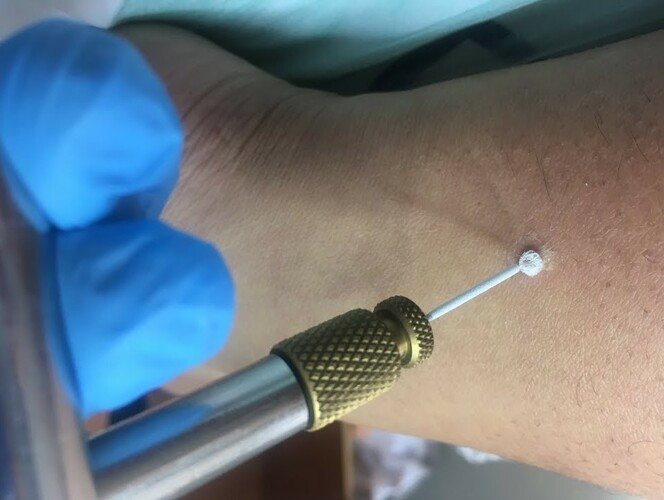

Preparation for manipulation is standard; the procedure is performed in several stages:
- The patient sits on the couch and removes clothing from the area where the mole is located.
- The nurse prepares all the instruments for the doctor. He anesthetizes the affected area with Novocaine and waits a while for the medicine to take effect.
- The next step will be exposure to liquid nitrogen. The device has a special handle that allows nitrogen to act only on the angioma. Within a few seconds, the substance penetrates into the depths of the tumor and affects the cells, coagulating the blood vessels.
- After the manipulation, it is better for the woman to stay in the office for 30-40 minutes, since unpleasant sensations can cause loss of consciousness.
The angioma does not disappear immediately after the manipulation. It changes color, becoming dark brown or black. After 5-7 days, the neoplasm disappears on its own, leaving in its place a small depression covered with delicate, renewed skin. There is no need to lubricate the affected area, as this may slow down the healing process.
In some cases, only part of the angioma becomes necrotic, while the deeper layers remain intact. Then the doctor performs the procedure again to remove the remaining changed cells. The price of manipulation in different clinics across the country ranges from 2500-5000 rubles. depending on the number of angiomas and the depth of tissue damage.
X-ray treatment
Angiomas on the body (the causes in women are often associated with hormonal disorders) are quite successfully treated with x-rays, but this method is used very rarely today. This is due to the occurrence of complications as a result of exposure to rays on the body.
The essence of the method is to carry out several procedures during which the angioma is exposed to rays using a special apparatus. Under their influence, the neoplasm brightens, decreases in size and gradually disappears. It is worth noting that the method is not so reliable, it can lead to the opposite effect and provoke complications.

The advantage of the method is the absence of pain and the need to violate the integrity of the skin. In addition, after the manipulation there are no scars left, and there is no need to use products to speed up healing.
The price of a course of treatment with X-rays ranges from 3000-5000 rubles. depending on the size, depth and number of tumors. After any removal procedure, experts recommend excluding the sauna, bathhouse, solarium for 4 weeks and avoiding direct sunlight on the delicate skin in the area where the angioma was.
Traditional medicine methods
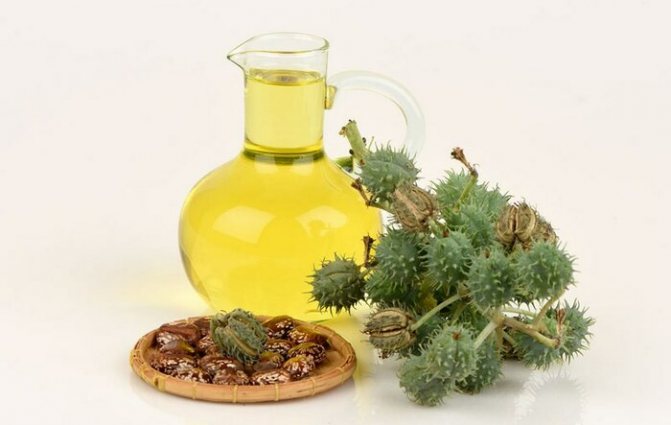
Alternative medicine recipes are often used to eliminate angiomas or reduce their size and lighten them. This eliminates discomfort, especially if the mole is located on an open part of the body. One of the popular recipes is castor oil purchased at a pharmacy.
It helps to reduce angioma, lighten it, make it less noticeable and eliminate the likelihood of cells degenerating into malignant ones. If the tumor is small, the oil can completely eliminate it. It is easy to use; you should treat the mole every day before going to bed, do not wash it off. Continue use for 2 weeks.


Flat and small angiomas can be lightened with black radish. For the procedure, you only need crushed root pulp. It must be applied to the mole area for 30 minutes, repeated 3 times a day. The duration of use depends on the color of the angioma.
If it is bright red, it will take 5-7 days. When a burgundy mole forms, the course lasts from 7 to 10 days. During the procedure, a slight burning sensation may occur in the area of application. For patients with sensitive skin, it is better to use a different recipe. Crushed dandelion root is also used to lighten and get rid of small angiomas.
The recipe for use is as follows:
- Collect raw materials and rinse thoroughly with running water.
- Grind using a meat grinder.
- Apply the resulting paste to the mole for 1 hour.
The procedure should be repeated daily, the course duration is 10 days. To achieve a better result, after spreading the pulp, it is allowed to fix it with polyethylene. Lubricating angioma with regular honey is also considered an effective way to eliminate or lighten it.
The method involves daily treatment of the mole 3 times a day for 2 weeks. This recipe is strictly contraindicated for patients with allergies to bee products. It is important to remember that traditional medicine recipes are allowed to be used only in the absence of negative manifestations from the angioma and after consulting a doctor.
If a mole hurts, increases in size, becomes heterogeneous, changes color and shape, provokes inflammation of the surrounding skin, it is strictly contraindicated to use any remedies at home. This can lead to a worsening of the condition, introduction of infection into the blood, its spread throughout the body and the development of diseases.
Is it necessary and how to get rid of angioma during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, the appearance of angioma is considered normal, since the lymphatic and vascular network becomes especially vulnerable as a result of changes in hormonal levels and increased load on all systems. This leads to the formation of red moles.

Experts believe that it is extremely undesirable to remove any tumors in the 1st trimester of pregnancy. If in the later stages the tumor does not bother the woman and is small in size, it is also not removed. After childbirth, angioma may disappear on its own.
In the 2nd trimester of pregnancy, neoplasms are removed when pain, bleeding appears, growth and changes in structure and color are observed. For removal, the laser method is predominantly used, since it is the safest and in some cases you can do without anesthesia. Other methods are not so harmless, so they are used extremely rarely.
The procedure is carried out in a standard manner, the healing period does not last longer than with removal for other patients. Angiomas on the body are neoplasms of different shapes and sizes that cause aesthetic and sometimes physical discomfort. The reasons for women may vary, but if the condition worsens, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor.
Possible complications in the future
Hemangioma of any type, with the exception of small capillary formations prone to regression, must be treated. An oncologist or surgeon in each specific case chooses the optimal method of therapy for the child, which helps to get rid of the tumor forever.
If the skin lesion is not removed in time, there is a constant risk of injury, infection or bleeding, tumor growth and aggravation of the child’s psycho-emotional discomfort due to a cosmetic defect.