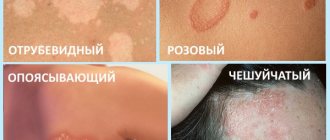
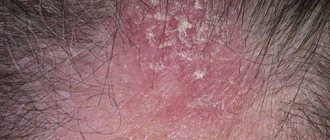
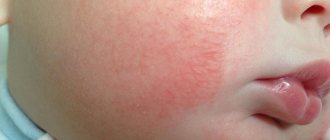
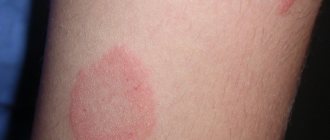
Tubular lichen is an infectious skin pathology that manifests itself in the form of spots that differ significantly in color from healthy tissue.
It mainly affects areas exposed to frequent and prolonged exposure to sunlight. Tubular (pityriasis versicolor) lichen is also called solar, colored or multi-colored, which is associated with the different shades of spots formed on the skin. The disease has a chronic course with frequent relapses, which are recorded mainly in spring and summer, i.e. during high solar activity. Without timely treatment, the elements begin to merge with each other, the pathological area increases, which causes significant aesthetic discomfort to the person. That is why, in order to prevent further progression of the disease, it must be quickly identified and treatment started.
What it is?
In simple words, tubular lichen is a disease of the superficial part of the skin, expressed in the form of brown-yellow spots of different shades, and has a fungal origin. Due to the difference in shapes and shades of spots, this type of lichen is called “colored”, less often “multi-colored”.
Due to the high probability of repeated manifestations provoked by visiting a solarium or excessive exposure to the sun, tubular lichen is called “solar”. The disease is not considered dangerous, but considerable discomfort is caused by frequent cases of renewed manifestations of tinea versicolor.
Causes
Fungi that provoke the development of tubular lichen live on the skin of every person without causing harm, but under the influence of external factors they are activated:
- Frequent exposure to sunlight, especially during “dangerous” hours, when the sun is too active, frequent visits to the solarium - yeast-like fungi under the influence of heat actively divide, thereby disrupting the functioning of melanocytes.
- Reduced immunity - the body weakens and cannot independently fight infections and control their development;
- Excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis);
- Abuse of antibacterial agents - they reduce the barrier functions of the skin;
- Clothing made from synthetic fabrics;
- Neglect of hygiene rules;
- In the presence of endocrine diseases;
- For acute and chronic diseases of the stomach and gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract).
Very rare, but there are cases of genetic predisposition associated with changes in the properties of the sweat glands. Basically, the cause of lichen is a combination of factors, and exposure to sunlight is the main reason.
Is it contagious and how is it transmitted?
Theoretically, it is possible to become infected with tinea versicolor, but in fact this is only possible if the environment is favorable for its development. When one of the family members falls ill, it is necessary to comply with sanitary standards, rules of personal hygiene and monitoring the health of those in the same apartment. This does not mean that someone will definitely become infected from a patient: the fungus can get on the skin on the street, in a supermarket, or in the gym.
Without receiving the desired favorable conditions, the fungus can remain in a passive state without presenting any danger, like other microorganisms that inhabit the surface of the outer layer of the skin.
Symptoms
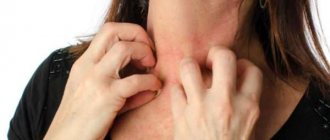
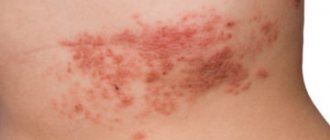
For a long time, the symptoms of tubular lichen may not bother a person. But when the body weakens and the protective properties of the skin decrease, the fungus begins to actively multiply, covering the surface of the body with dark yellow spots.
The change in color of the epidermis is associated with the destructive effect of lichen tubularis on melanin (responsible for skin pigmentation).
The color of the spots may vary; they cover the chest area, shoulder blades, lower back, hips, and armpits. The Malassezia fungus attaches to any skin surface, with abundant secretion of the sebaceous glands.
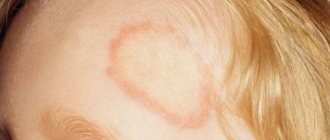
Over time, lesions of tubular lichen spread throughout the body. Individual plaques merge into large pigment spots. They are flat to the touch, with a slightly rough surface. In most cases, lichen spots do not cause discomfort. Without proper treatment, they disappear after 3-5 months, the disease becomes chronic.
How long does it take to treat
The minimum duration of therapy is 8-10 days. If tubular lichen just showed the first symptoms and did not have time to occupy large areas of the body, treatment will be quick and effective.
The course of treatment is selected by the attending dermatologist. If you self-medicate or choose the wrong medications, the disease can become chronic and bother the patient for several years.
It takes more time to treat advanced forms of the disease; if tubular lichen bothers the patient for longer than 1-2 years, the doctor prescribes systemic antifungal agents.
Diagnostics
Lichen tubularis can be recognized using physical and laboratory methods. Physical ones include:
- Examination of lesions with a dermatoscope (under lenses);
- Balzer iodine test - lubricate the skin with 5% tincture of iodine, then wipe with alcohol, iodine is absorbed into the affected areas, and they remain brown;
- Examination under a Wood's fluorescent lamp - lesions affected by the fungus differ from healthy skin due to fluorescence in yellow, reddish-brown or greenish color;
- Laboratory testing is mandatory. The scales in the area of the spots are scraped off, and they are sown on a nutrient medium containing fat. Colonies of the fungus germinate after 2 weeks and can be examined under a microscope. Determination of the “chips” symptom - when lightly scraped, the spots become covered with scales.
Treatment of tubular lichen
Tubular lichen, like any type of lichen in humans, is long-lasting and difficult to treat, but, unlike the same “pink lichen,” it is prone to recurrence. This is a disease that is almost impossible to get rid of completely; you can only apply a set of measures to prevent its manifestations.
The average duration of treatment with medications is up to 2 weeks with breaks, with ointments - up to 4 weeks. Most often, the duration is 1 or 2 weeks, subject to the recommendations of the dermatologist. It happens that treatment lasts up to a year.
Pills
To a greater extent, the use of tablets for the treatment of tubular lichen in humans is due to the severe course of the disease or the neglect of the case.
The following groups of drugs are distinguished, depending on the active substance in their composition:
- Itraconazole - inhibits the membranes of fungi, affecting them. Drugs: “Itrazol”, “Kanditral”, “Rumikoz”, “Orungamin”, “Irunin”, “Itraconazole”, “Mikonihol”, “Orungal”, “Orunit”, “Teknazol”.
- Ketoconazole is a substance with complex effects that increases skin resistance to new growths of lichen colorus and destroys affected cells. Drugs: “Fungistab”, “Ketoconazole”, “Oronazole”, “Mikozoral”, “Nizoral”, “Funginok”, “Fungavis”.
- Fluconazole - acts on the fungus at the molecular level, destroying it. Preparations: “Funzol”, “Flucostat”, “Fluconorm”, “Flucoside”, “Fangiflu”, “Nofung”, “Fluzol”, Mikosist”, “Medoflukon”, “Diflazon”, “Difluzol”, “Disorel-Sanovel” , “Mikomax”, “Mycoflucan”, “Mikomax”, “Procanazol”, “Fluzol”, “Fluconazole”, “Flunol”, “Forkan”, “Tsiskan”, “Diflucan”.
Ointments
The basis for the treatment of tubular lichen is a local effect on the lesions; for this, ointments are used, which, depending on the active component in their composition, solve a specific problem. May be in the form of a spray, gel or cream.
A medicine based on the following substance:
- Terbinafine - destroys the fungus, destroying its structure. Drugs: Exiter, Lamisil, Lamitel, Terbinox, Binafin, Lamisil Uno, Terbinafine, Terbizil, Ungusan, Tebikur, Termicon, Atifin , “Mikonorm”, “Terbifin”, “Terbized-Agio”, “Terbix”, “Fungotherbin”, “Exifin”.
- Sertaconazole - suitable for long-term use, actively fights tinea versicolor. Drugs: “Zalain”, “Sertamicol”, “Sertaconazole”.
- Isoconazole is a synthetic version of imidazole that actively acts on the fungus. Medicines: Travocort, Travogen.
- Naftifine - destroys fungal cells, helps destroy it. Preparations: “Exoderil”, “Mycoderil”.
- Ketoconazole - acts on synthesis in fungal formations, preventing neoplasms. Preparations: “Mycozoral”, “Nizoral”, “Sebozol”, “Mikoket”, “Dermazol”, “Dandrhotal”.
- Bifonazole - neutralizes the negative effects of the fungus and prevents its spread. Preparations: “Bifonazole”, “Mikospor”, “Bifasam”, “Bifosin”.
- Clotrimazole - impairs the penetrating properties of the fungus, which leads to preventing its spread and death. Preparations: “Candizol”, “Imidil”, “Candide”, “Funginal”, “Kanizon”, “Amiclon”, “Candibene”, “Clotrimazole”, “Fungitsip”, “Canesten”.
- Miconazole does not allow fungi to multiply, inhibits their reproductive properties, leading to death. Preparations: “Mikozon”, “Daktarin”.
- Econazole - destroys the structure of fungal compounds. Preparations: Ecodax, Ifenek.
A number of ointments are aimed at accelerating exfoliation and getting rid of problem areas:
- Salicylic ointment, 5% is used.
- Salicylic alcohol, 3-5% is used.
- Glycolic acid, 5-10% is used.
- Resorcinol alcohol, 5-10% is used.
- Salicylic resorcinol alcohol.
Shampoos (including lotions, oils)
This method is rather auxiliary; some people use it as a preventive measure, but this approach is very expensive and does not justify itself.
The active components are:
- Zinc pyrithione. Preparations: “Keto Plus” - usually shampoo, “Skin-cap” - can be shampoo, cream, aerosol, “Zinocap” - cream, aerosol.
- Selenium sulfide. Preparations: "Sulsen Mite" - can be shampoo or paste, "Sulsen Forte" - shampoo, "Sulsena" - lotion, shampoo, oil.
- Sodium thiosulfate solution. Drug: sodium thiosulfate.
- Ketoconazole. Preparations: “Keto Plus” - usually shampoo, “Dandrhotal”, “Mikozoral”, “Nizoral”, “Mikanisal”, “Sebozol”.
Personal hygiene
Treatment will be ineffective if the patient’s bed linen and clothing are not disinfected. During the course of taking antifungal drugs, bed linen is washed at 90 degrees. In addition, grated laundry soap is poured into the drum of the washing machine.
Linen must be changed daily; you cannot share a sleeping set with other family members during treatment. During treatment, you should try to wear only things made from natural fabrics, avoid hypothermia and overheating of the body. It is necessary to exclude hard work and psychological stress that lead to exhaustion of the nervous system.
Before going outside in extreme heat, it is better to first treat the affected skin with table vinegar, salicylic acid, and an alcohol solution of iodine. This will prevent the active proliferation of fungi under the influence of heat.
How to treat with medication
To cure the disease quickly and permanently, the course of treatment must combine a competent selection of antifungal drugs, antiseptic ointments, and vitamins. Without disinfection by boiling bed linen and observing personal hygiene rules, fungal spores will remain with the carrier and will wait for favorable conditions to become active.
Antifungal agents
As prescribed by a dermatologist, drugs are used orally that are effective in combating fungal spores:
- Terbinafine.
- Amphotericin.
- Posaconazole
- Voriconazole.
- Rumicosis.
- Oxiconazole.
- Isoconazole
- Mycoheptin.
- Flucostat.
- Griseofulvin.
The drugs kill the infection and prevent the proliferation of fungal spores.
Antifungal drugs have a long list of side effects. You should read them carefully before taking the medicine. It is preferable that the prescription of medications and monitoring of the disease picture be carried out by the attending dermatologist.
For external use, ointments and creams containing antimycotic substances are used:
- Econazole
- Clotrimazole.
- Amorolfine.
- Ketoconazole.
- Tioconazole.
- Fluconazole.
- Amphotericin.
Antifungals are often combined with vitamins to help the immune system block the fungus.
Antiseptics
To disinfect affected areas and nearby healthy skin, use external agents:
- 1% salicylic acid (do not wipe the face and other parts of the body with hypersensitive skin).
- Boric alcohol.
- Arievich ointment.
- Cream travogen.
- Alcohol solution of iodine.
- Ointment with calendula and chamomile extract.
During treatment and for the purpose of prevention, you can use tar soap for washing. After lathering, you don’t need to wash it off immediately; it’s better to leave it on the skin for 1-3 minutes so that the tar has time to be absorbed.
Allyl laminates
Of the four groups of antifungal drugs, allylamines are used to prevent relapse and block the growth of mold and yeast fungi. Allylamines are active against the causative agent of tubular (pityriasis versicolor):
- Terbinafine.
- Exoderil.
- Ciclopirox.
- Exiter.
- Naftifin.
- Exifin.
- Fungoterbin.
The drugs quickly suppress the activity of the Malassezia fungus and show effectiveness even with short-term therapy. They are used not only to treat the disease, but also help to cope with the itching that is characteristic of advanced cases.
Diet
When treating tubular lichen, you need to make some changes to your diet:
- exclude alcohol and carbonated drinks;
- limit the consumption of sugar, sweets, and baked goods;
- limit the amount of carbohydrates;
- exclude fried, fatty, spicy, smoked, pickled foods, hot spices;
- maintain a drinking regime, which should be based on clean water and green tea;
- ensure sufficient vitamins and minerals in the diet.
Traditional medicine recipes
Alternative treatment allows you to reduce the medication load or enhance the effect of medications.
The following remedies effectively cope with the disease:
- A paste of sorrel and sour cream is used to lubricate the affected areas of the skin for ten days.
- A mixture of St. John's wort and Vaseline. It is prepared as follows: dried herb powder is mixed with the second ingredient in proportions 1x4. The resulting ointment is applied to the spots every day for ten days.
- Ointment prepared from fresh St. John's wort and butter. The previously fresh leaves of the plant are crushed with a knife and then mixed in different quantities with the second ingredient.
- A remedy made from burdock, calendula and hops. All ingredients are taken in equal quantities, pre-chopped with a knife, and then filled with two glasses of water. The mixture is placed on the fire and heated for 20 minutes over low heat. After the finished decoction has cooled, it must be filtered and mixed with one hundred grams of petroleum jelly and two tablespoons of licorice root powder. The finished product is applied to the stains, left for forty minutes, and then washed off with water. The procedure must be repeated twice a day for ten days.
Following a restrictive diet helps to speed up recovery. The patient is advised to give up fried foods, exclude the consumption of sweets and starchy foods, and include more vegetables, fruits, dairy products, and greens in the diet. It is also useful to increase your drinking regime, lead an active lifestyle and give up bad habits.
During treatment, you should protect your body from direct sunlight. Patients with tubular lichen are contraindicated from visiting a solarium. After completion of therapy, it is necessary to constantly monitor the immune system, support it in every possible way, and pay special attention to the prevention of re-infection.
Folk remedies for treatment
It is possible to supplement the main treatment in the form of folk remedies. They include herbal decoctions, the production of tinctures, and herbal lotions. Most herbs can be purchased at the pharmacy. But their use must be approved by your doctor.
Most often, the following folk remedies are used for tubular lichen:
- Propolis is considered a natural antibiotic to which resistance does not occur. Has contraindications.
- Using recipes based on acids (vinegar, lemon) - an acidic environment prevents the development of fungi, but you should use them carefully to avoid getting burned.
- Celandine in the form of a decoction or tincture, the tincture is considered the most effective, the alcohol contained in the composition degreases the skin - making it unsuitable for the development of fungus;
- Tar is a popular remedy in the fight against various skin diseases; it has antiseptic and antimicrobial effects;
- St. John's wort, calendula, chamomile - have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Peppermint – soothes the skin;
- Sorrel - the composition is rich in vitamins and acids; for skin diseases it is used as an anti-inflammatory and antifungal agent.
It is important to remember that self-medication relieves symptoms, but only medications will help you completely get rid of the disease; in addition, not knowing whether this method is right for you can cause harm, the disease will take a chronic form or cause a relapse.
Classification
There are several clinical forms of tubular lichen:
- Erythematous-squamous. This form of the disease is also called typical, since it is diagnosed in the vast majority (over 90%) of cases of tubular lichen.
- Pseudo-papular. In this case, groups of nodules appear that rise above the skin. Their size is compared to lentils.
- Follicular. With it, damage to the hair follicles is observed with the formation of papules and pustules - seals and pustules.
- Inverted. This form is considered atypical. The affected area is the pubis, inguinal folds, thighs, and legs.
Other atypical forms of tubular lichen are also possible - urticariform and lichenoid. In the first case, the rash resembles blisters after a nettle burn, in the second, a small rash is observed that is scattered throughout the skin. There is also a vitiligo form of pathology, when certain areas of the skin lose melanin (pigmentation disorder).
With tubular lichen, the nature of the lesion may differ, so different colors of the rash are possible:
- yellow;
- pink;
- black (various shades of gray);
- achromic (lack of pigmentation).
Relapse of the disease
The state of the patient’s immune system plays a great role in therapy. If the body's protective properties are weakened, treatment may be ineffective and lead to relapses. To prevent tubular lichen from returning, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Maintaining personal hygiene,
- Prophylactic use of immunomodulatory drugs,
- Treating the skin with table vinegar and salicylic acid at the first sign of a return of symptoms.
In the initial stages, tubular lichen is treated with traditional medicine, topically (ointments, creams). Chronic forms can be treated with antifungal drugs, which are combined with taking vitamins to improve immunity.
FAQ
Question: Is lichen tubularis contagious?
Answer: The fungus that causes sunburn is an opportunistic microorganism and is normally present on the surface of the skin of most healthy people. There are cases where, through close and prolonged contact, the pathogen was transmitted from one person to another. However, with a normally functioning immune system, the disease does not develop.
Question: How can a pathology be quickly cured?
Answer: Active reproduction of the pathogen leads to the appearance of symptoms of the disease. You can get rid of them by destroying the cellular structure of the fungus. Only drugs with an antimycotic effect have this property. If a small area of skin is affected, complete recovery may occur within 3-4 weeks from the start of therapy.
Prevention
For effective prevention of lichen, disinfection of personal belongings is indicated. This way you can avoid re-infection and prevent cases of relapse of the disease. Basic measures to prevent tubular lichen include:
- strict adherence to personal hygiene rules;
- use of individual washcloths, towels and skin care products;
- preference for clothing (especially underwear) made from natural fabrics, the ideal option is cotton;
- sun protection - the use of special means against excessive ultraviolet radiation;
- normalizing weight and treating excessive sweating, if such a problem exists;
- timely treatment of endocrine diseases and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Prognosis, complications
The prognosis for tubular lichen is favorable. A correct diagnosis and competent and timely treatment ensure complete recovery.
Cosmetic defects of the skin are considered complications of tubular lichen. With properly organized treatment, this deficiency is completely corrected. There are no scar changes.
If treatment for tubular lichen is not started in a timely manner or the doctor’s instructions are not followed, then the rash may spread to a large area of the skin. Another possible complication is the duration of the pathology and the possibility of its relapse. This trouble can be avoided by following secondary prevention, which is based on eliminating risk factors for the development of tubular lichen.