Recently, many adherents of healthy eating have been talking about maintaining intestinal microflora. It's very simple: you need to eat fresh foods and also take in beneficial bacteria. Let's figure out what foods contain probiotics and prebiotics for the intestines and why they are needed.
About 100 trillion different bacteria live in the human body, a tenth of which is microflora. The rest are cells of microorganisms that live not only outside, but also inside a person. According to scientists, the human body contains about 2 kilograms of microbes that interact with cells and tissues.
What are prebiotics and probiotics for the gut?
Probiotics are live microorganisms that can be included in food products, for example, yogurt and kefir, medicines or dietary supplements. Their main task is to normalize the intestinal microflora, destroying bad bacteria.
Prebiotics are substances that are needed for the growth and development of good bacteria. If there are a lot of prebiotics in the body, beneficial bacteria feel comfortable and protect you from negative environmental factors.
The list of foods with prebiotics is long. These components are found in large quantities in fruits (bananas), vegetables (onions, corn, garlic, beans, peas), as well as in dairy products, bran and cereals.
Prebiotics include organic compounds:
- oligofructose;
- inulin;
- apple pectin;
- calcium pantothenate;
- lactulose;
- dietary fiber (fiber);
- algae extracts;
- glutamic acid;
- carotenoids.
When choosing probiotic yogurts in the store, pay attention to the number of lactic acid bacteria. In a high-quality drink there will be at least 10 7 CFU per 1 gram of product.
First aid for allergic itching
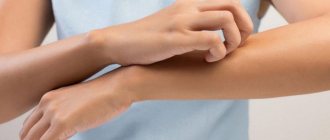
Itching in case of allergies must be relieved as soon as signs of skin irritation begin to appear. This will help prevent further rashes and will prevent the penetration of infectious pathogens through microcracks that form when vigorously scratching the itchy areas.
- First, you should rinse the affected skin surfaces with clean (cool) water, especially if the itching and redness are caused by cosmetics;
- you can then use soda water to reduce irritation. It is necessary to moisten a cotton pad (tampon) in it and treat the skin with it;
- You can use special ointments, creams or solutions.
You can reduce itching due to allergies by:
- pharmaceutical preparations for external use (sprays, ointments, gels);
- medicines for internal use (drops, tablets);
- folk home recipes.
Next, we will consider the list of such funds in more detail.
The role of pro- and prebiotics in the body
The main function of the intestines is to protect the body, which is impossible without good bacteria. This organ protects a person from poisoning, infections and eating disorders. Each organism has an individual intestinal microclimate - a community of bacteria that interact with each other and control everything that gets inside.
If harmful bacteria or other irritants enter the intestines, prebiotics and probiotics eliminate them, improving internal processes.
They supply the body with energy, biologically active substances, vitamins, regulate the digestion process and produce vitamin K, necessary for blood clotting. Due to stress, serious illness or treatment with antibiotics, bad bacteria penetrate the intestines and multiply, fighting the microflora. As a result of this struggle, there are fewer good bacteria, which affects your condition: the stomach begins to growl, flatulence appears, the digestion process is disrupted, which leads to nausea, diarrhea, or, conversely, constipation.
This greatly affects your immunity: it weakens and cannot fully protect against viruses coming from the outside, so you get sick more often.
"Ftorokort"
Antiallergic ointment "Ftorokort" is hormonal. The active component of the drug is triamcinolone acetonide, a synthetic corticosteroid hormone. In terms of strength, Fluorocort is classified as moderately active and is used to treat moderate skin lesions: inflammation, severe itching, eczema. The ointment is applied externally to the affected areas of the skin several times a day. Fluorocort has a number of contraindications, such as:
- lupus;
- skin diseases of various origins;
- precancerous diseases of the epidermis, tumors;
- manifestations of syphilis on the skin;
- individual intolerance to components.
Also, the drug is not recommended for use by pregnant and lactating women, children of all ages.
Use strictly in accordance with the instructions for use of Fluorocort ointment. Reviews indicate that side effects when using the drug appear quite rarely. With prolonged use, an allergic reaction, secondary infection, and skin atrophy may occur.
Pros and cons of probiotics and prebiotics
In recent years, the topic of restoring microflora with probiotics and prebiotics has become very popular, so many nutritionists and adherents of a healthy lifestyle are confident in their benefits. Many people take drugs in capsules, powders, and “live” yoghurts to eliminate dysbiosis, strengthen the immune system and cleanse the liver.
However, there are those who are skeptical about probiotics and prebiotics. They are confident that the diagnosis of “dysbacteriosis” is a myth, and tests to determine it are a simple marketing ploy, since the ratio of bacteria “out” is not related to what lives inside a person. Skeptics do not consider it necessary to help the intestines, since they can easily recover naturally, and the effectiveness of good bacteria has not been proven.
The third camp understands the benefits of pro- and prebiotics, but is not sure that they reach the intestines. People argue that most of these bacteria are killed by hydrochloric acid, so there is no point in spending money on products containing them.
Causes of itching
Itching is accompanied by burning, irritation and tingling. When body cells interact with an irritant, a sharp increase in histamine, a neurotransmitter of allergic reactions, occurs. This stimulates the nerve endings in the skin, which causes itching.
Important! Each person has their own level of sensitivity. The higher the susceptibility to allergens, the stronger the reaction, and vice versa.
Skin irritation can be due to a number of reasons:
- genetic predisposition;
- dehydration (dehydration) of tissues and organs, accompanied by metabolic disorders;
- lack of sufficient fluid in the diet;
- reaction to chemicals and medications;
- skin diseases, allergies;
- pathogens and parasites (lice, worms);
- reaction to insect bites;
- mental stress and emotional fatigue.
It must be remembered that according to the location of foci of inflammation on the body, there are 2 types of itching: localized (local) and generalized (general). The first form most often occurs in the anogenital area (the area where the genital organs and anus are located), as well as on the scalp. Itching is characterized by seasonal exacerbation and intensification of symptoms. All causes are of the localized type, but it can also be triggered by helminthiasis, disorders of the nervous and neuroendocrine regulation of the functions of the sebaceous glands of the skin, fungal infections, inflammatory processes and other local changes.
The causes of the generalized type may be:
- intolerance to certain foods (spicy foods, mushrooms);
- changes in weather and temperature;
- decreased function of the sebaceous glands;
- pathologies of the nervous system;
- dry skin (senile itching).
A great danger is posed by scratches, which are caused by disturbances in the functioning of internal organs and systems. For example, diabetes mellitus, inflammatory liver diseases, leukemia, Hodgkin's lymphoma and others. With such pathologies, itching is just a side effect or the first symptom signaling serious problems.
When you need beneficial bacteria
Probiotics help normalize intestinal function, and prebiotics (fiber) speed up the passage of food and its digestion in the intestines.
Probiotics are prescribed for irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory diseases, diverticular disease, and for the prevention of antibiotic-associated colitis they can be used together with antibiotics on the recommendation of a doctor.
Be careful: self-medication not only will not solve the problem, but can also harm the body. Prebiotics are contraindicated in cases of intestinal stenosis, such as Crohn's disease, and an allergic reaction may occur to probiotics.
Many people try to stop diarrhea with probiotics. It is important to establish the cause of the disorder, otherwise you may miss the onset of a serious illness. In addition, each bacteria has its own “specialization”. For example, lactobacilli suppress putrefactive processes in the intestines and stimulate the immune system. However, without a doctor’s recommendation, it is not worth treating diseases with them: the effectiveness of certain microorganisms has been proven, and some bacteria are only being studied by specialists.
Also, microorganisms that inhabit the intestines secrete gamma-aminobutyric acid, which affects your mood. When the microbalance is normal, your mood improves and stress goes away.
Evidence-based effectiveness
Abroad, the manufacturer is required to prove the effectiveness of its products. For example, if beneficial bacteria have been added to a new yogurt, this does not mean that the product is healthy. In Russia, the law does not oblige manufacturers to conduct serious research, but there must be an evidence base.
For example, a well-known food manufacturer conducted double-blind, placebo-controlled studies involving 600 people. One part of the experiment participants drank a “pacifier”, and the second part drank a lactic acid product with a probiotic. When the study ended, an independent organization compared the participants' medical histories and found that people who consumed the probiotic product had less illness. So probiotics do strengthen the immune system and can speed up the healing process, but their effectiveness and safety in a specific product must be proven.
Preparations for external use
Allergic skin itching is treated with antihistamines. This is a group of drugs that block and suppress the action of the hormone histamine. They are highly effective and very diverse, but have a number of contraindications. We must not forget that people with liver or kidney pathologies should not take them without consultation with a specialist.
Antihistamines are:
- non-hormonal;
- corticosteroid (hormonal).
Non-hormonal drugs
Non-hormonal drugs have minimal side effects, therefore they are approved for use in childhood and pregnancy. For mild allergies, accompanied by itching and irritation of the skin, it is recommended to use just such drugs. Let's look at the most effective of them.
"Skin-Cap"
- additional effect: antimicrobial, antifungal and anti-inflammatory effect;
- average cost: 800 rubles;
- Features of use: use 2 times a day for 3-4 weeks.
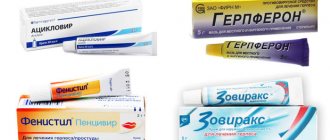
"Fenistil"
- additional effect: weak antiserotonin and antibradyuinine effect;
- average cost: 360 rubles;
- Features of use: apply the gel in small quantities to irritated areas of the skin 2-4 times a day.
"Protopic"
- additional effect: anti-inflammatory;
- average cost: 1600 rubles;
- Features of use: adults need to start treatment with 0.1% Protopic ointment. After 2 weeks you can switch to 0.03%. Use 2 times a day.
"Nezulin"
- additional effect: analgesic;
- average cost: 100 rubles;
- Directions for use: Apply to problem areas of the skin 4 times a day.
"Psilo-balm"
- additional effect: cooling and anesthetic effect;
- average cost: 250 rubles;
- Features of application: apply 2-3 grams. the drug on itchy skin areas three times a day.
Hormonal drugs
If it is not possible to relieve allergic itching with non-hormonal drugs, corticosteroids containing natural human hormones are used.
Hormonal agents guarantee a quick and visible result, eliminating all signs of an allergic reaction, but at the same time they are actively absorbed into the blood plasma and can have a systemic effect on the body. Therefore, they should not be used without the consent of a doctor.
Commonly prescribed hormonal medications to combat itching include:
"Gistan"
- additional effect: antipruritic and anti-inflammatory properties;
- average cost: 170 rubles;
- Application features: apply to areas of allergic itching 2-4 times a day;
"Advantan"
- additional effect: anti-inflammatory property;
- average cost: 530 rubles;
- Directions for use: Apply a thin layer to the area of irritation once a day.
"Flucinar"
- additional effect: anti-exudative and anti-allergic effect;
- average cost: 260 rubles;
- Application features: Apply a small amount of ointment (about 2 grams) to the itchy area in the morning and evening.
"Elokom"
- additional effect: anti-exudative and anti-inflammatory;
- average cost: 180 rubles;
- Directions for use: Apply to the itchy surface once a day.
"Beloderm"
- additional effect: vasoconstrictor, antiproliferative, anti-inflammatory effect;
- average cost: 130 rubles;
- Directions for use: Apply a thin layer twice a day.
Requirements for probiotic products
One of the main requirements for probiotic products is the survival of the probiotic strain in the gastrointestinal tract, as well as in the finished product throughout the entire shelf life.
For such control, modern production facilities operate research centers and laboratories. Their main task is to select probiotic bacteria and study their properties. Some large production facilities have microbiological laboratories in which about 4,000 different strains have been collected. They determine which prebiotics and probiotics are better and more effective.
Remedies for the fastest possible relief of itching
When deciding how to relieve skin itching at home in a short time, you should use one of the medications recommended below.
- Soda paste. This product is great for itching caused by insect bites, sunburn and allergies. Prepare a medicinal composition by combining baking soda with a small amount of warm boiled water. The result should be a mass similar in consistency to rich cream. Apply wet baking soda to the itchy area and leave for 30 minutes. This antipruritic folk remedy relieves discomfort within 5 minutes after application. The effect of using soda paste lasts for 4-6 hours. The medicine is suitable for both adults and children.
- Traditional medicine also recommends using medications based on table vinegar in the treatment of itchy skin. It is diluted in cold water in the following proportion: 1 tbsp. l. vinegar per 30 ml of water. A thick cotton cloth is soaked in the solution and applied to the itchy area. Vinegar relieves discomfort in 5-10 minutes. Once the itching has passed, you can remove the napkin soaked in the solution.
- A solution of boric acid in a tea decoction with alcohol soothes even unbearable itching due to eczema. Preparing the product is more difficult than the previous ones, but it can be used for all types of itching. To prepare the preparation, 50 g of high-quality black tea is poured into 500 ml of water. Bringing the mixture to a boil, boil it for 12 minutes and leave to cool. After straining the broth, dissolve 1 tsp in it. boric acid and mix the liquid with medical alcohol in a 1:1 ratio. Lotions with medicine eliminate even severe itching in 15 minutes.
Prevention of itching in old age
Proper prevention will help avoid age-related itching, and this is much easier than treating it.
Daily regime
In 99% of cases, correct, comfortable and healthy sleep and wakefulness, nutrition and hygiene will help solve the problem of itchy skin. A clear schedule normalizes metabolic processes and reduces the load on the body. Perhaps, after normalization of the regime and psycho-emotional state, other means will not be required.
Hygiene products and hygiene procedures
Hot baths are contraindicated for older people, as hot water dries the skin more. It is also important to avoid using alkaline-based detergents, since in addition to drying, they also degrease.
It is recommended to take a bath with warm, not hot water, and immediately before the procedure, lubricate the skin with olive or almond oil, if there is no individual intolerance. Instead of a sponge or washcloth, use your palms, gently wiping your armpits and other hard-to-reach places. After a shower and bath, it is advisable to use a cotton towel, and do not rub the skin with it, but lightly blot it so that it absorbs excess moisture, but does not take moisture from the skin.
To relieve an attack of itching, a tonic contrast shower helps.
You will also have to get rid of some bad habits in favor of a healthy lifestyle:
- Eliminate alcohol from your diet, stop smoking or reduce the number of cigarettes you smoke.
- Follow the diet recommended for older people.
- Avoid soaps and detergents containing large amounts of synthetic substances.
- avoid prolonged exposure to the sun.
- Avoid moisturizers containing mineral oils to prevent clogged pores.
- itching often occurs in areas of friction, so clothing should be comfortable, loose, made from natural fabrics, appropriate for the temperature.
- ventilation of the room, regular walks, physical activity if possible.
- full sleep.
Symptoms of itchy skin
For the appearance of skin itching sensations, both its intensity and the properties of the irritant may matter. When an irritating substance initially causes itching of the skin, then as the intensity increases, the itching gives way to pain. Certain irritants (for example, quinine, morphine, arsenic, etc.) have the effect of causing skin itching, while some medications may not cause it.
It is also worth noting that in the perception of itching, as well as pain, the subjective element can be of great importance. All patients perceive skin itching differently, depending on the functional characteristics of their nervous system. A good diagnostic criterion for determining the nature of itching is excoriation, as a final component of scratching. Often there are patients who complain of severe itching of the skin, which deprives them of sleep, but during an in-person examination, as a rule, they do not find any scratching or may have minor excoriations. In other cases, if the patient has a lot of scratching, there are practically no complaints of itchy skin.
Neurotics and psychasthenics may complain of severe itching of the skin, without significant clinical signs. For them, such an exaggeration of sensations is quite typical. Removing neurosis through hypnosis leads to a weakening or disappearance of skin itching altogether, which is proof of this. Based on the location of skin itching, a distinction is made between limited and generalized nature of its location.
An example of localized skin itching may include itching of the hands, feet, and anal area. An example of generalized skin itching is senile itching (with dry skin or diabetes).
Itching of the skin and the characteristic scratching of the skin usually lead to visible changes in the skin. The skin can react to scratching either by spasm of blood vessels or by their dilation. As a result, vascular ischemia occurs with simultaneous tissue edema. Often itching of the skin goes away along with an urticarial reaction, which is characterized by vasospasm and their expansion along the periphery of the vesicle, which can form with skin itching.
Prolonged itching of the skin can lead to the appearance of papules, excoriations, lichenification, and often eczematization of the skin. When these clinical manifestations appear, the disease should already be regarded as neurodermatitis.
Diagnosis of itchy skin
A wide variety of etiological factors requires a whole range of diagnostic measures.
Primary diagnosis is carried out by a dermatologist - it is this specialist who should be contacted first in case of damage to the skin. The clinician initially:
- interviews the patient regarding the first time of appearance, severity and presence of additional symptoms;
- studies the medical history and life history of the patient, which will help identify some of the reasons for the formation of the main symptom;
- performs a detailed physical examination, during which the condition of the skin is carefully examined.
The second stage of diagnosis consists of laboratory examinations, which include:
- clinical and biochemical blood test - will indicate changes in its composition and signs of a pathological process;
- general urine analysis;
- microscopic examination of feces - to exclude or confirm the presence of pathogenic bacteria;
- scraping from itchy and flaky areas of the skin - for possible detection of fungal or infectious lesions.
Then, if necessary, the dermatologist refers the patient for further instrumental diagnostics to other specialists in the field of gastroenterology, endocrinology, oncology, etc.