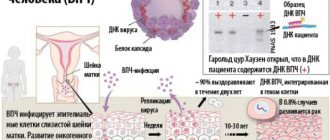
Condylomas in women on the genitals are not such a rare problem. The causative agent of this pathology is HPV (human papillomavirus). The disease itself is called condylomatosis and can occur without symptoms. With the development of this pathology, there is a threat of cervical cancer. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor in time and undergo the prescribed treatment.
- What are condylomas
- Causes
- Routes of transmission
- Types of condylomas
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Unsafe HPV vaccination
Causes
As noted above, HPV is the causative agent of condylomatosis. Today, more than 100 types of virus have been identified. Some of them provoke cancer, some are considered low-oncogenic. The latter include the sixth and eleventh types of HPV. Due to the penetration of these viruses into the body, condylomas appear. Cancer can be caused by types 58, 59, 52, 31 and many other types.
An infected girl or woman does not always develop growths on the skin and mucous membranes immediately after infection. There may be no symptoms; the virus is in a semi-dormant state. Then some factors appear that make it active, and then the growth of condylomas begins. Such HPV-activating factors include:
- decreased immunity due to chronic stress, tumors, chronic infection, hypovitaminosis, diets, long courses of antibiotics, etc.
- decreased immunity during pregnancy
- the period after childbirth, when the ratio of hormones in the body changes, the woman lacks vitamins, her body and nervous system are exhausted, etc.
- sexual relations with a person with HPV
- not using condoms when having sexual intercourse with a person whose health status you do not know
- promiscuity
- STD
- ignoring personal hygiene rules
Brief recommendations
In every third person who is cured, the infection reappears. Most often, relapses of the disease are caused by weakening of the body. To prevent the appearance of genital warts, it is recommended to follow the following rules:
- lead an active and healthy lifestyle;
- treat all somatic diseases, following medical instructions;
- Healthy food;
- take additional vitamins;
- walk more often and longer;
- give up alcohol, drugs and cigarettes;
- have only 1 sexual partner;
- do not engage in casual sex;
- use a condom;
- avoid stress;
- prevent hypothermia of the body;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene.
To prevent relapse of the disease, Immunal or Cycloferon can be used. Thus, the appearance of genital warts is caused by infection of the body with the human papillomavirus. This disease requires surgery. Self-medication can only cause harm and lead to complications (ulceration, cancer, suppuration). When the first symptoms of the disease appear, you need to visit a gynecologist, surgeon or urologist.
Routes of transmission
In most cases, HPV, which causes condylomas in women, is transmitted sexually. Infection is possible not only during vaginal intimate relations, but also through oral or anal contact. If you have had sex with an infected person, then your chance of getting sick is 75 out of 100, which is why HPV is considered a highly contagious virus.
There is a high risk of infection of the fetus through the placenta, as well as during childbirth (when the child comes into contact with the mother’s mucous membrane, which has the virus). There are also rarer routes of transmission: through household items, including towels, underwear, washcloths, etc.
Types of condylomas
There are two types of condylomas, which are distinguished by their shape:
- pointed
- flat
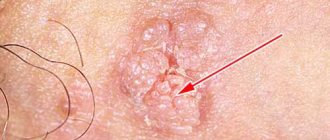
The former are known as exophytic and the latter as endophytic. Acute growth occurs outward. The patient may see small papillae on the skin or mucous membranes, which are caused by low-oncogenic types of HPV.
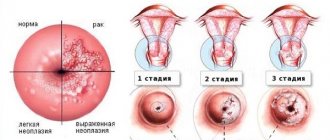
The flat type of condylomas forms deep into the epithelial layer, which ultimately provokes oncology. The later the disease is detected, the worse the prognosis, including early death. Flat condylomas in women mainly grow on the cervix. It is for this reason that they are at risk of cervical cancer.
Symptoms
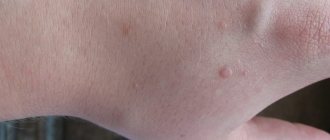
Genital warts are 2-5 mm in size and can mainly be seen on the genitals and near the anus. From the moment of infection to the appearance of growths, it takes from 2-3 months to 2-4 years. It all depends on the immunity of the person who “caught” HPV. Condyloma grows up to six hours. During this period, the patient feels that there is something burning and pinching in that area.
Not one, but 2 or more condylomas are formed at the same time. All of them, as already noted, are small. They look like cauliflower due to their bumpy surface. As soon as the growth of condylomas stops (when they reach their maximum size), the burning and itching disappear. Condylomas have a thin stalk. The color can be different: from flesh to burgundy.
Condylomas in women and girls can merge with each other. They can form a giant Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma. It may rot. If a patient develops condylomas in the rectum, it will be painful for her to have bowel movements. Blood may come out with the stool. Condylomas that form in the urethra cause symptoms similar to cystitis.
If condylomas form on the external genitalia, there may be no unpleasant symptoms. If they are localized on the mucous membrane of the vagina or cervix, the woman begins to have a white discharge that may smell rotten. During intimate intercourse, a certain amount of blood may be released, and the sensations will definitely not be pleasant.
Types of genital warts, what they look like
Benign genital neoplasms are classified as follows:
- Genital condylomas are exophytic - they grow outward, and accordingly, they are located on the skin.
- Flat condylomas - endophytic - grow inward, that is, they penetrate into the deep subcutaneous layers. It is these condylomas that have a high oncogenic index, which means they can provoke cancer. In addition, the danger lies in the fact that they are more difficult to detect than pointed ones.
When it comes to genital condylomas, we most often mean genital warts, but there are other types:
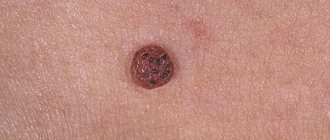
- Papular - the shape of such warts resembles a dome, the color is dark red, the surface is smooth.
- Keratonic - most often found in the pubic area, on the foreskin or on the penis itself. These warts have a stalk.
- Giant condylomas - look like separate patches of skin and can secrete an unpleasant-smelling secretion.
- Endourethral - develops mainly near the urethra.
- Wide - such formations only superficially resemble condylomas; in fact, they are not a consequence of the papilloma virus - they are caused by syphilis.
Diagnostics
Condylomas with HPV must be distinguished from similar formations with syphilis, from cancer of the mucous membranes, skin cancer, and molluscum contagiosum. Be sure to tell your doctor about all the symptoms that bother you. The gynecologist examines the external genitalia and cervix. Usually the diagnosis is simple. A colposcopy is performed to determine whether there are dysplasia processes that subsequently lead to cancer. The method is also relevant for detecting flat condylomas.
Also, for diagnosis, the mucous layer of the cervix is smeared with vinegar. A spasm of blood vessels occurs, including the one that feeds the condyloma, and the affected area becomes whitish. Patients usually must donate blood for testing using the polyplasma chain reaction method. The type of HPV is determined, how oncogenic it is, and how much of it is in the body. Blood must be donated to be tested for HIV and syphilis. The man (or men) you sleep with should also be tested.
During the examination, the doctor takes a smear from the cervical canal, cervix and the condylomas themselves. This is necessary for cytological examination. If cancer is suspected, a biopsy of certain areas is performed. The gynecologist may suspect that condyloma is growing in the urethra. Such patients undergo urocystoscopy. If pathological formations in the rectum are suspected, the patient is sent for diagnosis using anoscopy.
Treatment
It is impossible to completely kill the virus in the patient’s blood. The condylomas themselves are removed so that they do not affect the patient’s quality of life. The doctor also prescribes medications that kill HPV. They cannot completely destroy the causative agent of the disease, but make it inactive. You also need drugs that activate the body's defenses (increase immunity). It is also important to normalize your diet, get enough sleep and rest, treat any chronic diseases, and take vitamins as prescribed by your doctor.
Condylomas are removed surgically or chemically. The chemical coagulation method involves the use of chemically active substances that cause condylomas to dry out and fall off the mucous membranes or skin. The method does not pose any danger to a sick girl or woman. For chemical coagulation of condylomas, it is important to use the following agents:
- condiline
- bonafton
- solcoderm
Another method is diathermocoagulation. Pathological formations are affected by electric current. This is a cheap way to get rid of condylomas. But after such treatment, scars will remain at the site of the formations.
Cryodestruction is a modern method of treating condylomas in women and girls. The doctor treats the formation with low-temperature liquid nitrogen, as if freezing the condyloma. In this case, scars are not formed. The next current method is radio wave surgery using the Surgitron device. Condylomas are affected by the high-frequency waves emitted by it. It gives the desired effect in most cases. The procedure itself is not painful and there are no scars left. But treatment with this method is considered expensive, and not all clinics have the necessary equipment.
The effectiveness of such a method as laser coagulation reaches 100%. Before starting the procedure, local anesthesia is given. In some cases, scars remain at the site of condylomas. But none of the above treatment methods protects against relapses. The frequency of recurrence of condylomas in girls and women ranges from 40 to 80%.
You should not try to remove and burn out condylomas yourself. And don't let inexperienced doctors do this. If you receive a diagnosis of HPV, treatment should be carried out using one of the methods listed above. Condylomas have long stems and grow deeply, so if you cut them off, they will grow back. And when cutting, you can lose a lot of blood. Even children can have condylomas. Therefore, it is important to promptly seek a face-to-face consultation with a qualified gynecologist (or a pediatric gynecologist in the case of an illness in a minor girl).
Ointments with an antiviral effect are also used for treatment, for example:
- Imiquimod
- Keravort
- Aldara
The drug can only be purchased by obtaining a prescription from your doctor. It is not applicable for children under 12 years of age. It also has no effect on condylomas that are located inside the genitals or urethra. For treatment, it will not be enough to anoint the condyloma with ointment once; you need to treat the affected areas for a long time and systematically.
When using the above ointments for condylomas, side effects are likely:
- burning and itching
- swelling of the area
- erosion
- discharge of fluid from the affected area
- scab formation
- redness of the area treated with the drug
Imiquimod is applied to condylomas every other day (that is, 3 times a week). After you have applied the drug, 10 hours must pass, and it must be washed off with soap.
Other drugs for the treatment of condylomas in women:
- podophyllin
- podofilox
- podophyllotoxin
- Condyline
- Condylox
- Kondilin
It has a toxic effect on pathological formations. You need to lubricate the affected area twice a day for three days, and then take a break for 4 days. There should be 3-4 such courses in total. Do not smear healthy areas around condylomas, it can be harmful. The maximum dose of cream should be up to 0.25 g at a time.
Reviews
Condylomatosis in women is a problem that has become widespread. Here are some reviews that will help you believe that this disease can be successfully treated.
Irina, 29 “I first encountered the problem of condyloma four years ago. Initially, I tried to get rid of the tumors on my own using various ointments, but nothing helped. After going to the doctor, I decided to undergo cryodestruction of condylomas. They haven’t bothered me for several years now.”
Veronica, 25 years old “A year ago I decided to get pregnant. During a preliminary examination, I was diagnosed with condylomas. The doctor prescribed me a special gel - Panavir. But in addition to daily application of this gel, I regularly burned condylomas with celandine juice and took vitamins to improve immunity. I am now in my second month of pregnancy. Repeated examination showed that I do not have condylomas. I advise all women who want to have a child to undergo a preliminary examination so as not to expose the baby to the risk of infection in the future.”
Olga, 27 years old “I have repeatedly had to fight with condylomas. I first encountered this problem during my first pregnancy. For treatment I used mainly folk remedies, as well as special gels. Before the second pregnancy, condylomas reappeared. I decided to use a more radical method of treatment - cauterization with liquid nitrogen. I’ve been living without condylomas for the last three years.”
Yulia, 21 years old “Eight months ago, during a routine medical examination, I was diagnosed with condylomas. I treated these formations with gels for several weeks, but after a while the condylomas reappeared. The doctor advised me to get rid of them using chemotherapy. For the last six months, the problem of condylomas has not bothered me. I recommend using radical methods to combat these tumors, because ointments and folk remedies, as a rule, do not save for a long time.”
Unsafe HPV vaccination
Vaccines used include Gardasil and Cervarix. But not all gynecologists approve of them, because there is no accurate data that these vaccines protect against the disease. Vaccines are valid for 8 years from the date of administration. They prevent infection with HPV types 16 and 18. But there are many more types, as we noted above. There is currently no vaccine against other HPV viruses.
Some doctors believe that this type of vaccination may affect a woman's ability to conceive and carry a child to term. But this has not been proven by research. Vaccines have side effects:
- menstrual irregularities (which can cause infertility)
- hormonal imbalance
- inflammatory process in the uterus
- dysfunction of the ovaries, etc.
Condylomas in women in the urethra and genitals
As mentioned above, condylomas most often form on the genitals. They are also found in the perineal region, in the anus, in the vulva, and inside the vagina.
The reasons for the appearance of tumors on the genital organs are the same as in other cases:
- promiscuity;
- chronic skin diseases;
- severe stress;
- poor nutrition;
- unfavorable heredity;
- hormonal imbalances;
- various infections.
Condylomas in the groin and intimate places most often appear between the ages of 16 and 25 and from 35 to 40. It is during these years that a strong hormonal surge is observed in the female body.