The neck is constantly exposed to various contaminations. Dust and particles from the surrounding space are deposited on sweat secretions, which are a necessary element of the functioning of the skin. Together they form a layer of pollution on the surface of the skin. The neck is constantly in contact with the collar. Their contact leads to rubbing of dirt into the outer cover. In the event of microtrauma of the hair follicles, inflammation occurs and a boil forms on the neck.
If an abscess appears, it is necessary to remember that the person’s brain is located close to the site of the lesion. Self-treatment in the form of squeezing out boils, piercing or “picking out” can lead to the development of a pathological process called meningitis.
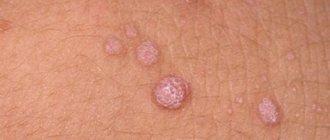
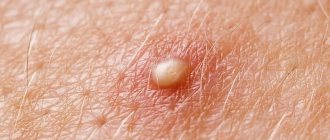
What does it look like
It is a red, painful pimple above the skin, about the size of a pea to a golf ball, filled with white pus, with a greenish shaft in the middle. The skin around it is red, inflamed and painful. The boil is usually located on the back of the neck, since here the skin sweats a lot and rubs against the collar and clothes. Once the bacteria gets under the skin, the immune system begins to fight the infection. That is why the boil has this appearance, because it is an accumulation of white blood cells that died in the fight against purulent inflammation.
Reasons for appearance
Boils never appear “on their own.” Their main “causative agent” is Staphylococcus aureus or white , which, upon entering the body and receiving favorable conditions, begins to actively multiply.
How does a pathogenic microorganism penetrate the skin? Through any kind of damage (trauma, cut, scratch). In addition, it is the neck that most often suffers from sebaceous/sweaty discharge - an ideal environment for the appearance of staphylococcus.
Popular reasons for the formation of a boil:
- weak immunity;
- low level of basic hygiene;
- poor quality nutrition;
- bad habits (smoking, addiction to alcohol, taking drugs);
- chronic diseases of any nature (rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, cancer, psoriasis);
- colds, ARVI;
- hypothermia, overheating of the neck and the entire body as a whole;
- disruption of the endocrine system/gastrointestinal tract;
- metabolic disease;
- hormonal disbalance.
Stages of boil development and symptoms
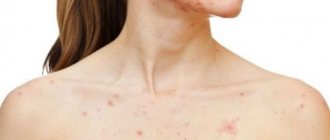
A boil on the neck develops very quickly due to the large accumulation of blood vessels in this area, which quickly spread the infection through the bloodstream. It is often difficult to determine the onset of a boil, but the following symptoms should alert you:
- soreness, swelling and swelling appear at the site of the lesion;
- against the background of increased body temperature, the pain in the neck becomes so severe that it is impossible to turn the head;
- General weakness and headache intensify, swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck appears, and a pustule with pus forms.
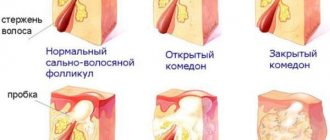
There are three stages of boil development:
- A bright red bubble appears in the hair follicles and connective tissue - a pustule. Over the course of several days it grows, the skin around it becomes painful, red, swollen and thickened.
- After another 3 days, pus from dead immune cells, bacteria, follicle cells and connective tissue forms in the pustule. A greenish colored bump forms.
- Cleansing and healing. Almost simultaneously, the top of the boil softens, breaks through, and pus mixed with blood comes out of it. 2-3 days after this, the rod itself is rejected, pain, inflammation, and swelling disappear. The wound scars and heals within 2-3 days.
In a patient with a normally functioning immune system, the boil breaks out and heals without a scar in a period of 2 days to 3 weeks.
Symptoms
The formation of boils on the neck occurs in stages. The following stages of abscess formation are distinguished:
- A small red spot appears on the neck, inside of which there is a seal. There is no physical discomfort.
- Several days will pass and the boil will begin to develop. There will be tingling, burning, and twitching. A white top will become noticeable inside the suppuration.
- After several days, the boil will open and the pus will come out. This will leave a slight deep wound that will heal. Usually small suppurations do not leave scars.
It is forbidden to break through a boil on your neck yourself. There is a high risk of adverse consequences in the form of tissue damage. This may lead to subsequent infection.
Why does it appear
The neck is a delicate and vulnerable area of our body. Therefore, boils appear on the neck more often than in other areas. There are external and internal causes of an abscess.
External risk factors include:
- neglect of personal hygiene rules, for example, irregular showering;
- using someone else's bed linen, towels and clothing;
- irritations and abrasions on the skin caused by tight clothing, shaving, insect bites;
- close contact with an already infected person.
Internal causes are more difficult to control and treat. These include:
- diabetes mellitus – high blood sugar reduces the immune system’s ability to respond to infection;
- skin diseases such as psoriasis, eczema and acne increase its susceptibility to Staphylococcus aureus;
- taking certain medications that weaken the immune system;
- obesity.
Causes of appearance on the neck
The neck is exposed to dirt, dust, and sweat and oil appear on the skin. Daily friction with clothing helps rub dirt into the skin. When combing or shaving, you can injure the skin, resulting in minor injuries, which allows germs to penetrate inside and cause a boil to appear.
The reasons that influence the appearance of chiria are poor hygiene, weak immunity, and the inability of the skin to resist bacteria.
The development of furunculosis is promoted by:
- hypothermia;
- unbalanced diet, lack of vitamins and minerals;
- indigestion;
- diabetes.
To prevent pathology in the neck area, take extra care of your health, devote time to hygiene, eat healthy food, and avoid hypothermia. The disease can occur in children and adults.
How can a boil be dangerous?
In most cases, a boil on the neck does not require medical attention. It breaks through on its own, clears itself and heals from a few days to 1-2 weeks. But in rare cases, it can lead to complex and life-threatening illnesses.
The great vessels supplying the brain with blood pass through the neck. Due to improper care of the resulting abscess, especially when trying to squeeze it out, the infection enters the bloodstream and sepsis develops - a general blood infection that can be fatal. Infection occurs in the heart, lungs, central nervous system, bones and joints. In this situation, emergency medical attention is needed.
Meningitis, an infection of the meninges, often develops against the background of sepsis. The infection can lead to partial loss of brain function, so prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential.
Another serious complication is the development of an infection resistant to methicillin. This is the main antibiotic for treating Staphylococcus aureus. This bacterium is resistant to many antibiotics used to treat boils. In such situations, doctors prescribe vancomycin.
To avoid these and other possible complications, never skip a visit to your doctor.
Diagnostics
If you detect the first signs of furunculosis, you should immediately consult a dermatologist.
Only after seeing the complete clinical picture will he be able to correctly diagnose and prescribe a course of treatment. To study the physicochemical and biological properties of microbes, bacteriological culture is used - analysis of the discharged boil to determine the pathogenic agent. If the disease recurs with a noticeable increase in inflammation, a number of tests are prescribed:
- clinical blood and urine analysis;
- blood sugar test;
- rhinoscopy (examination of the nasal cavity) and pharyngoscopy (examination of the mucous membrane of the throat);
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- fluorography.
These surveys are necessary under any circumstances. Depending on the complications of the disease, consultation with other doctors may be necessary.
Removal methods
It is better to understand how to treat a boil on the neck together with a dermatologist. If it is just maturing, the doctor will prescribe local treatment. If the rod appears or the abscess bursts, you should contact a surgeon to treat the wound. Boils can be treated at home.
First aid at home
The first and most important rule is that you should never squeeze a boil. The sore spot should be regularly disinfected with 2% salicylic or 70% ethyl alcohol several times a day. First cut off his hair.
Apply napkins with stretching and anti-inflammatory ointments - Vishnevsky or Ichthyol - to the boil, change them every 3-4 hours. To reduce pain, you can take ibuprofen-based medications.
Before and after each treatment of the skin, you should thoroughly wash your hands. Wash the patient's personal belongings and items separately to prevent the spread of infection.
Drug therapy
At an early stage of development of the inflammatory-purulent process in the neck, UVR (ultraviolet irradiation) of the blood and UHF therapy are prescribed. These procedures suppress further development of the disease. In some cases, novocaine injections of the site of infection are recommended.
Broad-spectrum antibiotics are used when the patient’s immune system is weakened, the infection has spread to surrounding tissues, the abscess has broken through but has not completely cleared. You need to take pills or get injections - it all depends on their absorption in the stomach. As part of the complex treatment of a boil, the doctor prescribes a staphylococcal vaccine, vitamins C, E, A, which strengthen the skin’s immunity.
You should definitely contact a medical facility if the boil enlarges and does not break out within 2-3 weeks.
How boils are removed in the clinic
A surgical method of getting rid of a boil on the neck is used in cases where there is a threat of blood poisoning and the spread of infection. Under local anesthesia, the surgeon dissects the boil, removes the rod and all contents, and disinfects the wound. If the wound is large, stitches are applied. Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and vitamins are prescribed.
Home methods
Treatment of boils at home is carried out very carefully, since carelessness when treating a purulent wound easily leads to the spread of infection. Do not pierce or squeeze out pus from the abscess.
You can treat boils at home with dry heat. Heat increases blood circulation, attracting white blood cells to the area of skin, which fight bacteria and speed up healing.
Traditional medicine offers effective methods for getting rid of boils:
- apply baked onion paste to the abscess several times a day;
- grind aloe leaves to a mushy consistency and apply to the wound;
- grate laundry soap, heat it with milk until smooth and apply it warm to the boil.
First aid at home
Be sure to treat your hands with antiseptic after or before contact with the wound. Antimicrobial solutions must be carefully applied to the boil 3 times a day, without causing injury to it. To speed up the ripening of a boil, apply a warm compress to it for 20 minutes. After such procedures, the boil is covered with a medical napkin.
Important! The boil must not be scratched, massaged or opened.
Only if it has opened on its own is it possible to carefully remove the pus, after which the wound must be treated with an antiseptic. A bandage is applied to the inflammation and these procedures are repeated until complete healing. In case of severe pain, taking painkillers is recommended.
Do not use antibiotic-based medications without a prescription from a specialist. Wash your hands after touching a boil, as bacteria can contaminate food and other objects you touch.
Features of treatment for children
Furunculosis on the neck in children appears either in the first years of life or in adolescence. But the cause of an abscess in them is always associated with a weakened immune system. Most often, this indicates that a hidden inflammatory process is going on in the child’s body. The most dangerous rashes are on the face and neck. Since infections develop much faster in children, the risk of complications increases significantly. While in an adult a boil can develop up to 2-3 weeks, in a child it takes no more than 10 days.
The symptoms are also somewhat different from those in adults:
- the skin around the abscess turns red, hurts, and adjacent lymph nodes become inflamed;
- aching pain, twitching, temperature rises to 38 degrees;
- the child's activity decreases and his appetite decreases.
At home, an abscess in a child is treated with Ichthyol ointment or Vishnevsky ointment. To prevent complications, a course of antibiotics and vitamin therapy are prescribed. To prevent childhood furunculosis, you need to stay clean, eat well, walk in the fresh air and get good sleep.
Treat or open?
At the first symptoms of a boil, it is recommended to seek medical help. Qualified treatment in the early stages of the disease can relieve suffering and pain during the development of an abscess, and break it off without leading to the stage of necrosis.
In the initial period of the disease the following may be prescribed:
- UFO (erythemal doses);
- UHF;
- treating the skin area with salicylic or boric alcohol to destroy the infection;
- injection of infiltrate with Novocaine solution and antibiotic 1-2 times.
Vishnevsky ointment helps well with furunculosis If a boil has already formed on the neck, then treatment of the skin around the abscess with boric (salicylic, camphor) alcohol or furunculin solution should be continued. Moreover, it is necessary to treat from the periphery of the affected area to the center.
Vishnevsky ointment (which has an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect) or ichthyol ointment is applied to the infiltrate itself to accelerate the maturation of the abscess twice a day. Ichthyol draws out pus better. Its remains are washed off with warm water.
The ointment is covered with a sterile napkin and secured with an adhesive plaster. It is not recommended to use bandages for securing, as squeezing will contribute to the spread of infection. Do not apply warm compresses or otherwise heat the affected area.
If the boil has already burst and the pus has not yet completely come out, then the wound should be washed with hydrogen peroxide and sodium chloride applied in the form of a hypertonic solution. Cover the wound with a sterile napkin. You can treat the wound with other means: Ethacridine, Rivanol, Furacilin.
Daily dressings are carried out until the wound is completely clean. With each dressing, healthy areas of the skin should be treated with one of the disinfectants (diamond green, 700 alcohol, methylene blue, etc.).
The rod can be removed using tweezers only when it is separated from the infiltrate, because early forced removal can cause an exacerbation of a purulent infection.
A clean wound is treated with ointment dressings, for which Levomekol ointment containing the antibiotic Chloramphenicol is often used.
Surgical treatment of boils is used in the following cases:
- the abscess did not burst within a week;
- the rod does not come off for a long time;
- an abscess has formed.
Anesthesia is carried out by irrigation with Chlorethyl or local infiltration anesthesia.
Along with local treatment, the doctor may prescribe oral medications - antibiotics (Ampiox, Amoxiclav, Ampicillin, etc.) or sulfonamide drugs (Biseptol, Sulfadimethoxine). Antibiotic therapy is indicated in complicated cases of the disease.
For furunculosis, complex treatment is carried out, including immunocorrection (autohemotherapy, Dekaris, Pyrogenal), the appointment of vitamin and mineral complexes. In case of frequently recurrent furunculosis, it is advisable to carry out a course of immunotherapy using a staphylococcal vaccine (preferably an autovaccine) or staphylococcal toxoid to desensitize the body.
Alternative traditional medicine recommends its own recipes for the treatment of boils. There are many of them, for example, drinking brewer's yeast and purified sulfur.
In order for the pus to come out faster, traditional medicine recommends applying:
- plantain leaf;
- flatbread made from rye flour mixed with honey and warm milk;
- gruel of chopped onion with milk, etc.
Draw out the pus well from the aloe leaf and baked onion. But it is better to discuss the use of folk remedies with your doctor.
Treatment prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for recovery when boils appear on the neck is favorable in almost 100% of cases. Rare cases of severe complications are associated with chronic diseases or untimely treatment.
Taking preventive measures will prevent primary infection and relapses. The main measures to prevent boils on the neck include:
- keep your hands, body and hair clean;
- shower regularly;
- treat any wounds, abrasions and cuts of the skin in a timely manner;
- Cover the treated areas of skin with a sterile bandage to prevent infection.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet and do regular exercise - this will strengthen your overall health, immune system, and reduce the risk of boils appearing on your body.
Effective folk remedies
They will be effective only in the case of single small boils. They can be used only if it is impossible to contact a dermatologist, as emergency measures:
- Aloe juice. You need to prepare aloe juice. To do this, cut off the leaves of the plant and put them in a plastic bag for 10 days in the refrigerator. Squeeze out the juice and soak gauze compresses with it. Apply to inflammation several times a day for 3 hours. In case of emergency, you can cut an agave leaf and apply it to the boil, bandaging it with gauze.
- Baked onions. The onion is baked directly with the husk, after which it is crushed and 20 grams of grated laundry soap are added to the mixture. At night you need to make a compress from the resulting composition.
- Buckwheat flour. 100 grams of buckwheat are heated in a frying pan until golden brown, then ground to flour. Add a spoonful of baking soda and water until the mixture resembles a thick dough. Apply to the area of inflammation twice a day for 6 hours.
- Grated potatoes. It is necessary to grate raw potatoes on the finest grater and apply to the boils for three hours. After the specified time, the dressing is changed and fresh potatoes are applied. Perform the procedure 3 times a day.
- Cranberry. Based on it, lotions are made in the area of inflammation. To do this, squeeze out the juice of the berries, soak gauze in it and make a compress. It needs to be changed after 6 hours 3 times a day. Both fresh and frozen berries are suitable for cooking.
- Lilac. Lilac leaves are crushed using a meat grinder and applied to the boil three times a day for 1.5 hours. A gauze compress is applied on top.
- Egg yolks. Mix one tablespoon of honey, two yolks and a spoonful of salt. Add a little flour to the mixture until it resembles a thick dough. Apply to the boil until it is completely opened.
- Honey cake. Mix equal amounts of honey and flour, make a cake and apply it to the area of inflammation. Bandage until the boil opens.
- Garlic compress. The affected areas are treated with an antiseptic, after which a thin piece of garlic is applied to it so that it completely covers the affected area. Secure the garlic with a gauze bandage.