Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease that can be contracted through unprotected sexual contact.
The course of the pathology is long and is characterized by certain stages.
The incubation period lasts approximately three weeks.
Then the primary manifestations of the disease appear on the genitals - rashes (chancroid).
The location of the rash depends on where Treponema pallidum (the causative agent of syphilis) entered the body.
If oral-genital sex took place, then the same elements are formed in the oral cavity and on the lips, and during anal-genital contact - in the anal area.
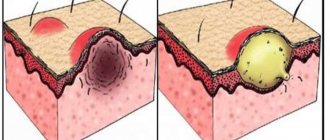
A chancre is an ulcer with a depression in the central part.
The infectiousness of such spots in syphilis is very high, since these areas contain high concentrations of the pathogen.
In the absence of timely therapy aimed at combating treponema, the disease moves to the next stage of development.
That is, into the secondary stage, which is characterized by the formation of a papular rash on the body.
Characteristic locations of spots in syphilis
Elements of the rash can appear on various parts of the body and mucous membranes.
But the most favorite places for localization of spots on the body with syphilis are:
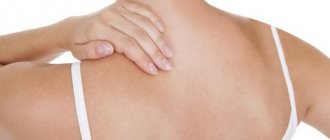
- chest and neck
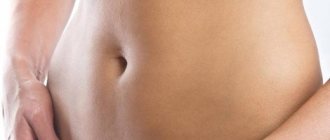
- stomach and back
- face
- shoulders
This feature of the location of syphilitic elements is taken into account by the doctor when making a diagnosis.
But this does not mean that there will be no such spots on other parts of the body.
For example, spots may appear on the legs, which is atypical for syphilis and can cause difficulties in making a diagnosis.
Spotted syphilide
The most common option.
It is observed in all patients without exception.
Most often - at the beginning of the secondary period.
Much less often - in case of relapse.
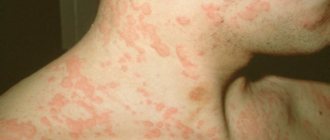
The most common element is roseola.
This is a small spot that starts out pink and then turns red.
Completely disappears when pressed.
The dimensions of one element can reach one and a half centimeters, although they are usually less than 1 cm.
The first spots may appear against the background of fever.
But then the body temperature returns to normal.
Features of roseola fresh syphilis:
- small sizes
- a large number of
- symmetrical arrangement
- pink color
- localization on the stomach and sides
Features of roseola recurrent syphilis:
- large sizes
- small number of elements
- asymmetry
- tendency to group with the formation of various figures (most often rings)
- bluish tint
Special types of roseola:
- raised - resembles a blister
- follicular - has a granular surface
- drain - formed by several adjacent elements
Types of spots with syphilis
A characteristic feature of the pathology is the manifestation of various rashes.
During the primary stage of the process, a hard chancre is formed on the skin and mucous membranes.
This is a painless ulcer, it does not increase in size and does not bleed, and does not grow together with surrounding tissues.
By the end of the primary period the element disappears without a trace.
When syphilis passes into the secondary form, papules, roseola and, in very rare cases, leucoderma are formed.
- Syphilitic roseola. They form on the body during the secondary stage of syphilis. They form on the skin gradually. These are small spots (up to 5 mm in diameter), pink or red spots that do not rise above the skin. When you press on them, they can disappear, and then appear again.
The localization of spots can be very different.
They can be found on the face, arms, back, and rarely on the palms and soles of the feet.
They can form on the chest and neck - a Venus necklace.
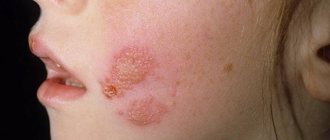
- Papule (papular syphilide) . The rashes are bright red spots that rise above the surface of the skin and do not disappear when you press on them. After some time, the element begins to peel off, starting from the center to the edge (symptom of Biette's collar). After the element disappears, pigment spots remain in its place.
Much less frequently, the disease can manifest itself as:
- Pustular syphilide. The element is filled with purulent contents, in place of which, after drying, a crust forms.
- Pigmentary syphilide. Elements in the form of white spots that form during syphilis in the neck area on its lateral and back surfaces and are called the “necklace of Venus”.
At the stage of tertiary syphilis, syphilides are formed, the formation of which can take months, in the absence of inflammation and pain.
After healing, scars remain instead.
There are:
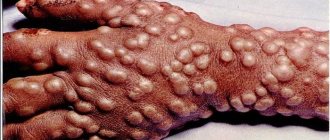
- Tuberous syphilide. It is a nodule protruding above the skin with an infiltrate, no more than 7 mm in size. The nodule is quite dense to the touch and has a red-brown color. The arrangement of the elements is symmetrical, they do not merge and can simultaneously be at different stages of development.
After some time, the syphilide undergoes necrosis and in its place remains a round ulcer with a clean bottom and a smooth edge.
At the base of the element there is an infiltrate.
The healing of the ulcer takes a very long time and a scar forms in its place.
The rashes no longer appear in the same place.
- Gummas. These are single syphilides, which are represented by painless nodes localized in the subcutaneous tissue. The location of the elements can be the forehead, forearms, elbow and knee joints, and shins.
At the initial stages of development, the gumma is characterized by mobility, but with growth the element loses mobility due to fusion with surrounding tissues.
Then a hole is formed in the central part of the syphilide, and gelatinous contents are released through it.
A characteristic feature of gumma is the formation of a crater-shaped pit with a necrotic core.
After its removal, the ulcer heals and leaves behind a retracted star-shaped scar.
In some cases, gumma does not develop into an ulcer.
In this case, syphilide reverses its development and is replaced by connective tissue.
The peculiarity of gummas is that they affect not only the skin and subcutaneous fat.
But they can also penetrate cartilage tissue, muscle tissue, and blood vessels and have a destructive effect on them.
Uncharacteristic spots with syphilis
Due to various reasons related to the individual characteristics of a person or the life activity of the pathogen, the presence of classical manifestations of syphilis may not exist.
The following may form on the skin:
- White spots. When the skin is infected with Treponema pallidum, the functionality of melanocytes may be impaired. As a result, white spots of various shapes and sizes are formed.
- Uncharacteristic locations of syphilides. The presence of spots on the legs, if they are located in the area of flexor surfaces, then as a result of the release of fluid from syphilide, weeping is formed, which leads to the development of microorganisms and the appearance of pain.
The appearance of white spots with syphilis
Colorless spots with syphilis can form on the skin of an infected person six months after the onset of the disease - in the secondary period.
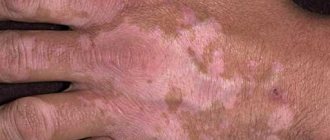
The white spots are called the “necklace of Venus” or syphilitic leukoderma.
These are areas of skin devoid of pigment, no larger than a coin.
The elements do not protrude above the skin and do not cause discomfort.
Externally, syphilitic leukoderma looks like lace.
The main location of the elements is the surface of the neck.
But, leucoderma sometimes affects other areas.
With syphilis, such spots may appear on the lower back, abdomen, chest, and back.
The spots may merge with each other.
Depending on this they distinguish:
- Spotted leukoderma. The elements are located separately.
- Mesh. With this form of pathology, partial fusion of elements is noted.
- Marble. Characterized by complete fusion of spots.
The appearance of white spots is more typical for women.
Such rashes do not contain pathogens.
Syphilides remain on the skin for eight to fourteen months.
The spots disappear on their own even if no treatment has been carried out.
According to one version, the mechanism of development of leukoderma is explained by a violation of melanin synthesis as a result of the action of Treponema pallidum.
According to another, the reason for the lack of pigment is the negative impact of infection on the nervous system, which leads to disruption of skin trophism and destruction of melanin.
Syphilitic leukoderma is a reversible process and after a couple of months the white spots disappear.
Can brown spots appear with syphilis?
Very rare, but they can also appear.
This is also due to disruptions in the pigmentation process of the skin.
Elements are formed during recurrent syphilis.
The color of the rash can be dark yellow to dark brown.
After about 14-21 days, hypopigmented areas of skin remain in their place.
Pigmentary syphilide plays an important role in the diagnosis of secondary syphilis.
Leucoderma must be distinguished from depigmented areas of skin remaining after psoriasis and pityriasis versicolor.
And also from cicatricial changes in the skin after acne, chickenpox.
Unlike scars, leucoderma does not leave behind permanent marks.
Treatment of syphilitic rash
Treatment of syphilitic rashes during all periods of the disease is not carried out separately, since it is only a separate symptom of the disease. Along with it, the entire body is affected and complex therapy for the disease is required.
To treat the disease, antibacterial agents from the penicillin series are used; if they are intolerant, other antibiotics from the group of macrolides, tetracyclines and cephalosporins are prescribed. The schematic prescription of drugs will depend on the stage of the disease and the general condition of the patient.
Treponema pallidum is most sensitive to penicillin-containing drugs that are administered by injection.
Table No. 2. Treatment at all stages of syphilis:
| Stage of syphilis | Features of treatment |
| First | Therapy at the first stage is carried out using water-soluble penicillins. Drugs in this group are most active against the causative agent of syphilis. Treatment is carried out in a hospital setting, since the drugs require frequent injections to maintain the required therapeutic concentration. The penicillin group is the drugs of choice, not only because of its high efficiency, but also because of its availability. The price of medicines is much lower than similar ones. Medicines:
|
| Second | Treatment of the second stage does not differ significantly from the treatment of primary syphilis; penicillin drugs are also prescribed. If they are intolerant, an alternative replacement is selected from the group of macrolides, tetracyclines and cephalosporins. Replacement drugs:
|
| Third | Therapy of the third stage is complicated by pathological lesions of the body, so treatment is prescribed based on the degree of damage to the body and the patient’s condition. As with the first two stages, the main thing is to take antibacterial drugs, but according to a specific regimen prescribed by the doctor. Further, complex treatment includes taking bismuth-based drugs and medications for the symptomatic treatment of damaged organs. |
Important. The instructions for bismuth preparations prohibit the use of the drug by patients with renal and liver failure.
The video in this article is about skin lesions caused by secondary syphilis.
Spots in children with syphilis
When elements of a rash appear, such symptoms cannot be ignored.
How to distinguish spots caused by syphilis from other pathologies?
When children become ill, specific spots form at the stage of secondary syphilis.
Moreover, the rashes are similar to the rash that occurs when infected with childhood infections (rubella, measles, chickenpox).
Another symptom similar to childhood infectious diseases is fever over several days.
The main differences between spots due to syphilis from elements formed due to other reasons:
- rashes remain on the child’s body for a long time – several months;
- the presence of a wave-like course of the disease. Alternation of the appearance of rashes with their disappearance throughout the entire period of secondary syphilis.
The spots, as in adults, can have different colors.
In children, rashes due to syphilis can manifest as:
- roseola
- papules
- pustules
After antibiotic therapy, their number may decrease.
If similar elements of a rash form on the child’s body, you should be examined for the presence of syphilis.
Pediatric doctors very rarely recommend such an analysis, which contributes to the progression of the pathological process.
It is necessary to take into account the fact that not only sick parents can infect a child; infection is also possible through contact.
For example, the patient may be among the adults and children surrounding the child.
The infection can be transmitted:
- when using one pan
- through drinking water
- through close contact with the patient
If secondary syphilis is not treated, the disease will progress to the next stage.
An untreated disease poses a danger not only to the child, but also to adults.
Pathology can negatively affect the functioning of internal organs, and even cause disability and death.
Treatment of the disease includes the mandatory use of antibiotics, and if necessary, the sick child is hospitalized.
Where to go for help
Which doctor should you contact if you suspect syphilis and have acne on your body that does not bother you at all, but does not go away after standard acne treatment?
A venereologist will help you make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment. The doctor will not only conduct an examination, but will also prescribe the correct tests, give recommendations, and, if necessary, advise you to visit a dermatologist or infectious disease specialist if contact with treponema pallidum is confirmed.
Self-medication for syphilis, even at the initial stage, is not recommended. It will not help get rid of the disease, but will only make it worse.
The first drug in treatment will be antibiotics. Local treatment of acne for syphilis is also carried out - antiseptics for topical use, antibiotic-based products and bandages are prescribed.
It is important to remember that any pimple that appears on the body, and especially on the genitals, is a reason to visit a specialist and find out the cause of its origin. Of course, this may be a normal manifestation of acne, but it’s still not worth risking your health.
Author - Anna Mikhailova, dermatologist-cosmetologist of the first category, specialist at the Academy of Scientific Beauty. Especially for the site “Treating Acne”.
When, after infection with syphilis, elements appear
After the infection has entered the body, there are no symptoms of the disease for 1-3 months.
At the end of the incubation period, chancre forms.
At this stage of development of the process, an ulcer forms at the site of infection.
It is saucer-shaped with a hard cartilaginous base of red color and edges that rise above the surface of the skin or mucous membrane - chancre.
With atypical syphilis, red spots may form in the mouth, anus and anus.
If the oral mucosa is affected by infection, the rash can be localized:
- on the tonsils
- palatine arches
- in the language
Syphilis spots in the oral cavity can only appear if pathogens have entered the body through the mouth.
In children, infection of the oral mucosa through domestic means occurs in extremely rare cases.
With secondary syphilis, chancre disappears, and pink spots form on the body - syphilitic roseola.
If the patient has not started a course of treatment, then the elements are capable of relapses at regular intervals.
Characteristic manifestations of syphilis during this period are:
- Roseola forms over the entire surface of the skin.
- Formation of leukoderma - a white rash “necklace of Venus”.
- The occurrence of condylomas in the anogenital zone.
- Formation of papules on the skin, including the scalp, and mucous membranes.
- Formation of pustular syphilides.
- Complete or focal alopecia “crown of Venus”, loss of eyelashes and eyebrows, hair in the pubic area and throughout the body.
- Erosive and ulcerative elements form on the tonsils, papules form in the corners of the mouth, and smooth red spots devoid of papillae form on the tongue - a symptom of a mown meadow.
- On the mucous membrane of the genitals in women, on the penis in men (on the glans, frenulum, foreskin) - roseola, papules.
The tertiary stage of syphilis is characterized by the appearance of tuberous syphilides and gummas on the skin.
During this period, tertiary roseola is formed, which is a large red spot.
The rash is localized on the torso, lower back, and buttocks.
After it disappears, a scar remains on the skin.
The main symptoms of tertiary roseola are as follows:
- scanty rashes
- large element sizes
- symmetrical location of the rash
Recurrent form
Understanding what the rash looks like with secondary syphilis, it is important to pay attention to the recurrent form of the disease. In this condition, the rashes are localized mainly in the area of the extensor surfaces of the arms and legs, as well as on the mucous membranes and in the folds between the buttocks and under the mammary glands.
In the relapse stage, syphilis leads to the appearance of a noticeably smaller number of spots than usual. The color of the rash is faded. Skin formations can be combined with pustular and papular rashes, which are observed more often in weakened patients. When a period of remission occurs, all types of rashes disappear.
It is important to understand that it is during the period of relapse that patients are especially infectious through any contact, even household contact.
During secondary acute syphilis, the rash can be defined as polymorphic. This means that pustules, spots and papules appear on the skin at the same time. Such elements are first grouped, and then merge and form rings, semi-arcs and garlands. Such formations are called lenticular syphilides.
What tests for syphilis are needed for spots
In order to make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to identify the cause of the appearance of the elements, i.e., identify the pathogen.
To do this, you will need to undergo an examination.
To diagnose syphilis, the following tests are performed:
- Microscopic examination of biomaterial taken from rashes. Elements of the rash can be located on the surface of the skin, oral mucosa, tonsils, and rectal mucosa. The technique is low sensitive and often gives a false negative result.
- Bacteriological culture of the contents of chancre and other elements of the rash.
- Lymph node biopsy.
- Serological reactions, ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), RIF, RIBT make it possible to determine the presence of antibodies to the pale spirochete in the patient’s blood.
- Histological study of syphilides.
- PCR from the surface of the spots. This diagnostic method is the most reliable, as it allows the detection of Treponema pallidum DNA in a sample.