Sometimes the treatment of tinea versicolor may be limited to the use of topical medications. Why is this happening? This can be understood if you know what kind of disease it is, the etiology of its development and characteristic symptoms.
Pityriasis versicolor or pityriasis versicolor is a fungal disease caused by increased activity of the fungus pityrosporum ovalis, which is an opportunistic microorganism that lives on the skin of every person.
The disease develops against the background of changes in the acidity of human skin, caused by various factors - abuse of tanning, stress, neglect of hygiene measures, or, conversely, too frequent ablutions. The activity of the fungus increases during allergic reactions, against the background of other dermatological diseases, etc.
The surface of the body is affected - regardless of the area, including the hair growth area. The risk group for the disease is age from 6 to 40 years.
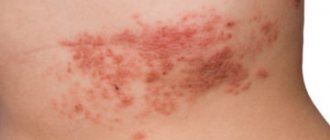
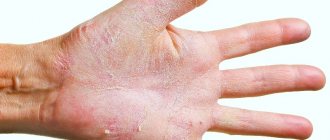
The disease is not dangerous, but due to the appearance of cosmetic defects, patients experience significant discomfort. The spots on the skin can have different colors - light, red, brown. The disease does not belong to the group of contagious ones, since every person has such a fungus, and it worsens only against the background of a decrease in local immunity.
Pityriasis versicolor requires mandatory treatment - if therapeutic measures are neglected, hyperpigmentation intensifies, the skin becomes almost completely covered with spots. You should not “grab” at antibacterial drugs or corticosteroids when you see spots on the skin - this can cause great harm to your own health. Pityriasis versicolor is treated by dermatologists by prescribing special external remedies.
Causes and risk factors of the disease
Under normal conditions, the fungus Pityrosporum orbiculare is not dangerous and does not cause disease. For a person to develop lichen, a combination of factors is necessary that damage the epidermis and promote the growth of the fungus. These include: Reduced immunity (under stress, chronic fatigue, other chronic diseases, fasting, taking glucocorticoids, cytostatics). The risk also increases when changing the climate zone of residence. • Hypo- and avitaminosis – can be caused by errors in diet or diseases of the digestive system. • Tuberculosis • Diabetes mellitus • Seborrhea or dermatitis • Sun or other radiation burns • Failure to comply with hygiene measures • Wearing tight or too tight clothing made of synthetic materials • Hyperhidrosis (the growth of the fungus is affected by the amount and composition of sweat). With this disease, mycosis begins to develop under the arms and in the area of skin folds. • Individual susceptibility of the body to fungal invasion.
In this case, the integrity and protective functions of the epidermis are disrupted, spores and fungal cells penetrate into it and can begin to grow. This is a long process. The rate of development of the disease varies from person to person, so the incubation period ranges from 14 to 180 days.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of pityriasis versicolor is based on a typical clinical picture and is confirmed by:
- examination of lesions under a Wood's lamp (yellow glow);
- microscopic examination (confirms the presence of fungal spores);
- Balzer's test (5% iodine tincture is used to treat lesions and healthy areas of the skin. In places where the stratum corneum of the epidermis is loosened by a fungus, the skin will turn dark brown, healthy areas of the skin will turn light orange.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with pityriasis rosea and secondary syphilis, which have similar symptoms.
How is the disease diagnosed?
Like many dermatological diseases, diagnosis is largely based on visual examination.
Features of spots
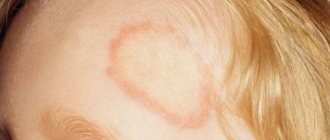
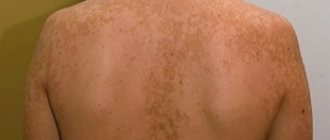
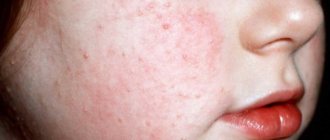
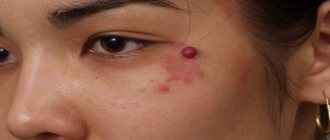
Location: on the sides of the abdomen and chest, on the shoulders and neck. Less often - on the back, legs, arms. Damage to the extremities is typical for patients in adolescence. In the rarest cases, the face or scalp is affected. In the latter case, they are difficult to notice, since the skin under the hair is quite light, and a special lamp is needed to detect the fungus.
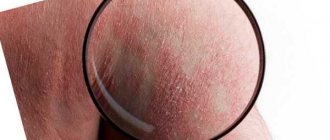
Color: yellowish, light pink or pale brown. This depends on the original pigmentation of the person's skin.
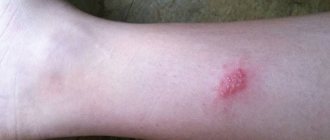
Shape: round spots are located randomly and asymmetrically on the affected areas. The edges are clearly defined, with an uneven contour. In one person, spots on different parts of the body may have different sizes and colors. Old spots are more elongated, oval in shape. The affected areas are located flush with the skin.
Size: at the beginning of the disease, the diameter of the marks is less than 1 cm. Over time, new spots appear, old ones increase in size and merge into continuous fields.
Itching and pain: absent.
Peeling: small scales in the central parts of old spots. It intensifies over time. On fresh affected areas it appears when the skin gets wet.
Diagnostics
Despite the rather characteristic symptoms, the disease can be confused with other types of lichen. Therefore, to make an accurate diagnosis, you need to contact a dermatovenerological clinic.
Differential diagnosis
It is required to exclude in a person: 1. Pityriasis rosea, a characteristic feature of which is pink scaly spots. The rashes are single and scattered throughout the body. 2. Vitiligo - spots that are sharply depigmented, with smoother edges, without peeling. 3. Syphilis - syphilitic roseola is a pink round spot up to 1 cm in size. They do not grow and do not merge with each other. When pressed they turn pale and disappear.
Diagnostic measures
To accurately diagnose tinea versicolor, specific tests have been developed to identify the fungus in the epidermis. 1. Scraping of the epidermis The upper layer of tissue is collected and microscopyed. The most reliable method. 2. Balzer test Allows you to diagnose solar bending without scraping. To do this, apply a 5% iodine solution to clean skin. The affected areas, if there is a Pityrosporum fungus there, are more intensely colored than healthy skin. 3. Wood's lamp Used to identify ringworm under the hair. In its light, the affected areas become yellow.
Additional symptoms
Allows one to suspect pityriasis versicolor. • Affected areas sweat more. • They do not tan. • If the sun hits the spots, they become lighter. In autumn and winter, when wearing closed clothing, the areas darken.
How to cure pityriasis versicolor: effective shampoos. Antifungal shampoos for ringworm
Ringworm is a fungal disease that affects the superficial, deep layers of the epidermis and hair.
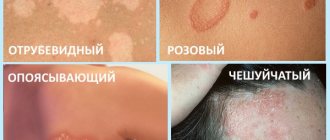
Based on the nature of symptoms, methods of infection, and degree of danger, the following types of lichen are distinguished in practice:
- pityriasis,
- shearer,
- red flat,
- pink,
- encircling.
The most dangerous diseases for humans are shingles and ringworm. They do not go away on their own and require complex treatment. You can also read in more detail why lichen is dangerous for humans.
Shampoo for lichen is the first remedy when choosing a treatment. It protects the hair from further destruction, restores the skin Ph-balance, promotes speedy healing and destroys the causative agent of lichen. Each antifungal shampoo has its own set of contraindications and application regimen. The selection of the remedy should be done by a doctor.
The benefits and harms of shampoos against lichen
Ringworm, pink, and pityriasis versicolor are treated with shampoos if rashes characteristic of lichen are found on the scalp. If the disease manifests itself externally, only these means can be used.
Main advantages:
- Makes the scalp and hair healthy, also eliminates dandruff, which can turn into seborrhea;
- They are easy to use at home;
- Few contraindications;
- They destroy the fungus in 3-8 days;
- Can be used as a prophylactic against the risk of contracting lichen.
Peculiarities:
- all contain ketoconazole;
- the shade varies from orange to pink;
- all have minor differences in composition.
If the shampoo is used incorrectly and intensively, the scalp may dry out and the course of the disease will become more complicated.
Antifungal shampoo is a medicine; it is not advisable to use it for normal hygiene without reason.
Nizoral
In addition to cleansing and tanning agents, Nizoral contains an antifungal component - ketoconazole. It quickly penetrates the fungal cell, destroying it. The appearance of new spots stops, old ones heal, and the hairline is restored.
Nizoral is a leader among other anti-lichen drugs for people. It needs to be used every day for a week. Shown even to babies. But women in the 1st-2nd trimester of pregnancy need to consult a doctor.
It is widely used by people in prevention when there is a risk of contracting lichen.
It is in a high price category (750-800 rubles), unlike its analogues.
Mycozoral
Antifungal shampoo that helps get rid of pityriasis versicolor, dandruff, seborrhea. Reviews indicate that after 3-5 days of use, itching, irritation, and pain in people disappeared.
It can be used at any age and condition. Ketoconazole, which is part of the product, does not completely penetrate the body. Rare side effects include local reactions: dryness, burning of the scalp, hair loss. If these symptoms appear, it is recommended to stop treatment with shampoo and go to the doctor.
To treat pityriasis versicolor in humans, a course of 10 days with daily use is required. If recovery does not occur, you can extend it for 2 weeks.
For preventive purposes against lichen, as well as to eliminate dandruff and seborrhea, the drug must be used for 30-60 days. Wash your hair once a week.
If a person has previously used hormonal ointments or anti-fungal tablets, they cannot be stopped immediately. The dosage is reduced over the course of a week until it stops completely.
Source: https://xn--80ahsaqcbqq.xn--p1ai/preparaty/horoshij-shampun-ot-lishaya.html
Consequences of the disease
Pityriasis versicolor itself does not pose a health risk. The fungus affects only the upper layers of the epidermis. The course of the disease does not cause physical discomfort, manifesting itself in most cases as cosmetic defects.
However, when multiplying, the fungus still damages cells, which can become an entry point for more dangerous pathogens. Fungal spots are easier to scratch; when wet, the epithelium peels off. When an infection occurs, the following may occur: • Seborrheic eczema • Dermatitis • Pyoderma Even after a course of treatment, white, depigmented areas remain on the skin, and it takes time for the natural color to be restored.
Therefore, if a dermatologist diagnoses a fungal infection, treatment should begin immediately. This will reduce the risk of infectious complications and eliminate appearance defects.
Side effects
Treatment must be both effective and safe. Adverse reactions after using antimycotic ointments occur if medical recommendations are not followed.
The most common symptoms that appear are:
- allergies in the form of angioedema or urticaria,
- accelerated hair growth in the application area,
- skin hyperemia,
- peeling of the affected area,
- swelling,
- feeling of burning and itching.
If the ointment gets inside, vomiting, nausea, and headaches may occur. To eliminate the reaction, you should rinse your stomach and consult a doctor.
Ointments for ringworm are highly effective, but provided that the treatment regimen is strictly followed. Therapy for the treatment of such a disease must be comprehensive. The use of ointments or gels should be supplemented with systemic medications. This approach will help to significantly shorten the period of complete recovery and prevent the development of relapses.
Treatment of ringworm
Since a sick person is not contagious, and the disease does not pose a threat to life, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis.
Hospitalization may only be required if pyoderma or other bacterial complications develop.
Preparations for external use
Local preparations (ointments: Nystatin, Levorin, Pimafucin, Clotrimazole, Ketoconazole, sulfur ointment; solutions with salicylic alcohol, sprays)
Preparations for internal use
1. Immunomodulators: echinacea, immunal.
2. Vitamin and mineral complexes.
3. Tablet drugs: Fluconazole, Itraconazole, Orungal, Rumikoz and others.
Taking systemic medications is necessary to destroy fungal cells that have penetrated deep into the dermis. They speed up complete recovery and eliminate the possibility of relapse if you take the full course of the drug.
In advanced cases of long-term disease, it may be necessary to prescribe medications to restore the integrity and pigmentation of the epidermis. These include neotigazon .
The doctor selects the medications taking into account the severity of the disease and the presence of concomitant pathologies in the patient.
The standard course of treatment lasts 2-3 weeks. The use of external agents continues until all lichen spots disappear. It is necessary to follow the instructions for the drugs and not skip treatments.
Additional measures
Needed to improve overall health and prevent re-infection. Compliance with the rules of a healthy diet: a diet without fried and fatty foods, with a reduced content of sweets and flour. The use of soda is not recommended. Drinking alcohol is prohibited. • Sunbathing • Careful body hygiene. It is recommended to replace regular shampoo with medicinal shampoo (Nizoral, etc.) • Disinfection of housing (surfaces, bed linen, clothes, towels)
Folk remedies
You can use various external agents if you are not allergic to their components. 1. Boric acid 10 g. the acids are diluted in 200 ml of boiling water and cooled. A cotton ball is soaked in the solution and the stains are wiped 2-3 times a day. 2. Celandine For infusion 10 g. chopped dry or fresh herbs pour 400 ml of boiling water. Cooking time – 20 minutes. Wipe the affected areas with the infusion 2 times a day. 3. Seed and eucalyptus Take the components in a ratio of 1:1 and 20 grams. pour 250 ml of boiling water over the mixture, close tightly and wrap for 30 minutes. Wipe the skin in the evening before bed. 4. Cocklebur For decoction 10 g. the herbs are poured into 500 ml of water, brought to a boil over high heat and boiled for 10 minutes on low heat. Leave for 2 hours. Strain the broth. Drink 50 ml once a day before meals for 7 days. Treating a fungal infection requires patience. Antifungal drugs, folk remedies and a healthy lifestyle will help you deal with the fungus once and for all and avoid the unpleasant consequences of this disease.
Mechanism of action of antimycotics
Regular treatment with antifungal ointments and creams is the main method of treating lichen versicolor. Before applying them, the affected areas are wiped with antimycotic drying liquids (salicylic alcohol and resocin solution).
External preparations have antibacterial properties. They violate the integrity of the membranes of fungal cells, which leads to the death of pathogenic microorganisms.
The active ingredients of local antimycotics destroy strains of fungi, staphylococci, streptococci, gardnerella, and trichomonas.
Ointments and creams cleanse the skin and restore the epidermis at the cellular level. Signs of the disease begin to subside when antimycotics are used. After applying the drug, the patient feels relief. His unbearable itching and flaking disappear, the number of rashes decreases, and his health improves.
With prolonged use of antifungal agents, metabolic processes occurring in the skin are improved. Creams and ointments relieve irritation and discomfort, promote depigmentation. Under their influence, the spots fade and become invisible.