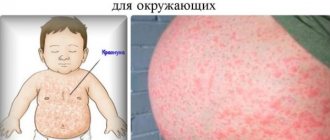
What is prickly heat
Miliaria (heat rash) is a skin disease that often occurs in newborn babies.
The skin of a child under one year old is very sensitive to even the slightest environmental influences and illiterate care, as a result of which redness and rashes may appear on it. In itself, prickly heat in newborns is not dangerous; it cannot be contracted.
However, inexperienced parents may mistake the symptoms of dangerous problems (allergies or infections) for signs of prickly heat, because they are often similar. But if prickly heat can be easily treated with home remedies, treatment of infections and allergies requires urgent medical attention.
Symptoms of the disease
In very young children it very rarely occurs exclusively in the form of redness of areas of the skin. They appear as red blisters and nodules, inside of which there is 1 to 5 mm of fluid.
Rashes on a child’s skin bring him unpleasant feelings because friction appears between the crust that appears, clothes and tissues.
Minor movements begin to cause discomfort, then the child begins to be very capricious, cry and get irritated at the slightest reason.
Miliaria in an infant can lead to secondary infections, as the affected areas of the skin become easily vulnerable.
At the first symptoms and suspicions, it is necessary to begin treatment. The doctor will tell you how to treat heat rash.
There is no need to look for how to treat miliaria on your own, because it is very easy to mistake it for an allergy, and in this case the treatment will not bring any results. The doctor will establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Why does it often occur in newborns?
If your baby has heat rash, don’t worry, because you can get rid of it quite quickly if you follow simple rules for caring for your child’s skin. Just try to start treatment as early as possible so that the process does not reach a serious stage.
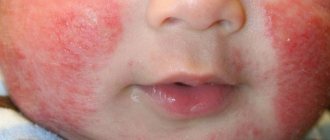
Usually prickly heat in babies occurs in the summer heat. But, if you are used to wrapping your child in a blanket that is too warm in winter and spring, then it may appear in the cold season. When a baby's sensitive skin is severely irritated, a small red rash appears on it - the main sign of heat rash.
Why is the skin of newborns prone to prickly heat? It's all about unformed sweat glands, which will begin to work in normal thermoregulation mode only by the age of 5-6 years. In addition, children's skin is still very thin and sensitive, it has very powerful blood circulation, and it consists of 85% water (unlike adult skin, which retains only 65% moisture).
The processes of constriction and dilation of blood vessels, which occur quickly in an adult body, are still slowed down in a child’s body - so thermoregulation also occurs very slowly. This is why the newborn’s body overheats and becomes hypothermic instantly.
Causes of heat rash in infants
And yet, even in hot weather, heat rash may not appear in a newborn if the baby’s skin is always breathing. But places where air flows poorly are high-risk areas. Most often, overheating of a baby’s body is caused by too warm clothes or a blanket, as well as tight swaddling: without air access, sweat cannot evaporate in time, and when it accumulates, irritation occurs.
The most common causes of prickly heat:
- keeping the child in a stuffy, hot and humid room;
- Irregular bathing of the child;
- frequent use of fatty cream, especially in hot weather;
- the use of children's clothing not made from natural, but from synthetic materials;
- the child is constantly in a diaper;
- heavy sweating due to increased body temperature;
- dressing the baby in tight and very warm (unsuitable for the weather) clothes;
- wrapping yourself in warm blankets.
The skin of children who were born prematurely, as well as those who are overweight and have diabetes, is more likely to develop rashes because their skin practically does not synthesize the pigment melanin. Normally, it is produced by special cells - melanocytes, “coloring” a person’s hair, skin and eyes a certain color. In addition, melanin has a special function - protecting the body from sunlight. When melanin is not synthesized enough in the skin, it becomes very sensitive to ultraviolet radiation.
Miliaria can also be a concomitant symptom when a baby is sick with acute respiratory infections, measles, tonsillitis, or pneumonia.
Prevention
You can prevent the appearance of prickly heat if you follow certain rules and avoid excessive sweating.
Often prickly heat appears due to obesity, and therefore getting rid of extra pounds allows you to take the first step towards normalizing the functioning of the sweat glands and preventing the appearance of a pathological process on the skin.
Necessary:
- In hot weather, wear light clothing made of natural fabric, thus providing ventilation to the body. Clothes should not fit the body; they should be changed as often as possible;
- Avoid excessive physical exertion, especially in hot weather;
- Take water procedures twice a day, then wipe thoroughly;
- Limit your time in the sun, and do not use cosmetics and creams that clog pores during the summer season. It is advised not to overuse deodorizing products in order to prevent the appearance of a sweaty odor, since the use of some products in large quantities can cause irritation;
- Ensure regular ventilation of the premises, avoid high humidity and stuffiness.
Miliaria can be cured completely if therapy is organized in a timely manner. To prevent relapse, it is necessary to observe preventive measures and personal hygiene standards.
Symptoms and types: what does prickly heat look like and how does it manifest in infants?
Miliaria can manifest itself with various symptoms:
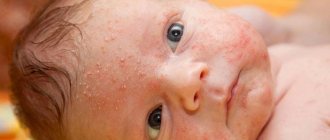
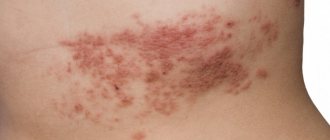
- in the form of nodules or bubbles against the background of red skin, which does not merge into a single “picture”; such rashes can most often appear in skin folds - on the neck, groin, armpits; they can cause pain and also be very itchy (this becomes obvious when the baby tries to scratch the redness); similar symptoms may last 1-2 weeks;
- in the form of silver or white bubbles that appear on the neck, torso or face. Bubbles with contents can merge into a single large spot, then they burst, gradually dry out and peel off; such a rash is usually not painful or itchy, and symptoms last no more than three days;
- in the form of flesh-colored bubbles: they may appear several hours later, after the baby has overheated and sweated; bubbles appear on the torso, arms and legs and disappear quite quickly, leaving no traces;
- in the form of complicated forms (white and yellow prickly heat).
Types and signs
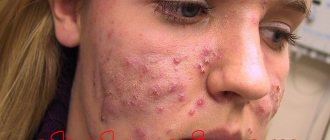
Miliaria in an adult can occur in three clinical forms: papular, red, crystalline. Depending on the manifestations and severity of damage to the skin, the following types of prickly heat are distinguished: crystalline, red, white, papular, or deep. In adults, the papular type of the disease is most often recorded. There are 4 types of prickly heat, each of which has its own symptoms: crystalline, red, apocrine and papular.
Based on the degree of skin damage, a distinction is made between localized, when rashes appear on individual parts of the body, and generalized, when rashes are spread throughout the body.
Signs of prickly heat include a small rash in areas that are more susceptible to increased sweating, or on the folds of the skin, itching, swelling, sometimes crusts form in areas of scratching, hyperhidrosis, accompanied by peeling, and weeping skin. The color of the bubbles or nodules varies from pearlescent to crimson. The patient becomes nervous, sleep and rest patterns are disrupted, and he can only fall asleep in a room where the air temperature is quite low. With severe types of prickly heat, an increase in temperature and loss of appetite may occur.
Crystal prickly heat
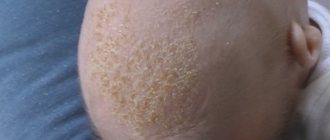
This type of disease is considered the mildest and most harmless. The rash is pearlescent, small in size (1 – 2mm). A rash appears as a result of the active work of the sweat glands, mainly on the legs and arms, and on the torso. There is no itching or irritation. Symptoms go away on their own within 3 to 5 days, after which flaky skin remains.
Miliaria rubra
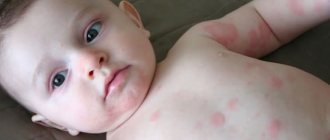
The skin rash has the form of blisters filled with liquid. Rashes with a diameter of about 2 mm are surrounded by inflammation. The liquid inside the blisters is cloudy, sometimes white, which indicates the severity and severity of the condition. The itching is very strong, which leads to scratching. As the disease progresses, weeping wounds form at the sites of the blisters, which become covered with a crust that tends to become soggy. The disease requires treatment; lack of therapy can aggravate the condition by adding secondary bacterial infections. Miliaria rubra appears mainly in the groin and armpits, in the area of skin under the mammary glands and on skin folds. The duration of treatment for this type is on average 10 days.
Miliaria alba
Miliaria alba is of the papular type. With miliaria alba, flesh-colored rashes appear, no more than 3 mm in size. Residents of tropical weather zones, who are unaccustomed to such a climate, are especially susceptible to this species. The disease is easily treatable; lack of treatment leads to progression to pyoderma.
Miliaria profuse
Represents a more severe course of the disease. This species is considered the next stage after miliaria rubra. Papular or deep miliaria occurs with a sharp change in climate, is characterized by an acute inflammatory process in the superficial layers of the skin and is accompanied by the development of papular vesicles (vesicles - papules). This type of prickly heat is detected by an increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels, pain in the affected areas of the skin, as well as swelling of problem areas and hyperemia.
Apocrine miliaria
The cause of this heat rash is a disruption of the apocrine glands located in the armpit, labia majora, nipple areola and around the anus. At the beginning of the disease, a small pink rash appears, after which infiltrates and painful pustules develop. The disease requires timely treatment.
Intertrigo
The human skin contains a large number of microbes, bacteria and fungi. If a person's immune system is functioning normally, these pathogenic agents are not a threat and cannot cause disease. With overheating, prolonged wetness, skin friction, increased sebum production, insufficient ventilation of the dermis, an allergic reaction, sweating or poor hygiene, the protective layer is destroyed. The skin becomes vulnerable to pathogens, which in a humid and warm environment begin to actively multiply, which causes irritation - diaper rash.
In adults, diaper rash can occur due to incorrectly chosen synthetic underwear, which rubs the skin and impairs its ventilation. Diaper rash often appears in obese people as a result of increased sebum production, when skin ventilation is impaired, sweating and irritation are observed.
People who are seriously ill, especially those with fever, kidney problems, endocrine diseases, or people with limited mobility are at risk of developing diaper rash. In this case, skin irritation can occur not only in the area of skin folds, but also on the back or shoulders. Diaper rash most often appears in the inguinal-femoral folds, on the buttocks, between the fingers, under the mammary glands, in the armpits, in the abdominal folds and cervical folds in overweight people.
Signs of diaper rash are:
- Redness of the skin (erythema) at the site of inflammation;
- Attachment of pimples (papules) to erythema;
- The appearance of wet areas (dry) with elevated local temperatures;
- Burning, itching and pain in the affected areas of the skin;
- The appearance of pain and burning when in contact with feces, if diaper rash forms in the groin.
Diaper rash develops in stages. In the initial phase, the skin becomes red in the area of inflammation. The second stage is characterized by bright erythema, the presence of cracks and erosions. The third stage is the most severe, since a secondary infection joins the inflammatory process.
To prevent the appearance of diaper rash, personal hygiene is recommended; diaper rash at an early stage can be treated using air baths, irradiation with a Minin lamp, UV irradiation and EHF therapy.
Diaper rash of the first and second stages is treated with Guardian balm. The product contains oils, vitamins e and a. The balm has antiseptic, antipruritic, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects, and also promotes the regeneration of affected skin and increases the barrier functions of the skin.
Infected heat rash
Inadequacy of the sweat glands, as well as the effect of their secretion on the skin (sweat contains various salts and some substances harmful to the body) cause the development of prickly heat. As a result, skin irritation and an inflammatory process develops, which reduces natural defenses and makes the inflamed area permeable to various pathogens. If personal hygiene rules are not observed and severe forms of the disease are not treated, there is a risk of the inflammatory process spreading, as well as the introduction of pathogenic microorganisms into the skin, which leads to the development of infected miliaria.
Infected miliaria manifests itself in several types of rashes:
- Red infected prickly heat. The rashes have the form of red, itchy blisters that do not merge with each other and are characterized by relative homogeneity. On palpation, the blisters are painful; the pain may intensify when being in a warm room with high humidity. The most common localization of the red rash is the neck, axillary and buttock folds.
- White infected miliaria. In most cases it occurs in children. The cause of the development of miliaria alba is the penetration of pyogenic microflora into the thickness of the epidermis.
As a result, the development of bubbles filled with cloudy gray or white liquid is recorded.
The main causative agent of the disease is staphylococcus, which, if not treated in a timely manner, can lead to secondary skin changes and the formation of scars and depigmentation in place of former miliaria alba.
- Crystalline infected miliaria. May act as the initial phase of miliaria alba. It looks like bubbles with a clear liquid (accumulation of droplets of sweat). The rashes can merge with each other to form large areas. It often goes away on its own after washing or drying the skin with talcum powder.
- Deep infected miliaria develops quite rarely. Infection occurs when scratching at the time of their formation. Has a tendency to transform into other forms. It is localized, in most cases, on the skin of the torso, thighs and shoulders.
Allergies, chickenpox and prickly heat: how to distinguish?
As already mentioned, the main symptom of prickly heat is a rash and redness of the skin. These manifestations of miliaria may affect only one area of the baby's body (for example, the armpits or groin), or they can spread more widely. If your child is very young, the symptoms of heat rash can be irritating, causing anxiety and disrupting sleep. But since chickenpox, measles and allergies begin with symptoms similar to prickly heat, it is better to show the baby to a pediatrician.
How to understand that a child has heat rash and not another disease? Remember: have you violated the hygiene rules for caring for your baby’s skin over the past few hours? Namely:
- if you have poorly maintained hygienic skin care, miliaria in newborns appears in the neck area;
- if the child overheats and has been wearing clothes made of synthetic fabrics for some time, prickly heat will appear on the back;
- if you often apply a rich cream in the groin area and rarely remove your baby’s diaper, prickly heat will develop in the groin area and buttocks;
- if the rash from prickly heat that appears on the neck is not treated in time, it can spread to the face;
- when the baby is constantly wearing a hat (even at home and on hot days), a rash may appear in the head area.
If you treat the baby’s delicate skin in a timely manner and follow the rules of care, the prickly heat will go away quite quickly. But a rash due to infection or an allergic reaction, on the contrary, will spread progressively.
Treatment of heat rash in infants
In order for the treatment of prickly heat in newborns to quickly give the desired result, you must first get rid of the causes that provoked prickly heat:
- Monitor the air temperature in the room where the child is constantly located; it should not be higher than 22 degrees; at higher temperatures, try to ventilate the room more often;
- do not use synthetic fabrics for your child’s clothes and bedding;
- leave your baby without a diaper more often - especially when he is awake at home;
- do not be afraid to “catch” the child in a warm room, constantly wrapping him in a warm blouse and rompers: at a temperature of 20-22 degrees, a healthy child will not freeze;
- do not use fatty creams and oils - especially for the groin areas, it is better to use powders;
The following will help eliminate the symptoms of heat rash in newborns:
- the use of herbal decoctions of string, chamomile and special mixtures while bathing a child: you can brew herbs according to the instructions, preparing about a liter of decoction in advance and then adding the cooled infusion to a bath of water; you can wipe the areas of the skin where prickly heat occurs with a decoction after taking a bath; A weak solution of potassium permanganate added to the bath has a slightly drying effect;
- After taking a bath, the baby's skin must be thoroughly dried with blotting movements - especially in the armpits and groin areas, as well as on the neck. Areas affected by prickly heat can be treated with a powder containing zinc oxide, starch, talc, anesthesin (for easy cooling) and panthenol (for rapid healing of wounds);
- on the recommendation of a doctor, you can use creamy products Bepanten, Desitin, Drapolen: they will help cope with rashes faster.
- For prickly heat in newborns, folk remedies can also be effective: wiping the affected areas with soda (1 tsp) dissolved in water (1 tbsp.); sprinkling the rash with starch; rubbing with infusion of bay leaves (7 pieces per 1 tbsp. boiling water).
How to help a baby - competent therapy and prevention
Surely you yourself already understand that effective treatment of prickly heat without eliminating the factors that provoke it is impossible. But removing the root cause is not so easy - habits, the opposition of grandmothers-controllers, and the imperfection of centralized heating get in the way. However, there is an action plan that will make prickly heat a rare guest in your home.
The most important step is eliminating the cause
First of all, help your baby get rid of excess heat and also clean out clogged pores. For this:
1. Undress and bathe him in boiled warm water using a bath or shower. It is strictly not permissible, especially if there are ulcers, to swim in a children's pool or in a bath with artesian unboiled water.
2. If it is impossible to organize a full bath, wipe the affected areas with damp antibacterial wipes that do not contain alcohol.
3. If the room temperature is 24–25°, after the hygiene procedure, leave the baby completely naked - do not even put diapers on him.
By allowing the affected areas to air, you thereby accelerate the heat exchange of the skin and give it the opportunity to cleanse itself, without any additional drugs. However, make sure that the baby does not scratch the rash - to reduce the risk of infection, you can even put anti-scratch guards on the hands.
The next stage is antiseptic treatment of redness
To speed up the healing process, treat your child's skin with a safe antiseptic. Do not under any circumstances use iodine, brilliant green or alcohol-containing liquids, and do not apply thick creams based on mineral oils and petroleum jelly. Here is a list of remedies that are usually prescribed by doctors to treat prickly heat at home:
- baby powder, ointments or talc with zinc;
- 5% soda solution (for 1 glass of boiled water, 1 teaspoon of baking soda);
- a decoction of herbs with an anti-inflammatory effect - string, oak, calendula, chamomile (brew 75 g of dry raw material in a liter of water, leave for 30 minutes and add to the bath or wipe areas with rashes with it).
Sometimes, to reduce the manifestations of prickly heat, antihistamines are used - Fenistil (gel or drops), Suprastin, Tavegil. However, without instructions from the treating doctor, it is not permissible to use them as self-medication for infants.
If you understand the principle correctly and follow the recommendations exactly, you will see signs of improvement within 24 hours. Keep up the good work and the results will stick. Now your task is to prevent a relapse, and this requires re-evaluating some points.
When is urgent pediatrician care needed?
- if, subject to hygiene rules and treatment, the rash does not go away after 3 days;
- if the rash interferes with the child’s normal sleep, causes itching, pain and anxiety;
- if there is serious inflammation and swelling at the site of the rash;
- if ulcers with an unpleasant odor or cracks have formed in the affected areas;
- if the baby has a fever;
- if prickly heat in an infant continues for more than three days, and instead of improvement (drying out of the rash), the opposite process occurs (yellow or white liquid appears inside the blisters, the scale of the rash increases, and the child behaves very restlessly), consult a pediatrician immediately;
- If bloody contents are released from the rash, and the baby begins to vomit, call an ambulance immediately.
Such symptoms may signal an infectious process, and it will be difficult to cope with it without the help of a doctor. Contact your pediatrician: he will either prescribe treatment on his own or refer the child for a consultation with a dermatologist.
Complications
If the symptoms are not eliminated, the disease progresses to vesiculopustulosis. It manifests itself as purulent blisters, with crusts forming after they burst. Complications can be in the form of:
- otitis;
- pneumonia;
- omphalitis;
- pyeloniphritis.
The most dangerous complication after vesiculopustelesis is sepsis. The baby becomes weak, has a high temperature, and stops breastfeeding. Elimination of purulent diseases in children is always carried out in the hospital; in such situations, the doctor prescribes antibacterial therapy and detoxification drips if necessary.
How to prevent heat rash in newborns
- Your baby will not develop heat rash even in the hot summer if you always dress your child according to the weather and monitor the temperature in the children's room;
- choose clothes for your baby not based on “beautiful”, but on the quality of “breathable” materials;
- dress your child in loose clothing;
- change your baby’s diapers regularly and often leave him naked to “ventilate”;
- bathe your baby daily;
- do not swaddle your baby too tightly;
- use powders and baby creams exclusively on a water basis;
wash children's clothes with special hypoallergenic products.