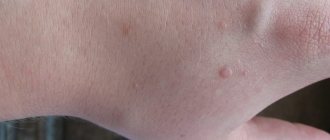
When immunity decreases, human papilloma viruses (HPV) present in the body may appear on the human body.
The appearance of neoplasms causes anxiety in the carrier, due to the possible belonging of the wart to structures that are a marker of the presence of a highly oncogenic virus in the body.
Having information about how papilloma differs from condyloma makes it possible to confirm or exclude concerns before consulting a dermatologist and receiving test results.
general information
Constant rashes on the skin, according to most doctors, indicate the presence of pathogenic microorganisms, which we know as parasites. Thanks to them, our immunity weakens and the body is poisoned. And therefore, in order to avoid skin problems, it is so important to cleanse yourself of all uninvited guests.
As for such a pathogen as the papilloma virus, there are up to 60 types of it! Moreover, among them there are also those that lead to the development of oncological processes in the human body. Now it’s time to move on to the question: “What is the difference between micro-papillomas and condylomas?”
How not to get confused?
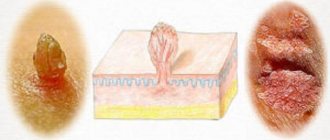
Both formations are not much different from each other. However, condylomas tend to grow in places where there is contact with clothing. The reason for this is that friction causes a slight inflammatory process and damage to the epidermis, which reduces the protection in this area. Against the background of decreased local immunity in this area of the skin, the likelihood of penetration of pathogenic microorganisms increases, which often leads to secondary infection. Papillomas are more varied in shape and color, but these benign formations have a neat, close to round shape. But this does not exclude cases of papillomas of other forms. Both formations are in fact pathological growths of tissue and their shape may vary from case to case.
What are papillomas?
These are benign neoplasms that can be attributed to symptoms of papilloma viral infection. These growths appear in most people, regardless of age. They have a soft structure, round or irregular shape, and feel rough to the touch. The size can be about 10 mm in diameter, brown or flesh-colored.
As a rule, neoplasms can be localized on any part of the body, but they can often be found in the following places:
- on the neck;
- in the axillary region;
- on the back:
- on the fingers;
- on the palms;
- on the sole of the foot.
Moreover, thread-like neoplasms appear on the neck, under the armpits and below the chest, which in medical language are called acrochords. Their appearance may be due not only to a decrease in immunity, but also to a number of other factors, which include excessive physical activity, hormonal imbalance, frequent stress and the presence of chronic diseases. Also at risk are those people who abuse bad habits (smoking, alcohol). In the photo, papillomas and condylomas do not look very attractive, and in general, they cause a lot of inconvenience to a person, so it is worth taking care of their removal.
What is typical is that the pathogen can be present in the body without revealing itself, and is activated only under favorable conditions. And while it is in sleep mode, comprehensive diagnostics will be required to identify it.
As a rule, with age, not only the number of papillomas can increase, but also their size. At the same time, this does not cause any noticeable physical discomfort, and there is no threat to life from the presence of these formations.
What are condylomas
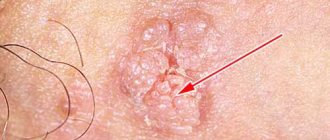
Now it’s time to consider another type of neoplasm - condylomas. They are often localized on the mucous membrane, and in appearance they are more similar to papillae, chicken comb or cauliflower. Moreover, condylomas can not only be pointed, they also have a wide apex.
As a rule, these neoplasms are also benign and are often localized in the perineal area singly, but most often in groups. Only, unlike papillomas, condylomas are prone to fusion, due to which a shape similar to cauliflower is formed.
The incubation period of the virus usually ranges from 7 days to six months, and during this period there will be no growth on the body. But after the appearance of condyloma, it reaches its maximum size within a few hours.
Other types of growths caused by HPV
Papillomas, unlike condylomas, have more varieties, which are also caused by papillomavirus:
- Vulgar (simple) - affects the skin of the face, hands, knees. The growths are round in shape, grow up to 5 mm in diameter and rise above the surface of the skin like a hemisphere. Commonly called warts.
- Flat (youthful) - affect the skin of the face and hands, protrude slightly above its surface, have a rounded shape, and often cause itching and burning.
- Plantar - occurs on the soles of the feet. At the beginning of their development they resemble calluses, but gradually the edges of the growths expand, and the papilloma itself grows inward.
External differences
Now it’s time to find out what, in fact, is the difference between papilloma and condyloma. Both of them have several varieties. Among condylomas, two forms are common:
- Wide – fixed on the surface of the skin thanks to a wide base. These growths appear due to the re-development of syphilis. And they pose a threat due to the fact that in the area of their localization the layer of epithelium changes, which leads to malignant formations.
- Pointed - such neoplasms are attached to a stalk, often appear on the mucous membrane of the genital organs, mouth, throat and armpits. At first, these growths look more like just a cosmetic defect on the skin, but over time they begin to bleed and an inflammatory reaction occurs.
Papillomas also have several forms:
- Keratopapillomas. They are popularly known as simple warts. Initially, they look like pigment spots on the skin, but quite quickly grow to the size of the growth itself, with a diameter of 10 to 15 mm.
- Thread-like growths. They are also called true papillomas and initially appear as a yellow spot. Over time, it begins to stretch out and acquire a rounded shape. A thin stem is used for attachment, and such growths are most often localized on the neck, back, and face.
- Flat papillomas. These are round growths no more than 2 mm high. Their shape is mostly round, but can also be irregular. Their main habitat is the face.
Knowing how condylomas differ from their opponents is necessary in order to determine further actions.
Of course, many doctors recommend getting rid of any type of growths on the human body, due to the risk of developing oncological processes. At the same time, some of these growths can remain with a person all his life and not cause him any concern.
Symptoms and signs
The symptoms of HPV depend on the underlying cause. The disease has no general clinical symptoms. But the following signs stand out:
- formation of growths,
- skin irritation,
- discomfort during sexual intercourse,
- redness and itching.
Attention! Skin irritation and itching sometimes indicate other pathologies. If such symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
A number of other distinctive features
It is not difficult for a specialist to identify the difference between condyloma and papilloma from a photo, while ordinary patients do not always succeed. But in addition to the above, these neoplasms can be distinguished by a number of other factors. An important indicator is density - papillomas are harder to the touch, which cannot be said about condylomas. They also mostly occur in different places. Condylomas, as a rule, are localized exclusively on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, in the genital area or around the anus. As for papillomas, they occur on the mucous membrane in rare cases; they often appear on the surface of the skin.
It is condylomas that are prone to frequent fusion, which leads to the formation of groups; this does not happen with papillomas. And if you remove mucous tumors, the risk that they will reappear exists and is quite higher than with the same procedure in the case of papillomas.
In addition, papillomas do not pose a serious danger to humans. You can calmly decide to remove them or live with them without paying any attention to them. You need to be careful with condylomas, and it is better to get rid of them to avoid the appearance of malignant neoplasms.
In other words, despite the differences, condylomas and papillomas have the same nature of origin.
Top 15 remedies for the treatment of papillomas
We present 3 effective methods of combating papillomatosis, each of which contains 5 methods.
Hardware techniques
They are used only to remove external manifestations of papillomavirus. Each procedure is carried out with painkillers and under the supervision of a doctor.
- cryodestruction - freezing the wart using liquid nitrogen;
- removal with a radio wave knife is the latest development of scientists, expensive, but the most effective procedure;
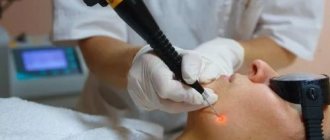
- laser removal - using a laser device, the growths are burned out to the very base;
- electrocoagulation - removal occurs due to the effect of high current on the formations;
- surgical method - the oldest method, suitable for large warts, a scalpel is used.
Medications
- Solcoderm is a local solution consisting of acids that can burn out papillomas and condylomas;
- Viferon - available in the form of ointment, gel and suppositories, affects formations from the outside and helps the body cope with growths faster;
- Cryopharma - operates using the cryodestruction method and is available in aerosol form;
- Supercleaner is a chemical solution that removes even more build-up;
- Salicylic ointment - gently removes condylomas and papillomas, suitable for use on open areas of the body.
Traditional methods
- Dough . Wheat flour is mixed with vinegar to form a dough. The piece is placed on the papilloma without affecting healthy tissue, fixed with adhesive tape, and left overnight. Repeat for 7 days;
- Onion essence . The cut onion is soaked in vinegar for 2 hours, then a piece is taken out and the cut is applied to the papillomas for 20-40 minutes twice a day, the course of treatment ends after the growths are completely removed;
- Aloe or Kalanchoe . If the plant is 3 years old, you can cut off a leaf and attach it to the wart overnight. It is necessary to soak the growth with juice - this will destroy it faster. Duration of treatment – 1 month;
- Celandine . Soak the growths in juice once a day. When the affected area turns black, stop processing - soon the papilloma will disappear on its own;
- Herbal decoctions . Infusions of chamomile, St. John's wort or sage help increase immunity and help reduce HPV activity.
Distribution routes
As is now known, the neoplasms in question appear as a result of exposure to the papilloma virus, and its different types. If it enters the body, then with the advent of favorable conditions for it, the virus is activated. Type A can be transmitted either through domestic or sexual contact, with the latter being the most common.
Other types are primarily spread sexually. For this reason, doctors classify the appearance of condylomas as an STD. As for papillomas, they are often transmitted through household contact.
How is HPV diagnosed?
Papillomas, like condylomas, arise as a result of the papillomavirus entering the body, but each specific manifestation depends on the type of pathogen. Therefore, it is not enough to identify the virus; it is also important to determine what type of HPV and in what quantity caused the formation. This will help identify the risks of developing cancer. And quantitative indicators will make it possible to find out whether condylomas appeared due to a short-term weakening of the body’s protective functions or whether it is a chronic course of the disease that develops over several years.
Most often, the DNA diagnostic method (PCR) is used to detect the presence and type of HPV. Such a study is recommended for patients with papillomas, and if they are found to have genital warts, then for their sexual partners. If there are no manifestations of the disease, and the analysis reveals the presence of the virus, then it is necessary to undergo preventive treatment. It is impossible to completely get rid of the disease, but treatment with modern methods of papillomas and condylomas makes it possible to suppress the activity and manifestation of the virus.
PCR is complemented by other diagnostic methods:
- Colposcopy - to identify formations inside the genital organs.
- Biopsy - for timely detection or exclusion of the development of oncology.
Diagnostic methods are often complementary to each other: if neoplasms are detected in the patient or his partner, then PCR diagnostics are prescribed. And in case of a positive result - colposcopy and biopsy.
PCR analysis, diagnosing the virus strain by its DNA
Causes of neoplasms
As is already known, the appearance of any neoplasm on the human body is caused by exposure to the papilloma virus, but skin manifestations do not appear immediately. The virus can remain in “standby mode” for quite a long time while the person’s immunity is strong. A number of factors can provoke its activation:
- Immunodeficiency.
- Nervous overstrain.
- Respiratory disease of a viral nature.
- Taking certain medications for a long period (antibiotics, steroids, cytostatics).
- Exacerbation of urogenital infections.
- Herpes type II.
It is also possible that papillomavirus infection from mother to child during childbirth cannot be ruled out.
Characteristics of papillomas
HPV manifests itself in different ways and has the following characteristics:
- is located inside the body without the formation of new growths on the skin. In such a situation, the doctor diagnoses a hidden form of pathology. It is possible to detect a pathogen without skin manifestations using PCR,
- form as growths on the skin in the episomal form of the virus,
- promote the degeneration of epithelial cells from benign to tumor neoplasms.
Carrying out diagnostics
We have already figured out what the difference between papilloma and condyloma is, but in order to make sure that you have HPV (human papillomavirus), you need to consult with specialists such as a dermatologist or venereologist. A diagnosis can be made based on a visual examination of the patient, but this only applies to classic cases with genital warts.
But without tests it is impossible to determine the type of virus, as well as the degree of threat to the human body. For this, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- Cytological examination.
- Histological examination.
- PCR.
- Digene test.
A cytological examination is carried out using a microscope, and pathologically altered cells of the cervical mucosa can be detected, which should not normally be present. This is called cervical dysplasia. If changes were detected at an early stage, this process is still considered reversible.
During histological examination, a small amount of tissue is taken for analysis by a gynecologist or urologist. The condition of the tissues is assessed under the same microscope.
The PCR test must be performed correctly, otherwise the results may be false (impaired implementation or transportation). This study is considered the main one and allows not only to identify the difference between condyloma and papilloma, but also to determine the 16th and 18th types of the virus and its other highly oncogenic varieties. The material is collected from the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix (in women), as well as from the mucous membrane of the male genital organ.
The Digene test will allow you to determine the degree of risk from papillomas or condylomas. That is, this study allows us to identify the concentration of the virus and thereby determine whether there is a threat.
Patient reviews of procedures
Tatyana 22 years old 07/31/2017
I removed condylomas using radio waves. 3 years have already passed and still nothing. The doctor advised removal, because in fact the human papillomavirus lives in these growths.
Irina 31 years old 11/16/2017
I went for cryodestruction, but then they started doing it again - not even a year had passed. I decided to be treated at home, without going to the doctors. I bought tea tree oil and applied it twice a day. I did this for a long time, probably 2 months. But now I don’t even remember about my papillomas.
Mikhail 43 years old 06/14/2018
For a long time I did not pay attention to the sores in my groin - I hoped they would go away, but no. After 7 years, I decided to treat myself at home - I just wasted a year on these folk recipes. Then I decided to go to a dermatologist - after electrocoagulation they went away, but six months later they came out again. My nerves began to fail me and I went to a paid clinic and had it removed with a laser. 2 years have passed, no condylomas yet, let's see what happens next.
Treatment
The issue of treating tumors on the body is the prerogative of the person himself, but consulting a professional dermatologist will not hurt, for which it is worth visiting a specialized clinic. Only in such conditions can an accurate diagnosis be made with the availability of modern diagnostic tools.
Here it is important to understand one important point - under no circumstances should you self-medicate, much less get rid of tumors on your own! This is a direct path to the development of oncology.
If this problem is detected, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment for condylomas and papillomas using antiviral and antifungal medications. The main thing is to increase the body's resistance and restore immunity.
If there is a suspicion of the development of malignant formations, the specialist will refer the patient for additional research (for example, identifying tumor markers). In this case, cytostatics will be involved.
Indications for removal
Condylomas must be removed, even if they do not cause discomfort. This is primarily due to the risk of infecting a sexual partner.
Whether or not to remove papillomas located on the skin is a personal matter for each patient. The risk of degeneration of benign papillomas into an oncological neoplasm increases when the body of the growth is damaged. This may be caused by friction with clothing, accidental damage with nails or a washcloth during hygiene procedures.
You should consult a dermatologist if:
- the papilloma has greatly increased in size;
- when pressing, discomfort is felt;
- there is bleeding or purulent discharge;
- the skin around the growth becomes inflamed.
Removing the growth is a matter of five minutes. The procedure is almost painless. It is important to understand that timely diagnosis will allow timely detection of the onset of cell degeneration and stop the development of oncology.
Methods for getting rid of papillomas and condylomas
Currently, you can get rid of tumors on the body using proven and modern means:
- Surgery. For some time, this method was considered the only and effective method for removing condylomas and papillomas. At the same time, the procedure has its consequences in the form of scars and scars that lag behind on the body, which causes a cosmetic defect. Therefore, there was a need to find more rational ways to remove skin tumors.
- Chemistry. Here special products are used, which contain strong acids.
- Low temperature. The procedure is called cryocoagulation, in which neoplasms are exposed to liquid nitrogen at an extremely low temperature. However, in this case, the risk of relapse is quite high, which is a significant drawback.
- Radio waves. This is not only a painless, but also a quick way to remove unwanted growths on the body or mucous membranes.
- Laser. This is also a very effective technique, but it is not relevant for all tumors.
As we now know, unlike condylomas, papillomas do not pose a serious danger. But only the doctor decides which method to use in each specific case. Here you should take into account the severity of the illness that has arisen, whether the patient has any diseases in the chronic stage, how strong the immune system is, whether there are allergic manifestations and other factors.
How to remove papillomas
Papilloma is a benign structure that does not cause harm to the human body. However, the possibility of bleeding associated with damage to the wart due to mechanical impact or wearing tight clothing and the unpleasant appearance of the growth makes the wearer want to get rid of the defect.
An additional incentive to eliminate papillomas is the fact that the growth has a high probability of degenerating into oncological melanoma. Cosmetologists emphasize the need for preliminary analysis to determine the type of strain that caused the appearance and growth of the pathological structure.
After analyzing the information obtained from taking the sample, the dermatologist recommends removing the structure:
- The method of cauterization, performed by electrocoagulation.
- By evaporating the moisture contained inside the neoplasm cells under the influence of laser beams.
- Surgical excision of the area of pathological growths.
- Cryodestruction, based on freezing the wart with cold nitrogen supplied under pressure.
- Removal of papilloma using a radio knife.
Important point
Paradoxically, the papilloma virus has one unique feature - once it settles in the human body, it remains there forever. This does not threaten serious complications if its activity is contained. And for this you need to maintain your immunity in a healthy state.
The best prevention against the appearance of tumors is giving up bad habits, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, maintaining a balanced diet and timely contacting a specialist. For children, they should receive the required vaccinations from the age of nine.