Nail diseases can develop at any age; children and adults, men and women suffer from them equally often. Some of them act as an independent pathology, others as a symptom of diseases of the internal organs. They are treated by a dermatologist. If necessary, specialized specialists are involved in the development of therapeutic regimens.
What are fingernail diseases?
A person performs a huge number of actions with his hands. This promotes increased blood circulation, so the nail plates on the hands grow much faster than on the feet. The situation has a downside - injuries occur more often, infections occur, and exposure to aggressive materials occurs. All this leads to the appearance of fingernail diseases, which require:
- visiting a dermatologist;
- timely treatment.
Often, changes in the nail surfaces indicate the presence of pathologies in the body. Experienced specialists in nail pigmentation and defects can make a diagnosis when other symptoms have not yet appeared:
- yellow-gray color is evidence of liver disease;
- pale, thinned – anemia;
- brown, black stripes – melanoma;
- red color – pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- yellow tint – lung diseases, diabetes;
- thin plate – iron deficiency.
Infectious
A large group of fingernail diseases are caused by infections, each of which is characterized by its own symptoms and requires a special approach to treatment. Panaritium is caused by staphylococci and streptococci. There are many known fungal infections:
- ringworm - accompanied by the appearance of yellow stripes, white spots, the plate thickens;
- onychomycosis - caused by rapid proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, symptoms depend on the type of fungus;
- candidiasis of the periungual area is characterized by tissue damage, sometimes affecting the plate.
Non-infectious nail diseases
Often, changes in the nail surfaces on the hands are caused by hereditary factors, skin problems, and pathologies of internal organs. Non-communicable diseases can be caused by a lack of iron, calcium, lack of proper care, and exposure to chemicals. Such ailments include:
- onycholysis;
- leukonychia;
- hyperkeratosis;
- green pseudomonia;
- felon;
- paronychia;
- melanonychia;
- psoriasis;
- hypertrophy;
- chromonychia;
- onychatrophy.
Forms and stages
There are several forms of onychomycosis:
- Distal subungual. It is considered the most common form. At the initial stage of development of the pathology, a yellow spot appears on the nail plate, which grows over time, affecting the entire nail. If left untreated, the nail plate is easily separated from the skin.
- White superficial . Only the top layer of the nail plate is affected. The nail does not thicken and a white coating forms on its surface. Over time, the nail plate becomes softer and more prone to splitting. This form responds well to treatment, especially at the initial stage.
- Proximal subungual . The area of the nail fold is affected first, then the process spreads to the entire area of the nail plate, which acquires a white, opaque color. The pathology is considered quite rare and is mainly found in people suffering from HIV infection.
- Total dystrophic is an advanced stage of the forms of the disease listed above. Characterized by complete destruction of the nail plate.
The disease has a gradual course and develops gradually. At the first stage, the nail plate loses its transparency, becomes thinner, and flakes, while maintaining its integrity.
The second stage is characterized by the appearance of yellow spots of different sizes, loss of smoothness of the nail plate, and its slight thickening.
At the third stage, significant deformation processes are observed, destruction of the nail plate, its thickening, separation from the skin, the nail changes color and becomes completely opaque.
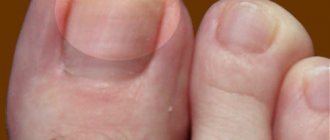
What healthy fingernails look like - photo
It's nice when a person's nail plates are in order. If they are healthy, they are pale pink in color. In the absence of disease, note:
- smooth shiny surface;
- at the base there is a lunula, similar to a crescent, having a white or pale pink tint;
- a dense roll of leather - a cuticle that protects the lower part from bacteria and foreign bodies;
- the convex shape of the plate in the form of a rectangle, trapezoid, circle or square, which is individuality;
- no defects or pigmentation.
Prevention measures
Preventive measures are needed to prevent nail fungus from developing in children. Mycosis is fraught with relapses, and therefore, even after undergoing therapy, it is important not to forget about prevention. It consists of the following steps:
- After the child has undergone therapy, all his things must be washed in an antibacterial mode. Shoes are treated with special compounds;
- The child should be protected from interaction with people with mycosis;
- The bath is disinfected after each visit;
- Children's shoes should be well ventilated. If it is tight, it may cause sweating;
- The child must be gradually accustomed to personal hygiene measures.
Parents must remember that the child's health is entirely in their hands. The disease itself cannot be cured. For recovery, you need to take a whole range of measures: drug therapy, and processing of all personal belongings.
Hand nail diseases
Each nail pathology has its own characteristics. Symptoms of diseases vary and require specific treatment. The following diagnoses are distinguished:
- paronychia - characterized by darkening of the nail surface, redness of the skin, caused by a bacterial infection;
- onychomycosis is a fungal infection, has symptoms depending on the type of microorganism, and spreads rapidly;
- lichen planus - characterized by separation of the plate from the nail bed, separation, and is provoked by problems of the immune system.
Non-communicable diseases include:
- chromonychia, in which the plates become yellow, which is characteristic of old age;
- onychorrhexis, onychoschisis, causing splitting of the nail tissue in the longitudinal and transverse direction, appear with chronic injuries;
- hyperkeratosis - intensive growth of plate cells due to genetic reasons;
- acquired or congenital atrophy of the nail, characterized by thinning of the surface and pale color.
How do children get infected?
The causative agents of onychomycosis include dermatophytes, molds and yeasts. Most often, the disease is caused by dermatophytes of the genus Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Epidermophyton floccosum. Yeast-like and mold fungi affect the nail plates much less frequently.
Routes of infection:
- In children under two years of age, onychomycosis develops most often if the child was born prematurely or has immunodeficiency diseases, Down syndrome . In newborns, the immune system is not yet perfect, so they are more susceptible to developing infection.
- Babies love to keep their fingers and toes in their mouths, warm and moist, thereby creating favorable conditions for the growth of fungus on their nails. A very thin and soft nail plate in infants predisposes to this. A one-year-old child may become ill after wiping his body with a contaminated towel.
- In healthy children, the appearance of fungus on the nails is associated with wearing closed shoes. The baby's feet sweat: this becomes the main factor for the growth and reproduction of the fungus.
- Mycosis is transmitted by contact, so one sick family member can infect everyone else through direct contact.
- A common cause of onychomycosis is foot injuries that occur in active children, especially if it occurs outdoors and without shoes.
- Because fungus grows in warm, humid conditions, using public showers, such as at a gym or swimming pool, encourages the development of infection.
Leukonychia - the appearance of white spots
This fingernail disease is often observed during adolescence. The plates are covered with white dots and stripes. The reasons for the development of leukonychia can be:
- zinc deficiency in the body;
- injuries;
- disruption of the process of formation of horny plates;
- exposure to chemicals;
- stressful situations;
- poor quality manicure;
- often practicing diets;
- arsenic intoxication.
To avoid the development of the disease and cope with the problem, dermatologists recommend:
- apply precautions when using chemicals;
- make baths with the addition of sea salt and essential oils;
- try to avoid hand injuries;
- take vitamin complexes including microelements;
- be smart about dieting.
Features of therapy in children of different ages
When treating onychomycosis in infants, doctors limit themselves to local medications so as not to provoke the development of complications from taking systemic medications. Adults in contact with the child also need to take a course of antifungal medications. This will prevent the baby from becoming infected again.
When treating preschool children, a dermatologist may, in addition to external agents, prescribe systemic antimycotic medications. Only a doctor can determine the dosage and duration of use.
Therapy for onychomycosis in schoolchildren differs little from treatment in adults, but the choice of drugs should be entrusted to a doctor.
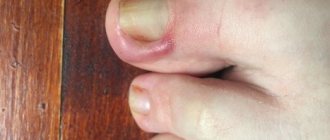
Onycholysis - dystrophic change in the nail
The danger of this disease of the fingernails is the separation of the plate from the bed with a change in color to gray-white. There are several reasons for the appearance of the disease. The disease onycholysis is provoked by the following factors:
- fungal infections;
- problems of the cardiovascular system;
- skin diseases;
- endocrine disorders;
- pathologies of the nervous system.
Nail dystrophy requires long-term treatment of the disease that caused changes in the nail plate. To eliminate the symptoms you will need:
- take vitamin complexes;
- drink calcium and iron supplements;
- take hot baths with essential oils;
- To improve blood circulation, massage your fingers;
- Apply bandages with synthomycin ointment after baths.
Folk remedies
Nail fungus in a child is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms. To reduce it, drug therapy can be supplemented with folk remedies. However, only those substances that will not harm the baby’s delicate skin are suitable. Among them it is worth noting:
- Iodine;
- Kalanchoe;
- Grapefruit seed extract;
- Vinegar essence (diluted);
- Tea or palm oil;
- Burdock extract.
Before lubricating the affected areas with these products, it is recommended to perform hot baths. A spoonful of soap and a spoonful of soda are added to them.
Traumatic damage to the nail plate on the hands
Very often, problems with fingernails arise as a result of injury. In this case, pain, pulsation appears, chips of the nail plate, and blue discoloration are observed. In case of minor injuries, treat the injury site with antiseptic drugs - hydrogen peroxide, iodine, and apply ice to eliminate the hematoma. Serious injuries require a visit to the clinic. Traumatic problems cause:
- mechanical impact on the plate;
- chemical, thermal burns;
- chronic injuries caused by professional activities.
Sprays are the best remedy for fungal infections
In fact, sprays are considered one of the most convenient means for treating fungal diseases. The thing is that they can be applied quickly, while your hands remain clean. Pharmaceutical companies offer a large selection of sprays, but Bifosin and Thermikon have proven themselves to be the best.
“Bifosin” will help in any case, since the active ingredient bifonazole almost always destroys the fungus. And all because pathogenic microflora cannot remain resistant to this component, unlike other drugs. Its main advantage is the possibility of using it even for the treatment of newborn children, but under the supervision of a doctor.
Bifosin
"Thermikon" will help eliminate the dermatological problem in a short period of time. It is enough to smear the nail areas 1 – 2 times a day for a week, avoiding contact with the mucous membranes. The spray is only allowed to be used by children over three years of age.
The price of sprays cannot but rejoice. The average cost is 200 rubles.
Bleaching
This type of disease does not require special treatment and is considered the safest of all lesions of the nail surface. It is important to eliminate the factors causing discoloration and grow a new healthy plate. The causes of the unpleasant symptom are:
- use of low-quality varnish;
- smoking tobacco;
- rarely – anemia, weakened immunity.
Onychoschizia - splitting of the nail tissue
This pathology is characterized by destruction of the surface of the plate. In this case, fragility, brittleness, and splitting are observed. The development of onychoschisia is provoked by:
- fungal infections;
- mechanical injuries;
- thermal burns;
- contacts with chemicals;
- deficiency of vitamins, microelements;
- use of low-quality varnishes;
- allergic reactions.
To cope with pathology on the hands, dermatologists recommend:
- taking vitamins A, group B;
- performing hot baths with gelatin and essential oils;
- applying masks with natural wax;
- rubbing olive, sea buckthorn oil;
- the use of bandages with hydrogen peroxide;
- carrying out physiotherapy – phonophoresis.
- Rejuvenating face mask with yeast
- Homemade hair highlighting
- Butter cream for cake - recipes step by step with photos
Causes of fungus
Infection can appear as a result of exposure to external and internal factors on the body:
- If a one-year-old or older child runs barefoot around indoors in public places .
- As a result of the baby wearing someone else's clothes and shoes.
- In children around one year of age, their feet sweat and the infection spreads faster.
- As a result of deformation of nails due to mechanical injuries or wearing uncomfortable shoes.
- Contact with other people who are carriers of the fungus;
- Weakened immunity.
Panaritium or nail-eater
The disease is characterized by the occurrence of an acute inflammatory process near the nail bed. When the cuticle is dry, an injury, abrasion, or injection occurs, a purulent infection enters the tissue on the hand through the site of injury, which begins to spread rapidly. This happens:
- compression of blood vessels;
- eating disorders;
- formation of necrosis;
- suppuration;
- the occurrence of severe pain due to the presence of a large number of nerve endings in the nail bed area.
If the abscess has not formed, its formation is provoked by physiotherapy - dersanval, ultraviolet radiation. When felon causes unbearable pain and prevents sleep, surgical intervention is prescribed:
- perform pain relief;
- make an incision;
- do thorough drainage;
- remove necrotic tissue;
- apply a bandage with erythromycin, tetracycline ointment;
- antibiotics are prescribed.
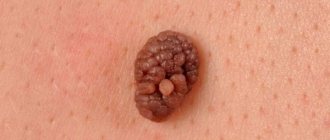
Ingrown nail
Incorrect trimming during manicure can lead to the appearance of such a disease on the fingernails. The sharp edge of the nail plate pierces the skin of the finger, in which inflammatory processes are already occurring. The disease is characterized by tissue redness, swelling, severe pain, and suppuration. The cause of ingrowth can be:
- fungal infection;
- injuries received.
To cope with the disease, you will need:
- carefully remove the ingrown piece of the plate;
- take warm baths using antiseptic drugs;
- wash your hands regularly with soap;
- exclude injuries;
- perform manicure correctly;
- cure fungal disease;
- in advanced forms of the disease, surgically remove part of the plate.
Is it possible?
Toenail fungus in children - photo:
Absolutely yes. A fungal infection affecting a child's nails is quite common . This is due to the imperfection of the baby’s immune system, and, as a result, the high sensitivity of his body to various types of infections.
However, fungal nail infections are somewhat less common in children than in adults (15-20% of children from toddlers to adolescence).
It is known that in regions with temperate climatic conditions, cases of the disease are more common, since children have to wear warm shoes for a large amount of time , in which their feet sweat; such conditions are considered favorable for the active reproduction of the fungus.
Fungal infection of fingernails
The occurrence of an infectious disease - mycosis - provokes rapid reproduction of fungal spores. Some of them are in the body, participating in life processes, but activate their growth during a sharp decrease in immunity caused by various situations. Fungal disease of the fingernails is caused by:
- work in a damp environment;
- contact with products contaminated with fungus;
- shaking hands with a sick person;
- poor antibacterial treatment of manicure tools;
- use of other people's hygiene items, gloves;
- visiting the swimming pool, sauna.
When the fungus affects the fingernails, the following is observed:
- color change to brown, green, yellow, black;
- thickening of the nail plate;
- the appearance of delaminations;
- cracking;
- spread of infection to the surrounding skin;
- occurrence of redness, itching, burning;
- fragility;
- violation of the integrity of the surface layer;
- the appearance of deformations of the nail plates.
Treatment at home involves:
- use of varnishes and solutions in the early stages of fungus;
- application of antimycotic ointments, sprays;
- use of antifungal drugs prescribed by a doctor;
- carrying out baths with solutions of salt, soda, iodine;
- using lotions of garlic juice, hydrogen peroxide;
- compresses with vinegar, propolis, celandine oil.
How to treat fungal diseases
Types of fungal infections on the legs, arms and their treatment are interconnected concepts: in order to defeat the disease, it is necessary to identify its causative agent, correctly determine the severity of the lesion and the duration of the course.
You can restore health to your nails by using systemic treatment and local therapy. Taking antifungal drugs orally ensures the penetration of the active ingredients of antifungals through the blood into the horny substance of the nail, which ensures the effective destruction of fungi and prevents the spread of infection.
External therapy (treating nails with solutions, varnishes, using peel-off patches) provides a direct effect on the causative agent of the disease. The active components accumulate in the nail plates and act, as they say, from the inside.
In the treatment of severe forms, surgical removal of the nail plate is also indicated. It becomes justified because fungal spores with total infection accumulate in the thickness of the horny masses located between the bed and the plate, and remain inaccessible to local and systemic antimycotics. Removing the plates eliminates the source of infection itself.
The choice of drugs and dosage should be made by the attending physician based on the results of laboratory tests.
Drug treatment of fingernails - general scheme
Diagnosis, determining the cause of the disease on the fingernails, and prescribing the correct treatment helps to cope with the pathology. With advanced forms, the process may take several months. Dermatologists recommend:
- local effect on the affected areas with creams, ointments, solutions;
- using compresses, baths, lotions with medications, essential oils, and natural products at home;
- use of tablets, capsules;
- laser treatment;
- physiotherapy;
- removal when other methods are not effective.
Local remedies
When hand nail diseases appear, the prescription of medications depends on the diagnosis. Local application involves applying drugs to the affected surface of the nail plate. Depending on the disease, the following is prescribed:
- for psoriasis - hormone-containing ointments - Triamcinolone, Prednisolone;
- in case of fungal infection - Lotserin varnish, Terbinafine cream, Fukortsin solution;
- for atrophy - rubbing in sea buckthorn and olive oil.
Systemic drugs
Medicines for the treatment of fingernail diseases differ in their effect. They are prescribed by a doctor depending on the diagnosis. Recommended use of drugs:
- antifungal, destroying cells of pathogenic microorganisms - Ketoconazole;
- antihistamines that eliminate allergic reactions in patients with eczema - Levocetirizine;
- reducing the formation of pathological cells in psoriasis - Dithranol;
- eliminating itching during the development of lichen planus - Loratadine.
How is the treatment performed?
At the moment, there are a lot of drugs that have a gentle enough effect that they can be purchased for children. Medicines can be supplemented with folk recipes. However, you need to remember that folk recipes are used only as a supplement. They are not used as independent means. Traditional recipes only alleviate symptoms, but do not eliminate the disease.
To prescribe therapy, you must consult a doctor. He will conduct all the necessary examinations and, based on their results, prescribe medications. This regimen is doubly important because not all medications are suitable for a child. There are many requirements for products for babies. If you take a drug intended for adults for children, side effects are likely.
The treatment regimen is divided into two types:
- Monotherapy . Involves taking only one group of drugs: external or tablets. Relevant in the first stage of the disease, when it makes sense to use only local remedies. Tablets have a lot of side effects and contraindications, and therefore monotherapy can be prescribed in childhood;
- Combined . Includes taking local medications and tablets. Can be supplemented with folk recipes. Prescribed in the later stages of the disease, when influence is required from the inside and outside.
To treat a child, therapy with local agents is predominantly prescribed, since they have a more gentle effect.
Removing the nail plate
When fingernail diseases are advanced and drug treatment has failed, removal of the affected plate is prescribed. There are two ways to perform the operation. Methods used:
- Surgical removal is painful, causes damage to the matrix, and disruption of the nail bed. There are contraindications for prescribing surgery.
- The use of keratolytic patches is considered a low-traumatic method. Under the influence of special preparations, the surface of the plate becomes softer and can be removed with scissors or a scalpel without pain.
Onychoschisis
A pathological condition that manifests itself as destruction of the nail as a result of destructive-dystrophic processes. With it, the nail plate becomes fragile and brittle, and changes color. This damage may occur against the background of:
- Contact with harmful substances.
- Thermal burn.
- Lack of vitamins and minerals.
- Using low-quality manicure products.
- Mechanical damage.
To eliminate the manifestations of onychoschisis, you should understand in detail the cause of its occurrence. If this condition is caused by a deficiency of vitamins, the person is advised to take oral vitamin preparations (mainly group A) and intramuscular injections of group B vitamins.
It is recommended to apply sea buckthorn or olive oil to the damaged nail. Maintaining personal hygiene and properly performed manicure (do not cut your nails short, file them frequently) and constant, careful care (using moisturizing lotions) significantly speed up the healing process.
Traditional methods of treating hand nail diseases
With a complex impact on the problem, traditional medicine recipes play an important role. The main thing is that the treatment is agreed upon with the doctor who established the cause of the disease. Helps cope with the disease:
- a mixture of equal proportions of honey and grated onion - eliminates cracks;
- red currant and cranberry juice – strengthens and nourishes the nail plates;
- baths of vegetable oil with lemon juice - eliminate fragility;
- honey, flaxseed, in equal parts - restore shine and strength;
- lotions with garlic juice – counteract the fungus.
Unconventional methods
In folk medicine, there are many different ways to combat damage to the nail plate. Today the most famous recipes are:
- Preparation of special hand baths with the addition of vegetable oil, cabbage and potato juice or chamomile and mint.
- The use of infusions based on parsley, celery and dill.
- Making a decoction of celandine with the addition of salt.
- Making tea from horsetail.
All the described recipes, according to reviews, are quite effective. However, in cases where the use of these remedies does not bring visible results, you should not hesitate to seek medical help in order to avoid possible complications.