Doctors started talking about the human papillomavirus after studies confirming a direct link between HPV and cervical cancer. More than 70% of women are infected with papillomavirus, vaccinating girls against HPV is dangerous in itself - these and many other common opinions only scare women.
However, few of them go to the doctor and undergo screening for HPV and related diseases. Is papillomavirus really that scary, what to do if it is detected, what is the treatment for HPV and how long to live - accurate medical information will give answers to all these questions.
Features of the development of oncogenic viruses
HPV (human papillomavirus) are viruses divided into groups and types. A total of 120 of them are known. The types in women (16-56) and in men pose a particular danger to the body, as they can cause serious illness and death. Viruses are transmitted mainly through sexual contact. A person is least likely to become infected through wounds and microcracks.
Types of viruses are also divided into levels of risk of oncogenicity: high, medium and low.
Once in the body, the papillomavirus produces special substances that facilitate penetration through the intercellular substance and further passage into the basal cells of the dermis. There he lingers. As soon as the papillomavirus DNA enters the human cell nucleus, it begins to rebuild. Before entering the nucleus, no changes harmful to the body occur.
Along with the restructuring process, the cell changes its own DNA and pathogenic growth and reproduction begins. As soon as the processes of change begin, the cells grow and multiply in disorder, which is why neoplasms (condylomas and papillomas) appear on the skin and mucous membranes of the human body, which at first they may be indistinguishable from the natural color of the skin.
Women are most susceptible to the disease; papillomavirus causes diseases associated with the reproductive system, including oncology. The risk of infection is especially high at the beginning of sexual activity. Promiscuous sexual intercourse, neglect of contraceptives - all this can lead to the development of HPV.
Much less often, infections occur through dirty medical devices or during procedures (including cosmetic ones). HPV has an incubation period - usually 15-20 years.
Papillomavirus is divided in most cases into types, including:
- Type 16 – the most dangerous for women; if it enters the body, the risk of genital cancer is the highest;
- Type 18 – also dangerous, causing the appearance of condylomas when it enters a cell;
- Types 31-33 are also oncogenic, more typical when Bowen’s disease occurs and are located in the scaly layer of the epidermis.
- Types 51-56 – medium-high risk of oncology, the disease develops only in an environment favorable for the virus (for example, with reduced immunity).
The latter types are also capable of causing mutations in the female organs, and are the cause of infertility and menstrual irregularities.
Causes of papillomas
Papillomavirus DNA can be functionally inactive and become more active under the influence of smoking, hormonal disorders, and concomitant STIs.
Papillomavirus DNA can be functionally inactive and activated under the influence of:
- smoking,
- hormonal disorders,
- concomitant STIs, and, above all, genital herpes, the causative agent of which is HSV-2.
Infection of the genital organs occurs in the presence of microtraumas in the genital area (mechanical trauma, bacterial microdamages, etc.), and it should be taken into account that the urethra, seminal fluid and prostate secretions can serve as a reservoir.
The incubation period for genital warts usually varies from several months to several years, and in most cases the infection is subclinical. Progression of a high oncogenic risk infection into cutaneous dysplasia and carcinoma in situ usually occurs within 5 to 30 years and rarely within a period not exceeding 1 year. Human papillomavirus infection of the genitals is often multifocal and associated with more than one type of human papillomavirus, as well as other pathogens of STIs In most cases, genital human papillomavirus infection remains unrecognized.
Genital infection is highly contagious and acquired during the first few sexual contacts; Infection occurs during a single sexual contact in approximately 60% of cases. In 65-70% of cases, papillomas (warts) are detected in both sexual partners.
The likelihood and frequency of developing a genital infection largely depends on a person’s sexual behavior. Risks increase when:
- early onset of sexual activity,
- frequent change of sexual partners,
- homosexual orientation, both in men (the incidence of anal cancer is significantly increased) and in women.
With immunosuppression and diabetes mellitus, papillomas, as a rule, are multiple and merge with each other. With genital papillomavirus infection in a pregnant woman, there is a high risk of infection of the baby in utero or during childbirth. At the same time, human papillomavirus infection (HPV types 6, 11 and 16, 18) can persist for a number of years in the cells of the mucous membrane of the child’s mouth and cause juvenile laryngeal papillomatosis. Juvenile laryngeal papillomatosis can develop if the mother has a history of genital warts, as well as with a subclinical course of her genital HPV infection. Children can be carriers of mucocutaneous types of the virus even if they are not present in the mother’s genital tract at the time of birth.
In this regard, one should remember about the increased detection of the virus in the woman’s reproductive tract during pregnancy (thrush of pregnant women), when the fetus becomes infected.
Cases of papillomatosis of the larynx, trachea, and bronchi in children born by cesarean section have been described, indicating the possibility of transplacental transmission of infection. This indicates the inappropriateness of delivery by cesarean section, the only purpose of which is to prevent infection of the newborn with the virus. Extrasexual transmission of genital warts is also possible
- when bathing children in a shared bath with adults infected with the virus,
- when using towels infected by adults,
- with sexual transmission of HPV infection to children.
Thus, unlike adults, infection of children with anogenital warts can occur in different ways.
Clinical manifestation of genital infection is accompanied by the appearance of genital warts (condylomas). The absence of clinical and histological signs when detecting human papillomavirus DNA indicates a latent (asymptomatic) infection.
How is HPV transmitted?
The cause of HPV can be not only unprotected sexual intercourse, but also:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- reduced immunity;
- disrupted eating patterns;
- consumption of low quality products.
It is worth noting that with frequent stressful conditions, the risk of suffering from HPV increases significantly.
Household way
In 85-90% of cases, infection can be transmitted through household means when one of the family members is infected. A pathogenic microorganism at home is very often transmitted from parents to children. The child’s immunity is not yet strong and therefore the baby is more susceptible to infection. Infection through domestic means can occur in the following ways:
In 85-90% of cases, infection can be transmitted through household means when one of the family members is infected.
- if there are lesions on the skin, infection can occur through the use of shared bed linen, towels, washcloths, soap, cosmetics and hugging;
- You can become infected through saliva by using the same utensils, a toothbrush, or by kissing a carrier of the virus;
- when wearing clothes of an infected person (especially underwear);
- In domestic conditions, self-infection can occur during shaving and hair removal.
Also, domestic transmission of the pathogen includes infection in public places. For example, in a swimming pool, bathhouse, sauna. And also with frequent handshakes and friendly hugs.
What danger does papillomavirus pose?
In the absence of proper treatment, as well as constant exposure to adverse factors, can lead to the development of dangerous pathologies:
- restructuring of vaginal cells and uterine canals;
- development of cancerous tumors of the vagina and anus;
- oncology in uterine tissue;
- a warty-looking neoplasm on the external genitalia and anus;
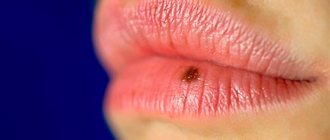
- pathogenic formations in the mouth and larynx;
- growth of papillomas and condylomas on the genitals of men;
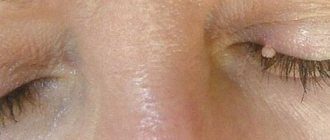
- damage to the mucous membrane of the eyes;
- cancer formations in the esophagus and nose;
- malignant formations on the feet.
Skin lesions are also an aesthetic problem. It is important to note that when new formations grow, they can involve nearby tissue in the process.
Thus, papillomas in the nose or larynx impair breathing and voice, and their occurrence on the male genitals leads to disruption of urinary function. The formations also provoke bleeding and bladder diseases.
HPV in men: consequences
The virus can cause condylomas, or genital warts, which, as the name suggests, are located in the groin, as well as on the head of the penis and foreskin. This kind of condylomas has very dangerous consequences for men and requires treatment.
Condylomas on the penis can lead to a narrowing of the foreskin, which can make it difficult to expose the head of the penis and lead to problems in your personal life.
It must also be remembered that in some cases such formations are not an indicator of HPV, but of other sexually transmitted diseases that have not yet manifested themselves (for example, syphilis).
Another danger of HPV is that a carrier of the virus can transmit it to their partner, also putting them at risk of developing cancer. Transmission of the virus is also possible to the fetus from an infected mother, so couples wishing to have children should pay special attention to HPV and other diseases of this kind.
Oncogenic classification of HPV
Oncogenic classification is the division of papilloma virus types into several large groups, indicating the degree of their danger. This is done in order to have a clear idea of which strains of the virus are dangerous for causing serious diseases and which are not.
First group
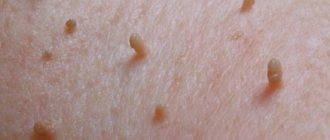
The first group is also called non-oncogenic. This includes HPV types 1,2,3,4 and 5. These papillomas do not degenerate into a malignant tumor and do not rearrange cells, forming mutations. The only thing that can happen is the formation of papillomas. If they are small and do not cause inconvenience, they are not removed and will not cause harm.
Second group
The second group is a low risk of cancer. It includes types 6, 11, 42-44. Vaccines have been developed against the most common ones (which are 6 and 11). If these strains are detected, the risk of cancer development is low. In order for pathology to begin, several factors are needed to provoke it.
HPV types in women and men.
People who are prone to cancer, have been exposed to radiation, or suffer from immunodeficiency should pay attention to this. Basically, neoplasms do not degenerate into malignant ones.
Third group
The third group is a high risk of oncogenicity. The types belonging to this group are 16, 18, 31-35, 45 and 51-56. These strains always provoke the appearance of cancer, which manifests itself mainly on the genitals.
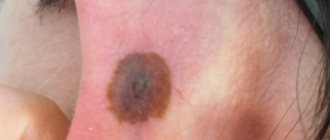
HPV and cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is statistically the most common malignant lesion of the reproductive organs in women. Every year, about 13 thousand representatives of the fair sex in Russia hear this terrible diagnosis addressed to them. At the same time, every second of the sick cannot cope with it.
This is a disease that, more often than others, can be diagnosed at an early stage and an effective course of treatment can be carried out. Many who survive this disease subsequently successfully give birth to healthy babies. But today the disease is “getting younger” and you can often find patients 18-19 years old with an extremely advanced stage, in which the only solution to save a life is the removal of the reproductive organs.
But as you know, not all types can cause cancer. Some of them, which have low oncogenicity, are still capable of darkening life, causing unpleasant neoplasms on the mucous membranes, including the genitals. For women, papillomaviruses are quite dangerous, so it is necessary to undergo timely examinations by doctors and systematically visit a gynecologist.
Diseases caused by a virus
The human papilloma virus can cause not only oncology and pre-cancer diseases, but also benign diseases of the skin and mucous membranes. But due to the virus entering the body, some other equally dangerous diseases can arise.
When examined and tested, their cause becomes known. When the virus enters the body, it does not manifest itself immediately, being in a latent state. If it continues to remain silent, no treatment is required.
Among women
The HPV type in women (16-18 most often causes serious illnesses) can provoke not only cancerous tumors of the uterus, external genitalia and anus.
The virus can also cause health problems such as:
- cervical dysplasia;
- diseases of the mucous membranes;
- diseases of the mucous membranes of the genital organs;
- erosion of the uterus;
- different types of warts (flat, plantar);
- condylomas.
A patient may be diagnosed with several types of HPV at once; this phenomenon is not uncommon.
In men
Men can also be significantly affected by the development of human papillomavirus, although the incidence is lower. Usually infected are men who are sexually active and often change sexual partners.
In this regard, diseases arise:
- genital warts on the genitals;
- oncology of the genital organs;
- difficulty urinating;
- sexual dysfunction.
If tumors appear, you should immediately seek help from a urologist or venereologist for further removal.
How to avoid getting infected with papillomavirus
How to avoid getting infected with HPV (papillomavirus):
- avoid frequent changes of sexual partners;
- protect yourself during intimacy;
- do not use other people's things;
- do not wear other people's clothes;
- avoid visiting public baths, saunas, swimming pools (or at least carry a personal towel and spare shoes with you);
- do not drink drinks or eat food from infected people;
- carefully approach the choice of cosmetology, clinic, hairdresser (you must be sure that the institution complies with all sterilization rules);
- do not come into close contact with carriers of the virus.
If you do develop papillomas, consult a doctor. He will conduct the necessary diagnostics, determine the strain of the pathogen and, if necessary, prescribe effective treatment.
If you do develop papillomas, consult a doctor
Diagnosis of HPV strains
HPV type in women (16 and others) and in men (it is believed that 31-33 are the most dangerous for the male body) can be diagnosed using different methods. However, diagnosis of certain strains is rarely sought. Most often, people come to the doctor to remove tumors, since they bring discomfort and aesthetic disgust.
Education does not allow one to maintain normal personal hygiene and lead a full sex life.
But when growths appear, you should be examined and tested - further development of the virus seriously threatens the body. It is recommended to carry out diagnostics immediately. People with the HPV virus are referred to a urologist, gynecologist, cosmetologist and venereologist.
Preparing for analysis
Before collecting material to study the presence of HPV, the doctor performs a visual examination of the patient. It is important to distinguish the papilloma virus from other dermatological diseases. The doctor evaluates the nature of the growths, their size, color, frequency of distribution, and will also ask questions from which the diagnosis will become clearer.
It is necessary to distinguish warts from lichen, calluses or syphilis. An enlarged mole can become a neoplasm, and in this case this already indicates possible oncology. The doctor should determine whether the growths on the patient's skin are cancerous. Additionally, a consultation with an oncologist is possible.
If there is a suspicion of HPV, the doctor will prescribe the following tests:
- PCR;
- Digene;
- DAD.
Several other tests may also be performed. Before visiting the hospital for tests, the patient needs to prepare. The further result depends on this (as well as on the quality of research procedures).
The requirements before submitting the material are as follows:
- do not take antibiotics 2 days in advance (or notify your doctor about taking them);
- men should not empty their bladder within an hour and a half;
- exclude sexual contact for 2 days;
- Women should not be tested during menstruation.
Also, you should not conduct research during the period of exacerbation of existing chronic diseases and infections. To take tests such as a Pap test, it is advised not to use medications in the form of suppositories or tampons.
Collection of material for research
After being examined by a doctor and given directions, the patient must undergo several mandatory tests that will help determine his disease, strain and risk level.
There are usually 2-3 mandatory tests:
- PCR. This type of analysis involves scraping from the urethra followed by examination of the material. Helps determine the type of papilloma virus and calculate the number of pathogenic cells. Also, thanks to this analysis, it is possible to identify the approximate timing of infection with the virus.
- Digene. This method (hybrid capture) examines women over 30 years of age. Diagnostics are carried out once every 3 years. The test is very sensitive and helps to accurately determine the degree of HPV infection and determine the genotype. The accuracy of the Digen test is 99%, it is available and can be performed in conjunction with cytological analysis. Does not require complex preparation.
- DAD. Used in gynecology and means scraping from the cervix. The Pap test allows you to determine the presence of malignant neoplasms and changes.
There are some other methods for studying biological material. Thus, HPV in a patient can be detected using ELISA. However, this test cannot determine the type of virus. The method is based on testing blood for the presence of antibodies that are produced as a result of a response to infection. With its help it is possible to determine whether it is a primary infection or a relapse.
Decoding the results
During the analysis, it is determined whether there is a papilloma virus in the human body, and what its concentration is. To evaluate the analysis, a special designation “Lg” is used.
| Meaning | Decoding |
| Lg less than 3 | The virus is present in the body, but it is in low concentration. |
| Lg 3, 4, 5 | The virus is present in the body in quite serious concentrations. |
| Lg more than 5 | The virus is in high concentration in the body. |
The test may fail and the result will be positive (false positive).
This phenomenon occurs due to:
- the patient was not properly prepared for the tests;
- before collecting the material, the person took certain medications;
- the material was collected incorrectly;
- biological material was contaminated.
Laboratory tests are combined into several groups that meet certain criteria for everyone who was analyzed. Some of these groups: women after childbirth, men and women from 25-30 years old and others. This is done in order to obtain normal indicators for a particular population group. If the result is positive, there is no need to worry too much.
According to statistics, 7 out of 10 people are infected with the papilloma virus. Some people live their entire lives without even knowing about their diagnosis. The pathological development of HPV begins with weakened immunity. Therefore, in cases of a non-hazardous type, the doctor prescribes immunostimulating medications.
However, if the results showed HPV type 16, 18, 31-33, 56, this means that the patient requires urgent treatment . This is especially important for women, since these types provoke diseases of the reproductive system.
Identified strains do not always mean oncology (although in most cases the help of an oncologist is necessary), however, it is necessary to especially monitor the condition of the body, undergo examinations and take courses of medications.
Does a condom protect?
If one of the partners has HPV, it is necessary to use a condom during sexual intercourse. However, a contraceptive is not a 100% guarantee that the infection will not be transmitted. Of course, the pathogen will not be able to break through the condom, but infection can occur in another way.
Infection can occur during foreplay. Through microcracks in the skin or in the oral cavity. In this case, a barrier contraceptive will not help.
HPV treatment depending on type
HPV type (in women 16, 18 and some others can cause pathologies of the genital organs, as well as the bladder) provoke diseases depending on which group they belong to. Each type has its own treatment methods; therapy is especially necessary for the second and third groups.
HPV in these groups does not always mean oncology, but other serious health problems may arise. Even the slightest deterioration in health or the appearance of neoplasms should be a reason to visit the hospital for examination.
14 type
Type 14 (for women and men) belongs to the group with a low oncogenic risk. The danger arises in people with malignancy, and in this case the doctor prohibits self-medication. Otherwise, type 14 causes the formation of warts, which can be removed both at an appointment with a specialist and at home. The doctor also prescribes antiviral drugs (for example, Isoprinosine).
To prevent further growth of formations on the skin, cryotherapy or its analogues are used. Some remove growths using caustic alkaline preparations. Type 14 is not dangerous and provokes cancer in quite rare cases (a combination of factors, severe weakening of the immune system).
16 type
HPV type 16 in women is considered one of the most dangerous. It increases the risk of malignant pathologies several times. Type 16 can cause cervical cancer - this type was found in approximately half of women with this disease.
Actively dividing, pathogenic cells cause the formation of papillomas and genital warts on the mucous membranes and skin. During the development of type 16 virus, cervical dysplasia appears - a sure sign of oncology of the reproductive organs.
18 type
Papillomas and condylomas grow most rarely with type 18 of the virus. However, with this type they also manifest themselves and can grow together into one large growth. Formation on the external genitalia, thighs, and oral mucosa leads to discomfort and other inflammations.
In men, type 18 can cause Bowen's disease (the formation of warts on the penis), which is also a prerequisite for the occurrence of cancer.
Typically, type 18 is not as common as type 16, but its development occurs much faster. Detection of this type means immediate therapy, the prescription of immunomodulators, vitamins and subsequent removal of unpleasant tumors.
31 and 33
Most often, these types of HPV cause diseases such as bowenoid papulosis and cervical neoplasia. Women's disease can be mild or severe.
The latter is already oncology. When combined with other types, women may develop neoplasms (condylomas). Bowenoid papulosis is most characteristic of the male body and occurs against the background of promiscuity.
51, 52 and 56
These strains also belong to the high-risk group and are transmitted mainly through sexual contact. These types provoke the occurrence of genital warts, including around the anus and rectum. In women, these HPV types cause cervical erosion and dysplasia. Types 51, 52 and 56 are the causes of oncology of external and internal diseases of the genital organs.
Symptoms and manifestations
It is difficult not to notice the clinical picture of HPV type 3. Round or oval elevations appear on the skin of the face, on the neck, on the back of the hands, and sometimes on the legs, the height of which is only 1 or 2 mm. As for the size, it usually does not exceed a couple of millimeters. However, in some cases, each flat wart may be 9 mm. But this is extremely rare.
The color of such formations ranges from flesh-colored to pink-brown. They often merge into one large group. Often their presence on the skin can cause severe itching. As a rule, flat warts do not cause any inconvenience or trouble. However, in some cases, you should definitely visit a doctor to prevent them from degenerating into cancer.
Such cases include the following symptoms:
- Heterogeneity of color.
- Bleeding.
- Very fast growth.
- Ulceration due to loss of skin integrity.
- Merging into one big group.
In any case, the doctor will help you accurately determine the diagnosis and prescribe the only correct treatment. Self-medication in this case is best avoided.
Is recovery from HPV possible?
Complete elimination of HPV is possible, but only at a young age. Almost 90% of cases of recovery are registered up to 25-26 years of age. For cure, immune therapy and removal of growths are used. The patient’s own immune system is no less important - if it is strong, there is a high chance of a complete recovery.
Immunomax, approved according to the instructions for the treatment of pathological conditions (condylomas, warts, dysplasia, etc.) caused by the human papillomavirus, is becoming increasingly popular among modern immunomodulatory drugs.
Immunomax
Experts note that the use of the drug Immunomax in the complex therapy of HPV-associated diseases leads to a decrease in the frequency of relapses and clinical recovery from infections.
When a person gets older, his immunity is no longer as strong as before. The virus remains in the body, waiting for the body to weaken, and then be activated (formations appear). A medicine that can destroy the virus has not yet been invented. The patient's recovery depends on himself and on auxiliary treatment.
Although HPV can no longer be eliminated after a certain age, therapy aimed at suppressing the activity of papillomavirus is still necessary.
Treatment of papillomavirus
The human papillomavirus can be hidden in the host’s body for a long time and not manifest itself in any way. Its development is stopped by the immune system, which should inhibit the spread of foreign DNA. One of the areas of treatment is aimed at maintaining and activating the immune system. This method is called conservative and includes the prescription of immunomodulatory and antiviral drugs (Isoprinosine, Allokin-alpha and others).
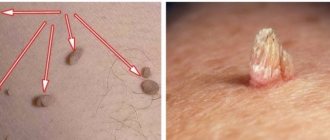
Another direction is aimed at eliminating the consequences of infection: removing existing papillomas and condylomas. There are several ways to do this:
- Surgical intervention. It is an operation to cut off tumors. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. The disadvantages of this method are not only possible consequences in the form of scars, but also the risk of blood loss. In addition, this method does not guarantee the removal of all papillomavirus cells.
- Electrocoagulation. The most common method of removing papillomas and warts due to its low cost and availability. It is carried out using high-frequency current, which acts specifically on the growths. Like the previous method, it leaves marks on the body from removed papillomas. It also does not guarantee the absence of relapses.
- Laser destruction. One of the most modern methods of removing papillomas. For this, a laser beam is used, which completely removes papilloma cells, affecting atypical tissues. This method is considered the most reliable and safe. It does not leave undesirable consequences in the form of scars and immediately seals the vessels to prevent bleeding.
- Cryodestruction. The procedure is carried out using liquid nitrogen, which is applied to a special applicator. Under the influence of liquid nitrogen, the growth gradually disappears. However, with this method it is possible to get burns, which will ultimately result in an unwanted scar. This is due to the deep effect of the substance on the skin.
Recipes for folk remedies to suppress activity
Traditional medicine can be used in treatment only after consultation with a specialist. It is impossible to replace full-fledged treatment with her, as this can lead to a worsening of her condition.
If the doctor has authorized the use of home remedies as additional ones, you can use the following 5 main opponents of growths:
- Onion or garlic. Vegetable juice is rubbed into the tumors 2-3 times a day. The course lasts approximately 3 weeks.
- Rowan . Berries cut in half or rowan puree are applied to the warts and then secured with a bandage.
- Potato . Raw potatoes are grated into a paste and applied to the formations. Use this method daily for 1 month.
- Wormwood . Wormwood seeds are poured with alcohol and a tincture is made (3 days). Then it is filtered and taken orally, 4-6 drops per day.
- Eggshell . Egg shells are ground and applied to the growths, covered with sterile cotton wool and fixed. The procedure is carried out once every 2 days. Course – up to 3 weeks.
These products should not be taken by people with an allergic reaction to these products, individual intolerance, or if the neoplasms are not identified (these are not papillomas or condylomas).
HPV detection tests
Early diagnosis is always an opportunity to reduce the risk of severe disease and complications. That is why gynecologists around the world recommend systematically visiting a gynecologist for a routine examination. If the doctor suspects that the patient has papilloma, but she feels completely healthy and has no complaints, he may prescribe screening for uterine cancer. This type of screening allows us to identify a precancerous condition or the presence of cancer in asymptomatic patients.
Today, several types of screening studies are available:
- visual inspection with acetic acid;
- testing for highly oncogenic types;
- Papanicolaou test and liquid-based cytology.
In addition, the doctor may recommend other types of diagnostics:
- cytological examination of biopsy samples;
- diagnostics for detection of antibodies;
- colposcopy;
- cytological method;
- amplification and non-amplification tests.
The most important point that anyone should remember is that test results should be deciphered exclusively by a doctor. You should not try to diagnose yourself based on recommendations from the Internet.
Can a vaccine protect against the virus?
The HPV vaccine exists and it gives the expected results. However, it is worth considering that it only works if the person is no longer infected with the virus. After the vaccine is administered, the body produces special antibodies that prevent HPV from entering cells and developing.
For vaccination, 2 drugs are used: Gardasil and Cervarix.
The vaccine is safe for humans. However, it cannot be used for treatment. The effect of the drugs was tested only on women, since the percentage of cases is much higher. Administration of the drug to men prevents the growth of condylomas.
When and how to vaccinate
The HPV vaccine is administered to girls aged 9-12, 16 and 17 years. Vaccination is mandatory and serves to strengthen immunity. Vaccination includes 3 stages. After 1 re-vaccination is carried out no earlier than 2 months. After 2 - not earlier than 4. If a woman is pregnant during vaccination, stage 3 occurs after childbirth.
HPV and its types that develop in women and men may well be preventable. Such dangerous types as 16 or 31 may not bother you if you use protection during sexual intercourse, conduct examinations and maintain the condition of the immune system.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky