Causes of papillomas on the genitals
The main causes of infection are sexual intercourse with sick people. Contact can be through the vagina, anus or oral. In some cases, infection can also occur through household means or during childbirth from mother to child. However, this is quite rare.
Factors that increase the likelihood of infection:
- Weakened immune system;
- Abuse of bad habits (alcohol, cigarettes, drugs);
- Severe stressful situations;
- Gastrointestinal diseases;
- Infectious diseases.
The risk group includes all people who are sexually active. It is worth noting that using a condom during sex does not protect against the papilloma virus. In order to become infected, it is enough to simply come into contact with the skin of the patient.
Risk factors also include visiting public places (bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool, beach).
This is due to the fact that such places have high humidity and minimal protection from germs (meaning lack of clothing).
Diagnosis of papillomatosis
To make an accurate diagnosis, a visual examination by a doctor is performed. In some cases, laboratory diagnostics may be necessary. In women, oncogenic and non-oncogenic formations are often very similar to each other, and they can only be distinguished with the help of a biopsy. In order to exclude infectious diseases, smears are made for microflora.
It is strictly forbidden to pull out, scratch, tear off or cut out papillomas on your own. This can cause the infection to spread and cause growths to appear on other areas of the skin. If you notice suspicious growths on the labia, immediately consult a dermatologist.
Do not wait for the formations to grow in size or disappear on their own. Timely treatment or removal will help avoid the development of infectious diseases, which in some cases can cause incurable harm.
Papillomas, polyps, warts on the genitals may indicate serious problems in the body. Most often they indicate impaired metabolism, advanced gastritis, colitis, liver and kidney diseases, and gynecological diseases. To get rid of tumors, you need to find out the cause of their appearance and prescribe treatment. It is worth noting that removing papillomas does not make it possible to avoid relapses. To prevent the disease in the future, you need to constantly strengthen your immune system.
When a virus is detected in the body using markers, treatment is usually not prescribed. Therapy is carried out only if the disease begins to manifest itself in the form of neoplasms on the skin or genitals. To get rid of papillomas, antiviral treatment and strengthening the immune system are prescribed. All activities must be carried out under the supervision of a qualified specialist.
Papillomas on the labia: how best to remove
They indicate that the human papillomavirus is present in the body. Now doctors know more than a hundred varieties of this virus. And statistics show that every fourth inhabitant of our planet suffers from papillomas.
How does infection with the human papillomavirus occur?
Most often during sexual intercourse without a condom, sometimes through domestic means. The virus can live in the human body for many years without causing any symptoms. An exacerbation is usually observed with a decrease in immunity or protective functions of the nervous system. Smoking, drinking alcohol, pregnancy, and hormonal changes can also trigger the appearance of papillomas.
How dangerous are papillomas?
Unfortunately, some forms of the papilloma virus can trigger the development of cancer. In 5% of cases, genital warts actually degenerate into a malignant formation. But even if papillomas are benign, most often women experience discomfort about this, considering them aesthetically unattractive.
Over time, formations on the genitals can increase in size and even close the entrance to the vagina. This leads to terrible discomfort.
How to remove papilloma from the genitals?
The most important thing to know and remember is that papilloma cannot be removed on your own. Under no circumstances! Forget about traditional methods - they increase the risk of malignant degeneration. If a genital wart bothers you, consult a doctor. Moreover, today there are several methods for removing it. Firstly, there are drugs for external use that slowly destroy papilloma cells. Secondly, antiviral injections are sometimes used, which are injected into the formation. Thirdly, papillomas are removed using both surgical excision and more modern methods - for example, the radio wave method .
The last method is the safest, most effective and painless. This is what is used in the Medical Network in Ukraine to remove papillomas from the genitals. The procedure lasts only a few minutes, after which the patient can go home or return to work. It's fast, comfortable and reliable!
Remember that papillomas can be removed from the genitals only after diagnosis - the doctor must make sure that the genital warts are not malignant in nature, and their removal will not entail a lot of health problems.
Methods for treating papillomas on the labia
- Laser removal. Can be used on any area of the skin and mucous membranes. After the procedure, there are no scars and no bleeding. The disadvantage is the long healing period - about two months.
- Cryotherapy is a method of removing tumors on the body with liquid nitrogen. The healing period is two weeks, and a small scar remains after the procedure. The disadvantage is that new papillomas may form at the site of the lesion in the future.
- Radio wave therapy. Removal of tumors occurs using the Surgitron apparatus. The healing period is about two weeks.
- Removal with super cleanser. This procedure is quite painful, especially in the labia area. The advantage is that wounds heal very quickly.
- In addition, electrocoagulation and surgical removal are used.
Review of medications for papillomas
Modern medicine has not yet developed drugs to treat HPV (human papillomavirus). All funds are aimed at alleviating the condition of patients, but not at eliminating the cause of pathology in the body.
- "Panavir"
It is an antiviral and immunomodulatory drug. Contains biologically active components - rhamnose, glucose, arabinose, xylose, mannose, galactose, uronic acid.
Indicated for papillomavirus on the labia, ophthalmic herpes, cytomegalovirus, orogenital warts, rhinovirus and adenovirus. Available in the form of a parenteral solution.
Directions for use: administer 5 ml of solution intravenously twice a day for two days. The action of the drug is aimed at reducing the activity of the papilloma virus. Side effects in the form of an allergic skin reaction are possible. Contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity, age under 12 years.
- "Kondilin"
It has cauterizing, mummifying, cytostatic and antimitotic effects. The active component is podophyllotoxin. Helps block cell division during metaphase. Indicated for external treatment of genital warts and papillomas. Available in solution form.
Method of use: if rashes are observed on the labia, you need to administer the solution orally 30 ml 2 times a day. The course of treatment is 10 days. Contraindicated in case of individual intolerance, under the age of 12 years.
- "Bonafton"
Has an antiviral effect. Indicated for papilloma virus on the labia, herpes simplex virus, adenoviruses, herpetic keratitis, herpes zoster, gingivitis. Available in tablet form.
Directions for use: 0.1 gram orally 3-4 times a day for five days. If necessary, the course can be extended after a two-day break. Possible side effects in the form of diarrhea, headache, irritation on the body. Contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
- "Podophyllin"
The main active ingredient is podophyllotoxin. Indicated for papillomatosis of the larynx, papillomas on the labia, fibroepitheliomas, and for the prevention of relapses of benign tumors. Available in powder form.
Method of use: a solution is prepared from powder and injected into the abdominal cavity through a catheter. Treatment with Podophyllin is carried out only in medical conditions under the supervision of doctors. Side effects are possible in the form of pain in the lower abdomen, burning in the bladder area, and urinary disorders.
Warts on the labia
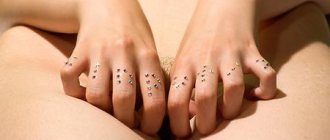
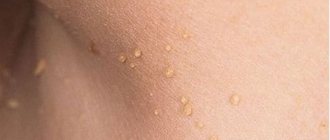
Papillomas on the labia, warts on the mucous membrane of the inner walls of the vagina, vestibule and entrance are small growths, balls, peas, “icicles” of flesh color. In most cases, these formations do not arise singly - they are a number of structures that gradually unite into tumor-like growths in the form of growths, “cauliflower”, “grapes”, “papillae”, “fringe” or “cockscombs” on a narrow stalk of various sizes . Blood vessels pass through the leg to the formation, through which the genital neoplasms are nourished and, accordingly, grow.
They can be single, more often multiple - they gather in groups, often the papillae grow very strongly and merge with each other into large conglomerates. Here you can see photos of condylomas in women.
With this localization, genital warts can be damaged by tight clothing, during intimate contacts, cosmetic and hygienic procedures, etc. Constant trauma to the external genitalia stimulates the relatively rapid growth and spread of papillomas and condylomas from the labia deep into the body - into the vagina, cervix, urethra, anus and rectum.
Photo of papilloma and condyloma on the labia
Since the woman herself usually cannot detect small formations, they are most often detected during an external examination of the genitals by a gynecologist. Although in our practice it is not uncommon for a patient with a sufficient number of small condylomas on the mucous membranes of the external genitalia to be the first to report the presence of these warts, although before that she regularly (more or less) visited other gynecologists.
Forum about papillomas of the labia
- Reasons for appearance? Infection with the human papillomavirus, and then its appearance on the labia on one or both sides, is always provoked by one of several factors: a). sexual contact with a virus carrier (a condom does not always protect against infection, since during foreplay the genitals come into contact with each other); b). sharing personal hygiene items with an infected person; V). visiting the same bath or toilet with a sick person (warmth and moisture favor the virus and condylomas grow faster); G). mechanical injury to the mucous membrane of the labia minora during masturbation, petting, shaving, etc. followed by the introduction of the virus. Since HPV can remain viable for a long time in the air, it can become infected in baths, saunas, public swimming pools, solariums, if you sit on benches with your genitals bare and use other people’s personal hygiene products.
- What is the difference between a sick person and a virus carrier? There are virus carriers - women who do not have pronounced signs of papilloma on the labia. They themselves do not suffer from HPV, but are carriers. Through close household or sexual contact, primarily oral contact, transmission of the virus to a partner is possible. An infected person is likely to remain symptom-free for many weeks, months, or even years. Factors that suppress the immune system (surgeries, stress, colds, injuries, pregnancy, abortion) are the reasons for the activation of infection and the impetus for the growth of genital warts, incl. on the labia minora and majora.
- Types of genital warts? Depending on the nature of their growth, warts can have external growth (exophytic) or internal growth (endophytic). The first ones are pointed. They appear on the outside of the labia in the form of growths and papillae, fimbriae. Endophytic, so-called “flat condylomas” are growths that extend into the surface epithelium. Condylomas inside the labia are caused by a type of HPV with high oncogenic activity, and in women they often spread to the cervix.
- What symptoms might there be? After the introduction of infection or activation of the virus in the submucosa, the woman initially experiences unpleasant sensations: itching, itching, stinging, burning. After some time (from several hours to days), small papillomas form on the labia (multiple or single). Sprouts of new elements can spread through the capillary network to neighboring areas and appear on the clitoris, near the urethra and anus.
- Can girls and teenagers have papillomas of the labia or not? Warts on the genitals are not the exclusive prerogative of sexually active women. In approximately 25-35% of cases, HPV of the labia minora is transmitted through household contact and its clinical manifestations in the form of condylomas in virgins can be at any age, from childhood to older reproductive age.
- Can papillomas appear from masturbation? As is already known from what we read above, infection occurs in the presence of injuries to the skin or mucous membranes of intimate places (lips, clitoris, vestibule, and anus), through which the virus easily enters the body. Such microdamages occur under intense mechanical influence as a result of masturbation, petting, fisting, improper use of sex toys or similar improvised objects, which, if there is a virus on the affected object, can subsequently lead to the appearance of warts on the labia majora or minora.
What to do if there are papillomas on the labia, how to remove them?
- Visit a competent and attentive gynecologist;
- Undergo a complete gynecological examination;
- Do a vulvoscopy (a type of colposcopy);
- Get tested for HPV (Digen test);
- Get tested for “hidden” infections.
If warts are detected on the genitals, the patient is recommended to undergo blood tests for syphilis (genital warts on the labia must be distinguished from broad ones, which are a manifestation of syphilis) and HIV (decreased immunity may be a consequence of AIDS). The table below presents an approximate list of tests that a woman should undergo if she has papillomas or condylomas on her labia.
| Analyzes | Price | |
| HPV types 6/11 | Not really | 650 |
| HPV genotypes (16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59) | typing | 2 350 |
| Blood tests for syphilis (RS), AIDS (HIV) | ELISA blood | 750 |