Burns from salicylic acid in the home, as a rule, do not pose a great danger. Serious injuries are more often suffered by people whose work is directly related to chemicals. Salicylic acid is considered moderately dangerous. It is often used in cosmetology and medicine.
According to statistics, the skin most often exposed to chemical burns is the skin of the hands, feet, face and neck. The mucous membranes fade into the background. The basic rule to follow in an emergency is not to panic. This will make it possible to understand what to do next so as not to harm the victim even more.
Normal or complication
Normally, a controlled facial burn appears only after a chemical peel, regardless of the depth of penetration of the active components. This side effect is a protective reaction of the body to the chemical ingredients used in peeling, which activate the regeneration process at the cellular level.
Expert opinion
Elena Apostolyuk
Cosmetologist
If the concentration of the active component is correctly calculated and the protocol for the peeling procedure is followed, a first-degree burn occurs, manifested by itching, mild swelling, hardening of the skin and severe redness. The absence of the described side effects indicates that the peeling was performed incorrectly.
Complications arise due to overexposure of the drug, treatment of areas with open wounds or ulcers, as well as individual intolerance to the components of the chosen product. They appear in the form of burns:
- second degree - pronounced peeling and blisters with liquid form on the face, which burst after a while, which increases the risk of spreading the infection;
- third degree - the skin dies and scabs appear;
- fourth degree - in addition to the epidermis, muscle tissue is damaged.
Deep scars can most often be eliminated only through laser resurfacing or plastic surgery.
Acid burn: features, danger and first aid
Burns
An acid burn is damage to the skin, subcutaneous tissue, internal organs and mucous membranes by liquids with a pH less than 7.5. Emergency first aid for acid burns will preserve the integrity of the integument, eyes, larynx, and respiratory tract in case of chemical injury.
Features and differences from other types of burns
Burns of this type occur when the rules of use when working with hazardous liquids are violated. According to ICD 10, such lesions are assigned codes T20–T30 depending on the location of the damage.
Acids and alkalis are widely used in household use. You need to know how to help yourself and others when coming into contact with caustic liquids.
Features of burns:
- There are strong and weak acids. The former have a pH value of less than 3 units. They cause extensive tissue damage.
- After contact with an aggressive liquid, a scab is formed, distinguishable from healthy tissue.
- The degree of damage depends on the acid, its concentration, duration of contact, its individual properties and ability to penetrate tissue. A concentrated product will cause more extensive and deeper damage to the skin and subcutaneous structures.
- Some acids (sulfuric acid) generate heat upon contact with moisture contained in the skin. This increases skin damage.
- Burns of this type to the eyeballs, respiratory tract, and digestive tract are considered severe injuries.
- Burns of different types of aggressive substances have characteristic symptoms. Based on the appearance of the injury, it can be assumed what substance was used to inflict it. A burn with sulfuric acid cannot be confused with a lesion with acetic or carbonic acid.
- The degree of damage depends on the quality of first aid. Sometimes symptoms appear 2 days after injury.
Degrees
The degree of damage depends on the concentration of aggressive substances, duration of exposure and depth of tissue damage, and the quality of first aid.
Degrees of chemical injury:
- At the first stage, only the upper layer of the epithelium of the arm, leg, and body is affected. After removal of the aggressive substance, hyperemia of the surface is observed. Healing occurs within a few days. As a rule, drug treatment is not required and scars are not formed.
- In the second stage, a blister forms and the deeper layers of the skin are affected. The prognosis is favorable, but seeking medical help is a must. With high-quality first aid and following the doctor’s recommendations, scars will not form.
- At stage 3 – extensive burned areas with the formation of necrotic zones. Treatment is only inpatient.
- At stage 4 – muscles, fiber, and bone structures are affected. The prognosis is unfavorable.
Chemical lesions of the esophagus, respiratory system, digestive tract, throat, and eyes require separate classification. Damage to these organs is considered severe trauma. It is impossible to determine the depth of exposure of the tissue to the caustic substance at the stage of examining the victim. Such patients require hospitalization in a medical facility.
First aid
In case of a burn, care and first aid consists of neutralizing aggressive chemicals and removing them from the skin.
The algorithm for providing assistance is as follows:
- Remove clothing from the affected area.
- Rinse the affected area with plenty of running water. The processing time is at least 15 minutes. If emergency assistance is provided with a delay - this may be the time spent on freeing the victim from clothing - rinsing should be done for at least 40 minutes.
- Do not wipe the burn area with cloth or napkins.
- If the burning sensation does not stop, continue rinsing.
- Proceed to neutralize the aggressive substance. For this, alkali is used. In everyday life, use a weak solution of soda and laundry soap. Some substances - fluoride, phosphorus, nitrogen, sulfur - require specific neutralizers. The likelihood of using them in everyday life is low.
- First aid for a burn with sulfuric acid differs little from the algorithm for exposure to hydrochloric, salicylic, acetic and other chemically active substances.
If aggressive chemicals are swallowed, the victim should be given a weak solution of soda to drink. This is 1 teaspoon per 1 glass of water. If the eyes, face and visual analyzer area are affected, treat the tissue with plenty of running water.
If vapors of aggressive substances are inhaled, remove the victim to fresh air and rinse the mouth with an alkaline solution. This is the only possible first aid.
What substances neutralize the effects of various acids?
The principle of neutralizing aggressive acid remains the same - exposure to an alkaline solution.
| Acid | Neutralizing agent |
| Sulfuric | At home, only a solution of baking soda and laundry soap. |
| Nitrogen | Baking soda solution. |
| Boric, citric, acetic are weak acids. Only vinegar essence can cause significant harm to the body if it enters the gastrointestinal tract | Baking soda solution. If it enters the digestive tract in a hospital setting, it is recommended to use magnesium bicarbonate. |
| Salicylic acid – used for peeling | For home treatment, they sell products containing no more than 10% salicylic acid. Simply rinse off with plenty of water. |
| Carbon or coal is an extremely weak compound. In the presence of heat, it breaks down into water and carbon dioxide | Does not require neutralization, is an unstable compound. |
Further treatment and healing prognosis
A combusiologist treats chemical injuries. Treating an acid burn is a complex process. It is impossible to predict how deeply the tissue is damaged.
Only after 2 weeks does the scab come off. There is a wound surface underneath. Regeneration rate is low. The formation of extensive scars is possible, which need to be smeared with special products.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fDMvtUQbpH0
General treatment method:
- Pain relief – analgin, paracetamol, ibuprofen. In severe cases, medications are administered by injection.
- Healing ointments – Sudocrem, Panthenol, Solcoseryl.
- Vitamin complexes to accelerate regeneration processes.
- Physiotherapy – at the stage of epithelization of the wound surface.
Damages to the respiratory system, mucous membranes, digestive tract, and eyes recover more slowly than in areas of the skin.
In what cases does tissue necrosis occur?
Necrosis is the destruction of tissue under the influence of external or internal factors. Acid necrosis is called coagulation - protein molecules coagulate under the influence of an aggressive agent.
Chemical necrosis is the result of complex trauma. It includes:
- thermal damage - many acids release heat when interacting with water;
- tissue dehydration – substances are hypertonic solutions;
- coagulation or folding of proteins under the influence of hydrogen ions contained in the substance.
Acid necrosis is a characteristic feature. It is a black charred surface. Under the influence of nitric acid, the area of necrosis looks like a yellow-brown plate.
Tissue necrosis occurs with prolonged exposure to a damaging agent, when concentrated solutions of strong acids - sulfuric, nitric, hydrochloric, or aqua regia mixtures - are ingested. Weak compounds such as carbonic, citric, and acetic acids do not cause tissue necrosis.
The consequences of necrosis are disability. A long recovery period, operations to reconstruct the skin, the formation of scar tissue (can be found in the photo on the Internet).
To avoid such consequences, we advise you to follow safety instructions, use masks and other protective equipment when working with substances of this type.
The article has been verified by the editors Link to the main publication
articles:
(1 5,00 of 5) Loading...
Didn't find suitable advice?
or see all questions...
Source: https://BezTravmy.ru/ozhogi/kislotoj.html
Causes of burns
During chemical peeling, under the influence of acids, the stratum corneum of the skin is destroyed, and along with it, the active substance also affects the healthy epidermis, which leads to a burn.
A complication in the form of a burn above the first degree after any chemical peel appears due to:
- overexposure of the active substance beyond the recommended time;
- hypersensitive skin;
- allergic reaction to the ingredients of the composition;
- the presence of open wounds on the skin;
- using acid concentrations greater than 30%.
Often the reason for getting a severe burn is the unprofessionalism of the cosmetologist, who incorrectly assesses the initial state of the dermis, and, as a result, makes the peeling with an inappropriate composition.
Salicylic acid burn: what to do at home
Category: chemical burns
Burns from salicylic acid in the home, as a rule, do not pose a great danger. Serious injuries are more often suffered by people whose work is directly related to chemicals. Salicylic acid is considered moderately dangerous. It is often used in cosmetology and medicine.
According to statistics, the skin most often exposed to chemical burns is the skin of the hands, feet, face and neck. The mucous membranes fade into the background. The basic rule to follow in an emergency is not to panic. This will make it possible to understand what to do next so as not to harm the victim even more.
Treatment
You can speed up recovery by using drugs based on natural products and medicines, which should be prescribed by a doctor.
Drugs
The following medications are used to treat burns:
- Panthenol. The active substance is dexpanthenol. Increases the density of collagen fibers, has an anti-inflammatory effect and accelerates the regeneration process. Frequency of application – from 2 to 4 times a day. Pantestin or D-panthenol has a similar effect.
- Elokom. A hormonal drug containing mometasone. Available in the form of lotion or ointment, it eliminates itching, swelling and inflammation. Apply to affected areas no more than 1 time per day.
- Bepanten Plus. The base of the cream consists of chlorhexidine and dexpanthenol. Reduces the risk of infectious complications and scars, has a moisturizing, regenerating and antibacterial effect. You can treat the skin 2 times a day.
- Olazol. Anesthetic spray containing sea buckthorn oil and satin. Helps eliminate swelling and severe flaking. Frequency of use: 1–2 times a day.
In case of severe burns, which are accompanied by the appearance of blisters, the specialist prescribes the following therapeutic regimen:
- treating the skin with regenerating preparations to accelerate the healing process - Panthenol or Bepanten;
- the use of glucocorticosteroids to prevent the spread of inflammation - Diprosalik or Elokom;
- the use of antihistamines to eliminate redness, itching and swelling - Zodak or Claritin;
- taking antibiotics in case of infection spreading - Sumamed or Amoxiclav.
Therapy is prescribed by a doctor only after accurately determining the degree of damage to the epidermis.
Folk recipes
Effective natural remedies for the treatment of burns after peeling:
- Vegetable mask. Grate half a peeled cucumber and a medium potato on a fine grater, add a chopped sprig of parsley. Add 1 tsp to the resulting composition. aloe juice, 1 tsp. freshly squeezed lemon juice and 1 tbsp. l. olive oil. Distribute the mixture evenly over the damaged dermis, leave for 15 minutes, rinse with warm water. Repeat treatment once every 5 days for 3–5 weeks. The mask eliminates itching and swelling, and also has a whitening effect.
- Oatmeal decoction. Make a decoction of 100 gr. oatmeal, add 2 tbsp. l. potato starch. Apply to affected areas, leave for 15–20 minutes, rinse. Do the procedure 3 times a week until the epidermis is completely restored. The product will help get rid of burns and red spots in a short time.
- Avocado mask. Mix 1 tsp. liquid honey and 2 tbsp. l. Avocado puree. Heat the resulting mixture in a steam bath and apply to the affected skin, rinse after 20 minutes.
Before using any folk recipe, you should consult a specialist.
Providing assistance to the victim
The first thing you need to do if you are injured by salicylic acid is to interrupt the contact of the chemical element with the victim’s body. If the substance has been spilled on clothing, it should be removed immediately, being careful not to touch the contaminated part to undamaged areas. If things are difficult to remove, it is recommended to cut them.
The shorter the exposure time to the irritant, the better for the patient, since the substance will penetrate less intensely into the deeper layers of the skin.
You should not try to remove acid with a regular towel or napkins, including wet ones. It is recommended to wash off the chemical with water. Keep the affected area under a running stream for 15 minutes. If the contact of the acid with the body was prolonged, then the washing time is increased to an hour. Do not use soap or other detergents to clean your skin. The components included in the hygiene product can enter into a chemical reaction with salicylic acid, which can aggravate the situation.
When acid gets into your eyes, you can wash them with water, milk, or a baking soda solution. If the esophagus is damaged, the victim needs to drink a large amount of water with soda dissolved in it. Sodium bicarbonate is a substance that neutralizes the effects of acids.
If you do not use an acid-neutralizing solution, even after washing, chemical residues will continue to have a negative effect on the fabric. Immediately after providing first aid to the victim, you must call an ambulance. If possible, it is recommended to transport the patient independently to the hospital. The affected area should be covered with a sterile bandage, especially if the journey to a medical facility will be long. When pieces of clothing or dirt remain in the wound, it is not recommended to try to remove them yourself.
After professional treatment of the wound by medical staff, the doctor will assess the extent of the damage and prescribe appropriate antiseptic and regenerative treatment. In case of severe pain, the patient is prescribed analgesic medications.
Skin care rules
Recommendations for skin care after peeling:
- The burn after glycolic or salicylic peeling is treated several times a day with healing agents based on panthenol. These ointments accelerate the regeneration process and promote skin renewal at the cellular level. Damaged skin should be treated at least 3 times a day.
- The burned epidermis is restored with the help of disinfectants and antiseptics. If there is extensive redness, a specialist may prescribe antihistamines.
- If there is a risk of developing skin diseases, the doctor may prescribe oral antibacterial medications.
- To moisturize your face, you need to regularly apply moisturizing and soothing professional products.
- When going outside, it is imperative to use high-protection sunscreens.
- The skin is protected from sudden temperature changes; it is also necessary to refrain from using scrubbing products, visiting the pool, sauna or solarium.
- The crusts that appear on the face cannot be removed on their own; after washing, the face is wiped with cosmetic wipes - rubbing with a towel will aggravate the existing problems. In case of severe itching, you should treat your face with Elok lotion daily.
- Avoid excessive physical activity, which causes excessive sweating and increases the risk of spreading infection.
- For the entire recovery period, you must avoid using drying cosmetics, as well as foams or wash gels that contain sulfates.
- You should drink at least two liters of water per day - this will help restore water balance and speed up recovery.
- Fatty and salty foods are excluded from the diet.
The average duration of skin restoration is a month. During the entire rehabilitation period, the use of decorative cosmetics, scrubbing and drying agents should be avoided.
Question answer
What can lead to overexposure of the cleansing composition on the face?
Overexposure of the mixture to the skin leads to burns of varying severity. Then, to restore the skin, you should be examined by a doctor who will prescribe a course of treatment.
For minor damage, it is enough to use a vegetable mask and treat your face with Elok ointment.
How to reduce the risk of burns?
After any chemical peel, a first-degree burn occurs. To quickly get rid of side effects after peeling, it is recommended to smear the skin with Bepanten or Panthenol, try not to go outside during solar activity and remove the crusts yourself.
Degree of damage
The severity of the situation depends on the extent of the chemical damage. It’s difficult to determine right away.
If the acid is not neutralized, it continues to affect the skin for several hours and even days, aggravating the victim’s condition.
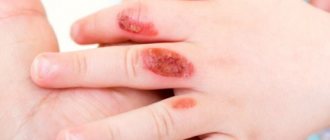
In medical circles, there are 4 degrees of acid burns:
- The first is a minor injury, manifested by swelling, pain and redness of the skin.
- The second is severe damage, characterized by burning, redness and the formation of a scab with clear outlines around the perimeter.
- The third is characterized by the appearance of non-healing wounds. The color of the epidermis may darken or become light. The scab often cracks, which threatens infection.
- The fourth is characterized by tissue death. The dermis, fatty tissue, and muscles are affected. In severe cases, destruction can affect joints and bones.
The degree of burn depends on various factors. Of great importance are:
- duration of exposure to the substance;
- chemical properties of acid;
- area of the affected area;
- concentrated content of hydrogen ions in the composition.