Today, very often doctors are asked for help in removing warts of various locations. Electrocoagulation is considered the most effective technique. One of the main advantages of this procedure is the removal of warts even in hard-to-reach places. The only exception is warts that are localized on the sole. They have a rough and dense structure. Warts are removed with a special device – an electrocoagulator.
Specifics of the procedure.
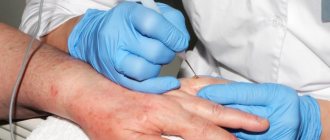
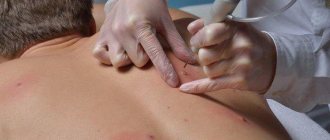
The procedure technique depends on the shape, size and thickness of the tumor, so the specialist chooses the most convenient attachment for the device for greater reliability, efficiency and ease of manipulation, and the ability to control the parameters (frequency and current) for electrocoagulation. Nozzles are used in the form of a metal loop or a thin electrode with a spherical thickening at the end. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia on any area of the skin or mucous membranes; removal of tumors in children is often performed under general anesthesia. A loop or a special electrode is used to influence the tumor or excise its stalk, followed by burning out the tumor or its base with a constant high-frequency or alternating current. At the same time, coagulation of the capillaries of the dermis occurs, which significantly reduces the likelihood of bleeding and disinfection of the skin, eliminating the addition of a secondary infection. After removing the papilloma, the skin is treated with an antiseptic solution. Electrocoagulation of papillomas is considered one of the reliable and time-tested methods, but, like other methods, it has its pros and cons.
What warts can be removed with electric current?
Removal of warts by electrocoagulation is suitable for areas on the arms, back and other covered parts of the body. This method of removing papillomas is relevant for multiple formations. Moreover, several defects can be eliminated at once in one session. As a rule, this is done under local anesthesia, but if the treatment area is very small, anesthesia is not particularly necessary.
The method is not suitable for removing very large warts. Cosmetologists undertake to remove defects larger than 10 mm, but healing in this case will occur with the formation of a scar. Plantar, or plantar, warts can theoretically be removed by electrocoagulation, but the procedure is painful, and healing takes a long time and involves scarring.
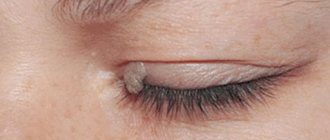
Due to the high risk of keloid formation, current is not recommended for removing large warts, moles and papillomas in the face, décolleté, neck and where a cosmetic defect will play a significant role. The electrocoagulation method is not suitable for removing genital warts, which are located on the eyelids, mucous membranes and genitals. It only gets rid of the external manifestations of the papilloma virus and does not guarantee the complete absence of relapses.
Advantages when removing papillomas using electrocoagulation:
- safety and effectiveness of the method, the ability to remove small tumors or pedunculated papillomas in one session, which lasts from 5 to 10 minutes;
- used for any age and skin type;
- the ability to regulate the therapeutic effect of electric current in strength and frequency, depending on the size, location and type of tumor - accuracy of settings and constant visual control;
- prevents the likelihood of infection (attachment of pathogenic microflora) and bleeding;
- the possibility of conducting histological studies of a removed tumor (as opposed to cryodestruction, laser removal and radio wave surgery) in order to predict possible recurrence of papillomatosis and confirm the benignity of the formation;
- relatively cheap method compared to other methods (laser removal, radio wave removal).
Is it safe from an oncological point of view?
Professional removal of ordinary, benign formations poses absolutely no threat
Professional removal of ordinary, benign formations poses absolutely no threat. What is really unsafe is to ignore large moles that have recently increased in size, become very dark or damaged.
Such moles can turn into malignant formations and require immediate removal. But any large mole can be removed without waiting for alarming symptoms - this will be the best prevention.
In our clinic, moles are removed quickly and painlessly, and the cut sections of tissue are immediately sent for histological examination. It is also necessary to get rid of warts, since they are very contagious and can spread to all family members.
Electrocoagulation of papillomas. Disadvantages of the method:
- with the wrong choice of duration, frequency and strength of electric current on the papilloma:
- the risk of formation of residual scars due to a large area of necrosis (if parameters are exceeded and deeper exposure) or with large papillomas, therefore this method is used with extreme caution to remove papillomas on visible areas of the skin;
- the possibility of relapses at the site of removal - the growth of new papillomas (with insufficient exposure and failure to remove all elements of the neoplasm);
- if the skin is not properly cared for after electrocoagulation, there is a high probability of pigment spots;
- the relative pain of the method, especially in people with increased sensitivity to pain - most patients tolerate the removal procedure (cauterization of papilloma) quite easily, but there is discomfort and unpleasant sensations;
- healing time is up to 10 days, which significantly exceeds the recovery period after removal of papilloma by laser (5-7 days) or radio wave method (2-3 days).
What you need to know about papillomas
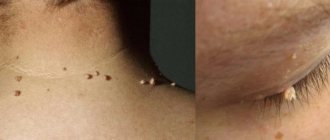
Papillomas look like single or multiple skin formations with an uneven surface, located on a stalk or broad base and rising above the skin level
Papillomas look like single or multiple skin formations with an uneven surface, located on a stalk or broad base and rising above the skin level. The color of the papilloma may match the color of the skin, or it may be dirty gray or brownish. The pedunculated formation is well mobile. The size of the papilloma varies from 3 mm to 3 cm, the surface is often uneven, with partial keratinization. Papillomas grow slowly and stop when they reach a certain size.
They are caused by the human papillomavirus. By the way, this virus causes the appearance of not only papillomas on the skin, but also warts and genital warts. It is transmitted by contact, but can also be transmitted in utero - from mother to child. Moreover, the virus tends not only to cause localized formations, but also to infect neighboring areas of the skin.
Contraindications to removal of papillomas by electrocoagulation:
- individual intolerance to electrical procedures or allergies to painkillers;
- hereditary or acquired bleeding disorder (increased bleeding);
- acute infectious or somatic diseases, exacerbation of chronic diseases, presence of a pacemaker;
- malignant nature of the neoplasm;
- herpes in the active phase or other inflammatory diseases of the skin;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding.
This procedure should be performed with caution in case of diabetes mellitus and a tendency to form keloid scars.
Wound care after electrocoagulation.
After thermal exposure to the papilloma, dry crusts form in the operated area, which eventually fall off on their own. It is unacceptable to independently remove crusts or papilloma tissue unless they are immediately rejected. Dry crusts or remnants of “evaporated” papilloma are a biological dressing, and their early removal often causes bleeding, and in the future can lead to the formation of scars and/or age spots. Therefore, proper wound care after removal of these cosmetic defects is considered an important factor. At first (several hours or days) after electrocoagulation, slight discomfort or pain may be observed in the wound area, but this should not cause concern - they go away on their own and do not require treatment. The crusts that form after the procedure are rejected on their own after the wound heals, on average after 8-10 days. The crust and the area around it must be treated 3 times a day with a weak solution of potassium permanganate (5% potassium permanganate solution) or another antiseptic (furacillin solution, chlorhexidine) - this is not only the prevention of secondary infection, but also an opportunity to avoid the appearance of a scar. Also, at this time, you should not apply various cosmetics to this place and avoid contact with water (any moisture contributes to the crust becoming soggy, which creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic flora and infection of the wound).
Is one time enough?
Sometimes even one session of electrocoagulation is enough to radically remove a papilloma or even several in one place. Usually these are small formations, “on a stalk”.
In other cases, you will have to undergo a course of treatment, sometimes even with the addition of medications - antiviral, immunomodulatory, etc.
For example, this is possible in the following moments:
- with deeply located papillomas on a flat base;
- with multiple formations;
- in case of recurrence of papilloma at the site of removal.
Complications after electrocoagulation of papillomas.
The decisive role in electrocoagulation of papillomas is played by the qualifications, experience and professionalism of the doctor or cosmetologist who carries out the procedure, the type, size and location of the tumor being removed, proper wound care, as well as the prevention of relapses. All complications during the procedure or during the recovery period arise as a result of violation of the surgical technique, incorrect choice of nozzle or current strength, incomplete examination of the patient or ignoring contraindications:
- bleeding from the wound in case of trauma to a large vessel or in the presence of blood diseases with problems with the blood coagulation system;
- allergic reaction (if you are allergic to painkillers and/or intolerant to electrical procedures).
Complicated course in the recovery period after removal of papilloma can be observed with improper care of the postoperative wound:
- suppuration (with early forcible removal of the crust and infection entering the wound);
- the formation of pigment spots or depigmented whitish scars;
- the formation of large connective tissue scars in those cases with a genetic predisposition to the proliferation of connective tissue;
- proliferation of atypical cells at the site of electrocoagulation (in case of injury, burn or constant exposure to aggressive chemical and physical agents), their malignancy (malignancy);
- recurrence of papilloma.
If any signs of a complicated course appear after electrocoagulation, you should immediately contact a specialist.
Why do papillomas appear?
Papillomas are formed:
- in areas of friction and frequent skin trauma
- in the folds of the skin
- with hormonal changes in the body (especially during pregnancy, during premenopause)
- with decreased immunity (after sunbathing, when using chlorinated water for washing)
Papillomas are viral in nature; sampapillomavirus lives in the blood and cannot be eliminated. With various provoking factors listed above, the papillomavirus is activated and manifests itself in the form of neoplasms on the skin - papillomas. There are many types of papillomavirus (more than 20); the formation of skin papillomas is associated with the presence of a non-oncogenic virus in the body. Papillomas on the skin rarely undergo degeneration. However, skin papillomas are capable of multiplying on the surface of the skin: many daughter papillomas appear near the mother papillomas.
Prevention of scar formation, age spots and recurrence of papillomas.
After the crusts fall off, delicate pink skin appears at the site of the wound, which must be protected from injury and exposure to sunlight - this can cause burns and age spots.
Therefore, after the natural rejection of the crusts, the skin must be carefully lubricated with sunscreens with a high degree of protection or sealed with a bactericidal patch for the duration of exposure to the sun (this does not depend on the time of year). To prevent the formation of pigment spots at the site of the removed papilloma, it is necessary to avoid visiting a solarium and/or exposure to ultraviolet rays. Until the young epithelium at the site of papilloma removal gets stronger and acquires the color of the surrounding tissues, you should not use decorative cosmetics and foundation (even if the operated area is on the face). Also, you should not treat your skin with scrubs, alcohol lotions, irritating ointments, or expose your skin to various chemically active substances containing acids, chlorine or alkalis. Various hygiene procedures should be carried out with caution: do not rub with a pumice stone or washcloth, avoid visiting saunas and baths for two months after the procedure. After removal of papillomas during the recovery period, to increase the regenerative ability of the skin, its elasticity and resistance to external negative influences, patients are recommended to take vitamins A and E (“Aevit” 1 capsule once a day, oil solutions of tocopherol acetate (10 mg), vitamin A ( 2300 IU daily) or multivitamin-mineral complexes). To prevent secondary infection and recurrence of papillomas, experts recommend taking measures and taking medications aimed at strengthening and increasing immunity - healthy sleep, hardening, ascorbic acid, herbal adaptogens (tinctures of echinocea, ginseng, eleutherococcus). In contact with
Price
The price for electrocoagulation depends not only on the clinic and city, but also on the following points:
- number and size of papillomas;
- location of the papilloma (more expensive in the eye area - eyelids, etc.);
- the need for subsequent histological examination.
Removing a papilloma up to 2 mm in diameter without subsequent analysis of the formation will cost about 200 - 300 rubles. From 3 mm or more - 500 - 600 rubles. Histological examination costs about 1000 - 1500 rubles.
Often there are promotions and discounts for the removal of several papillomas at once.
We recommend reading about laser wart removal. You will learn about the benefits of laser, indications and contraindications for this procedure, and the method of its implementation. And here is more information about wound care after laser wart removal.