Why do warts appear in the vagina, why do they grow quickly, disappear spontaneously, or, conversely, degenerate into malignant formations?
These questions still arouse research interest among doctors.
Warts near the vagina, in the vagina, on the labia, on the cervix, in the urethra or near the anus are most often a manifestation of human papillomavirus infection.
They are called anogenital (venereal) warts.
Infection with human papillomavirus infection occurs mainly as a result of sexual contact (including anal/oral-genital).
Anogenital warts on the genitals of pregnant women can cause infection of the child during the passage of the mother’s birth canal.
The risk of intrauterine (transplacental) infection cannot be excluded.
The risk of infection through household contacts currently remains unknown, although the possibility cannot be ruled out.
It has been established that warts on the labia majora, near the vagina, etc. are caused by representatives of the group of human papillomaviruses (HPV) with low oncogenic risk.
They are capable of causing malignant transformations only in special conditions, in 90% of cases, types 6 and 11.
Before the actual warts appear in the vagina, the incubation period after the virus enters the body can range from weeks to several months.
On average, about six months for women.
There is evidence that the disease can “sleep” in the human body for many years without showing itself in any way.
In general, a wart near the vagina is found in only 2% of infected people.
Warts in the vagina: factors contributing to their development
- frequent change/multiple sexual partners;
- early onset of sexual activity;
- decreased immunity (for example, due to hypothermia, general diseases, including ARVI, hormonal disorders, etc.);
- infection with HIV and other sexually transmitted infections;
- disruption of the normal composition of the vaginal microflora;
- pregnancy (in this situation, after childbirth, formations often disappear spontaneously);
- vitamin deficiency;
- stress, etc.
It has been established that in almost 90% of episodes, papillomavirus infection is combined with infection with other sexually transmitted infectious diseases.
Most often, HPV is detected simultaneously with ureaplasma.
Chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, and candidiasis are less frequently detected (vaginal warts, when clarifying the diagnosis, necessitate additional research due to the high risk of other STIs).
Prevention of genital warts
The virus manifests itself when a person’s immune system is weakened. Accordingly, you will need to treat other diseases in a timely manner, observe personal hygiene rules, take immunostimulating drugs and antiviral drugs.
For healthy people, it is important not to use other people’s personal belongings and hygiene items (towels, toothbrushes, combs, shoes). It is better to refuse sexual contact with someone who has HPV, since a condom will not protect against the virus, especially when there are warts on the person’s skin.
What are warts around the vagina and perigenital area?
Formations are classified depending on their location.
For example, a wart may appear on the labia (external anogenital), on the walls/at the entrance of the vagina (vaginal), uterine cervix, etc.
Moreover, the primary appearance of such papillomas in one area may or may not be accompanied by their development in another part; it is impossible to clearly say how often they “transition” from the labia to the vagina and cervix.
Oral-genital contacts contribute to the formation of condylomas in the oral cavity and larynx.
Also, infection of newborns can lead to the development of laryngeal (respiratory) papillomatosis.
It manifests itself as hoarseness and difficulty swallowing (in severe cases, breathing problems are possible).
In adults, this disease is often associated with concomitant HIV infection.
This requires appropriate research.
Causes of appearance and methods of treatment in children
The appearance of papillomas on the genitals in children can be caused by several reasons:
- Infection during childbirth from the mother. The infection is not transmitted in utero, but during passage through the birth canal.
- Through the use of common household and hygiene items with infected family members (towel, bathtub, toilet) or in a public place.
In addition, there are other skin diseases that are important not to be confused with papillomatosis: molluscum contagiosum, lichen planus.
In any case, the appearance of skin formations in a child indicates a weak immune system. It is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible to agree on a further plan of action.
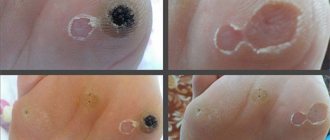
Warts in the vagina: types
There are several types:
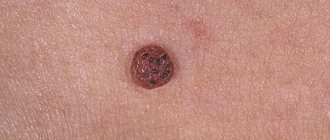
- Genital condylomas are peculiar protrusions on a leg of a lobular structure (similar to cauliflower or cockscomb buds) with a variegated/“loop-shaped” pattern, mainly localized at the entrance or inside the vagina, on the labia minora, near the anus, in the groin, on the uterus cervix;
- keratotic warts (the main causative agent is HPV type 6) - horny-looking papules with a dense apex and a thin stalk, located mainly on dry skin (labia, groin);
- in the form of papules - dome-like formations without protrusions on the lateral part of the vulva, in the pubic region, near the anus, in the perineum, pinkish, up to 4 mm in size, with a smooth surface, located on the keratinized epithelium;
- in the form of spots – localized on the skin/mucous membranes, brownish-red, reddish-pink or whitish-gray;
- warts in the vagina, giant condylomas - small wart-like papillomas merge into one formation on a broad base (when discussing the question of why Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma is formed from a wart in the vagina, attention is drawn to the tendency to this process in people with reduced immunity or during pregnancy) .
When warts are detected in the perigenital area, it is important to differentiate relatively harmless condylomas acuminata from serious pathologies.
Thus, with bowenoid papulosis, warts with a smooth or velvety surface on the mucous membranes of a brownish or reddish-orange color form in the affected areas.
The skin has a blackish-brown, ashy tint.
Bowenoid papulosis is provoked by papillomaviruses from the highly oncogenic risk group and in 3% of cases leads to malignancy of the formations.
Differential diagnosis of warts in the vagina
A common problem in differential diagnosis is the question of what is the difference between condyloma lata due to syphilis and warts in the vagina.
True, it is more often necessary to distinguish between such formations located in the anal area.
The main differences between genital and lata condylomas:
- syphilitic formations have a wide stem, and HPV-provoked ones have a narrow stem;
- with syphilis the formations are dense, with HPV they are soft;
- The color of genital warts is usually dark red, lilac, red, anal condylomas are flesh-colored, pinkish.
Formations on the uterine cervix are also of two types:
- exophytic – absolutely similar in appearance to external anogenital formations;
- endophytic (otherwise flat) – located in the epithelial layer, virtually invisible, can become malignant (in approximately 4–10% of cases over two years).
If warts appear in the vagina or on the labia, then subjectively at the site of the lesion the following may be felt:
- itching, tingling, burning, discomfort;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- bleeding, cracks.
If formations occur in the area of the urethra, then in addition to the above manifestations, pain and difficulty urinating are sometimes noted.
Cervical condylomas usually have no symptoms and can only be detected during a special gynecological examination.
Patient reviews
A wart appeared on the penis. I consulted with a venereologist. Laser removal was prescribed. In 2 procedures I got rid of the growth. The therapy was completed without pain or other side effects.
Andrey, 29 years old
After hospital-acquired pneumonia, a wart appeared in the anus. Drug treatment with Ferezol was prescribed. Within a month the formation disappeared. The drug itself does not provoke pain, only a slight burning sensation.
Svetlana, 39 years old
A condyloma appeared in an intimate place.
The doctor prescribed surgery for me due to a secondary infection. The manipulation was carried out under anesthesia. There were no complications after the operation. Alexander, 43 years old
How are anogenital warts detected?
As a rule, the diagnosis is made based on a visual examination.
In a number of situations, it becomes necessary to differentiate such warts from other pathological formations.
For example, with condylomas lata in syphilis, bowenoid papulosis, which is discussed above, and normal variants.
Thus, the appearance of warts is similar in appearance to micropapillomatosis of the vulva.
This variant of the norm is found in almost every twentieth woman.
It appears as small pinkish nodules on the inner surface of the labia minora.
A test with acetic acid allows you to distinguish warts from such micropapillomas.
When the wart is lubricated with a 5 percent solution, the surface of the wart acquires a characteristic grayish-white color.
Whereas micropapillomatous formations do not change color.
In addition, with micropapillomatosis, the “tubercles” are soft and linearly symmetrical.
The formations of molluscum contagiosum also have a similar appearance - dense, round, painless nodules of flesh-pink color.
They are distinguished by a shiny, smooth surface with a depression in the center.
When pressed, a cheesy whitish mass is squeezed out of it (studying the latter under a microscope confirms the diagnosis).
Flat wide uterine condylomas are difficult to distinguish visually and require colposcopy.
It is also important to distinguish such formations, which are alarming in terms of the risk of developing cancer, from the normal variant - Naboth cysts.
They are white/whitish-yellow cysts that form when the lumen of the gland is blocked and the outflow of secretions from it is disrupted.
Quite often found in women who have given birth.
Particular attention is paid to differentiating warts from malignant neoplasms.
There are diagnostically problematic situations when the patient’s condition does not improve for a long time.
Or the formations are excessively dense and inactive, bleed, or ulcerate.
Or such warts form in the vagina due to HIV (features of the latter condition worsen the course and prognosis of papillomavirus infection),
Then the following studies are prescribed:
- Papanicolaou cytological (the so-called PAP test, which, as part of early screening for cervical cancer, is in principle prescribed to all women for annual testing) - a microscopic examination of a smear from the cervix stained with special dyes in order to detect changes in cellular structures;
- histological – microscopic examination of a tissue sample (section from a lesion);
- PCR diagnostics - using the polymerase chain reaction technique, the type of specific human papillomavirus is determined using the DNA of the pathogen, which is important when assessing cancer risk;
- The Digene test is a hybrid capture method that, unlike the overly sensitive PCR, detects only a clinically significant amount of virus.
At the same time, taking into account the frequent co-occurrence of HPV infection with other infectious diseases of the urogenital tract, tests for sexually transmitted infections are carried out.
PCR, ELISA, culture, smear microscopy, etc.
What types of HPV cause groin warts?
Anogenital and genital warts are caused by about 20 types of HPV. Infection of the genital and urinary tract is asymptomatic. The subclinical form of the disease is rarely diagnosed. Visible genital growths occur when infected with VPH types 6, 11. The appearance of anogenital warts is associated with the persistence of HPV types 16, 18, 33, 35 in the body. These strains of viruses are activated in areas of cervical dysplasia and urethral tumors.
Modern research methods help accurately determine the type of HPV. The Dajane test will show the presence of oncogenic strains of papillomavirus.
Removing external signs of papillomatosis does not mean curing the patient. Information about the type of HPV makes it possible to promptly identify oncopathology and not to worsen the patient’s condition.
How are warts in the vagina and perigenital area treated?
For a condition such as warts in the vagina, on the labia, treatment, first of all, involves clarifying the cause of the disease.
In most cases, the culprit of the problem is the human papillomavirus infection.
A variety of specialists deal with the problem of diagnosing and treating human papillomavirus infection.
These are dermatologists, oncologists, obstetricians-gynecologists, virologists, urologists, immunologists, venereologists.
This interest is due to the recent increase in the incidence of this disease.
By the age of 50, about 80% of women are infected with the virus.
And, especially, the ability of some types of HPV to initiate malignant processes.
A feature of the infection is its tendency to spontaneously heal in some cases.
Approximately 90% of episodes within two years (usually between six months and a year) result in laboratory-confirmed resolution of the virus.
The period during which such a development of events is possible is determined both by the type of virus itself and by a number of other factors.
That is, the patient’s age, use of oral contraceptives, pregnancy/childbirth, attitude towards smoking, etc.
In other situations, a long-term recurrent course is possible with a certain risk of malignant degeneration of formations (this risk is determined by the type of HPV).
Or the virus persists in the body without clinical manifestations.
The absence of spontaneous disappearance of genital warts can also be associated with re-infection with new types of HPV.
Reinfection with the same virus is extremely rare due to acquired immunity.
Currently, there are no proven methods for eliminating the pathogen itself from the body.
Therapeutic measures are aimed primarily at removing formations using various methods.
In the post-Soviet space, methods of antiviral and immunocorrective therapy are used, although they are not included in medical treatment guidelines.
These are drugs such as groprinosine, isoprinosine, interferons, etc.
It is difficult to assess the effectiveness of such drugs precisely due to the high probability of spontaneous cure, but research in this area continues.
As a result, the general therapeutic tactics are reduced to dynamic observation (with regular cytological monitoring) or to removal of formations.
Treatment prognosis
With a timely reaction and a qualified approach, the disease can quickly be transferred to a latent state, but one should not forget about it. It is impossible to completely remove the infection from the body. This means that if unfavorable factors occur, warts will appear again.
However, in medical practice, cases of complete recovery from infection within one year have been observed. Therefore, you never need to despair, you just need to keep your body healthy.
Warts in the vagina: when and how to remove
Removal is recommended if:
- symptomatic manifestations in the area of papillomas;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- injury to condylomas, which is often accompanied by inflammation;
- psychological discomfort;
- planning pregnancy (due to a natural decrease in immune defense, the growth of papillomatous formations is possible);
- preparation for childbirth in pregnant women (to reduce the risk of infection of the child).
When dealing with a problem such as warts in the vagina, a comparison of removal methods shows a variation in the effectiveness of different approaches from 30% to 90%.
However, it is impossible to achieve a 100% result if the virus persists in the body or, less commonly, is reinfected.
In this regard, relapse after removal of a wart in the vagina depends little on the choice of therapy.
There are different methods for removing condylomas.
Physical impact:
- surgically (especially when confirming malignant transformations, may require hospitalization);
- electrosurgically - through electrocoagulation, electric knife, etc. (requires anesthesia, protective equipment for personnel);
- radio waves (radio knife, Surgitron);
- cryotherapeutically - local cold action of liquid nitrogen, nitrogen oxides or carbon (to reduce damage to surrounding tissues, the surface of the formation is pre-treated with a special gel);
- laser (neodymium/carbon dioxide laser), performed under local anesthesia;
Cytotoxic effects - when using drugs podophyllotoxin, podophyllin, rarely 5-fluorouracil, destruction processes are induced in papilloma cells;
Chemical exposure - when using acids, for example, the drug Solcoderm - a combination of nitric, lactic, acetic and oxalic acid, nitric or trichloroacetic acid itself;
Intralesional administration of interferon (it is also known that local application of interferon solution to the area of the wart after laser removal reduces the likelihood of relapse);
Surgical and laser removal is carried out using special equipment.
While some drugs with cytotoxic effects (prohibited for use during pregnancy!) can be used at home.
It is recommended to remove warts in the vagina using chemical methods (chloroacetic acids) or cryotherapy.
When treating large formations using laser, cryotherapy, electrocoagulation and a number of others, scar formation is possible, which should be taken into account when choosing an intervention technique.
With extensive lesions of the skin and mucous membranes, Buschke-Levenshtein condylomas, hospitalization may be indicated.
The risk of relapse, regardless of the method used, is about 20-30%.
Care after removal of a wart in the vagina involves careful adherence to hygiene rules.
After using some methods, slight swelling and redness in the area of intervention may occur.
In order to eliminate unwanted manifestations, the doctor may prescribe local analgesic and anti-inflammatory agents.
Therapeutic techniques
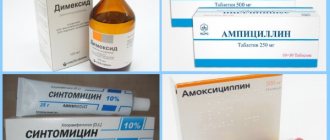
Treatment is selected by the doctor on an individual basis. If the growths are located on the genitals and intimate area, the use of immunostimulants, antiviral agents, and cytostatics is indicated. To boost immunity, the patient is prescribed Epigen, Viferon, Genferon, Cycloferon.
If itching and burning occur, it is recommended to cauterize the papillomas. The following medications are used for this:
- Super clean. The solution is presented in the form of a mixture of alkalis. Before the procedure, healthy tissue is treated with baby cream. Cream is applied to the formation for 5 days. Gradually the growth disappears.
- Solcoderm. The drug is presented in the form of an acid concentrate. It can cause burns and scarring. If condylomas appear in the cervix and vagina, doctors advise using Solkovagin.
- Feresol. The medication is presented in the form of an oily liquid with a phenol odor. Apply the product to the growth for 45 minutes. If there is a thin stalk, only the surface of the wart is treated.
- Condilin. The skin is first lubricated with Vaseline or zinc ointment. The drug Condilin is applied twice a day with an applicator. Apply twice a day with a break of 4 days.
The above products are used only as prescribed by a doctor. If the wart is located near the genitals, therapy is carried out by a doctor.
Ointments and folk remedies
More delicate areas of the intimate areas are treated with cream. For example, Oxolinic ointment with antiherpetic and antiviral effects is used to treat warts in the intimate area. The growths are treated three times a day. The course lasts from 2 weeks to 2 months.
Other means can be used for therapy:
- San fen zhong. The Chinese drug quickly destroys microbes, burning out papilloma. The composition is applied carefully to the affected area. After 3 months it is washed off. The course consists of five procedures.
- Stefalin. The composition of the herbal base effectively fights papillomas in the intimate area.
If the growth is small, you can use folk remedies, but only after consulting a doctor. To treat the problem area, celandine juice is used. The course consists of two manipulations per week. Treatment continues until the growth completely disappears. This remedy is effective if filiform condyloma is detected.
To destroy the growth, you can use red potato juice. To prepare it, you will need to grate the tuber, squeezing out the juice with gauze. The liquid is taken orally 30 minutes before meals. Treatment lasts 2 months. Can be used externally by treating papilloma juice every day for a month.
Garlic cream is used to treat growths. The method for preparing the composition is as follows:
- peeled cloves are passed through a garlic press;
- the gruel is mixed with cream;
- the composition is laid out on a bandage;
- the compress is fixed on the papilloma with a plaster;
- after 5 hours the composition is washed off.
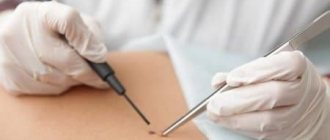
Surgical removal
In advanced cases, doctors prescribe surgical removal of the wart. For example, during an exacerbation period, a laser is used. With its help, the growth is eliminated, regardless of its depth. The advantage of manipulation is the absence of scars. Other methods for removing warts in the intimate area:
- Cryotherapy. The growth is frozen with nitrogen and then removed. The method works if the formation is localized on a visible area of the body. If the wart is located in the vagina, cryotherapy is contraindicated.
- Radio waves. The Surgitron device is used to carry out the procedure. It affects the growth without affecting healthy skin.
- Electrocoagulation or electrodestruction. The papilloma is excised with an electric knife. At the same time, the vessels are coagulated. The wound heals quickly. No scars remain.
- Surgical removal. A reliable and simple way to treat warts, for which local anesthesia is administered. The wart is cut off with a scalpel.
- Electrotherapy. The papilloma is burned out by electric current.
The prognosis of the disease is positive if the patient receives timely and competent assistance. To prevent relapse, preventive measures must be followed. Since growths appear during the transmission of HPV, it is therefore recommended to use contraception and eat right. Intimate hygiene is maintained. If you suspect genital papilloma, you should immediately consult your doctor.