Human papillomavirus belongs to the group of the most common diseases characterized by an increased level of infectiousness.
Certain strains of pathogenic microorganisms can lead to the appearance of numerous growths on the mucous membranes of the genital organs. Infection with a papilloma virus of this type most often occurs through the parenteral route, but domestic and vertical variants of invasion are possible.
Most types of infection are not dangerous to health and are characterized by the manifestation of exclusively dermatological defects. However, there are strains of the virus, infection of which is fraught with the development of malignant tumors affecting the internal genital organs.
Causes of papillomas in intimate places
The virus enters the body through microscopic lesions on the skin and mucous tissues. From the moment of invasion until the first external signs of infection appear, a long period of time may pass, during which the infection remains latent in the body. However, if the condition of the immune system worsens, there is a decrease in the body's resistance, the virus is activated, leading to the appearance of growths and warts on the skin.
The following factors can also provoke the appearance of papillomas in intimate places:
- hormonal imbalances and disruptions caused by pregnancy, taking a number of medications, and other factors.
- The presence of bad habits, which include smoking, use of illegal drugs and drinks containing alcohol.
- Metabolic disorders, for example, due to prolonged adherence to a monotonous diet or poor nutrition.
- Having a large amount of excess body weight.
- Infection with viral diseases occurring in acute form.
- The presence of chronic diseases that occur over a long period of time.
- Systematic stress, nervous overstrain, chronic fatigue, lack of sufficient sleep, lack of important microelements in the body.
Thus, any factors that contribute to a decrease in immune strength and weakening of the body can provoke the growth of tumors on the skin and mucous tissues of the genital organs. The growth of small lumps can be caused, for example, by a common cold, as well as by taking medications that alleviate the course of an existing disease.
Prevention
It is much easier to prevent any disease than to treat it. HPV is not excreted from the human body, and therefore it is very important to avoid infection. First of all, casual sex and a large number of sexual partners should be avoided.
If the virus does get inside, then it is necessary to take all measures to increase immunity and eliminate provoking factors.
A healthy lifestyle will help with this - giving up bad habits, optimal nutrition, combining activity with proper rest.
Diseases, especially those related to the genitourinary system, must be treated promptly and adequately. Taking vitamin complexes will help strengthen the immune system.
Symptoms in women and men
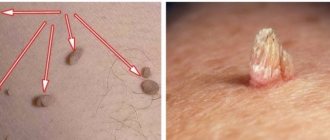
It is important to know what papillomas look like in intimate places, as well as their usual locations. Timely detection of pathological tissue growths will allow you to consult a doctor in a timely manner, thereby preventing the transformation of growths into malignant tumors.
Typical clinical signs of papillomavirus in intimate areas are the following:
- Common locations for growths in women are: mucous tissue of the vagina and cervix, labia majora and minora, and perineal area.
- In men, growths are located on the scrotum, head of the genital organ, and in the groin.
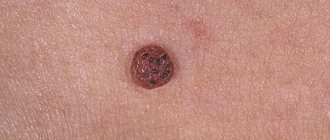
- The appearance of intimate growths may vary depending on the strain of the virus. More often, papillomas of this kind have a large, rough surface located on a relatively thin base, and therefore they are often compared to cauliflower forks or a cockscomb.
- The color of papillomas can also vary from flesh-colored to burgundy.
As a rule, the appearance of growths is not accompanied by pain or other unpleasant sensations, however, papillomas in the groin, if they come into contact with clothing during movements and walking, can cause a lot of inconvenience, get wet, and bleed. Constant damage to the growths can cause them to increase in size and transform into malignant tumors.
Preventive measures
To prevent the appearance of growths on the genitals, it is necessary to eliminate the provoking factors of the disease.
For these purposes it is important:
- strictly observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- practice protected sexual intercourse;
- be faithful to one sexual partner;
- try to prevent injury to the mucous membranes of the external and internal genital organs;
- treat any viral and sexually transmitted infections in a timely manner;
- stop drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking cigarettes;
- eat properly, balanced;
- control hormone levels;
- refuse to wear other people's underwear.
If you feel unsure of your sexual partner after sexual intercourse with him, you need to treat the entire surface of the genitals with a liquid antiseptic. Miramistin or Chlorhexidine are best suited for these purposes. It is important to remember at all times that the speed of spread of the virus directly depends on the state of the immune system. Therefore, experts recommend that everyone, without exception, constantly strengthen the body’s defenses.
Types of papillomas in the intimate area
Papillomas between the legs, that is, located in the intimate area, are usually classified into several main groups depending on the characteristics of their appearance.
The main options for growths are:
- genital warts. They most often affect women and have an appearance somewhat reminiscent of cauliflower. It should be noted that only genital warts are transmitted exclusively parenterally, that is, during sexual intercourse.
- Thread-like. In the early stages of formation, such growths look like small compactions or bumps, having a shade close to the color of the skin. Subsequently, the formations significantly increase in length, taking the form of thread-like processes, soft to the touch.
- Flat. They may have a whitish or yellowish tint, practically do not protrude above the surface of the skin, having the appearance of slight compactions. More often, such papillomas are located on mucous tissues. Lack of treatment against the background of their appearance can lead to the development of inflammatory processes.
In addition to purely genital organs, papillomas can also be located on the mucous tissues of the urethra. With this type of invasion, patients often experience burning and itching when urinating.
Types of neoplasms
There are a fair number of varieties of the papilloma virus. The main classifications consider the types of papillomas from the point of view of oncogenicity, types of affected areas, and characteristics of manifestations.
In medical language, condylomas are divided into:
The first ones are pointed . They appear on the outside of the labia in the form of growths as a consequence of HPV with low oncogenicity. Endophytic, that is, flat condylomas , are growths that extend into the epithelium. Flat formations are caused by a type of HPV with high oncogenic activity; a malignant process develops rapidly and often affects the cervix of the uterus in women.
Pointed
Condylomas acuminata symptomatically appear as small formations on the genitals. The human immune system is able to prevent pathology from developing for a long time, completely hiding it. Several years may pass from the moment the virus enters the body until symptoms appear.
At first, the patient experiences unpleasant sensations: itching, itching, stinging, burning. After a few hours, a small condyloma forms (just a few millimeters) and cannot always be seen with the naked eye.
The formation is similar to cauliflower, lumpy, characterized by the presence of a “leg” of a pinkish or pale tint. They are able to develop, grow and form entire groups of growths.
This is how Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma is formed. This is a huge growth that can rot. Zonal sprouts are located within the vagina, at the junction of the labia or near the clitoris. The localization expands over time, and unpleasant neoplasms can affect the intestine.
This consequence is fraught with pain during defecation, the condyloma bleeds. A damaged growth on the labia can cause cosmetic discomfort, but nothing more.
Genital warts differ in:
- syphilitic (wide leg);
- molluscum contagiosum;
- cancer pathologies on the skin and mucous membranes.
Flat
The presence of flat condyloma implies a serious examination and elimination of a dangerous source of the disease. The doctor's job is to prevent cancer from occurring. Flat papillomas are a sign of human infection with oncogenic HPV.
The most common human papillomaviruses, types 6, 11, 16, 18, have oncogenic activity. In addition, the risk of developing cancer is inherent in HPV types 31-33, 45, 51-52, 56, 58, 59.
It is easy to check for condyloma. It is enough to treat the affected area with vinegar. If it turns white, it's condyloma.
Are papillomas in intimate places contagious?
Papillomas on the genitals pose a particular danger, which lies in the increased risk of infection. Even a person who has no external manifestations of the disease on the skin can be a carrier of the virus, but for others he is a potential source of infection.
According to statistics, at least seven out of ten representatives of the average population of the planet are carriers of papillomaviruses of various types, including intimate ones. This is due to the fact that genital growths can be transmitted not only parenterally, but also through household means, for example, through personal hygiene items, towels, toothbrushes, and so on. There is a risk of infection when visiting a bathhouse, sauna, or swimming pool.
Are papillomas dangerous?
Neoplasms of any type, and especially papillomas in the groin, can cause a lot of health problems. At the same time, the risks of developing various complications increase significantly if the patient does not take any therapeutic measures. So, why are papillomas in intimate places dangerous?
The main dangers of neoplasms lie in the following aspects:
- with constant trauma to papillomas, for example, when they rub against clothing or each other, there is a danger of growth and increase in size of the tumors.
- Papillomas located in intimate places are oncogenic in nature, that is, they can develop into a malignant tumor.
- If papillomas are damaged, there is a risk of bacterial or viral infection, which can lead to the development of inflammatory processes and suppuration.
According to experts, in five out of ten cases, the cause of the development of uterine cancer in representatives of the fair half of humanity is infection with the papilloma virus and the lack of timely treatment.
Features of condylomas on the labia
During sexual contact, the papilloma virus spreads from an infected person to a healthy person. Moreover, there are virus carriers - people who do not have pronounced signs of papilloma. They themselves do not suffer from the virus, but are carriers of the disease .
An infected person may very likely not notice any manifestations of the disease for many weeks, months or even years until the “trigger” is activated.
What is this very mechanism? Various diseases that undermine the immune system, surgeries, stress, colds, injuries are the reasons for the activation of the disease. The virus invades a healthy cell and begins to multiply and divide uncontrollably, infecting surrounding cells.
As a result, external manifestations of the disease form in the form of neoplasms. Condylomas on the labia are tissue growths with a narrow base and a voluminous apex. At the base there are blood vessels that feed the growth. If you do not resort to treatment, there is a high probability of growth.
Treatment methods
When unpleasant neoplasms appear on the skin, almost everyone is interested in the question of how to treat papillomas in intimate places. It is important to know that effective removal of growths is possible only with complex therapy, including the use of local agents that help eliminate external manifestations of infection, as well as immunomodulatory and antiviral drugs that help suppress the activity of pathogenic flora.
It is strictly not recommended to remove growths on your own, without first consulting a specialist.
Self-medication of intimate tumors is associated with the risk of bleeding, infections, and a number of other problems. Additionally, home remedies may not be effective.
Consequences of the disease
It is dangerous to underestimate the risks of possible complications in the case of manifestations of tissue proliferation. They are not harmless. Such neoplasms in an advanced state are harbingers of cancer.
Long-term condylomatosis increases the likelihood of the formation of a malignant tumor by 60 times . Condylomas cause significant damage to health, which is manifested in the following unpleasant consequences of infection:
- discomfort in the affected area.
- Sexual imbalance.
- Concern about a cosmetic defect.
- Psychological discomfort.
- Spread beyond the labia, causing problems with bowel movements.
- They often get injured and bleed.
- At birth there is a high risk of infection of the child.
- Transmission of the virus to a sexual partner through contact.
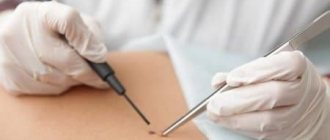
Removal of papilloma
Unfortunately, there is currently no universal cure for papillomas in intimate places. In addition, the viral infection is incurable, that is, with a single invasion, it remains in the body for life, periodically showing activity. However, it is still necessary to remove the external manifestations of the disease, that is, papillomas from the genitals, since there is a risk of developing malignant neoplasms.
There are many ways to remove intimate papillomas. To get rid of small tumors, it is enough to use antiviral agents for local action and oral administration. To remove large tumors, it may be necessary to use more radical measures, which include surgery, laser and radio wave therapy, cryodestruction, and many others.
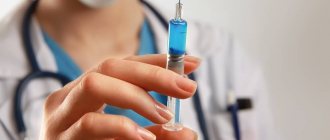
Drug treatment
For small tumors, treatment of papillomas in intimate places, for example, in the groin area or on the genitals, can be done through the use of antiviral drugs. It is important to remember that the choice of the appropriate medication should be made only according to the recommendations of the attending physician.
The following products are particularly effective:
- Acyclovir. The product is presented in the form of tablets and ointments. It has a powerful antiviral effect, quickly suppressing the activity of pathogenic flora. In addition, its regular use to eliminate papillomas in intimate places helps to increase the body's protective functions.
- Oxolinic ointment. A simple but highly effective remedy for the treatment of papillomas. It can be used to remove small tumors.
- Panavir. A broad-spectrum medicine that helps increase the body’s resistance functions and suppress the activity of viral flora. It is recommended to use it to remove existing growths, as well as their reappearance.
- Viferon. One of the most effective immunomodulatory agents, which also has antiviral properties.
To effectively treat intimate papillomas, a specialist can prescribe the patient the complex use of two or more drugs.
The most common combinations of medications are complexes of products for internal and external use.
We should also talk about radical methods for removing papillomas in intimate areas.
If large growths are present on the skin and mucous membranes, the following methods for eliminating them are recommended:
- cryodestruction. The method involves exposing papillomas to liquid nitrogen, which literally freezes pathological tissue, promoting their destruction. Due to the somewhat painful nature of the method, the procedures are carried out using anesthetics.
- Electrocoagulation. One of the most effective methods, which involves removing tumors using high-frequency current. This method allows you to get rid of even large growths.
- Laser therapy. One of the most gentle methods, the use of which allows you to avoid the occurrence of inflammation and bleeding at the site of removal of the growth.
- Surgery. Removal of intimate papillomas using a scalpel is practiced quite rarely, since the use of this technique is fraught with the development of complications. More often, this method is used only for large tumors, the removal of which by minimally invasive methods is not possible.
The choice of a suitable treatment method for papillomas is made individually after examining the patient by a specialist. In case of significant damage to the skin, complex therapy can be used, combining invasive and medicinal methods of treatment.
Folk remedies
Procedures for removing papillomas on the genitals can be carried out independently using folk remedies. However, this is only permissible when the growths are small in size. In addition, before removing papilloma in intimate places at home, you need to consult a specialist.
The following methods are popular:
- aloe or kalanchoe juice. To obtain this antiviral agent, it is enough to grind several leaves of the selected plant to a pulp and squeeze out some juice using gauze. Next, you need to regularly apply fresh juice to the surface of the papillomas, as well as to healthy skin, which will help prevent the spread of infection.
- Propolis infusion. To remove growths, it is recommended to use pharmaceutical medicine. Using it is more than simple: to get the effect, it is enough to treat the growths at least three times throughout the day. It should be remembered that treatment of mucous tissues requires special care.
- Celandine juice. One of the most effective natural remedies for treating papillomavirus is fresh celandine juice. To remove tumors, it is enough to apply it to the surface of the growths. When processing, it is important to be careful not to get the product on healthy tissue, as this can cause severe burns.
Treatment of papillomas in intimate places with the help of folk remedies should be carried out until the growth is completely removed and the affected area is healed. You should know that even with small growths, treatment with home methods can take more than one week.
Features of treatment during pregnancy
Genital papillomas on a woman’s genitals, identified during the gestational period, can cause many problems. This is due to the fact that during pregnancy the use of most antiviral agents is not recommended. However, treatment is still recommended, since there is a high risk of infection of the fetus when passing through the birth canal.
If a woman has papillomas on her intimate organs, the use of invasive treatment methods is recommended. It is recommended to remove growths using a laser, radio wave technique, scalpel or other methods. It is important to remember that any manipulation is permissible only after receiving medical advice.
How to treat genital papillomas yourself?
The virus, once in the blood, is constantly in the body, and it is completely impossible to get rid of it. The number of HPV decreases with the removal of condylomas and antiviral therapy. There are medications that destroy papillomas in the groin of women, which are suitable for external use at home. Elimination of genital warts alleviates the symptoms of infection and serves as a preventive measure to prevent the appearance of other neoplasms.
Medicines intended for self-treatment of genital warts (have received official approval from the relevant International and National Committees):
| Name, form | Active Ingredient | Effect |
| “Imiquad”, cream (other trade names are “Aldara”, “Ziklara”) | Imiquimod | Significantly increases local immunity of the skin, activates antitumor and antiviral factors. Gets rid of genital warts in 2–8 weeks if you follow the regimen suggested by the manufacturer |
| "Kondilin", 0.5% alcohol solution; "Condilox", gel (another name is "Podofilox") | Plant alkaloid podophylline | It inhibits cell division, which causes condyloma necrosis. Treatment is carried out for 1–5 weeks according to the scheme: 3 days of treatment - then 4 days break |
| "Veregen", 15% ointment. | Synecatechin is a composite component of green tea catechins. | It has antiviral, immunostimulating and antioxidant effects. The product is applied in a thin layer to the affected area. The frequency of use per day is 3 times. Maximum duration of treatment - 16 weeks |
Development mechanism
The formation of papillomas on the clitoris and labia is the result of the action of the human papillomavirus, which can spread in a variety of ways. The smallest microcracks and damage to the skin make it possible for HPV to penetrate and, under various provoking factors, contribute to the development of single or multiple papillomas (papillomatosis).
The most dangerous strains of the virus include those that penetrate the skin of the mucous membranes of the genital organs. Benign papillomas caused by their action are considered the most aggressive. They arise quickly, grow and cause significant inconvenience. This type is also referred to as genital warts.
Papillomavirus is the main impetus for the development of benign tumors, but there are other factors that influence their formation. When papilloma develops on the labia, the reasons may be:
- promiscuity and unconventional types of sex;
- lack of normal sexual hygiene;
- constant moisture of the mucous membranes;
- regular abortions;
- weakening of local and general immunity;
- hormonal disruptions (pregnancy, menopause, disruptions due to long-term use of hormonal medications);
- stress and bad habits;
- failure to comply with hygiene measures when visiting public baths, saunas, swimming pools;
- lack of vitamins A, B, C, folic acid;
- presence of sexually transmitted diseases;
- the presence of severe chronic diseases (HIV, diabetes, asthma, etc.).
The appearance and growth of papillomas, along with the human papillomavirus that causes them, are determined by individual characteristics: they can immediately announce their appearance or in the first stages disguise themselves as other diseases, causing discomfort and bewilderment.
The disease can develop in different ways. The incubation period for infection with condylomas can range from a week to several years, depending on the state of the immune system. It depends on him exactly how the neoplasms will behave. May be observed:
- rapid increase in number and size of neoplasms;
- unchanged condition of emerging condylomas for a long period of time (more than 2-3 years);
- voluntary self-healing - some time after the formation of condylomas, they disappear on their own.
Probability of infection
HPV infection of the genitals and perineum is highly contagious, or contagious. Infection during a single sexual contact with a partner who has the virus occurs in six out of ten cases. The possibility of genital warts increases even more in the presence of a number of conditions.
| Predisposing factor | Characteristic |
| Young age | Most often, clinical signs of HPV infection appear in patients aged 20 to 24 years. In general, the age range from 17 to 33 years is the most likely for women in terms of the growth of papillomas in intimate areas. |
| Early sexual debut | Early onset of sexual activity, when the processes of hormonal changes have not yet been completed, is a factor that increases the risk of genital papillomatous formations. |
| Frequent change of sexual partners | A large number of sexual partners, frequent and promiscuous sexual contacts significantly increase the chances of contracting human papillomavirus infection. |
| Unprotected sexual contacts | Barrier contraception - the use of a condom - still remains the only easily accessible and relatively inexpensive means of possible, but not absolute, protection against HPV. It is impossible to completely get rid of the likelihood of infection with its help, since a condom may not isolate all contacting areas of damaged skin. But unprotected sexual intercourse is an almost guaranteed infection. Unprotected anal sex is an even greater risk factor, as it is often accompanied by microtrauma to the mucous membrane and skin. |
A combination of factors greatly facilitates the possibility of infection.