Benign formations that affect the human body are usually called wen. The term has become so popular among people that few people realize what diseases are actually hidden under this name. Atheroma and wen are the most common “wen”, which have significant differences. Consequently, different treatment methods are used for these diseases. To begin topical therapy, a person needs to undergo a diagnostic examination. This can only be done by consulting a doctor.
What is atheroma
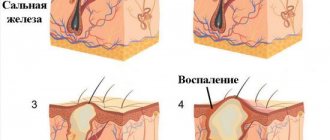
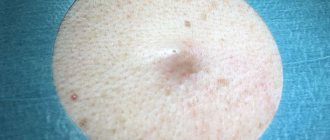
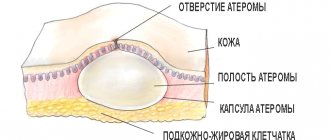
Atheroma is a formation on the skin that occurs due to blockage of the sebaceous gland and has a tumor-like shape. The disease can appear on any part of the body and affects areas with oily skin. The most common locations for atheromas are the brow ridges, ears, chin and nasolabial triangle.
Wen is a capsule that reaches the size of a chicken egg. The formation is soft to the touch and can be either single or multiple.
Atheroma is a benign formation that can grow, which leads to infection. In rare cases, it leads to the formation of squamous cell carcinoma.
Appearance mechanism
The difference between atheroma and lipoma lies in location, symptoms, cells forming the formation, appearance, characteristic signs on ultrasound or MRI. If there are complications, the disease can only be treated surgically. For mild cases of the condition, drug therapy is used.
To confirm the diagnosis, a differential examination is required, which can only be carried out at a medical institution.
Atheroma
Benign tumor of the sebaceous gland of the skin.
Factors that provoke development and determine the difference between formations:
- excessive sweating;
- disruption of the skin exfoliation process;
- hormonal imbalance;
- increase in secretion viscosity;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- the use of drugs that narrow the ducts of the sebaceous gland.
Appearance: round in shape, smooth, mobile. Has clear boundaries. The difference between the diseases lies in the presence of the opening of the gland duct.
The condition is not life-threatening, but the development of a bacterial infection can trigger the occurrence of an abscess, accompanied by pain, fever, and hyperemia of the skin around the affected area. Sebaceous seals are capable of spontaneous opening, which leads to the release of pus and sebum.
The difference lies in the contents of the tumor - a mixture of sebum and fragments of the epidermis. Dimensions can reach 40-50 mm in diameter.
In advanced stages of the disease, surgery is used. Minimally invasive techniques are used to remove the lump. After removal, the risk of developing an inflammatory process is minimal. Scars do not form.
Lipoma
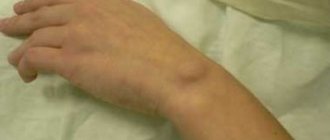
A benign formation located in the subcutaneous layer or on internal organs. The structure of the lipoma is soft, there is no pain on palpation. The difference between atheroma and wen is the compression caused by the enlargement.
The cause of lipoma is associated with hereditary predisposition and lipid metabolism disorders. Histology reveals unchanged fat cells.
Factors contributing to the onset of the pathological process:
- endocrine diseases;
- hormonal imbalance;
- alcoholism;
- features of immunity.
For small sizes, dynamic observation is indicated. If the tumor enlarges and signs of compression of nearby organs appear, surgical removal of the wen and capsule is indicated.
Lipoma disease
Lipoma is a benign neoplasm on the skin. It is located in the subcutaneous fatty tissue, localized on the back, neck and limbs, and on internal organs. Its cells are located on internal organs.
Education most often affects people over the age of 30.
Attention! A disease in which foci of neoplasm become numerous is called lipomatosis.
The formation does not cause pain upon palpation, is easily displaced, and does not grow into surrounding tissues. As the size of the lipoma increases, it becomes dense and enters the stage of fibrolipoma. There are varieties: angiolipomas, myxolipomas, myolipomas.
The formation has a size of no more than 5 cm, but in rare cases it increases to 10 cm.
What is a wen with a black spot?
Lipoma is also a benign formation. Unlike atheroma, it consists entirely of adipose tissue. Subcutaneous formations are soft and elastic. Soreness is not inherent in them. Such formations can grow to enormous sizes. The use of the term “wen” is more relevant in this case. A lipoma in the abdominal cavity sometimes reaches 10 kilograms.
The specific cause of this tumor has not yet been established. Nevertheless, factors provoking its occurrence have been identified.
- Genetic predisposition. If there are precedents of this disease in the family, the risk of the disease increases.
- Problems of the metabolic process in the body. In this case, there is an accumulation of fat cells that tend to merge.
- Hormonal imbalances in the body. This phenomenon often causes a variety of diseases, including the appearance of lipoma.
- Mechanical tissue damage.
By itself, lipoma is not dangerous. The threat of this disease lies in the effect of the tumor on nearby organs and tissues. For example, a tumor of the peritoneal space can compress internal organs and nerve fibers. In the later stages, the lipoma displaces organs from their usual location. Located on the limbs, the tumor often grows into muscles or bone tissue. One of the varieties is fibrolipoma. It has a denser consistency and consists of connective tissue. It is impossible to recognize such a formation visually without medical diagnosis.
The concept of a wen with a blackhead is sometimes applied to a lipoma. This is more than wrong. After all, it is the black dot that is the hallmark of atheroma.
Causes of atheromas and lipomas
Lipoma and atheroma are outwardly similar formations; only a doctor can distinguish them by appearance. If any wen appears on the body, you should immediately consult a dermatologist.
Factors that provoke the appearance of tumors on the human body have been identified. These include:
- metabolic failures;
- damage to adipose tissue;
- bad habits – smoking, drinking alcohol;
- disorders of the liver or pancreas;
- diabetes;
- unbalanced diet, fatty, spicy foods;
- hormonal disbalance.
Hereditary predisposition is of great importance.
Lipomas most often appear due to improper liver function (fatty liver disease). People who lead a sedentary lifestyle are predisposed to the appearance of such neoplasms.
Features of the development of lipomas
Lipomas develop slowly, they do not cause discomfort to a person, and are painless upon palpation. They have several distinct characteristics:
- They increase or decrease in size if their appearance is associated with liver dysfunction.
- Localized in places where there are skin problems.
- They do not respond to traditional medicine methods.
When a lipoma first appears, you should consult a specialist. Only with proper diagnosis can you choose a treatment method. It is not recommended to excise small tumors surgically.
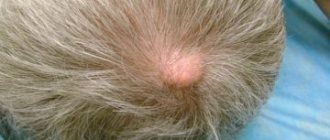
Clinical manifestations of atheroma
Atheroma appears in areas of the skin where there is a large accumulation of sebaceous glands. Localized on the neck, armpits, chin, back, scalp.
The neoplasm has clear boundaries and a spherical shape. It is soft to the touch and becomes mobile upon palpation. The consistency is dense and does not cause pain or discomfort. Size 3-10 cm. Large formations are recommended to be removed surgically, as they cause inconvenience to the patient. Localization can be either single or multiple.
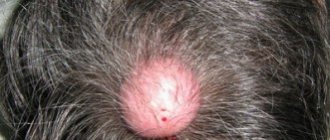
The neoplasm does not pose a threat, but in complicated cases there is a risk of a subcutaneous abscess. In this case, swelling and severe pain are possible. The infection process is accompanied by fever and symptoms of general intoxication. Such an atheroma can spontaneously open.
Symptoms
Identifying the problem in both cases is usually not difficult.
mobile and painless, sizes can range from a few millimeters to 10-15 cm;
to the touch - doughy or dense;
not fused to the skin - the skin easily moves over the formation;
never becomes inflamed – i.e. There is no redness or swelling of the skin above the lipoma.
Most often, lipomas are located on the limbs, head and torso; they are almost never on the face.
Symptoms of atheroma:
The formation is in the form of a tubercle, painless, mobile, fused to the skin, you can often see the opening of the excretory duct of the gland. Most often, the “bump” is located on areas of the body where there is hair: on the face, scalp, in the genital area, on the legs, on the back, and is found on the face. If a suppurating atheroma appears, the formation increases in size over several days, the skin on the affected area may turn red and become painful, and the temperature may also rise.
Similar symptoms of atheroma and lipoma
Lipoma and atheroma are visually no different. Only a specialist can determine the type of wen during examination and diagnosis.
These neoplasms have a number of similar characteristics:
- formations of a benign nature, the risk of degeneration into an oncological process is minimal;
- same shape;
- similar causes of appearance - poor nutrition, nervous tension, metabolic failures;
- hereditary factor;
- are not amenable to alternative treatment and can only be removed surgically;
- upon palpation, both neoplasms become mobile;
- are localized on any part of the body, but affect those places where there is a large accumulation of sebaceous glands.
Prevention for neoplasms is identical. It is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, spend more time in the fresh air and adhere to proper nutrition, eat fresh vegetables and fruits. A balanced diet will help to avoid metabolic disorders that cause the appearance of wen. Preventive measures reduce the risk of tumors.
Wen have common symptoms, but to treat them it is necessary to accurately distinguish lipoma from atheroma.
How to distinguish by appearance
There are some signs by which a person can independently recognize the type of a certain growth.
The size of the atheroma is usually much smaller and may have pus discharge. This symptom is not possible with a lipoma. It is also worth paying attention to the structure of the growth. Wen is softer, it easily changes its location under the skin. Atheroma is characterized by growth dynamics; this characteristic is not characteristic of wen.
Regardless of what kind of education a person has, the main action is going to the doctor. Only a qualified specialist can provide relevant assistance in solving this problem. Ignoring symptoms or attempting self-treatment can lead to complications.
Neoplasms on the body are usually called wen, but in fact, all formations have differences and look different. To distinguish atheroma from lipoma, you need to know their symptoms.
Differences between atheromas and lipomas
There are a number of signs that help you make the right conclusion.
The first is the presence or absence of an inflammatory process. If inflammation is present, this indicates that the wen is an atheroma.
Lipoma and atheroma arise due to the same reasons, but the mechanism of development for each neoplasm is different. Atheroma is localized on the skin, and lipoma is located under the skin. It is soft to the touch. The subcutaneous formation is denser in consistency.
The difference between the two neoplasms
- Atheroma is an accumulation of fat in the gland, progresses quickly, increases in size, and has a hard consistency. It is subject to inflammation and suppuration.
- Lipoma is a cluster of cells in a capsule, localized in the subcutaneous tissue, soft to the touch.
It is impossible to distinguish these two formations on your own. Incorrect diagnosis leads to complications. Only a doctor can correctly determine the type of tumor through examination and diagnosis.
What is the difference between atheroma and wen
In order to accurately find out the type of formation, you need to visit a doctor, but by some distinctive features you can distinguish atheroma from lipoma yourself:
- the wen always has no inflammatory process;
- lipoma does not have an outlet;
- the cyst is harder and denser;
- the wen is easy to move;
- the epidermal formation is adhesive to the skin;
- the growth of an epidermoid neoplasm is more rapid than that of a fatty one;
- an epidermal cyst never develops on the surface of internal organs.
The fatty tissue does not have to be removed if it does not cause any aesthetic discomfort, since this type of neoplasm almost never leads to complications.
Reasons for appearance
Based on the cause of its occurrence, the doctor can determine whether the patient has a lipoma or atheroma. Wen occurs due to the fact that adipose tissue begins to grow rapidly. This can be caused by factors such as trauma to the localization site, metabolic disorders, and heredity. An epidermal cyst grows in places where there are a large number of sebaceous glands and occurs due to blockage of their duct with detritus. The patency can be disrupted by particles of the upper layer of skin or mechanical damage to the gland.
The appearance of atheroma is often associated with damage to the skin, with the introduction of particles from the upper layer into the deeper layers of the skin, as well as with an increase in the density of detritus. Cyst factors include genetic predisposition, metabolic disorders, neglect of personal hygiene, and improper use of cosmetics.
Appearance and structure
The visual manifestations of a wen and an atheroma (cyst) are similar, so outwardly they can be confused, but there are also some differences. A cystic neoplasm is often smaller in size than a fatty one. Purulent contents can be released from the opening of the epidermal cyst when pressed, which never happens with a lipoma. If you touch the wen, it has a softer consistency, because it is a growth of adipose tissue under the skin. The cyst has a dense capsule, so it feels harder to the touch. If you press on the wen, it will move to the side without any problems. The epidermoid cyst is fused to the skin; it can only be slightly moved relative to the deeper tissues.
Subjective sensations and symptoms
There are no symptomatic differences between these two neoplasms. They do not cause pain, itching or discomfort. Lipoma never becomes inflamed, which often happens with atheroma.
We recommend reading Causes of foot hygroma and its treatment
Symptoms of an inflamed epidermal neoplasm:
- Redness of the skin over the cyst.
- Swelling of the tissue around the tumor.
- Pain syndrome on palpation.
- Isolation of purulent exudate during purulent course.
If there is at least one sign of the development of an inflammatory process, you should immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment.
Risks and complications
Lipoma can have one complication. Very rarely, a wen degenerates into a malignant tumor, liposarcoma. An epidermoid tumor never becomes malignant, but it very often becomes inflamed. Detritus, which is located inside the capsule, is a breeding ground for the development of bacterial flora, so inflammation of the cyst is not uncommon. The purulent contents corrode the membrane of the tumor and the skin above it, and can break out or in. In the second option, soft tissue phlegmon develops. The inflammatory process can develop without infection. In such a situation, doctors first stop the inflammation with Levomekol or Vishnevsky ointment, and then remove the epidermal neoplasm.
An epidermoid cyst is dangerous because it ruptures, which can cause the development of an abscess. When localized in the genital area, both the wen and the cyst can disrupt the process of urination or cause difficulties during sexual intercourse. After surgery to remove an epidermal cyst, it may grow back. When removing an inflamed atheroma, there is a possibility that the doctor will not be able to remove the entire cyst membrane, which becomes the main reason for the development of relapses.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is a set of diagnostic measures that allow one to distinguish one disease from another. It is used for similar symptoms.
Differential diagnosis helps distinguish a lump from a malignant tumor called lymphosarcoma. Visually, oncological formations and wen may not be different, so you need to consult a doctor in time and carry out a diagnosis.
To distinguish a neoplasm from a malignant tumor, a biopsy is performed, and the material is sent for cytological examination. Based on the results, treatment is prescribed. More often, therapy consists of removing a benign tumor.
Lipoma and atheroma are benign formations that do not pose a danger to humans. But you shouldn’t put off seeing a doctor, as they are no different from each other. In some cases, a wen may turn out to be a malignant tumor that requires urgent surgical intervention.
Treatment of fatty cyst
Like lipoma, atheroma can only be removed surgically. Conservative methods or treatment with folk remedies do not have an effective effect on the wen.
On this topic
- Atheroma
All about atheroma removal
- Irina Nasredinovna Nachoeva
- August 19, 2021
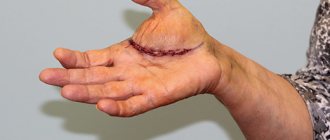
Surgical removal of atheroma and lipoma is performed on an outpatient basis, but the duration of the procedure is shorter, about a quarter of an hour. This completely removes the sebaceous capsule.
It is recommended to perform surgery to remove the wen without waiting for it to become inflamed or break through. This will complicate the treatment, and the postoperative scar will have a larger cosmetic defect.