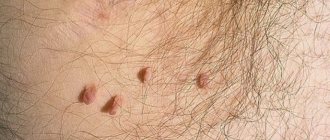
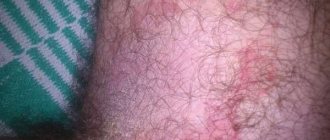
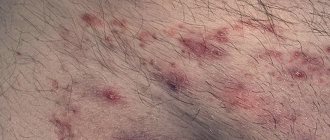
Atheroma is a cystic neoplasm that is benign in nature and occurs as a result of blockage of the sebaceous duct. In medicine, such a tumor is called an epidermal cyst. The place of its localization can be various parts of the body where there are hair follicles. Atheroma in the groin in women is a common occurrence, but men with a similar pathology are much more common in medical practice. In most cases, the tumor occurs between the ages of 20 and 45 years.
Features of cysts in the groin
An inguinal cyst (atheroma) is a cavity formation that develops as a result of blockage of the sebaceous glands.
The tumor is benign and resembles an inflamed lymph node in appearance. Atheromas have a dense structure, which is explained by the presence of a dense capsule that hides the liquid contents.
The risk group for developing inguinal cysts includes men and women aged 20-40 years. This is due to the fact that neoplasms are formed due to blockage of the sebaceous glands.
The work of the latter is regulated by androgens and testosterone. And this group of people more often experiences fluctuations in hormonal balance.
Causes
The growth of atheroma begins with blockage of the sebaceous glands. Despite the obstacle, the latter continue to produce the secret. Over time, a tumor forms in the groin with a capsule that covers sebum and dead epithelial cells.
- urinary system
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 9, 2021
A black dot remains in the central part of the tumor, representing the exit site of the duct. Therefore, atheroma is differentiated from other inguinal tumors.
The following factors can provoke the appearance of cysts in the perineum:
- hormonal imbalance;
- increased sweating;
- metabolic disease;
- genetic predisposition;
- injuries and other tissue damage in the groin area;
- poor nutrition;
- toxic effects on the body;
- failure to comply with intimate hygiene rules.
The most likely causes of atheroma include mechanical damage to the skin or hair follicle. Wearing low-quality or uncomfortable clothing, shaving hair in the groin area - this contributes to infection and blockage of the sebaceous ducts.
The second probable reason lies in profuse sweating. This explains the high incidence of cysts in the groin area compared to other parts of the body.
The perineum contains many hair, sweat and sebaceous glands. This combination (especially in the warm season) creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
Any changes in the structure of the skin in the genital area, even the most insignificant at first glance, most often indicate an imbalance in the functioning of the body. The formation of lumps in the groin area in women may be associated with the development of internal pathologies, so if lumps are detected, you should seek medical help.
In most cases, timely diagnosis of the causes of tumors and competent therapy aimed at eliminating the effects of pathogenic factors help to completely get rid of the disease and prevent its possible relapses.
What is an inguinal cyst in women
Any changes in the structure of the skin in the genital area, even the most insignificant at first glance, most often indicate an imbalance in the functioning of the body. The formation of lumps in the groin area in women may be associated with the development of internal pathologies, so if lumps are detected, you should seek medical help.
In most cases, timely diagnosis of the causes of tumors and competent therapy aimed at eliminating the effects of pathogenic factors help to completely get rid of the disease and prevent its possible relapses.
What is atheroma
Atheroma is a benign cystic neoplasm resulting from blockage of the sebaceous duct due to injury to the skin. In other words, it is an epidermal cyst, since it is localized in areas of the body covered with hair. The cyst in the groin in women is dense, elastic and round. The neoplasm consists of gray matter in a capsule with an unpleasant odor.
Due to the structure of the reproductive organs, women 20-45 years old suffer from tumors more often than men. Unlike representatives of the stronger half of humanity, the lymph nodes of the weaker sex react more strongly to deviations in health. Microbes that negatively affect human health are killed by lymph.
If it is impossible to cope with the assigned function, inflammation occurs.
Source: https://ginekologiya-urologiya.ru/kista/chto-takoe-pahovaya-kista-u-zhenshhin
Causes
A lump in the groin area is a dense, mobile neoplasm that protrudes above the surface of the skin. The appearance of a lump may be accompanied by pain, burning and itching, an increase in body temperature, or it may be asymptomatic, disturbing the woman as a cosmetic skin defect.
Only a doctor can correctly establish the cause that provoked the development of a neoplasm, determine the degree of danger to the body and select appropriate methods of therapy after an initial examination and palpation of the lesion, as well as studying the results of laboratory tests. Lumps in the groin area can be a symptom of the following pathological processes:
- Folliculitis. Caused by the penetration of a bacterial infection into the hair follicle, the development of the inflammatory process in the hair follicle is usually accompanied by the formation of a dense subcutaneous formation - a painful purulent compaction surrounding the hair shaft and the adjacent sebaceous gland. The appearance of a small (from 1 to 3 mm in diameter) lump on the pubis with pus can be caused by microtrauma of the skin received during depilation, increased sweat production, and irritation by synthetic fabrics of the underwear. Antibacterial drugs are used to treat the disease.
- Furunculosis. When folliculitis becomes complicated due to overactive sweat glands or irritation of the skin, foci of infection can rapidly spread to the surface of the skin. This process is accompanied by the formation of dense, painful neoplasms filled with purulent exudate, enlarged lymph nodes, and an increase in body temperature. In order to relieve inflammation and eliminate the pathogenic influence of infection, a course of antibiotics and local application of antibacterial ointments are prescribed.
- Inguinal lymphadenitis. Against the background of the development of a sexually transmitted disease, as well as during inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs, concomitant inflammation of the lymph nodes is observed with an increase in their size, the appearance of noticeable pain and discomfort when performing movements. This process is also accompanied by an increase in body temperature and general weakness. At an early stage of pathogenesis, conservative drug therapy is prescribed. If a purulent process develops at the site of compaction, surgical intervention is recommended.
- Lipoma. If there are metabolic disorders, weakened immune defenses, or diabetes mellitus, a benign tumor formed by adipose tissue cells may appear in the groin area. Lipoma has the appearance of a limited, painless new growth of soft consistency, not fused with the surrounding tissues. The elasticity and color of the skin at the site of tumor development are preserved. A benign lump is removed surgically to prevent its degeneration into liposarcoma, a malignant tumor.
- Pseudofolliculitis. When the direction of hair growth is disrupted, when the hair shaft does not break through the skin and begins to grow deep into the epidermis, a red, painful and itchy lump is formed. Hyperkeratosis and shaving of unwanted hair in the intimate area can provoke pathology. The inflamed purulent abscess is opened by a doctor using a sterile instrument.
- Atheroma. Atheroma is often localized in the groin area - a benign cyst that occurs against the background of poor personal hygiene, hormonal imbalance, sexually transmitted infection or mechanical trauma to the skin. Such a seal is movable, elastic, outlined with a clear contour. When atheroma suppurates, swelling, pain and redness are observed. To prevent secondary infection and transformation of the tumor into a purulent abscess, the lump is surgically removed.
- Inguinal hernia. Women who have suffered damage to the ligamentous apparatus of internal organs or who are obese may develop an inguinal hernia. A movable seal appears on the pubis, which protrudes when exerting itself or coughing. The hernia must be removed through surgery.
A lump in the groin of women on the left is formed under the influence of the same reasons as on the right. The pathogenesis of the disease differs only in the opposite location of the tumor. Seals can also be formed on both sides simultaneously. Self-medication of pubic lumps in women on the right, on both sides or on the left is strictly not recommended. The use of traditional and alternative medicine methods and self-removal of the seal is fraught not only with the development of sepsis and the rapid spread of infection on the surface of the skin, but also with the formation of malignant tumors. To protect your health and effectively get rid of an uncomfortable problem, you need to promptly seek medical help.
Signs and symptoms of tumors in the groin
There are many hair follicles in the groin area, next to which the ducts of the sebaceous glands are located. The canal becomes clogged, and the gland functions by secreting sebum, which is needed to lubricate the outer layer of human skin. The secretion does not come out and is not filled with sebaceous secretions, so a cyst forms in the duct.
Examination of the lump is done because there is a possibility of a malignant tumor of the lymph node. Doctors have not determined for sure where the disease comes from, but heredity and endocrine diseases play a role in the course of the disease.
Atheroma in a woman’s groin grows slowly and does not bother her. But when the hairline is damaged, inflammation occurs. The temperature rises, aching pain appears and swelling develops. Visually, nothing changes; the lump is detected by palpation. A consultation with a dermatologist is required, who will collect anamnesis and examine the results of the tests. If necessary, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs for the woman. X-rays, biopsies, CT scans and MRIs help clarify the picture. the correct treatment is prescribed based on these actions. Self-healing and squeezing out the capsule is fraught with unpleasant consequences.
Cones in a woman appear on the right and left sides. They appear for the same reasons, only pathological processes occur either on the right or on the left side. Atheromas thicken and protrude for the following reasons:
- the hair follicle becomes inflamed;
- the sweat gland becomes inflamed;
- the sebaceous gland becomes inflamed;
- Varicose veins occur on the right or left side.
During inflammatory processes of the sebaceous or sweat glands in the groin, pain appears at the location of the cyst, and the skin turns red. An abscess appears on the lump, and then, after opening, the pain decreases and disappears.
Sources of lumps in the groin area:
- Lymph node infection
- Inguinal hernia that appears when coughing and carrying heavy objects
- Femoral hernia can lead to intestinal obstruction
- Varicose veins in the groin
- Accumulation of pus in the groin area
- Oncological diseases, blood poisoning
- The location of the cecum is lower
- Increasing wen
- Violation of the structure of the hip joint
- Protrusion of the femoral artery
- Neuroma
- Lymphoblastoma
Causes of epidermal neoplasms
- hereditary diseases;
- thyroid disease and cardiovascular problems;
- careless depilation;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- skin injury;
- tendency towards acne and blackheads;
- drinking alcohol and smoking;
- eating fatty and fried foods
Epidermal cyst during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a woman's weight and hormonal levels change. Body weight increases and provokes the appearance of a hernia in the groin. The expectant mother is susceptible to colds and infections. Due to inflammation of the lymph nodes, a tumor or sexually transmitted disease develops.
Varicose veins in the groin area appear during pregnancy. Wearing a special bandage and limiting loads are necessary recommendations for a woman in an “interesting position.” If there is no pinching, the hernia in the groin is not operated on until childbirth. Treatment is carried out under the supervision of a doctor due to fear of risks for the unborn child.
Prevention and treatment
Treatment at home is allowed only if you are sure that the cause lies in folliculitis or a regular purulent pimple. And even here there is a risk of infection, which can lead to an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system. As for seals in the groin, which can be lipomas or atheromas, the need for their removal is determined by the doctor. Inflammatory processes are treated with medication.
As a preventive measure, it is recommended to avoid casual sexual contact, hypothermia and injury to the groin area. If you find hard or soft lumps, it is better to consult a doctor immediately. Timely treatment can help avoid surgery.
The groin area is rich in hair follicles, which are considered fertile ground for the development of benign subcutaneous formations. Atheroma in the groin in women and men occurs when the sebaceous glands located in the duct of the hair follicle are blocked. It is a benign tumor, round and firm to the touch. A capsule is formed inside the sebaceous duct, in which a thick, pasty mass of yellowish-white color with an unpleasant odor is collected. Even if the tumor is asymptomatic, if it is detected, you should immediately see a doctor.
- Why do inguinal atheromas form in women and men?
- External symptoms and subjective sensations
- Risk of complications
- How is it diagnosed?
- Treatment options
- Pharmacy and folk medicines for topical use
- Radical cyst removal
- Prevention of neoplasms
The influence of atheroma on a woman’s life
A woman's body is created more complex than a man's body. It is so arranged that representatives of the fairer sex give birth to children, experience pain during menstruation, and follow a diet to avoid diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. A cyst in the groin in women is not an acute cause for concern, but it adds worry and discomfort.
Signs and symptoms of tumors in the groin
There are many hair follicles in the groin area, next to which the ducts of the sebaceous glands are located. The canal becomes clogged, and the gland functions by secreting sebum, which is needed to lubricate the outer layer of human skin. The secretion does not come out and is not filled with sebaceous secretions, so a cyst forms in the duct.
Examination of the lump is done because there is a possibility of a malignant tumor of the lymph node. Doctors have not determined for sure where the disease comes from, but heredity and endocrine diseases play a role in the course of the disease.
Atheroma in a woman’s groin grows slowly and does not bother her. But when the hairline is damaged, inflammation occurs. The temperature rises, aching pain appears and swelling develops. Visually, nothing changes; the lump is detected by palpation.
A consultation with a dermatologist is required, who will collect anamnesis and examine the results of the tests. If necessary, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs for the woman. X-rays, biopsies, CT scans and MRIs help clarify the picture. the correct treatment is prescribed based on these actions.
Self-healing and squeezing out the capsule is fraught with unpleasant consequences.
Cones in a woman appear on the right and left sides. They appear for the same reasons, only pathological processes occur either on the right or on the left side. Atheromas thicken and protrude for the following reasons:
- the hair follicle becomes inflamed;
- the sweat gland becomes inflamed;
- the sebaceous gland becomes inflamed;
- Varicose veins occur on the right or left side.
During inflammatory processes of the sebaceous or sweat glands in the groin, pain appears at the location of the cyst, and the skin turns red. An abscess appears on the lump, and then, after opening, the pain decreases and disappears.
Sources of lumps in the groin area:
- Lymph node infection
- Inguinal hernia that appears when coughing and carrying heavy objects
- Femoral hernia can lead to intestinal obstruction
- Varicose veins in the groin
- Accumulation of pus in the groin area
- Oncological diseases, blood poisoning
- The location of the cecum is lower
- Increasing wen
- Violation of the structure of the hip joint
- Protrusion of the femoral artery
- Neuroma
- Lymphoblastoma
Causes of epidermal neoplasms
- hereditary diseases;
- thyroid disease and cardiovascular problems;
- careless depilation;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- skin injury;
- tendency towards acne and blackheads;
- drinking alcohol and smoking;
- eating fatty and fried foods
Epidermal cyst during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a woman's weight and hormonal levels change. Body weight increases and provokes the appearance of a hernia in the groin. The expectant mother is susceptible to colds and infections. Due to inflammation of the lymph nodes, a tumor or sexually transmitted disease develops.
Varicose veins in the groin area appear during pregnancy. Wearing a special bandage and limiting loads are necessary recommendations for a woman in an “interesting position.” If there is no pinching, the hernia in the groin is not operated on until childbirth. Treatment is carried out under the supervision of a doctor due to fear of risks for the unborn child.
Lipomas and atheromas: similarities and differences
A lipoma, like a node in the groin, is a benign tumor on the skin. The two neoplasms are identical in appearance: round with clear contours, develop painlessly and do not itch. But they differ from each other.
- The lipoma is less mobile under the skin. When pressed with a finger, the cyst will pop out, but the wen will remain in place.
- A black dot is visible on the cystic formation - a duct that is clogged.
- Inflammation for cysts is a common occurrence.
- The fatty tissue does not change size.
The cyst breaks out on its own, and the pus comes out. But it happens that the contents of the atheroma leak into the tissue. This is dangerous due to intoxication, infection and sepsis.
Cyst in the perineum
Problems with the function of the glands, failure to comply with personal hygiene rules, and contact with tight underwear lead to a paraurethral or Bartholin gland cyst. The size of which reaches 4 cm.
Bartholin's gland. Narrowing of the excretory duct is the cause of the disease. STDs affect inflammation of the gland. E. coli, staphylococci and streptococci reduce the body's resistance. Chronic diseases are the cause of infection. Sometimes an abortion results in the appearance of a cyst.
A Bartholin gland cyst causes discomfort when moving and discomfort during sex. An abscess in the perineum is the cause of fever and a sharp deterioration of the condition.
Paraurethral cyst is round. The development of the disease is caused by inflammatory processes of the urethra and vagina, and sexually transmitted diseases.
Cysts in the perineum cause painful urination, pain, burning and itching, and the release of pus. If a ball or swelling is detected in the perineum, contact a gynecologist or surgeon.
If the process is severe, the tumor is removed in a specialized room - a capsule containing masses of the result of decomposition is removed. It is not recommended to open it yourself.
This provokes the development of new pathologies.
Methods for removing a tumor in the groin in women and preventing the disease
The only way to get rid of atheroma is removal. Capsules are removed using three methods.
- Surgical - done under anesthesia and if the cyst is larger than 5 cm.
- Radio wave therapy is a matter of minutes and leaves no trace after the operation.
- The laser is used to cauterize the blood vessels and disinfect the sore spot. A 5-7 mm incision is made and the contents are destroyed along with the sebaceous mass.
Surgeries to excise atheroma are carried out in one day. Sutures are placed with absorbable threads and a sterile bandage is applied. In addition to surgical interventions for inflammatory processes, antibiotics are taken and Vishnevsky ointment is used, which has a beneficial effect on wound healing.
To avoid epidermal cysts, a woman needs a strong immune system. Giving up bad habits, proper daily routine and lack of stress help to avoid illness and disorder of the body.
Source: https://kistayaichnika.ru/klassifikaciya/kista-v-paxu-u-zhenshhin.html
Why do inguinal atheromas form in women and men?
Atheroma in the groin most often looks like several small cysts covering the groin area. It starts with blockage of the sebaceous ducts. Despite the inflammation, the sebaceous gland continues to work and secrete sebum onto the surface of the skin. A dense capsule containing sebum and dead epithelial cells gradually forms. It is located in the lowest layer of skin - the dermis, and hurts when pressed. In the center there is a characteristic black dot - this is the exit of the sebaceous gland duct. Based on this feature, atheroma in the groin is distinguished from other subcutaneous neoplasms. This tumor occurs twice as often in men than in women.
The groin area is constantly subject to friction and compression, whether from uncomfortable underwear or tight clothing. If we add here a polluted environment and poor body hygiene, we get the main set of reasons for the occurrence of atheroma in the groin:
- Unsuccessful shaving and epilation, ingrown hairs.
- Groin damage, irritation from clothing.
- Poor hygiene of intimate areas.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Profuse sweating.
- Allergic reactions, including to medications.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Hypothermia or overheating.
Although these cysts are not true tumors, when inflamed they pose a serious threat to your health.
The pubis is the second most common place for cystic rashes after the head. The peculiarity of the formation of atheroma in this zone is as follows: in addition to the abundance of hair follicles, many external secretion glands are concentrated in the groin - sebaceous, sweat. The secretion they produce creates good conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, which, when they enter the excretory ducts of the hair follicles, cause inflammation.
The older the atheroma in the groin, the larger it is, it can reach 5-7 cm in diameter, therefore, it will be more difficult to remove it.
Atheroma on the pubis looks like a small, clearly defined dense lump. It does not hurt until inflammation begins in it. And this happens quite often and is caused by poor body hygiene, irritation of the groin from wearing low-quality clothes and underwear.
Causes and symptoms of atheroma in the groin in women
The groin area is second on the list for the location of the epidermal cyst after the scalp. This is due to the large number of hair follicles located there, next to which the ducts of the sebaceous glands are located.
For various reasons, the canal becomes clogged, but the exocrine gland continues to function and secrete sebum, which is necessary to lubricate the outer layer of human skin. And since the secretion cannot come out, it fills with sebaceous secretions and forms atheroma in the duct.
Medicine has still not been able to determine the exact causes of such a formation as atheroma in the groin. But a number of factors influencing the occurrence of neoplasms have been identified:
- heredity of the disease;
- increased sweating associated with impaired thermoregulation in a general disease (thyroid dysfunction, vegetative-vascular dystonia);
- hormonal imbalance, caused by age-related changes in the body, an unpleasant odor may appear;
- metabolic disease;
- skin injury;
- insufficient attention to personal hygiene;
- the body's tendency to develop acne and acne;
- wearing underwear that is too tight;
- damage to hair follicles during shaving.
Atheroma on the pubic part is very easily confused with a lipoma, which is also a benign tumor on the skin.
Its external signs are similar to those of an epidermal cyst, namely: round shape, clear contours, normal skin condition in the pathological area, as well as painless development and absence of itching. But there are still points by which atheroma can be distinguished from lipoma:
- Atheroma is more mobile under the skin than lipoma. If you press the cystic formation with your finger, it will pop out nearby, and the wen, as a lipoma is also called, will remain under the finger.
- If you carefully examine the growth, you will notice a dark point in the enlarged pore - a clogged duct.
- The fatty tissue rarely becomes inflamed, but for cysts it is a common and common occurrence.
We recommend reading:
- Wen removal with laser
- Atheroma on the back
- HPV type 31 in women
The tumor can reach enormous sizes - more than 20 cm.
Unlike lipoma, atheroma tends to grow rapidly and become frequently inflamed. It is the suppuration of this formation that poses a danger to women’s health.
An epidermal cyst can rupture on its own and its contents come out, but sometimes the capsule breaks inside and the accumulated sebum with purulent masses flows into the tissue. This circumstance can provoke infection, sepsis, and intoxication of the body.
External symptoms and subjective sensations
Normally, perineal atheroma behaves asymptomatically if it is not inflamed. This is a small bump under the skin that moves slightly when pressed; in its center is the outlet of the sebaceous gland. Its contents enter the duct in the form of a cheesy mass with an unpleasant odor. Such formation is more often a cosmetic defect than a disease.
Atheroma in the groin in men usually occurs on the scrotum, testicles and pubic area. In women, it affects the labia area. The formation is rarely single and large; usually it is a small rash of several small cysts. If you notice that the lumps in the groin are red and hurt when touched, it means that they have become infected and an inflammatory process has begun. Do not delay visiting a specialist - inflamed atheroma threatens major complications if not treated in a timely manner.
Symptoms of the disease
Atheroma of the inguinal region can behave as an asymptomatic neoplasm. It first appears as a small bump and grows over time. Can reach large sizes. Upon palpation, the formation has a dense consistency, “walks” under the skin and does not cause pain when pressed. In the groin of men, it often appears on the scrotum or penis, and atheroma may appear on the testicles. Atheroma in the groin in women is localized on the labia (both the mucous membrane and the area of the labia minora), near the anus. It is characteristic of the disease when atheroma appears on the pubis in women.
Such a neoplasm is not life-threatening and the patient may not feel it for a long time. The lump has clear boundaries, is surrounded by a capsule on top, and the skin on it has the same color as in nearby areas. In the middle of the tumor, the shaft of a blocked sebaceous duct is visible. With inflammation, the symptomatic picture changes. The perineal atheroma begins to turn red, tissue swelling appears, and internal suppuration is possible. When pressing on the tumor, the patient complains of sharp pain. In such a situation, immediate treatment is required.
Features of inguinal atheromas
Inguinal atheromas are often multiple, and are also prone to suppuration in the event of a breakthrough.
Unlike other types of atheroma, a neoplasm in the groin area is often presented as many small nodules, and less often as one large lump. This cyst is prone to inflammatory processes and purulent formations, which is very painful. The pathology of atheroma in the groin can cause many diseases. There are frequent cases of relapse with infection entering the body. When such a lump becomes inflamed, there is a high probability of:
- the appearance of an abscess if it bursts from the inside;
- transformation into an ulcer if it bursts from the outside.
Risk of complications
Atheroma in the groin is constantly subject to friction and compression by clothing and linen, which is why it often becomes inflamed. The appearance of neoplasms on the labia is caused by frequent shaving and epilation of this area, poor-quality intimate care products, and wearing tight, uncomfortable underwear. Unprotected sexual contact can also infect atheroma in the groin and trigger an inflammatory process.
The most dangerous complication of atheroma in the intimate area can be its spontaneous breakthrough. Moreover, this can happen in two directions:
- If the atheroma in the perineum breaks out, this will be a favorable outcome, since the sebaceous masses with suppuration will come to the surface of the skin, the wound will cleanse and heal. But the capsule remaining inside will fill up again over time. As a result, it will still have to be removed surgically.
- When an inguinal atheroma erupts internally, its contents penetrate the bloodstream and adjacent tissues, inflammation of the lower layers of the skin occurs and sepsis begins. This condition requires urgent hospitalization, as there is a direct threat to life.
Atheromas, unlike lipomas and fibromas, do not tend to degenerate into malignant tumors. But if you misdiagnose yourself, you will miss valuable time to treat more dangerous skin growths.
Possible complications
Inflammation of atheromas is the most common complication caused by constant friction of the tumor with items of clothing. Cysts on the labia become infected due to unprotected sexual intercourse. In both cases, due to the proximity of the location, the inflammatory process can transfer to the organs of the reproductive system.
When a cyst ruptures, pus and other contents leak out. Over time, the problem area is restored. However, the cystic membrane remains inside, as a result of which atheroma relapses in the future.
Complications develop when the tumor breaks through. In this case, the contents penetrate into the bloodstream and neighboring tissues.
On this topic
- urinary system
Prostate adenoma and potency
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- November 29, 2021
As a result, the inflammatory process spreads downwards. Also, when atheroma breaks through, sepsis develops, which requires immediate medical intervention.
Paraurethral cysts without treatment contribute to the appearance of fistulas and hematomas. The prolonged course of the inflammatory process causes a narrowing of the urethra.
Unlike other tumors that arise in the groin area, cysts do not degenerate into malignant neoplasms.
How is it diagnosed?
Diagnosis of atheromas in the groin area is carried out by a gynecologist or dermatovenerologist during physical examination and palpation. The fact is that many subcutaneous growths are similar in appearance. For example, people often call both atheromas and lipomas in one word - wen. Although these are completely different formations in structure and origin. Unlike a soft and mobile lipoma, atheroma almost does not move when pressed and has a dense consistency.
In addition, there is a dot on it indicating the presence of a sebaceous gland duct. This is its main distinguishing feature.
If the doctor has doubts about the benign nature of the cyst, you may be prescribed other examinations - ultrasound, biopsy, and after removal - histology.
Treatment options
There are only three ways to get rid of atheroma in the groin once and for all - using a scalpel, laser or radio wave. All other options, such as synthetic drugs or grandma's recipes, will bring nothing but disappointment from wasting time. Such drugs are effective only for treating a postoperative suture or accelerating the spontaneous opening of a festering cyst for its further removal.
Ointments and gels for atheroma in the groin are used in cases where it is necessary to provoke a rapid outflow of pus. After the contents come out, an operation is performed to remove the atheroma. There is no point in using ointments in the hope that the lump in the groin will resolve on its own.
External remedies for atheroma in the groin can be used in the following situations:
- After opening and draining the cyst, anti-inflammatory ointments are prescribed - Solcoseryl, Vishnevsky ointment, propolis ointment.
- For resorption of postoperative sutures, Troxevasin, Heparin, Mederma are prescribed.
At home, you can try to open the inguinal atheroma using traditional medicine methods:
- Compress from coltsfoot leaves: clean fresh leaves of the plant are applied to the cyst, fixed with a bandage, changed 2 times a day. Therapy is carried out for 3-5 days. After the atheroma breaks through, the wound still needs to be shown to a doctor.
- A compress of plantain leaves: fresh, cleanly washed and slightly mashed leaves should be applied to the sore groin area and changed every 12 hours. If the cyst does not come out within 10 days, be sure to consult a doctor.
- Compress from cabbage leaves: take a fresh leaf, mash it slightly so that it releases the juice, and fix it on the wound. Change the compress as the sheet dries.
The main rule when treating with traditional medicine is: you must be confident in your diagnosis. Therefore, before starting therapy, be sure to consult with your doctor.
Many patients mistakenly believe that only large atheromas in the groin need to be removed. In fact, the smaller the tumor, the smaller the postoperative mark and the better the cosmetic effect of treatment.
Large and purulent atheromas are surgically removed. As a rule, surgery to remove a cyst is urgent when it becomes inflamed, ruptures and provokes an abscess or sepsis. During the procedure, the pus is squeezed out and a drain is placed for several days. After the inflammation subsides, the capsule is removed from the duct and sutures are applied. All manipulations are performed under local anesthesia. After the procedures, a visible scar remains on the skin of the groin, but the risk of relapse is completely excluded.
Laser surgery can be performed as planned - it is less traumatic, and the risk of wound infection and large blood loss is minimized. The essence of the method is to evaporate the inguinal atheroma along with its membrane. This excludes her subsequent relapse. After the operation, the wound is also sutured, but after the sutures are removed, a barely noticeable mark remains in its place.
The most progressive way to get rid of atheroma in the groin area is the targeted destruction of cells in the cyst itself using radio waves. It is used only on small cysts - up to 5 mm. After the procedure, a crust remains, which dries and disappears after 5-7 days.
Treatment
Conservative treatment of inguinal cysts is ineffective. Medications are used to suppress bacterial microflora, as well as accelerate the release of pus from the problem area.
Cyst removal is carried out using open surgery, laser excision, electrocoagulation or radio wave exposure. The choice of method depends on the characteristics of the atheroma.
Uncomplicated small cysts are removed using laser treatment. This method is one of the least traumatic. Complications and relapses rarely develop after laser removal.
On this topic
- urinary system
What are the symptoms of prostate adenoma?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- May 27, 2021
Radio wave exposure is considered a more effective treatment method. The latter is used in cases where the size of the cyst does not exceed 5 cm in diameter.
During this procedure, radio waves are applied to the problem tissue, which leads to the death of local cells. After the procedure, a crust remains on the treated area, which disappears within a week.
Electrocoagulation helps achieve similar results. In this procedure, alternating current is applied to the cyst, which causes cell necrosis.
Minimally invasive treatment methods are not used during pregnancy, oncological pathologies, inflammatory processes, or disorders of the hematopoietic system.
In case of suppuration of the cyst, open surgery is used. This procedure is carried out in several stages.
First, the surgeon excises the problematic tissue and drains the cavity, treating the latter with antiseptic and antibacterial drugs: Vishnevsky ointment or propolis, Solcoseryl. Later, when the medications eliminate the inflammatory process, the doctor removes the cyst capsule and sutures the wound.
To speed up tissue recovery after surgery, Troxevasin, Heparin, and Mederma are used. If necessary, during the rehabilitation period, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed: UHF, magnetic therapy and others.
Prevention of neoplasms
Atheroma in the groin area can appear at any age in both men and women. Some precautions will help you reduce the risk of its occurrence and reduce the incidence of relapse:
- carefully observe intimate hygiene, use high-quality products;
- choose the right underwear according to size and fabric composition;
- practice protected sex;
- do hair removal only from highly qualified professionals;
- razors must be of high quality and kept clean;
- Eat a balanced diet to strengthen your immune system.
In general, atheroma in the groin area is not a health hazard. You just need to be attentive to your body and health, and if necessary, do not put off visiting a doctor for too long.
Benign neoplasms appear in different parts of the body when the excretory ducts are blocked. In the presence of risk factors, atheroma may form on the pubis in women. Since it can reach large sizes, its removal is indicated. Large lumps cause discomfort, and an inflammatory process can develop inside them.
Inguinal atheroma in women can reach large sizes, so its removal is indicated.
What is atheroma?
Atheroma in the groin is a rounded compaction that occurs due to blockage of the excretory duct in women. Since the secretion is not removed, it forms a cyst or atheroma. It consists of a capsule filled with liquid contents. There may be pus or blood clots inside (if the vascular walls are damaged).
A rounded compaction that occurs due to blockage of the excretory duct.
Unlike lipoma, this neoplasm is more mobile. In women, it rolls under the skin if you touch it with your finger. The lipoma remains in place, while the atheroma on the labia moves in different directions. The lump often contains a black dot. It is a blockage of the duct, which is located in the center.
Benign tumors are often localized where the sebaceous glands pass. In the groin of women, the contents sometimes leak out of them and settle on the skin. They smell bad.
Causes
Atheroma occurs on the labia, pubic area, vulva and other groin areas. The exact reasons for its formation are unknown. Experts name the main risk factors due to which women may encounter a neoplasm:
- hormonal disorders, endocrine disruption;
- mechanical damage to the skin, increased trauma to the skin and hair follicles;
- hereditary factor;
- frequent use of underwear made of synthetic materials that restrict movement;
- excessive use of low-quality cosmetics intended for intimate care for women;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- bad habits (alcohol, smoking);
- eating large amounts of fatty, spicy foods, as well as confectionery;
- diseases associated with excess sebum production.
Frequent depilation provokes injuries to the hairline and, as a result, atheroma appears in the groin. In addition, its formation in women is facilitated by diseases of the genital area.
Symptoms of atheroma
When atheroma appears in the groin in women, signs may not appear for a long time. In most cases, this tumor slowly increases in size, so it does not bother the woman. It is often not noticed until a mechanical injury occurs that damages the capsule.
The body temperature rises, the thickening hurts even when it is not touched.
In this case, an inflammatory process develops. The body temperature rises, the thickening hurts even when it is not touched. The affected area swells.
In women, the appearance of atheroma on the labia is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the tumor is mobile, moves under the fingers and is not tied to a specific place in the groin;
- Abscessation of the labia majora contains a dark dot in the center - a blocked duct;
- When inflamed, the skin in the localized area in women turns red and becomes hot to the touch.
Since perineal atheroma is located in a sensitive area, underwear or clothing often puts pressure on the capsule, causing constant friction. Because of this, a tumor in women can spontaneously open. In this case, the unpleasantly smelling light-colored contents will end up on the skin and underwear. After this, the capsule will begin to fill again and the thickening will form again.
Symptoms
Atheromas are localized mainly in the pubic area. Less commonly, such neoplasms occur on the labia of women. The development of the cyst is asymptomatic, except in cases where the problem area becomes inflamed.
Atheromas protrude slightly above the surface of the skin. When pressed, the tumor moves slightly to the side, which is explained by the growth of the cyst in the fiber layer.
As the tumor grows, it causes discomfort. The nature of the symptoms is determined by the location of the tumor. In some cases, atheromas interfere with sexual intercourse or complicate the process of urination.
If the cyst is injured, the contents come out, which is accompanied by an unpleasant odor. Due to damage, pathogenic bacteria penetrate into the neoplasm.
The activity of pathogenic microorganisms causes an inflammatory process, in which painful sensations appear, the problem area turns red and swells. A short-term increase in body temperature is also possible.
In the case of the formation of a cystic cavity in women, the Bartholin gland becomes blocked in the vestibule of the vagina. The latter produces a secretion necessary to moisturize the mucous membrane of the vulva during arousal.
Bartholin gland cysts also develop predominantly asymptomatically. If the tumor grows, movement causes discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse.
On this topic
- urinary system
What do calcifications in the testicles mean?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- November 29, 2021
Infection of this tumor leads to a sharp increase in body temperature (up to 39 degrees) and intoxication of the body. The neoplasm increases to 12 cm in diameter, which provokes intense pain of a pulsating nature.
Due to the fact that a tumor of the Bartholin gland occurs against the background of infection with sexually transmitted infections, signs of colpitis or urethritis may be added to these symptoms.
Another unpleasant neoplasm that occurs in the perineal area is a paraurethral cyst. This tumor forms near the urethra.
The cyst occurs due to blockage of the Skene gland, which is responsible for moisturizing the urethra. In addition to the symptoms characteristic of other similar neoplasms, this type of tumor provokes frequent urination and involuntary release of urine.
Danger of complications
In most cases, in women, atheroma in the groin does not pose a threat to life or health. However, this statement is valid only until the neoplasm reaches a large size and there is a risk of its suppuration. The contents can penetrate the internal tissues, and sepsis will develop.
If the thickening is not removed in time, the woman risks encountering the following complications:
- an infection will penetrate into the wound, which will provoke increased growth of a benign tumor;
- the process of suppuration leads to spontaneous rupture of the capsule and the entry of purulent contents into the body;
- benign atheroma in some cases can transform into cancer;
- if the membrane opens spontaneously, long-term non-healing wounds often form in its place.
Therefore, if a suspicious lump appears in the groin area, a woman should definitely visit her doctor.
Diagnosis of pathology
To accurately determine atheroma on the labia, a woman will need to make an appointment with a gynecologist. The doctor may prescribe an additional consultation with a surgeon. The diagnosis is made based on examination of the groin area, as well as by palpating the lump. Usually this is enough to diagnose the pathology.
An ultrasound is performed before the operation.
Additionally, the doctor takes a smear, prescribes an ultrasound, as well as a biopsy. Using a puncture, the contents of the capsule are pumped out and then sent for histological examination. This will exclude the malignant nature of the tumor.
Treatment of sebaceous cysts in the groin
For atheroma, the same treatment methods are used as for other cystic formations. Since they are not amenable to drug therapy, the woman is recommended to have the capsule removed surgically.
However, if there is suppuration, the procedure is not carried out. In this situation, drugs are first used to eliminate the inflammatory process, and then surgery is prescribed.
To eliminate atheroma, doctors use one of the following intervention methods:
- classic surgical operation. This is the most common way to remove benign tumors in women. With this type of intervention, the skin is excised, as well as the capsule is opened. It is removed along with the contents, then stitches are applied. The operation is performed under local anesthesia and is most often prescribed if the lump has reached a large size. In this case, traces of the stitches remain, and they are removed after a couple of weeks, after the excised tissue has healed. The possibility of re-development of atheroma with the classical procedure is minimized;
The operation is performed under local anesthesia and is most often prescribed if the lump has reached a large size.
- Radio wave radiation involves the destruction of the structure of neoplasm cells using radio waves. During the operation, the woman experiences virtually no discomfort; moreover, it does not last long (a few minutes). There are no scars left at the site of exposure, but only a small depression appears, which will disappear in the future;
- The laser procedure is used for different types of cystic lesions. Using a laser, the atheroma is opened using a bloodless method. The skin is instantly cauterized, so the risk of tissue infection is minimized. Using a small incision made with a laser scalpel, the neoplasm is opened and the capsule is cauterized, simultaneously removing its contents. After the operation, the sebaceous masses are evaporated and the membrane is destroyed. Relapse is excluded.
If a woman has inflammation of the atheroma or its spontaneous opening, treatment with antibiotics and treatment with antiseptic drugs is prescribed. After removal of the purulent contents, 2 to 3 months must pass before the surgical procedure can be performed.
Methods for removing a tumor in the groin in women and preventing the disease
The only way to get rid of atheroma is removal. Capsules are removed using three methods.
- Surgical - done under anesthesia and if the cyst is larger than 5 cm.
- Radio wave therapy is a matter of minutes and leaves no trace after the operation.
- The laser is used to cauterize the blood vessels and disinfect the sore spot. A 5-7 mm incision is made and the contents are destroyed along with the sebaceous mass.
Surgeries to excise atheroma are carried out in one day. Sutures are placed with absorbable threads and a sterile bandage is applied. In addition to surgical interventions for inflammatory processes, antibiotics are taken and Vishnevsky ointment is used, which has a beneficial effect on wound healing.
To avoid epidermal cysts, a woman needs a strong immune system. Giving up bad habits, proper daily routine and lack of stress help to avoid illness and disorder of the body.
How to take basal temperature with a corpus luteum cyst?
Previous article
Formation of ovarian cysts in girls
Next article